Today, the issue of energy efficiency has become an issue. Therefore, everywhere, and ventilation systems are no exception, energy-saving installations and machines are used. A careful attitude towards energy forces consumers to increasingly turn to heat recovery systems.
Depending on specific conditions, an installation with a built-in recuperator can save up to 90% of energy needs compared to an installation without it. This is theoretical data. In practice, our research has shown that the most efficient rotary heat exchanger saves a maximum of 75%, but this, you see, is also a rather impressive figure. The ventilation with recovery itself and the principle of operation were previously mentioned in the article at the link. We will not repeat ourselves and will consider the recuperator itself.
What are recuperators?
"Recuperatio" is a word meaning "getting back" something. In our case it is air. The task of recuperators is to return part of the heat to the room by transferring it from the outgoing heated flow to the cold incoming one. This equipment is part of the supply and exhaust system; it helps to minimize losses for “street heating”.
There are two large classes of recuperators - rotary and plate. They have their advantages, but they also have some disadvantages. The feasibility of using a particular unit is largely determined by the characteristics of the room, but plate models are more popular. It is better to dwell on them in more detail.
A plate device is a cassette (block, heat exchanger) in which there are many thin partitions - smooth or corrugated sheets, they are made of various materials. Warm air moving through the plate exchanger gives off heat to it. Due to it, cold masses coming from the street are heated. The result is partial heating of the air, which means saving energy from the heaters.
Device cassettes are made from aluminum foil, galvanized steel, plastic or paper that has undergone special treatment. The gaps between the plates are 2-4 mm. Recuperators differ not only in the materials of the heat exchanger partitions. Models have different directions of air flow:
- in the more common type of equipment - cross-flow - the outgoing and incoming flows are perpendicular to each other, the efficiency reaches 65%;
- in counterflow recuperators - in opposite directions, since non-contacting flows must ensure ideal heat exchange.
Thanks to this principle of operation, plate units make it possible to guarantee constant heating of the cold air entering the room. Heat losses trying to “warm the street,” on the contrary, are minimized.
Another difference between recuperators and conventional (natural) ventilation systems is their ability to eliminate unpleasant odors. Some models - membrane ones - have another additional advantage: they successfully combat high humidity in the room.
Design examples
In order not to make a mistake when choosing a recuperator, you should calculate the efficiency and operating efficiency of the device. To calculate the efficiency, use the following formula: K = (Tp - Tn) / (Tv - Tn), where Tp denotes the temperature of the incoming flow, Tn is the street temperature, and Tv is the room temperature. Next, you need to compare your value with the maximum possible efficiency indicator of the purchased device. Typically this value is indicated in the model’s technical data sheet or other accompanying documentation. However, when comparing the desired efficiency and that indicated in the passport, you should remember that in fact this coefficient will be slightly lower than stated in the document.
Air recovery principle
To understand the advantages and benefits of using recuperative heat exchangers, you first need to understand the very essence of their work. Literally translated from Latin, recovery is called “return of used, spent.”
It is the energy return effect that is used in climate control devices of this design. Air flows passing through the unit exchange thermal energy with each other, allowing the air conditioner to subsequently maintain a comfortable temperature, using less energy. On particularly cold days, this allows you to significantly save on heating the room.
Example: the air temperature outside has reached minus 20°C. For residents to feel comfortable, the air conditioner must create a room temperature of at least + 25 C. The temperature difference is easy to calculate - 45 degrees Celsius. Of course, some part of the air will heat up due to the heat capacity of the walls, furniture, and heat exchange between the incoming and outgoing flows. But the air conditioner will still require a significant amount of energy to maintain comfort.
Plate and any other recuperator of the chosen design allows you to move the point of contact of cold and warm air outside the room. The device conducts active heat exchange between them, allowing the incoming flow of fresh air to reach a more comfortable temperature value than the original one.
In winter, warm exhaust air partially warms the incoming cold flows, and in summer it slightly cools them. This helps not only to reduce energy costs from using an air conditioner, but also to increase the stability of maintaining the selected climatic conditions.
We consider the technical justification.
Table 1 Temperature range at which the heat exchanger can operate without condensation.
Questionable operating ranges of the recuperator are highlighted in color.
Yellow color – condensation zone with the formation of a liquid phase
Blue color – condensation zone with ice formation
Based on the data in this table, we have the right to assume that operation in modes below minus five degrees is impossible or undesirable due to the risk of damaging the installation by the generated moisture and its freezing.
Recuperators are part of the forced ventilation system
A plate air recuperator, like any other device of this type, is only part of a forced ventilation system. You should not expect a more or less noticeable improvement in the microclimate in the house when using only a recuperator. Combining it with a natural supply and exhaust air exchange system, it is quite difficult to achieve any noticeable effect. For effective heat exchange between streams, they must constantly move through the device.
For the same reason, installing a recuperation system is not always considered effective and economically justified in a home. Before choosing or making a recuperator with your own hands, it is recommended to calculate:
- Energy consumption before upgrading ventilation.
- Approximate lifespan of the system after upgrade.
- The cost of purchasing and installing the necessary units.
- The cost of annual system maintenance.
Cases where the above-mentioned costs are unable to completely cover the cost of using the ventilation system “as is” are not as rare as it might seem. Especially when it comes to factory devices. Homemade recuperators often help to slightly reduce coolant consumption, and their cost is low.
Installation of a recovery system is necessary only when it really seems quite effective based on calculations. In all other cases, modern air conditioners do an excellent job of maintaining the given climatic conditions.
Types of recuperators
Recovery systems can be divided into several types.
- Direct-flow, counter-flow, cross-flow recuperators differ in the way they move air flows.
- Depending on the design features, recuperators can be ribbed, tubular, plate or plate-fin.
- Based on the material of manufacture, heat exchangers can be metal, plastic, or membrane.
- According to the principle of operation, they distinguish: plate (cross-flow) recuperator - the most popular type of simple design, used in houses and apartments;
- rotary recuperator - operation requires a source of electricity that rotates the rotor element, are large in size and have high efficiency (up to 87%);
- roof-mounted recuperator – industrial level installation;
- coaxial recuperator - easy to implement even without experience;
- recirculation (liquid) recuperator - transfers heat to the air using water or antifreeze, has a complex design and efficiency comparable to the efficiency of a plate heat exchanger.
What needs to be taken into account in the operation of different equipment models
Each air recovery system for a private home has its own strengths and areas of application.
The ventilation system in a private house with recuperation involves not only maintaining temperature and humidity levels, but also eliminating unfavorable odors. There is a varied selection of models on the market, differing in their functional characteristics and installation methods.
For example, a hood installed in the ventilation allows you to remove soot, odor and grease. At the same time, clean air enters the room, and greasy dust does not settle on the furniture. Such conditions have a beneficial effect on well-being and make cleaning the room easier.
Plate heat exchanger
The design of the heat exchanger is such that, due to separation by metal plates, the air flows do not mix. This simple engineering solution provides more efficient heat transfer. To create such equipment does not require large investments. Due to the absence of moving parts, such a device will last a relatively long time. Currently, the efficiency of such devices reaches 60-65%.
The elements are made of aluminum alloys. They are not subject to corrosive changes and have high heat transfer rates.
Rotor system
In such equipment, a small part of the air flows is mixed, since the air flow insulator is a brush with fine bristles. The rotor system occupies a larger area than the plate system, but also has high efficiency (up to 86% in the best models). The rotating rotor and the belt that turns it reduce the overall reliability of the device and increase energy costs for recovery.
Liquid recuperator in an office building
Scheme of liquid recovery in an office building
These are expensive models, but their efficiency is no higher than that of similar equipment. The main positive difference is the ability to place individual blocks at a great distance from each other. Therefore, liquid recuperators are mainly used in large commercial buildings. In private residential premises, a plate or rotary air recuperator for the home is usually used.
Breezer
An air recovery system for a private home and a breather differ in their purposes. The direct purpose of a breather is to heat the air. There is no heat exchange process in it, so it will take a lot of electricity to increase the air temperature.
Compact recuperator model
This model is local ventilation with a recuperator in a private house. Its use is worth thinking about. Compact models can be installed in the walls of different rooms. They operate separately, so they do not require connection to a centralized installation that configures and controls the operation of all devices.
In such models, due to the built-in fans, two air flows move synchronously. Work productivity can be changed using the remote control. At night, the device can be switched to quiet operation mode.
To prevent freezing, special channels are provided, next to which some of the warm air passes. But the effectiveness of this protection remains only up to -15ºС. Activating the exhaust mode helps remove frost and ice from the surface of the heat exchanger. This mode will also cope with purifying the air in the room from choking smoke and other pollutants.
A built-in filter protects against the penetration of debris from the street. The size of the filter cells is selected in such a way that it does not create any special obstacles to air flow, but protects against the penetration of insects and plant fluff. For maintenance, a removable cover is attached to the inside of the recuperator.
Elements of a plate recuperator
The main parts of the recovery system are the fan and the main unit (cassette) with plates. Other elements:
- The condensate removal system is a condensation bath. The device is necessary to remove moisture from the plates, since it will inevitably lead to liquid entering the air channel, in which ice may form. If there is a large accumulation of liquid, the operation of the supply and exhaust system is blocked by the water seal of the condensate collector.
- Bypass valve. Its task is to regulate the intensity of both air flows. Unlike a rotary heat exchanger, this unit and valve have absolutely no moving elements.
Now it is necessary to dwell on the materials used for the production of plate recuperator heat exchangers. There are no ideals: they all have strengths and weaknesses.
- Aluminum or galvanized steel. Models with these heat exchangers are invariably successful due to their reasonable price. If we talk about the disadvantages, the main one is low efficiency, because in winter such devices have to be constantly thawed.
- Plastic. He is completely unaware of the problems of the imperfect “union” of water and metal, so the efficiency of such recuperators is all right. But their infallibility is the reason for their much greater cost.
- Special paper. The efficiency of this equipment is quite high, however, there are fly in the ointment here too. This makes it impossible to use them in rooms where the humidity level is very high: in swimming pools, bathrooms, etc. Although double paper cassettes are more effective, they are just as afraid of moisture. Absorption of odors is another disadvantage of the material.
Brass and cast iron are also used in the production of units. However, most often the plates are made of a certain grade of stainless steel - AISI 316, with molybdenum and nickel added to its composition. These components significantly increase corrosion resistance in aggressive environments. To ensure greater efficiency of the devices, an additional heat exchanger is installed inside. This improvement allows increasing efficiency to 85%.
The heat is returning
The warmth returns When, if not in winter, we remember the warm summer days and wait for the warmth to return. But, as the famous Soviet biologist Ivan Vladimirovich Michurin said, “we cannot expect favors from nature; taking them from her is our task.” This slogan, addressed to fruit growers, has long been adopted by manufacturers of energy-saving equipment, who take the maximum possible from nature, reducing the damage caused to it to zero. Today our focus is on a recuperator - a device that allows you to recover heat.
Recuperatio & ventilation
In heating engineering of construction, the topics of recovery and ventilation are inextricably linked, because heat return (recuperatio - “return”) comes from air heated in the room and “thrown out” during the ventilation process.
In Soviet-era buildings, the issue of organizing ventilation in residential buildings was not as pressing as it is today. The imperfection of window structures, on the one hand, forced the population to seal the windows in winter, but on the other hand, it ensured natural air circulation. With the replacement of windows with plastic or more advanced wooden ones, the topic of ventilation becomes more and more relevant.
When using natural ventilation, to achieve the required intensity of air mass circulation, windows must be open around the clock, which is unattainable in the cold season. That is why a forced ventilation device is considered a more correct and rational approach. Sometimes, for example, in industrial premises, it is simply impossible to do without it.
Modern housing construction is increasingly turning towards energy efficiency, but often, in pursuit of savings, owners of cottages, country houses or apartments invest a lot of money in insulating and sealing their homes, forgetting about the other side - the need for fresh air to flow into the room. Forced exhaust ventilation with heat recovery allows you to ensure both proper air exchange and energy efficiency.
A recuperator is...
Essentially, an air recuperator is a heat exchanger in which the heated air leaving the room gives off most of its heat to the cold air entering from the street. That is, the outgoing air heats the incoming air.
“The market for recuperators in our country is quite young and for a long time was focused exclusively on the production of large installations with a capacity of 3,000–20,000 cubic meters. m for the industrial sector, as well as for large business complexes and swimming pools, where mechanical ventilation has always been required by regulations. But more often these installations worked only to automatically supply and remove air, and it was heated by centralized heating systems. As for residential and commercial construction (including low-rise), five years ago Yandex. The search did not produce practically any real proposals for recuperators of this type (except for Swedish rotary ones), and the path to the supplier was long and thorny. Now the situation is gradually changing, and buying a recuperator is no longer a problem” (Svetlana Duving, https://green-city.su).
THE RECOVERER HEATS THE COLD AIR ENTERING THE ROOM DUE TO THE HEAT RECEIVED FROM THE EXHAUST AIR. AND IN SUMMER, ON THE OVERSEAS – IT COOLS THE SUPPLY AIR. AND ALL THIS IS PRACTICALLY FREE OF COST!
The most important characteristic of a recuperator is determined by the recuperation efficiency, or efficiency. Knowing the efficiency of the recuperator, you can determine how much the street air will be heated. This depends not only on efficiency, but also on temperatures - external and internal.
t (after the recuperator) = (t (indoors) - t (outdoors)) x K (recuperator efficiency) + t (outdoors)
For example, with an efficiency of 77%, indoor temperature 20°C, outdoor temperature 0°C, the temperature of the recovered air will be 15.4°C.
A pleasant surprise - the recuperator is capable of not only heating the supply air, but also cooling it. In the summer, when the air conditioner is running in the room, using a recuperator you can ensure that already cooled air comes from the street.
t (after the recuperator) = t (outdoors) + (t (indoors) - t (outdoors)) x K (recuperator efficiency)
That is, at an outside temperature of 35°C and a room temperature of 21°C, the recuperator will cool the incoming air to 24°C.
It would seem that there is a heating boiler for heating, an air conditioner for cooling, why another device that still cannot fully provide the required indoor climate? The answer is simple: the recuperator does not need energy to heat and cool air. Therefore, using a recuperator is, first of all, a real cost saving.
The efficiency of recuperators can vary over a wide range: from 30 to 96%. Naturally, the higher it is, the higher the energy-saving properties of the device. The efficiency of a recuperator is largely determined by its design.
THERE ARE FIVE MAIN TYPES OF AIR RECOVERY RECOVERY DESIGNS. OF THEM, THE MOST COMMON ARE PLATE-TYPE DEVICES.
Species diversity
Despite the seemingly low prevalence of recuperators, there are several types of devices based on the design principle:
1. Plate recuperators 2. Rotary recuperators 3. Recuperators with intermediate coolant 4. Chamber recuperators 5. Heat pipes
Plate recuperator
- the simplest type of device. The heat exchanger of the device is a cassette equipped with many thin sheets, which can be made of various materials: galvanized steel, aluminum foil, plastic or special paper. Sheets can be either smooth or corrugated.
The plate-type recovery system includes:
• main block with plates; • fan; • a system for removing condensate that inevitably forms on the plates; • a special bypass valve that regulates the intensity of air flows.
An important positive design feature of the plate recuperator is the complete absence of moving parts. The efficiency of plate recuperators is quite high and depends on the type of plates used:
• Aluminum plates or galvanized steel heat exchangers are quite popular due to their relatively low cost. However, they regularly need to use the defrost mode. • Plastic heat exchangers have a higher efficiency, but are also much more expensive. • Plates made of special paper are also highly efficient, but such heat exchangers cannot be used in rooms with high levels of humidity (swimming pools, car washes, some industrial premises), since condensate quite easily overcomes the walls of the cassette. Recuperators with double paper cassettes are also used. Their efficiency is significantly higher due to additional heating of the air, but they are also afraid of high levels of air humidity.
For the sake of objectivity, it must be said that in twenty-degree frosts, the plate recuperator will freeze and noticeably reduce its efficiency. In order for the efficiency of the recuperator to remain at a high level, the incoming outside air must be at least –5… – 7°C. And since in most of Russia the temperature is below these levels for significant periods of time, maintaining the efficiency of the recuperator requires the use of additional equipment that allows the air to be heated to the required temperatures.
The next most popular type of recuperator is rotary. The main part of this device is rotary
heat exchanger rotating at a certain speed. Rotating, the heat exchanger heats up in the exhaust duct area and then cools in the supply duct area. As a result, heat is transferred from the exhaust air to the supply air. Some moisture is also returned as a result of condensation from the exhaust air and evaporation in the flow of supply air from the street. Rotary heat exchangers have higher efficiency than plate heat exchangers. In addition, they can be used at lower temperatures, down to -20... -25°C, without installing additional devices.
However, rotary recuperators have a number of disadvantages. The first is the transfer of exhaust air into the supply air. In the microchannels of the rotary recuperator, either exhaust or supply air flows pass alternately - part of the exhaust air enters the supply air. To minimize this phenomenon, purge sectors are installed on rotary recuperators, where the microchannels of the recuperator are purged with supply air, which is immediately sent back to the hood, but this action reduces the overall efficiency.
The complex design of a rotary heat exchanger includes the rotor itself, a belt, and a rotor drive. The more components, the more frequent maintenance and the likelihood of failure. This is the second disadvantage of rotary systems. And finally, the drive of a rotary recuperator consumes electricity, that is, it reduces resource savings, for which, in fact, the recuperator is used.
Recuperators with intermediate coolant
are structured completely differently. Water or a water-glycol solution circulates between two heat exchangers, one of which is located in the exhaust duct and the other in the supply duct. The coolant is heated by the exhaust air and then transfers heat to the supply air. The coolant circulates in a closed system, and there is no risk of transferring contaminants from the exhaust air to the supply air. Heat transfer can be regulated by changing the circulation rate of the coolant. This type of recuperator is optimally suited for upgrading existing separate ventilation systems.
But this type of device also has a drawback - rather low efficiency. Recuperators with intermediate coolant allow you to recover from 25 to 55% of heat.
THE MOST IMPORTANT CHARACTERISTIC OF A RECOVERY RECOVERER IS THE EFFICIENCY, OR RECOVERY EFFICIENCY, SHOWING WHAT PERCENTAGE OF HEAT THE DEVICE CAN RECOVER FROM THE EXHAUST AIR. FOR NIBE RECOVERY RECOVERERS THIS INDICATOR REACHES 96%.
A distinctive feature of chamber recuperators
is the presence of a damper dividing the heat exchanger chamber into two parts. High efficiency (70–80%) is achieved due to the ability to change the direction of air flow by moving the damper. The disadvantages of chamber recuperators include slight mixing of flows, transfer of odors and the presence of moving parts.
And finally, the typology of recuperators is completed by devices consisting of a closed tube system
, filled with freon. When heated by the removed air, freon evaporates. When the incoming cold air passes along the tubes, the steam condenses and turns back into liquid. The efficiency of this type of recuperator is 50–70%.
NIBE chooses plate
The Danish plant Genvex, which became part of the NIBE group in 2011, was founded in 1974 in Copenhagen. It was then, in May 1974, that the plant produced the first passive heat recovery system. Over 40 years of development, Genvex has significantly expanded its product line, but ventilation and recovery systems remain the company’s leading area of activity.
The NIBE GV-HR110 recuperator, developed in Denmark, which EVAN offers on the Russian market, is a plate-type device with the highest efficiency, reaching 96%. The NIBE GV-HR110 is supplied with a counterflow heat exchanger, energy-saving fans with forward-curved blades, brushless electric motors, a filter for suction and exhaust air, a container for condensate drainage, and a control panel for full control of the system.
In a counterflow heat exchanger, the exhaust and supply move in opposite directions, thereby achieving the maximum heat exchange area and, accordingly, high efficiency. Additionally, NIBE GV-HR110 can be equipped with an electric heat exchanger to reheat the air to prevent freezing of the device at low outside temperatures.
The NIBE recuperator is available in two modifications: NIBE GV-HR110–250 (for houses with an area of up to 180 sq. m) and NIBE GV-HR110–400 (for houses with an area of up to 380 sq. m).
NIBE GV-HR110
The recuperator efficiency (heat transfer efficiency) is not a constant value and depends on the supply air temperature, exhaust air temperature, air flow speed and even room humidity. The dependence of the efficiency of the NIBE GV-HR110 recuperator on the air flow speed is illustrated in Fig. 1.
Rice. 1. Heat recovery efficiency according to EN 308 certificate with uniform flow on the supply and extract air side*, under the following conditions:
• supply air temperature 5°C • exhaust air temperature 25°C • exhaust air humidity *excluding possible icing at low outside temperatures
According to various estimates, from 50 to 70% of heat loss from a room is due to ventilation. You can insulate facades, install energy-saving windows, optimize the heating system, but all efforts will be nullified by open vents. The use of recuperators, which radically reduce ventilation heat loss, is an absolutely necessary element of energy-efficient construction.
Principles of operation of the recuperator
The operating principle of the recuperator depends on its type. Obviously, all of the listed types of construction have their own operating characteristics. Let's list the most common ones here.
Plate recuperator
This type is a monolithic cassette made of metal sheets. Air passes through such a cassette through special channels stamped on the sheets or laid with a special intermediate seal. The flows in such a recuperator are not mixed. The heat exchange process is carried out due to the simultaneous heating of the plates by one flow and cooling by another. Plate heat exchangers have a number of advantages that make them the most common type of thermal barrier for homes.
The main features of the plate recuperator are:
- low price;
- elementary design;
- compactness;
- ease of maintenance;
- easy to clean (if the cassette is disassembled)
- availability of materials for manufacturing;
- lack of mechanisms.
Collapsible heat exchangers are able to provide the highest level of hygienic purity of incoming air during operation of the device without loss of efficiency.
When using these devices, you should always remember about dew points and the fact that condensation forms during the operation of such heat exchangers. At negative air flow temperatures, the plate recuperator unit may undergo a process such as frostbite and block access to air.
The most common type of recuperator, due to the simplicity of its design, is the cross-flow one. Its efficiency can be defined as “Medium Type”, some sources indicate that their efficiency is up to 60%.
Rotary recuperator
This type of heat exchanger has the shape of a short pipe, filled with corrugated steel plates along the body. The rotating mechanism is installed along the tidal axis. The rotor first passes the heated internal air, and then the cold incoming air. The plates are heated and cooled in turn, maintaining the internal air temperature. This type of recuperator is considered the most effective. However, the design feature does not allow it to be made compact; experts recognize the bulkiness of such a device as a disadvantage.
Heat exchanger with intermediate coolant
Such recuperators use liquid heat exchangers where an ethylene glycol solution (an effective coolant) circulates. In such waste heaters, the tidal and exhaust sections are separated and separated by a certain distance. This feature allows the use of such devices for environments where incoming and outgoing flows cannot be mixed. The coolant circulates either naturally or through a pump. To increase the efficiency of such a heat recovery device, fine adjustment of the coolant flow is necessary in accordance with the design.
Advantages and disadvantages of different types of recuperators
The advantage of recuperators is obvious - they allow you to significantly save on heating the supply air in winter and cooling the supply air in the summer. Among the disadvantages of recuperators are the following:
- They create additional aerodynamic resistance in the network. Indeed, like any other element in the ventilation network, recuperators have some resistance, which should be taken into account when choosing a fan. However, this resistance is not high (usually no more than 100 Pa), and does not lead to a significant increase in fan power.
- Recuperators increase both the cost of the ventilation unit and the cost of its maintenance. Like any other solution aimed at increasing the energy efficiency of the system, recuperators cost some money and require regular maintenance. However, experience has repeatedly proven that the costs of heat recovery are much lower than the benefits obtained.
- Rotary, chamber and, to a much lesser extent, plate heat exchangers have one drawback, which can be critical at some facilities - leakage of air flows is possible in them. In this case, the danger is the flow of exhaust air into the supply air. Such leaks are undesirable in clean room ventilation systems and are not acceptable, for example, in infectious diseases departments of hospitals and operating rooms. The reason is the danger of viruses that have entered the hood from any room flowing into the supply air flow with subsequent spread throughout all rooms of the facility. As a result, recuperators with intermediate coolant or freon recuperators are used at such facilities.
- Recuperators increase the dimensions of the ventilation unit. This primarily applies to plate recuperators, since they are air-to-air heat exchangers and are quite large in size. In addition, this applies to recuperators with intermediate coolant due to the presence of two separate heat exchangers, two pipeline lines and piping units near each of the heat exchangers.
Design of a unit with a recuperator
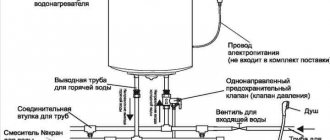
The internal structure of supply and exhaust ventilation systems with an integrated recuperator is quite simple, so it is possible to independently purchase and install them element by element. If assembly or self-installation is difficult, you can purchase ready-made solutions in the form of standard monoblock or individual prefabricated structures to order.
A typical design of a supply and exhaust ventilation system with a recuperator located in a single housing can be supplemented with other components at the user’s discretion
Main elements and their parameters
The body with heat and noise insulation is usually made of sheet steel. In the case of wall installation, it must withstand the pressure that occurs when foaming the cracks around the unit, and also prevent vibration from the operation of fans.
In the case of distributed air intake and flow into various rooms, an air duct system is attached to the housing. It is equipped with valves and dampers to distribute flows.
If there are no air ducts, a grille or diffuser is installed on the supply opening on the side of the room to distribute the air flow. An external type air intake grille is installed on the inlet opening on the street side to prevent birds, large insects and debris from entering the ventilation system.
Air movement is provided by two fans of axial or centrifugal action. In the presence of a recuperator, natural air circulation in a sufficient volume is impossible due to the aerodynamic resistance created by this unit.
The presence of a recuperator involves the installation of fine filters at the inlet of both flows. This is necessary to reduce the intensity of clogging of thin heat exchanger channels with dust and grease deposits. Otherwise, for the system to function fully, it will be necessary to increase the frequency of preventive maintenance.
Fine filters must be changed or cleaned periodically. Otherwise, increased resistance to air flow will cause fan failure.
One or more recuperators occupy the main volume of the supply and exhaust device. They are mounted in the center of the structure.
In the case of severe frosts typical for the territory and insufficient efficiency of the recuperator to heat the outside air, you can additionally install a heater. Also, if necessary, a humidifier, ionizer and other devices are installed to create a favorable microclimate in the room.
Modern models include an electronic control unit. Complex modifications have functions for programming operating modes depending on the physical parameters of the air environment. External panels have an attractive appearance, thanks to which they can fit well into any interior.
Solving the problem of condensation
Cooling the air coming from the room creates the prerequisites for the release of moisture and the formation of condensation. In the case of a high flow rate, most of it does not have time to accumulate in the recuperator and goes outside. With slow air movement, a significant part of the water remains inside the device. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that moisture is collected and removed outside the housing of the supply and exhaust system.
An elementary device for collecting and discharging condensate is a tray located under the heat exchanger with a slope towards the drain hole
Moisture is removed into a closed container. It is placed only indoors to avoid freezing of the outflow channels at sub-zero temperatures. There is no algorithm for reliable calculation of the volume of water received when using systems with a recuperator, so it is determined experimentally.
Reusing condensate for air humidification is undesirable, since water absorbs many pollutants such as human sweat, odors, etc.
You can significantly reduce the volume of condensate and avoid problems associated with its occurrence by organizing a separate exhaust system from the bathroom and kitchen. It is in these rooms that the air has the highest humidity. If there are several exhaust systems, the air exchange between the technical and residential areas must be limited by installing check valves.
If the exhaust air flow is cooled to negative temperatures inside the recuperator, condensate turns into ice, which causes a reduction in the open cross-section of the flow and, as a consequence, a decrease in volume or a complete cessation of ventilation.
For periodic or one-time defrosting of the recuperator, a bypass is installed - a bypass channel for the movement of supply air. When a flow bypasses the device, heat transfer stops, the heat exchanger heats up and the ice passes into a liquid state. The water flows into the condensate collection tank or evaporates outside.
The principle of the bypass device is simple, therefore, if there is a risk of ice formation, it is advisable to provide such a solution, since heating the recuperator by other means is complex and time-consuming
When the flow passes through the bypass, there is no heating of the supply air through the recuperator. Therefore, when this mode is activated, the heater must automatically turn on.
Self-production of a plate-type recuperator
Since the average cost of a plate heat exchanger is 300 USD. That is, it makes sense to make this easy-to-make air recuperator with your own hands.
In order to make a recuperator yourself, you will need:
- sheets of galvanized metal (4 sq. m.);
- technical cork 2 mm thick;
- silicone sealant with neutral reaction;
- tin box for the body or sheets of MDF, metal or plywood for its manufacture;
- glue;
- insulation 4 cm thick (mineral wool or polystyrene foam);
- corners for racks;
- plastic flanges;
- jigsaw or grinder.
Stages of work:
- We cut the material into small squares with a side size of 200 to 300 mm. The plates must be identical and perfectly flat; it would be better to cut the folded sheets with a grinder rather than use metal scissors. There should be about 70 such plates, which serve as blanks for the recuperator cassettes.
- In order to create a gap between the sheets, we use a technical plug. The point is to make a section at which the air flow speed will be 1 m/s. We glue the cut cork along two opposite edges of the square blanks, without touching the latter.
- After waiting for the glue to dry, we create a heat exchanger cassette by gluing the sheets so that each subsequent one is located at an angle of 90 degrees to the previous one. The cassette produces alternating channels perpendicular to each other. The last one will be the sheet on which we did not glue the cork.
- After connecting all the plates using a corner, we tighten the structure with a frame.
- We carefully seal all cracks with sealant.
- On the walls of the cassette we place fastenings for flanges having a diameter corresponding to the air duct pipes. It is advisable to place the cassette vertically, then condensation will collect at the very bottom. A drainage channel is prepared in the same place: a hole with a tube for draining liquid.
- In order for the cassette to be removed from the case, guides from the corner must be installed inside it.
- The housing with the cassette is placed in a box made of thick plywood or tin. An important point will be the use of thermal insulation materials (mineral wool or polystyrene foam), which are used to cover all sides of the box from the inside.
Note! The width of the recuperator body should correspond to the width of the cassette, the height and length should correspond to the diagonals of the square plates.
For more reliable operation of the recuperation system in conditions of negative supply air temperatures, when the heat exchanger plates can ice up, a bypass is added to the system, through which the supply air flow is directed, if necessary. At this time, only warm exhaust air will pass through the heat exchanger, and under its influence the frozen heat exchanger plates will thaw.
The efficiency of a homemade recuperator will be about 60–65%, which will ensure that an optimal indoor microclimate is maintained.
How to make an air recuperator with your own hands for a private home
The first stage is the development of a drawing and selection of materials. The volume of passing air is taken into account. The air exchange rate is at least 0.35 per 1 hour or 30 m³/hour per resident. In the kitchen this figure is equal to or more than 75 m³/hour. These values depend on the fan performance and the useful cross-section of the air ducts.
Performance is calculated using the formula:
L is the required capacity, n is the calculated air exchange rate, and v is the volume of the room. Air duct diameter – 100, 125 or 150 mm. Depends on the size of the impeller. Artificially reducing the fan pipe can lead to the formation of a pressure difference.
Lamellar
A homemade plate recuperator differs in the directions of circulating flows. In direct-flow ones they have one vector of movement, in counter-flow ones they move towards each other. For self-production, it is better to apply the third principle - cross-cutting. The directions in the design intersect crosswise.
A plate recuperator can be easily made with your own hands
- Aluminum, galvanized metal. They bend easily, which simplifies processing, and they have a relatively low cost. But it must be taken into account that metal has a high thermal conductivity coefficient, which leads to freezing and the appearance of condensation.
- Polymers (plastic). Reliable, low probability of condensation. The disadvantage is the high cost.
- Special pulp. They have the highest efficiency and are easy to process. But they quickly collapse under high humidity in the building and are not suitable for swimming pools, bathhouses and similar premises.
For production you need plates. They are made from aluminum, steel, paper or plastic. Total area – up to 4 m². The gaps are formed from technical cork (roll) 2 mm thick. The elements are fastened with metal corners. The body is made of galvanized iron or plastic. You also need glue and sealant.
Manufacturing procedure
- Formation of sheets measuring 20*30 cm in the amount of 70-75 pieces.
- Glue three strips of sealant (cork) onto one side of the plate. One is located in the center, two are located on opposite edges.
- Glue the two finished platinums through the spacers. The stripes are perpendicular.
- This is how a sectional core is formed, in which the channels alternate in direction by 90°.
There are no cracks in the box and it is sealed. To reduce heat loss, insulation is installed on the inside. To connect to the air duct, inlet and outlet flanges are attached to the ends.
In the same way, you can make a plate recuperator from polycarbonate. Its advantage is that the gaps are already formed in the sheets. The polycarbonate should be cut into plates and glued together, taking into account the 90° offset of the direction of the air ducts relative to each other.
Tubular
The operating principle of this air exchange scheme is similar to the coaxial air duct for gas boilers. The tubular recuperator has two channels - external and internal. In the first, flows from the street pass through the space between the outer casing and the inner pipe. To exit the building, a pipe of smaller diameter is installed. Heat exchange occurs through its walls.
The outer box will be a sewer plastic pipe with a cross-section of 15 cm; a corrugated sleeve of 10 cm is used for the internal pipe. Adapters (adapters) from 150 to 100 mm for the tightness of the corrugation. Tees are used to form an air channel.
Manufacturing procedure
- Cut the plastic blank and trim the edges.
- Install two tees along the edges of the structure.
- Install the corrugation. It should be located in the center of the polymer pipe, without touching its walls.
- Connect the adapters using rubber seals and secure the edges of the corrugation. The joints can be treated with sealant.
For better circulation, a fan is installed in the reversible pipe. Ventilation grilles will provide protection from debris and dust. However, they will artificially reduce productivity due to a decrease in the useful cross-section of the line.
An alternative is to install a set of plastic pipes with a diameter of up to 16 mm and with a minimum wall thickness instead of a corrugated hose. Such drawings and diagrams will ensure maximum heat exchange, as the contact area of two media with different temperatures increases.
The feasibility of purchasing a recuperator
This device is only part of the forced-exhaust ventilation system. It is impossible to achieve maximum efficiency of its operation using one recuperator and only natural ventilation. For heat transfer to be ideal, constant movement of both flows - incoming and outgoing - is necessary.
Before making the final choice in favor of purchasing or making it yourself, it is better to make some preliminary calculations. The list includes calculations:
- energy consumption before installing a new ventilation system;
- the cost of purchasing and installing all necessary elements;
- its approximate service life;
- annual maintenance costs.
Often, after calculations, it turns out that the costs do not cover the cost of using factory ventilation systems. If we talk about homemade recuperators, then in this case their low cost gives a chance to stay in the black - to slightly reduce coolant consumption. In other cases, an air conditioner is the equipment that will fully cope with its task - maintaining a favorable indoor microclimate.
Determining system efficiency
In order to determine whether it is necessary to install a heat redirection system, efficiency studies are carried out. We will give an example of such a calculation using a relatively small private house. Features of the calculation include:
- According to calculations, approximately 35% of the heat is lost through the ventilation system. Let’s take 30% as the average value, since modern ventilation systems are more efficient in terms of energy savings.
- The average show power consumption is 500 watts. Note that this indicator was chosen taking into account the location of the house in Sevastopol. The average temperature in January is about 3.5 degrees Celsius. Energy consumption in colder climates will be significantly higher.
- If a plate-type recuperator design is installed, then the consumer power will be limited to 30 watts.
- The system efficiency indicator is at around 40%.
According to calculations based on the entered data, the payback period is approximately 114 years. Therefore, it does not make sense to purchase a plate heat exchanger for a private home.
Model overview
Let's look at several popular models of recuperators.
"Vents PR 600x300"
The plate recuperator model is designed to remove used air from the room. The material of the internal equipment is aluminum, and the material of the body is galvanized steel. The device weighs 31 kg. For installation it is necessary to use a pipe with a diameter of 300 mm.
To connect the model to the air duct, you will need an elbow with a rectangular cross-section.
Thanks to the aluminum plate, there is highly efficient heat transfer. This recuperator provides for the collection of a small amount of condensate that forms on exhaust surfaces. The kit includes a condensate drain fitting, which is installed in the bottom panel.
"Vents PR 700x400"
The rectangular plate heat exchanger is made of galvanized steel with a connecting pipe . This model weighs 47.8 kg. It has a cross-shaped air passage and is designed to remove the latter from the room through the ventilation and air conditioning system. This device is connected to an air duct with a rectangular cross-section, with a parallel routing, and can also be connected with a perpendicular or diagonal routing at an angle of 45 degrees.
You can choose any of the options. In any case, it is necessary to purchase a knee for a given position . The heat exchange device consists of special thin aluminum plates that ensure active heat transfer. In summer, the heat exchanger can be replaced with a VL summer rate; it does not produce heat, but reduces pressure loss by 10%.
Vaillant recoVAIR VAR 60/1 D
The recuperator is designed for a decentralized system with supply and exhaust air exhaust in two directions. The model is wall mounted with a mounting hole diameter of 162 mm. The minimum productivity is 30 m3/hour, and the maximum is 60 m3/hour. There are three fan speeds. During operation, the device produces a noise level of 34 to 46 dB.
Equipped with a plate heat exchanger with an efficiency of 85%. The minimum temperature for the device to operate starts from -20 degrees.
For more convenient control there is a remote control, it is possible to control via the Internet. Power consumption is 9 W from a voltage of 220 V. Mounted on a wall with a minimum thickness of 30 cm. Weighs 3.4 kg.
Mitsubishi Electric VL-50ES2-E
The recuperator is designed for decentralized supply and exhaust ventilation. The device weighs 6.2 kg and has dimensions of 522x245x168 mm. This channel model is mounted on a wall with a mounting hole diameter of 120 mm. Performs the functions of a recuperator with a capacity of 15 to 54 m3/h. During operation, the noise level varies from 15 to 37 dB. The model is equipped with a plate heat exchanger with an efficiency of 86%. During operation, it consumes power of 19 W with a voltage of 220 V.
Daikin VAM 350 FC
The recuperator is designed for a centralized system with supply and exhaust ventilation. It has the following characteristics: weight – 33 kg, width – 828 mm, height – 310 mm, length – 816 mm.
It has a suspended mounting method with a mounting hole diameter of 150 mm.
Performs the function of a recuperator with a capacity of 210 to 350 m3/hour. It has three fan speeds with a maximum noise level of 32 dB. External static pressure – 103 Pa. The plate heat exchanger has an efficiency of 84%. The minimum temperature for operation of this device is -15 degrees. During operation, it consumes power of 71 kW from a voltage of 220 volts.
Cooper Hunter CH-HRV2K2
The recuperator is designed for a centralized system with supply and exhaust ventilation. It has a suspended mounting type with a mounting hole diameter of 145 mm. The minimum productivity is 150 m3/h, and the maximum is 200 m3/h. There are three fan speeds. During operation, the noise level is 27 dB. The device is equipped with a plate heat exchanger with an efficiency of 75%. The minimum operating temperature is -15 degrees. A control panel is provided. During recovery, it consumes 105 W of power. It weighs 23 kg and has dimensions of 580x264x666 mm.
Electrolux EPVS-450
The Electrolux EPVS-450 air handling unit is a compact device that includes fans that provide air flow from the street into the room and in the opposite direction.
Membrane-type design, the distinctive feature of which is the effective extraction of moisture from the air. The fan impellers are equipped with curved blades and are driven by asynchronous motors. The design of the device includes thermal contacts that ensure automatic restart of the equipment when the threshold temperature value is reached. The recuperator has two fan speeds and protection against freezing of the plates. Installation in round air ducts is recommended.
Model features:
- built-in automation system;
- Efficiency - 80-90%
- programming of work and self-diagnosis of errors.
At temperatures below -15°C, two operating modes are possible:
- auto defrost;
- connection of external heating.
Specifications:
- remote control;
- maximum power - 140 W;
- noise level - 36 dB;
- productivity - 440 m3/hour;
- dimensions - 275x815x860 mm;
- weight - 33 kg.
The manufacturer provides a 1-year warranty for its products. Average price 44,100 rub.
Recuperator Marley MEnV-180 Plus
A small-sized installation from a German manufacturer has many advantages:
- almost silent operation;
- ceramic honeycomb heat exchanger with many channels for air flows;
- purification of incoming air masses using filters of class G3 and G4;
- noise reduction system;
- remote control using a remote control;
- low power consumption: 3.5-11 kW.
The heat exchanger body can be adjusted depending on the thickness of the wall into which the device is installed. The casing of the device is insulated, and there is a power on and off button on the front decorative panel. When installing two devices, a synchronized ventilation mode is possible: one heat exchanger works for air flow into the room, the second for air outflow.
The recuperator design includes:
- filter that retains dust;
- sensors: temperature, carbon dioxide, humidity;
- electronic boards coated with a moisture-proofing agent;
- coarse filter.
Specifications:
- power - 3 kW;
- noise level - up to 22 kW;
- performance - 60 dB;
- cross section - 180 mm.
The average price is 29,300 rubles.
Exhaust unit Shuft RHPr 400×200
The Shuft RHPr 400×200 plate heat exchanger is designed for installation in residential, public and industrial premises. The body of the device is made of galvanized steel with a thickness of 0.7 mm. The heat exchanger cassette consists of aluminum plates 0.2 mm thick. Moisture extracted from the air accumulates in a removable tray.
The specificity of the use of the recuperator is that it cannot be installed in air transportation systems that contain aggressive gases, sticky dust (including flour), metal and other heavy particles. Only horizontal installation of the recuperator is permissible.
Specifications:
- Efficiency - 70%;
- dimensions - 222x474x474 mm;
- weight - 19 kg.
Average price RUB 24,822.
Power calculation rules
When making a device with your own hands, you need to correctly calculate its power. Determine the amount of heat passing through the plates. For this, the formula is used: P=0.36xQxdT; Where:
P – recuperator power in watts: Q – energy required to heat or cool the air flow.
It is determined by the formula: Q=0.335xLx(t k.-t n.); Here:
L – air flow. Calculated in m3/hour. For 1 person this value corresponds to 60. t n. – initial temperature value; tk – final temperature, which increased as a result of heat exchange; dT – temperature.
After manufacturing and installing the recuperator, it is necessary to ensure the efficiency and duration of its operation. It is better to integrate special filters into the system, which include aluminum. Change them promptly if they become dirty. In winter, prevent the formation of an ice crust. To do this, sometimes it is necessary to turn off the fan that provides the flow of cold air.