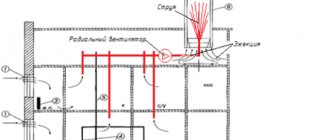
One of the indicators that influences the provision of an optimal microclimate in premises for various purposes is the air exchange rate. This term refers to the number of complete cycles of changing air masses in a room within a unit of time, for example an hour.
The rotation of air masses ensures:
- removal of air containing pathogenic and pathogenic microorganisms;
- replacing oxygen containing carbon dioxide with a new volume of air, which creates comfortable conditions for human mental activity;
- optimal values of temperature and humidity in the room, which influence human performance and create the specified conditions for storing various products;
- elimination of air containing unpleasant odors.
The required values of air exchange rates, depending on the purpose of the room, are indicated in special SNiP tables. Rotation of air masses is ensured through the combined use of natural and artificial ventilation.
The flow of oxygen is ensured through windows, doors and using special fans. However, given the tendency to use materials and technologies that ensure the tightness of these structures, close to absolute values, the use of systems that provide oxygen flow in the construction of buildings is a prerequisite for achieving air exchange rates.
These problems are solved by equipping walls and windows with supply valves, which, in addition to tightness, ensure the supply of the required amount of oxygen per unit of time.
Air exchange concept
Basic requirements when designing air conditioning systems include determining the number of air exchange cycles. This term refers to the creation of conditions to ensure circulation and complete replacement of the volume of oxygen in the structure. This parameter depends on the concentration of harmful components in the air, the presence of places where excess heat and moisture are released and the frequency of changes in the volume of oxygen in the room.
The air exchange rate is an indicator that determines the intensity of the complete change in oxygen volume. In other words, organized and regulated air exchange is defined as the number of complete cycles of oxygen changes within an hour. This parameter relates to sanitary standards and determines the degree of safety and comfort of a person’s stay in the building. The normative and permissible values of this indicator are determined by the adopted SNiP standards, which contain various requirements depending on the purpose of the room.
Air exchange can be natural or artificial. In the first case, the air flow is ensured due to the difference in air pressure inside the room and outside it. In the second option, replacing the volume of air masses involves the use of forced oxygen supply systems, entering through openings in doors and walls and ventilating the premises. The organization of removal of contaminated oxygen involves the installation of exhaust systems in rooms with the most polluted air. In an apartment, such places can be a bathtub, toilet and kitchen; in the first two cases, the ventilation system can be equipped with devices that suck in polluted air or air valves; in the case of a kitchen, in most cases we are talking about equipping the space above the stove with various types of exhaust hoods .
Ventilation systems control
Automation of ventilation system control allows you to optimize the process and reduce operating costs. This approach allows us to minimize human participation in management and reduce the risk of the “human factor”. Automatic control involves the installation of sensors that record air temperature/humidity, concentration of harmful substances, degree of smoke or gas contamination. All sensors are connected to a control unit, which, thanks to the specified settings, turns the equipment on or off. Thus, automation helps to comply with sanitary standards, quickly respond to emergency situations and save significant money.
Calculation of air exchange rate
When determining the air exchange rate for each specific room, designers take into account the regulatory indicators recorded in sanitary and hygienic standards, GOSTs and building codes, for example SNiP 2.08.01-89. Without taking into account the content of harmful impurities in the air, the number of substitutions for premises of a certain volume and purpose will be calculated based on the values of the standard multiplicity indicators. The volume of the building is determined by formula (1):
where a is the length of the room; b – room width; h – room height.
Knowing the volume of the room and the amount of oxygen supplied within 1 hour, you can calculate the ratio Kv using formula (2):
Calculation of air exchange rate
where Kv is the air exchange rate; Qair – supply of clean air entering the room for 1 hour.
Most often, formula (2) is not used to calculate the number of cycles of complete replacement of air masses. This is due to the presence of air exchange rate tables for all standard structures for various purposes. With this formulation of the problem, for a room having a given volume with a known value of the air exchange coefficient, it is necessary to select equipment or select a technology that ensures the supply of the required amount of oxygen per unit time. In this case, the volume of clean air that must be supplied to ensure complete replacement of oxygen in the room in accordance with the requirements of SNiP can be determined by formula (3):
According to the given formulas, the unit of measurement of the air exchange rate is the number of complete oxygen replacement cycles in the room per hour or 1/hour.
Using a natural type of air exchange, you can achieve 3-4 times replacement of indoor air within 1 hour. If it is necessary to increase the intensity of air exchange, it is recommended to resort to the use of mechanical systems that provide a forced supply of fresh oxygen or the elimination of contaminated oxygen.
Which air ducts to choose?
Round pipes with a smooth inner surface have low resistance; in rectangular shapes, turbulence at the corners slows down the flow. The rough surface of brick channels and corrugated pipes have maximum resistance to air movement. Therefore, the walls of the brick shaft are plastered, and the “corrugation” is used only for flexible turns and short sections.
The movement of air is hampered by the accumulating static electricity on the walls of plastic pipes. Therefore, galvanized steel pipes remain the best material for ventilation in a private house.
Ventilation ducts are insulated in cold areas (attic). The supercooled walls of the shaft slow down the draft and collect condensation. Therefore, in winter the canal can be completely covered with frost. A layer of insulation (50-70 mm) corrects the situation.
Condensation also settles on the pipes due to lack of draft. This is a signal to review the entire system. It is necessary to reduce the length of the air ducts, the number of turns and horizontal sections. In summer, it is advisable to increase the draft with fans. With constant air movement, moisture is not retained.
Calculation methods for residential building premises
The flow of the required amount of air into residential premises, depending on the type of room, can be ensured through autonomous air valves in the walls with adjustable opening parameters, vents, doors, transoms and windows. Experts draw the attention of designers to the fact that when calculating the indicators for complete replacement of air in living rooms, it is necessary to take into account a number of parameters, including:
- purpose of the premises;
- the number of people permanently present in the building;
- indoor air temperature and humidity;
- the number of operating electrical appliances and the rate of heat they generate;
- the type of natural ventilation and the oxygen replacement rate it provides for 1 hour.
To create comfortable conditions in accordance with the standards of SP 54.13330.2016, the amount of air exchange should be:
- If the area of the room per person is less than 20 m² for a children's room in an apartment, bedrooms, living rooms and common areas, the air supply should be 3 m³/h per 1 m² of area of each room.
- If the total area per person exceeds 20 m², the air exchange rate should be 30 m³/h per person.
- For a kitchen equipped with an electric stove, the minimum oxygen supply cannot be less than 60 m³/h.
- If a gas stove is used in the kitchen, the minimum air exchange rate increases to 80-100 m³/h.
- The standard air exchange rate for lobbies, staircases and corridors is 3 m³/h.
- Air exchange parameters increase slightly with increasing humidity and temperature in the room and amount to 7 m³/h for drying, ironing and laundry rooms.
- When organizing a bathroom and restroom in a residential area, located separately from each other, the air exchange rate should be at least 25 m³/h; if the toilet and bathroom are located together, this figure increases to 50 units.
Considering that during cooking, in addition to steam, a number of volatile compounds containing oil and soot are formed, when organizing an air exchange system in the kitchen, it is necessary to prevent these substances from entering the living room. To do this, the air in the kitchen room is removed outside by creating a draft in a ventilation duct at least 5 m high and using a special exhaust hood. This type of organization of air mass rotation ensures the elimination of excess heat. However, in order to prevent exhaust air from entering apartments located on the upper floors during the construction of the structure, an air seal is installed to ensure a change in the direction of the air flow.
Exhaust areas
Exhaust ducts remove exhaust air, excess moisture, and odors to the street. Outflow areas for natural ventilation of a private house are equipped in the kitchen, bathroom, bathroom, and, if necessary, in other rooms. Air intake grilles are placed at a height of 0 to 25 cm from the ceiling.
A separate shaft is allocated for the kitchen hood, which is not taken into account in the general calculations (it is turned on temporarily). If there is only one channel, then the equipment is connected through a tee with a check valve. The blades open when the hood is turned off, then the room is ventilated. The mine is considered working, but its increased resistance is taken away in the calculations.
Several channels can be combined into one only with the installation of a fan above all connections; without it, odors will flow between rooms. For the same reason, individual inflow/outflow is organized in technical rooms (basement, garage, furnace room). The doors are closed hermetically so that the flows do not mix with the home air exchange.
Administrative and service buildings
As already mentioned, the multiplicity indicators have different values for different buildings, while in some cases the operation of systems for ensuring the rotation of air masses involves the use of natural ventilation in the cold season. At the same time, in some of the rooms used, for example showers and restrooms, the exhaust ventilation system must work more intensively than the fresh oxygen supply system in general-purpose rooms. Thus, the parameters of air and steam removed hourly from shower rooms should be based on the calculation of 75 m³/h per 1 mesh, and when organizing the removal of contaminated air from restrooms, at the rate of 25 m³/h per 1 urinal and 50 m³/h per 1 toilet .
Multiplicity table for retail premises.
When ensuring air change in a cafe, the organization of the ventilation and air conditioning system must ensure the frequency of air replacement in the supply system at the level of 3 units/hour; for the exhaust system this figure should be 2 units/hour. The calculation of a complete air replacement system in a sales area depends on the type of ventilation used. So, if, in the presence of supply and exhaust type ventilation, the air change rate is determined by calculation for all types of sales floors, then when equipping a structure with an exhaust hood that does not provide air flow, the air change rate should be 1.5 units/hour.
Multiplicity table for cafe premises
When using rooms with a large amount of steam, moisture, heat or gas, air exchange can be calculated based on the existing excess. In order to calculate air exchange based on excess heat, formula (4) is used:
where Qpom is the amount of heat released into the room; ρ – air density; c is the heat capacity of air; t output - temperature of air removed by ventilation; t supply - the temperature of the air supplied to the room.
The organization of the air exchange system in the boiler room depends on the type of boiler used and should provide 1-3 times replacement of the entire volume of oxygen within an hour.
Influx places
By natural draft, fresh air enters the house through slightly open windows, however, then most of the home heat evaporates. To avoid heat loss, air inlet valves (inlet valves) are used, which constantly allow a certain volume of air to pass through.
The pipe, limited by gratings, goes right through the wall. The position of the lid regulates the flow rate from 40 to 100 m3/hour. The installation is located far from the doors, often behind radiators, above 2 m above ground level. The base valves are manually adjusted.
Rice.
2 — Supply valve KIV Automatic ventilators (breathers) are adjusted by humidity and temperature sensors, which saves time and up to 5% of heating costs. Inside the case there is a built-in fan, which is set with parameters for a certain volume of air (power 3-7 W). The inflow rate is adjustable from 12 to 150 m3/hour.
Rice. 3 — Automatic ventilator (breather)
The installations create excess pressure in the rooms, which helps move stagnant air into channels with natural draft (even if the draft is weak). Ventilators are often equipped with filters for dust removal (fine - F or coarse - G), ionizers, and heaters for heating the inflow.
Supply ventilation with a water heating circuit requires hydraulic piping, which should preferably be done before finishing the walls. In this case, the heater becomes sensitive to frost and may freeze. Electrical installations are less demanding, but increase energy consumption in the home.
New generations of breathers are equipped with climate control systems and a whole set of filters that retain pollen, heavy metals, and bacteria. True, purchasing and operating the device (electricity costs, replacing filters) is expensive.
In houses with an area of more than 150 m2, it is more rational to equip an air duct system with mechanical drive. Where street air is prepared as much as possible before entering the room and distributed by fans to different rooms through a network of air ducts. An exception is that an individual supply must serve the kitchen, garage, bathroom, or bathroom.
Rice. 4 - Mechanical ventilation of a private house
Sports and recreational institutions
When exercising in a gym, the rate of air exchange plays an important role, since during physical activity it is necessary to ensure the flow of fresh oxygen into the lungs of each visitor, taking into account the fairly large volumes of the hall. Thus, the requirements stipulate the need to ensure that 80 m3/h of air enters the gym when there are visitors.
The calculation of the air exchange rate for a swimming pool is based on the number of people in it and should be 20 m³/h per 1 person. At the same time, taking into account the specifics of being in a sauna or bathhouse, it is necessary to ensure a change of 10 m³ of air every hour. At the same time, taking into account the large volumes of saturated steam produced, it is possible to calculate air exchange based on moisture emissions.
I “recently” had my ventilation checked, why should I check it again???
This question may be asked by many residents of multi-apartment residential buildings, to which they came with a (formal) check of natural ventilation, attaching a piece of paper or placing a match (highly not recommended for fire safety reasons) to the ventilation duct.
Practice shows that a piece of paper “sticking” to the grille of a ventilation duct cannot always indicate the serviceability of the ventilation system.
Let's look at the ventilation grille located in the kitchen area of a two-room apartment. The kitchen area is 6 m2, the grate is located at a height of 2.4 meters.
A new vent was installed in the cleaned and inspected duct approximately one year ago from this inspection.
Inspection of the ventilation grille, apparently nothing special
Judging by the traces of dirt on the grille, it can be assumed that the ventilation in the room was functioning until recently. An anemometer (a device for measuring air flow speed) shows a speed of 0.5 m/s, which is low for the winter period of the year, but there is still a slight draft. In this case, most likely, the attached piece of paper will stick to the ventilation grille.
If it were not for the readings of the device, then a piece of paper stuck to the grille of the ventilation duct would give reason to assume that the ventilation in the apartment is working properly.
Now let's take a closer look at the ventilation grille
dust on the ventilation grill after a year of operation
I emphasize that the grate was used for only one year in a kitchen area of 6 m2, in an ordinary two-room apartment (Khrushchev), with three people living in it.
Now let's see what's going on under the outer part of the grille
The mosquito net of the ventilation grill is clogged with dust
The photograph clearly shows that the mosquito net of the grill is approximately 70% clogged with dust. And this is just in one year.
You can also understand from the photograph why you cannot check ventilation using a lighter, match, candle, etc. The accumulation of dust and grease deposits can easily ignite, causing fire and fire.
The above example clearly shows the need to periodically check and clean at least the ventilation grilles!
Health care institutions
The air exchange rate in institutions belonging to the healthcare system has the highest values for wards in which inpatient treatment of patients with detected pathologies of infectious (160 m³/h) and non-infectious (80 m³/h) origin is carried out.
According to the standards, most other premises, including doctors’ offices and treatment rooms, must have an exhaust ratio with a natural type of air exchange organization equal to 1-2 units/hour.
A separate point worth mentioning is the organization of the ventilation system for operating rooms. According to modern requirements, they must use a 3-fold air purification system, while operating devices must provide a minimum flow of 1200 m³ of air per hour.
Effective Paint Shop Ventilation - Design Principles
Mixed-type supply and exhaust ventilation systems (local and general exchange) contribute to the creation of a microclimate that is safe for health only if sufficient air exchange is ensured. With a significant concentration of harmful substances released during the process of painting large parts using powder coating, the task of ventilation of the paint shop comes down to maintaining fire safety by achieving maximum permissible concentration values.
Sources
- https://mega.ru/ventilyatsiya/kak-sostavlyaetsya-proekt-ventilyatsii-tseha
- https://ecoenergovent.ru/info/sistema-ventilyaiya-i-kondiionirovanie-v-proizvodstvennom-ehe
- https://www.AirClimat.ru/Ventilyatsiya-tseha.htm
- https://foundmaster.ru/climatic/ventilyatsiya-proizvodstvennogo-tseha.html
- https://www.PromKlimat.ru/Ventilyatsiya-tseha.htm
- https://www.air-ventilation.ru/ventilyatsiya-proizvodstva.htm
- https://otivent.com/ventiljacija-proizvodstvennyh-pomeshhenij
- https://foundmaster.ru/ventilation/ventilyatsiya-goryachego-tseha-osobennosti-ustanovki.html
- https://www.provento-ventilation.ru/info/articles/ventilyatsiya-pokrasochnogo-tsekha/
Premises of preschool organizations
Ensuring the required air exchange standards in preschool organizations is a basic condition for the health and normal mental activity of children. However, when providing ventilation, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of drafts; taking into account this requirement, ventilation in preschool organizations is carried out in accordance with the daily routine of the institution.
According to the standards outlined in SNiP 41.21-2003, to ensure ventilation, the air exchange rate in the classroom, locker room, playroom and bedroom for children under 2 years of age should be 1.5 units/hour. More stringent requirements are imposed when ensuring a complete replacement in the area of the washbasin, toilet, medical station and kitchen, for which this figure is 2-3 units / hour.
How often should you check and clean the ventilation in your apartment?
There are general rules for checking and maintaining ventilation systems for residential multi-apartment buildings, and separately prescribed rules for buildings using gas equipment.
1. General rules for residential buildings.
Resolution of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2003 N 170 “On approval of the Rules and Standards for the technical operation of the housing stock”
5.7.5. Dust cleaning and disinfection of attic spaces should be carried out at least once a year, and ventilation ducts - at least once every three years.
5.7.11. The list of deficiencies in the ventilation system that must be eliminated during the renovation of a residential building should be compiled based on the spring inspection data.
View the full text of the document >>>
2. Rules for buildings using gas equipment.
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 14, 2013 N 410 “ On measures to ensure safety when using and maintaining indoor and indoor gas equipment”
12. Checking the condition of smoke and ventilation ducts and, if necessary, cleaning them is carried out: a) when accepting smoke and ventilation ducts into operation during gasification of the building and (or) connecting new gas-using equipment; b) during the reconstruction and repair of smoke and ventilation ducts; c) during the operation of smoke and ventilation ducts (periodic checks) - at least 3 times a year (no later than 7 calendar days before the start of the heating season, in the middle of the heating season and no later than 7 days after the end of the heating season); d) in the absence of draft detected during operation, during maintenance and repair of in-house and (or) in-apartment gas equipment, diagnosing in-house and (or) in-apartment gas equipment and emergency dispatch support.
View the full text of the document >>>
Resolution of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2003 N 170 “On approval of the Rules and Standards for the technical operation of the housing stock”
5.5. Internal gas supply devices 5.5.12. Housing maintenance organizations responsible for the technically sound condition of ventilation ducts and chimneys under contracts with specialized organizations must ensure periodic inspections of: b) ventilation ducts of premises in which gas appliances are installed - at least twice a year (in winter and summer). 5.5.13. In winter, at least once a month, and in areas of the northern construction-climatic zone at least twice a month, the heads of chimneys and ventilation ducts must be inspected in order to prevent them from freezing and blocking. Based on the results of the inspection, there must be an entry in a special journal indicating all the faults identified and the nature of the work carried out to eliminate them.
View the full text of the document >>>
Climate control equipment for offices
- Supply ventilation unit for office. Brings fresh air from the street directly into the office space. The outflow of air occurs by displacing it into corridors and lobbies. With an area of more than 40 sq. meters the air is evacuated directly from it. Air supply units for office ventilation are used for areas up to 100 square meters. meters;
- Supply and exhaust office ventilation systems. This is the most widely used type of equipment that provides air outflow, purification and delivery. The kit may include cooling or heating devices, humidifiers. The equipment is very diverse, but the supply and exhaust ventilation of the office must be calculated and installed by professionals. Automatic control over functionality reduces energy consumption and increases efficiency;
- Duct ventilation system in the office. Duct air conditioners with outside air are installed in small and medium-sized offices. Combined with supply and exhaust equipment that brings the outside air temperature to the required level. After which it is served to the rooms;
- Central air conditioning and ventilation in a large office. In large office buildings, the climate is controlled by chiller-fan coil systems and multi-zone VRF systems. The latter consist of many indoor units that provide different temperatures and humidity in the rooms. Central air conditioners are supply and exhaust ventilation in offices with cooling and heating units. This type of climate system is suitable for large offices that are not divided into separate rooms.