Rating:
395
In order not to freeze on cold winter evenings, you need to take care in advance about heating your home, as the popular proverb says: prepare your sleigh for winter in the summer. To solve this issue, the ideal options are panel ones.
Owners of country houses are paying more and more attention to panel heating radiators made of steel. Their heat transfer rate is very high. And, if you compare them with devices of other types, this advantage becomes very noticeable. Panel radiators are produced in different sizes, which allows them to fit into the interior of any room. The power parameters of panel batteries are different.
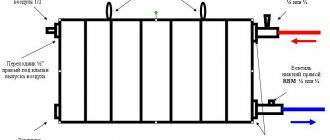
Heating battery panel devices are designed in such a way that two sheets are located in the center, welded together. The sheets are cut with channel grooves. These grooves are needed for coolant circulation. The radiator sheets are covered with a grille on top. Its shape is U-shaped. The role of this grille is to increase the level of heat transfer.
Sectional panel radiator
The top layer is covered with a decorative panel. The width of the radiators varies: from forty to three hundred centimeters, while their height reaches from thirty to ninety centimeters. As you can see, the dimensions and design of panel radiators allow them to be located in any room, even the smallest areas.
Kinds
The degree of power parameters of a panel heating radiator is associated with the peculiarity of its design, with the number of connected panels. Each radiator device has a marking that contains all the information characterizing each device and will show how each heating device differs from each other.
Types of panel radiators
Let's look at some types of panel radiators:
- Type 10. The first number means there is one panel. Zero indicates the absence of ribs. One steel plate that has no side walls and no grille to release air. This is what this species is all about.
- Type 11. Two units indicate the presence of one panel and one row of ribs, which is welded to the back.
- Type 20. This device is represented by two panels and a complete absence of ribs.
- Type 21. It has two rows in depth, that is, two panels plus a row of ribs between them.
- Type 22. The depth is two panels, two rows of ribs, each row of ribs is welded to one of the two sheets.
- Type 33. The deepest type. It is represented by an assembly of three sheets and three rows of ribs located inside the panels. In cross-section it would look like this: leaf – ribs – ribs – leaf – ribs – leaf. Each row of ribs is attached to one panel.
Depending on the model type of radiator, connection methods are distinguished: side and bottom. A radiator with a side connection option can be connected from either side. doing it yourself is not difficult at all. Connecting radiators from below is considered more acceptable.
A thermostatic valve is included in the battery components upon purchase. Its task is to help regulate the heating temperature in the room. It operates manually. Installed directly on the device itself. The bottom connection of a panel radiator has the advantage of being able to hide the supply lines in the floor or walls. In terms of price, it will certainly be more expensive.
When purchasing, it is important to pay attention to the battery power of the devices. Correct calculation of radiators will avoid difficulties in the future.
Calculation of the power of panel radiators
If you buy panel batteries for heating without special calculations, and they turn out to be inappropriate for a given room, this will affect the quality of heating.
The heating device cannot be supplemented with anything. It would be good if they accepted him back and gave him another one in return. Otherwise, you will end up wasting money, since you will still have to buy another one.
To make the correct calculation of radiator power, you need to go through two steps:
- Correctly calculate the area of the entire room and its volume.
- Multiply the figure obtained by measuring the volume by forty-one watts.
Forty-one watts represents the power level taken as an average. This is how many watts of power are needed to heat one cubic meter of room. A corner room will require significantly more power.
The advantages of this type of radiator:
- A small volume of water is required for operation,
- high heat transfer,
- the price is available to anyone who wants to purchase them,
- light weight, which does not require much effort during installation,
- Another plus is their pleasant appearance, shape, color, variety of sizes.
In addition to their advantages, panel heating radiators also have disadvantages. This is evidenced by the reviews of those owners who remain, who are somehow dissatisfied with their operation. Therefore, before purchasing heating devices, read reviews from other buyers.
Disadvantages of panel radiators for apartment and house heating systems:
- Do not buy panel heating radiators if the house is left without water for a month or more. They must always be filled with liquid, otherwise oxygen contact with the radiator wall occurs inside them.
- The heating devices described above require little pressure during operation. The maximum level allowed for this type of device is nine atmospheres.
- According to their characteristics, these devices are suitable for low-rise buildings. Consequently, they will find ideal use in a house outside the city.
- Test the water to determine its hydrogen content. This is due to the fact that these devices are subject to corrosion, and every owner needs a stably operating device. With traditional heating, there is no way to control the level of hydrogen in the water. The high level of pressure existing in the heating system of a multi-storey building and the resulting water hammer will quickly destroy such radiators, which is very undesirable to happen during the winter cold.
So, having become acquainted with the technical characteristics of panel radiator devices for home heating, having studied all the reviews, having measured the volume of the rooms, go shopping. Do not forget to also look at the thickness of the metal, the type and dimensions of the radiator when purchasing.
Your contacts in this article from 500 rubles per month. Other mutually beneficial options for cooperation are possible. Write to us at
Steel ones are widely used for heat supply to private homes and offices. These devices are made in the form of a rectangular panel, tubular structure or sections. Their main advantage is low weight and high heat transfer.
A steel radiator is well suited for heating rooms with an autonomous heating unit. But before installation it is important to calculate the pressure. Thus, such systems are not suitable for heating apartments in high-rise buildings precisely because of the pressure: reaching 25 atmospheres, it can damage the heating device.
What are the main criteria for choosing radiators?
Heating system type
Perhaps this is precisely what we should start from first of all. In our country there are two types of heating systems: centralized and autonomous. Moreover, both of them require the use of different radiators.
1. Domestic central heating is characterized by high operating pressure, as well as its surges. The fact is that, unlike Europe, we have a one-pipe system, in which radiators are connected in series. In addition, no one worries about the smooth start of the centrifugal pump. And turning it on abruptly is fraught with water hammer. And the water in such a system does not shine with either purity or neutrality. It is hard, its acidity is high, and in the summer it is drained, which causes corrosion in many radiators. Therefore, for such a system, radiators are needed that can withstand an operating pressure of 6, and possibly 9 atmospheres (they will tell you more in detail in DEZ). Don’t forget about the acidity of the water when choosing radiators that can operate at high pH levels.
The best choice for a central heating system would be:
- Cast iron radiators are durable and non-corrosive. Working pressure – 6-16 bar.
- Bimetallic radiators, also not subject to corrosion and withstanding pressure up to 35 bar (sectional models) or up to 100 bar (monolithic models).
2. Autonomous heating is fundamentally different from central heating. The water here moves in a circle (two-pipe system), its pressure does not exceed 3-5 bar, and the acidity also meets the standards. There are no foreign impurities in this water. Therefore, almost all types of radiators are suitable for autonomous heating.
For an autonomous heating system, experts recommend:
- Aluminum radiators with the highest heat output.
- Steel radiators have a low price, are distinguished by their beautiful appearance and original design.
- In some cases, you can use good old cast iron radiators.
The use of bimetallic radiators in an autonomous heat supply system is not entirely justified due to their high cost and lower heat transfer compared to aluminum radiators.
Heat transfer of different types of radiators
Let us give specific figures on thermal conductivity (the value is indicated for one section). Naturally, the average values are indicated. You can find out more accurately the characteristics in the passport of a specific radiator.
Heat transfer of one section:
- Cast iron radiators - from 100 to 160 watts.
- Aluminum radiators - from 82 to 212 watts.
- Bimetallic radiators - from 150 to 180 watts.
Total heat transfer of non-sectional radiators:
- Steel radiators - from 1200 to 1600 watts.
- Convectors - from 130 to 10,000 watts.
Let's summarize. The leader in heat transfer is aluminum. Steel takes second place. The third one will be given to cast iron, which also takes a very long time to heat up (that is, it has greater inertia). But it also takes a long time to cool down, which sometimes comes to the rescue.
Which radiators are more reliable and durable?
We will again provide in the form of a list the duration of uninterrupted operation guaranteed by the manufacturers.
- Cast iron radiators – more than 50 years.
- Aluminum radiators - from 15 to 20 years (provided that the pH of the water is not higher than 7-8).
- Steel radiators – up to 15-25 years
- Bimetallic radiators - up to 20-25 years.
- Convectors – 10-25 years.
So, if, when figuring out which heating radiator to choose, you set durability as the main criterion, then you don’t have to look far. Take cast iron - not a single newfangled radiator will last longer. Only choose a proven manufacturer who makes really high-quality batteries using excellent raw materials and components. Following this are bimetallic and steel radiators.
As for reliability, there are two aspects here - the ability to withstand pressure and how demanding a particular type of radiator is on the coolant. If we talk about pressure, then the undisputed leader will be bimetallic radiators, followed by aluminum, cast iron and steel radiators.
But radiators treat coolant differently. The most durable in this regard are cast iron radiators, followed by bimetallic ones. For steel radiators, it is important that water is not drained from the system for a long period, otherwise corrosion may occur when oxygen enters the system. Well, the most “delicate” are aluminum radiators, which require Ph in the range of 7 - 8 units.
Appearance and finishing
1. Cast iron radiators - models from domestic manufacturers, although they have become smaller in size, having undergone changes in design (their facade has become flat), but cannot boast of finishing. They are coated only with an anti-corrosion primer, which requires subsequent painting. But the models from European manufacturers and the coating are beautiful and durable, and the design is quite modern.
Separately, it is worth mentioning retro-style radiators; they are expensive, but their appearance is simply delightful.
Option for cast iron radiators in Retro style.
2. Aluminum radiators are distinguished by a variety of designs. Many manufacturers produce multi-colored radiators that look very elegant and attractive. Models of aluminum radiators are distinguished by a wide range of center distances and standard sizes. This allows them to fit perfectly into any corner of the house.
3. Panel-type steel radiators can fit into almost any apartment interior. Smooth panels are not very noticeable, blending harmoniously with the surroundings.
And tubular steel radiators are often distinguished by their unconventional shape. For example, they can be angular or made in the form of a trapezoid. They are also used to protect staircase steps and fit into niches and attic spaces. And everywhere such radiators look fresh and modern, shining with multi-colored paints.
4. Bimetallic radiators are very sophisticated in design. There are many models that have curved rather than straight surfaces. This allows them to fit perfectly into rooms with smooth angles. Such products are produced, in particular, by the RIFAR plant. The RS Bimetal radiator from SIRA also boasts smooth and beautiful curved lines.
Model of RIFAR FLEX bimetallic radiators with a rounded shape.
5. In terms of appearance, floor convectors differ only in decorative grilles.
Price categories
- Cast iron radiators (except for retro models) - from 300 rubles per section.
- Cast iron “retro” radiators - from 2000 rubles per section.
- Aluminum radiators - from 300 rubles per section.
- Steel radiators (price for a whole radiator) - from 1,500 to 10,000 rubles.
- Bimetallic radiators - from 500-600 rubles per section.
The cheapest radiators are steel panel and cast iron, especially those made domestically. After them will come aluminum injection molded radiators; extrusion models will be slightly cheaper. But the most expensive ones will be bimetallic radiators, retro-style cast iron radiators and steel tubular radiator models.
About the manufacturers - the most famous and reliable brands
Cast iron radiators in a classic style are produced by such companies as the Czech manufacturer VIADRUS, the Spanish one - ROCA, the Italian one - FERROLI, the Belarusian one (MZOO), the Turkish one (DEMIR DÖKÜM). We make them in Cheboksary (manufactured by ROCA (Epoca model), DEMIR DÖKÜM (Retro model).
Aluminum radiators are mainly made by Italians. So, these are the companies RAGALL, ROVALL, DECORAL, MECTHERM, FARAL, INDUSTRIE PASOTTI, GLOBAL, FONDITAL, RADIATORI 2000. For us, this is the Stupino SMK plant, as well as the company from Mias MMZiK. Each has protection for radiators from corrosion. In particular, FARAL produces zirconium treatment of their internal parts. Calidor Super Aleternum radiators, manufactured by FONDITAL, also an Italian company, also have a good anti-corrosion coating.
Tubular steel radiators are produced by German companies ZEHNDER, BEMM, ARBONIA, KERMI. Italian manufacturers are the company TET-A-TERM, and in Russia – KZTO from the city of Kimry, producing the “Zavalinka” model, on which you can even lie down. However, models of the same type (benches) are made by both ARBONIA and ZEHNDER. As for panel steel radiators, they are produced by the following manufacturers: German company KERMI, Czech - KORADO, Belgian - RADSON, Dutch - STELRAD, Turkish - DEMIR DÖKÜM, Polish-Finnish - PURMO), Italian - BIASI. In Russia we can name two enterprises: “MECHANICAL PLANT” from St. Petersburg and from Tver.
Bimetallic radiators are made by companies from Italy (GLOBAL, SIRA), the Czech Republic (ARMATMETAL), Russia (the Ryazan plant TSVETLIT-R, the Moscow plant SANTEKHPROM and the enterprise from the Orenburg region RIFAR). It is the products of the latter manufacturer that are very in demand and popular.
Convectors are produced by Russian (KZTO, ISOTERM and SANTEKHPROM), American (SLANT/FIN), and European companies. For example, Slovenian VTS CLIMA, Polish CONVECTOR, German KAMPMANNAN, English BISQUE RADIATORS, Belgian JAGA.
Classification
Steel batteries are available in three types:
- tubular - welded structure made of pipes with a working pressure of up to 15 atmospheres;
- sectional - durable sections are connected by spot welding, operating pressure up to 16 atmospheres;
- panel ones are the most popular, they are made of two welded rectangular sheets with stamped recesses.
In panel pipes, the operating pressure reaches 13 atmospheres at a coolant temperature of no more than 110 degrees.
Choice of heating radiator: cast iron or bimetallic, comparison table of heat transfer
At the house design stage, space heating batteries are selected. In private construction, this right is sometimes given to the homeowner. How to choose the right heating device: cast iron, bimetallic, metal? Healthy sense and the actual data of heating systems do not always dominate the selection; the financial component of the cost of the house outweighs. It’s not always practically free, it’s a good choice, let’s try to discover the heat transfer parameters of various heating devices.
Heating radiator, comparison of different types
The main characteristic of a heating device is considered to be heat transfer; this is the ability of the heating device to create a heat flow of the required power. When choosing a heating device, you need to understand that for any of them there are specific conditions under which the heat flow indicated in the passport is created. The key heating devices of choice in heating systems are:
- Sectional radiator made of cast iron.
- Metal heat supply device.
- Bimetallic sectional heat supply devices.
We will compare different types of heating devices according to indicators that influence their selection and installation:
- The amount of heat output of the heating device.
- At what operating pressure does the device operate effectively?
- The required pressure for crimping battery sections.
- The volume of coolant occupied by one section.
- What is the weight of the radiator?
It should be noted that in the comparison process it is not necessary to take into account the highest temperature of the coolant; a large indicator of this value allows the use of these heating devices in residential premises.
In urban heating networks, the operating pressure parameters of the coolant are always unequal; this indicator must be kept in mind when selecting a heating device, as well as test pressure parameters. In houses outside the city, in villages with country houses, the coolant is almost always below 3 Bar, but in urban areas mechanized heating is supplied at a pressure of up to 15 Bar. High pressure is needed because there are many buildings with several floors.
Important nuances of choosing a heating device
When choosing a heating device, you must not forget about the water hammer that occurs in central heating networks when the system is first put into operation. Due to these reasons, not every heating device is suitable for this type of heating system. It is best to transfer heat from a heating device taking into account the strength parameters of the heating device.
Important criteria for choosing a heating device are its weight and capacity of the coolant, especially for private construction. The capacity of the heating device will help in calculating the required amount of coolant in the private heating system, and making calculations of the energy costs of heating it to the desired temperature.
When selecting heating devices, it is necessary to take into account the climate conditions of the region. In most cases, the heating device is fixed to a load-bearing wall; heat supply devices are placed around the perimeter of the building, so it is important to know their weight for calculating and choosing the method of fastening. As a comparison of the heat output of heating radiators, the table contains data from the popular company RIFAR, which produces heating devices made of bimetal and aluminum, as well as the parameters of cast iron heating systems of the MS-410 brand.
Explanations of comparative values of heating systems
From the data presented above, it is clear that the bimetallic heating device has the highest heat transfer coefficient. Structurally, this device is presented by RIFAR in a ribbed aluminum housing, which houses metal tubes, and the entire system is fixed by a welded frame. This type of battery is installed in high-rise buildings, as well as in country houses and private houses. The disadvantage of this type of heating device is its high price.
Metal heating devices are much more popular; they have slightly lower heat transfer parameters, but are much cheaper than bimetallic heating devices. Test pressure and operating indicators allow this type of battery to be installed in buildings without restrictions on the number of floors.
Important! When this type of battery is installed in houses with several floors, it is recommended to have your own heat-generating station, where there is a water treatment unit. This condition for the preparatory preparation of the coolant is related to the characteristics of metal batteries; they can be subject to electrochemical corrosion when it enters in poor condition through the central heating network. Due to this, aluminum heating radiators are recommended for installation in individual heating systems.
Radiators made of cast iron will lose significantly in this comparative system of indicators, they have low heat transfer and the radiator is heavy. But, despite these indicators, MS-140 heating devices are popular with the population, the basis of which is considered to be the following factors:
- Duration of trouble-free operation, which is important in heating systems.
- Resistance to the negative effects (rust) of the heat carrier.
- Thermal inertia of cast iron.
This type of heat supply devices has not stopped working for more than fifty years; for it there is no difference in the quality of the preparation of the heat carrier. They cannot be installed in houses where there may be a high operating pressure of the heating network; cast iron is not a strong material.
How to correctly calculate heat output
Proper arrangement of a heating system in a house will not be complete without a thermal calculation of the power of heating devices important for heating rooms. There are conventional proven methods for calculating the heat output of a radiator needed to heat a living space. Here the location of the room in the house along the light sides is also taken into account.
What you need to know to calculate heat output:
- The south side of the house is heated per cubic meter of room by 35 W. heating performance.
- The northern rooms of the house are heated at 40 W per cubic meter. heating performance.
To obtain the total heat output required for heating home premises, you need to multiply the actual volume of the room by the values provided and add them by the number of rooms.
Important! The type of calculation provided cannot be accurate; these are aggregated values, they are used to provide a general idea of the required number of radiator designs.
Calculation of bimetallic heat supply devices, as well as metal batteries, is carried out based on the indicators listed in the details of the product passport. According to the rules, a section of such a battery is equal to 70 units of power (DT).
What is this, how to understand it? The certified heat flow of a part of the battery can be obtained by implementing the condition of supplying a coolant with a temperature of 105 degrees. To obtain a temperature of 70 degrees in the return heating system of the house. The initial temperature in the room is taken to be 18 degrees Celsius.
Important! You need to understand that the data for batteries is shown when the coolant is heated to 105 degrees, which in real systems rarely happens, which means less heat transfer. To calculate the actual heat flux, you need to determine the value of DT, this is done using the formula:
DT= (flow medium temperature + return medium temperature)/2, minus home temperature. Then multiply the data in the product passport by the correction indicator, which for various DT values are given in specialized reference books. In reality it looks like this:
- The heating system does not stop working in direct supply 90 degrees, finishing 70 degrees, home temperature 20 degrees.
- According to the formula it comes out (90+70)/2-20=60, DT= 60
Using the reference book, we look for an indicator for this value; it is equal to 0.82. In our case, we multiply the heat flux 204 by 0.82, we get a real power flux = 167 W.
- Author: Dmitry Sergeevich Kirillov
Selection of heating radiators: What sellers are silent about. How to choose power
Design overview
A steel panel radiator is a convector, as it promotes the natural circulation of heated and cold air. This is due to the peculiarities of their design - the lower air intake holes take in cold air, and through the holes at the top it comes out already hot. This principle of operation due to the convention allows us to achieve a record efficiency of 75%.
Features of operation
Steel radiators do not heat up as much as cast iron ones, and therefore dust does not burn on them. The hygiene of these devices is ensured by the factory paint spraying method, which also protects them from corrosion.
And what’s important is that you don’t have to paint them; they will retain their appearance for many years. The decorative cladding on panel steel batteries is easily removed, so you can vacuum and wet clean the inside.
Care
Panel heating radiators are made of low-carbon steel, so when the device comes into external contact with water, there is virtually no oxidation or corrosion. Such technical characteristics increase the service life of the device in closed heating systems up to 40 years.
Features of radiators
Steel panel heating radiators are by far the most cost-effective option for solving the problem of autonomous heat supply for a private home. They combine the functionality of radiators and convectors. They are rectangular panels of various sizes. On the market you can find models with lengths from 30 to 90 cm and widths from 40 to 300 cm. The thickness (in this case, depth) depends on the type of device chosen, or more precisely, on its design.
Compared to other sectional radiators, this type of equipment has a higher efficiency. The efficiency of most models is at the level of 75%.
There is coolant inside the radiators. Its maximum temperature is 110-120°. The operating pressure in them can reach 9-10 atmospheres with a wall thickness of 1.2 and 1.4 mm, respectively. As tests carried out by one of the manufacturers show, the radiator will collapse when the pressure reaches 25 atmospheres. Therefore, the devices cannot be used in systems with higher pressure (central heating of multi-storey buildings where high-power water hammers occur).
Connection
The standard battery kit, as a rule, already includes everything necessary for its installation: dowels, fasteners, adapters, plug and Mayevsky tap.
Methods
There are four ways to connect a steel radiator to the heating system:
- bottom connection is considered the most optimal: the pipes will be practically invisible, and the built-in thermostatic valve will allow you to independently regulate the air temperature level in the room;
- diagonal (cross) connection - the hot water supply pipe is connected on one side of the radiator from the top, and the return pipe is located on the other side from the bottom;
- lateral connection - used to connect radiators to vertical risers of the heating system and is more often used in multi-storey buildings;
- universal connection - the design of the batteries has holes on the top, sides and bottom, which allows them to be used for any connection.
Technical characteristics of cast iron radiators
The technical parameters of cast iron batteries are related to their reliability and endurance. The main characteristics of a cast iron radiator, like any heating device, are heat transfer and power. As a rule, manufacturers indicate the power of cast iron heating radiators for one section. The number of sections may vary. As a rule, from 3 to 6. But sometimes it can reach 12. The required number of sections is calculated separately for each apartment.
The number of sections depends on a number of factors:
- room area;
- room height;
- number of windows;
- floor;
- presence of installed double-glazed windows;
- corner placement of the apartment.
The price given for cast iron heating radiators is per section, and may vary depending on the manufacturer. The heat dissipation of batteries depends on what material they are made of. In this regard, cast iron is inferior to aluminum and steel.
Other technical parameters include:
- maximum operating pressure – 9-12 bar;
- maximum coolant temperature – 150 degrees;
- one section holds about 1.4 liters of water;
- the weight of one section is approximately 6 kg;
- section width 9.8 cm.
Such batteries should be installed with a distance between the radiator and the wall of 2 to 5 cm. The installation height above the floor should be at least 10 cm. If there are several windows in the room, the batteries should be installed under each window. If the apartment is corner, then it is recommended to insulate the walls externally or increase the number of sections.
It should be noted that cast iron batteries are often sold unpainted. In this regard, after purchase, they must be coated with a heat-resistant decorative composition and must first be stretched.
Among domestic radiators, one can distinguish the ms 140 model. For cast iron heating radiators ms 140, the technical specifications are given below:
- heat transfer of the MS section 140 – 175 W;
- height – 59 cm;
- The radiator weighs 7 kg;
- capacity of one section - 1.4 l;
- section depth is 14 cm;
- section power reaches 160 W;
- section width is 9.3 cm;
- the maximum coolant temperature is 130 degrees;
- maximum operating pressure – 9 bar;
- the radiator has a sectional design;
- crimping pressure is 15 bar;
- the volume of water in one section is 1.35 liters;
- Heat-resistant rubber is used as a material for intersection gaskets.
It is worth noting that MS 140 cast iron radiators are reliable and durable. And the price is quite affordable. Which determines their demand in the domestic market.
Features of choosing cast iron radiators
To choose which cast iron heating radiators are best suited for your conditions, you need to take into account the following technical parameters:
- heat dissipation Select based on the size of the room;
- radiator weight;
- power;
- dimensions: width, height, depth.
To calculate the thermal power of a cast iron battery, you need to be guided by the following rule: for a room with 1 outer wall and 1 window, you need 1 kW of power per 10 sq.m. room area; for a room with 2 external walls and 1 window - 1.2 kW; for heating a room with 2 external walls and 2 windows - 1.3 kW.
If you decide to buy cast iron heating radiators, you should consider the following nuances:
- if the ceiling is higher than 3 m, the required power will increase proportionally;
- if the room has double-glazed windows, then the battery power can be reduced by 15%;
- If there are several windows in the apartment, then a radiator must be installed under each of them.
Modern market
Imported batteries have a perfectly smooth surface, they are of higher quality and look more aesthetically pleasing. True, their cost is high.
Among domestic analogues, we can highlight cast iron radiators Konner, which are in good demand today. They are characterized by a long service life, reliability, and fit perfectly into a modern interior. Konner heating cast iron radiators are available in any configuration.
- How to fill water into an open and closed heating system?
- Popular floor-standing gas boiler made in Russia
- How to properly bleed air from a heating radiator?
- Expansion tank for closed heating: device and principle of operation
- Gas double-circuit wall-mounted boiler Navien: error codes for malfunctions
Recommended reading
2016–2017 — Leading heating portal. All rights reserved and protected by law
Copying site materials is prohibited. Any copyright infringement will result in legal liability. Contacts
Dimensions
- height – 300, 350, 400, 500, 600 and 900;
- width – from 400 to 3000.
If necessary, you can select devices of non-standard sizes.
Increasing the heating area
To increase heat transfer, steel ribs - U-shaped plates - are welded to the panels. The number of plates increases the power of the radiator, as the heating area increases. Depending on the quantity, radiators are divided into three types:
- low power 11 – one plate;
- average power 22 – two plates;
- powerful radiators 33 – three plates.
Main characteristics
The main indicators that must be taken into account when choosing a radiator include power and overall dimensions.
Among the wide range of offers you can find models with different dimensions. This allows you to choose the right option for any room and any niche. Models are available with heights from 30 to 90 cm and lengths from 40 to 300 mm.
As the size increases, the power of the device also increases. The power of the most popular batteries can be seen in the table below.
Design
A steel panel radiator can become not only a source of heat, but also a stylish piece of furniture. In addition to the traditional white color, there are radiators on the market in a variety of colors, even with patterns.
Steel panel radiators can be “packed” into decorative boxes - screen and sidewalls, which... Decor for heating devices can be made to order according to an individual design or purchased ready-made from the manufacturer.
New items
Tubular heating radiators, due to the shape of the pipes, can be of a wide variety of designs: both classic options and bold interior experiments are available for them.
For example, a new popular design made of heating pipes has entered the market - bench radiators covered with varnished boards. This bench can be installed in the hallway, kitchen, children's room or winter garden. Its compliance with hygienic standards allows it to be placed in medical institutions.
pros
A steel panel radiator of any type has the following advantages:
- high heat transfer at low cost;
- the ability to create an interesting design due to a wide selection of colors, shapes and sizes;
- the ability to independently regulate the air temperature and calculate the heating area;
- small volume and weight;
- radiators are resistant to chemical solutions, including alkaline ones;
- optimal combination of radiator and convector properties.
Comparison of indicators: analysis and table
In addition to the material from which the device is made, the power factor is affected by the center-to-center distance - the height between the axes of the upper and lower outlets. also has a significant impact on the efficiency .
| Radiator type | Center distance (mm) | Heat output (kW) | Coolant temperature (0C) |
| Aluminum | 350 | 0,139 | 130 |
| 500 | 0,183 | ||
| Steel | 500 | 0,150 | 120 |
| Bimetallic | 350 | 0,136 | 135 |
| 500 | 0,2 | ||
| Cast iron | 300 | 0,14 | 130 |
| 500 | 0,16 | ||
| Copper | 500 | 0,38 | 150 |
Power and number of sections
The power of steel radiators is determined during production by the manufacturer itself: it is set according to the type of radiator - 11, 22 and 33 - and height - from 300 to 900. The power indicator will be determined directly by these values: as a rule, 1 section works per 1 m2 of heated area premises.
Factors for calculation
The calculation of steel radiators begins with determining the climate: for temperate - a variation of 60-100 W/m2, for northern regions - the norm is from 150-200 W/m2. These calculation sources rarely produce errors. The second criterion for calculation is heat transfer, which can be seen on the packaging or data sheet.
The height of the ceilings also matters - the standard value is 2.7 m, if more or less, then you need to adjust accordingly. To do this, the actual ceiling height is divided by 2.7, and the resulting coefficient is multiplied by the standard power. It is important to remember that when doing it yourself, it is better to take power with a reserve: the heat will “go away” to corner rooms, thin walls and other nuances that a simple user will not be able to take into account.
Simple formula
The calculation is carried out in several stages. An average power value of 100 watts per 1 m2 is taken. If the area of the house is 30 m2, and the power of 1 section of the battery is 180 watts, then the calculations will be as follows: 30 * 100/180, a total of 17 sections will be required to heat a space of 30 m2. If this is a corner room, then this value is multiplied by a factor of 1.2 - i.e. 20 radiator sections.
Heating devices are installed in almost every living space. Usually these are Soviet cast iron batteries, modern aluminum or bimetallic radiators. The house will be warm and cozy if the heating radiators are calculated
and well made.
Depends on several factors:
- technical feasibility of an autonomous or centralized heating system
- coolant quality
- individual choice of the customer, taking into account his idea of the quality of this device
- price policy
Correct calculation of the number of radiators
will provide a favorable microclimate in a heated building. It will provide the owner with the opportunity to independently regulate the temperature in the room. Will help in selecting the ideal heating equipment for your interior. This will be done with optimal calculation of radiators.
Every year the winters in our country become more severe, and many people are increasingly thinking about or installing an additional new one. Every third buyer wants to do it on their own. To do this, they have to face the issue of the size and calculation of heating radiator sections
. Next we will take a closer look at this issue.
Specified and actual heat transfer of the radiator
The parameters of any heating device are indicated in the technical passport. Typically, manufacturers declare the power of 1 standard section with an interaxle size of 500 mm within the range of 170...200 watts. The characteristics of aluminum and bimetallic radiators are approximately the same.
The trick is that the heat transfer rating cannot be stupidly used to select the number of sections. According to clause 3.5 of GOST 31311-2005, the manufacturer is required to indicate the battery power under the following operating conditions:
- the coolant moves through the radiator from top to bottom (diagonal or side connection);
- temperature difference is 70 degrees;
- the flow rate of water flowing through the device is 360 kg/hour.
Reference. Thermal pressure is the difference between the average temperature of the network water and the room air. Denoted by ΔT, DT or dt, calculated by the formula:
Let’s explain the essence of the problem; to do this, substitute the known values of ΔT = 70 °C and room temperature – plus 20 °C into the formula, and perform the reverse calculation:
- tsupply + treturn = (ΔT + tair) x 2 = (70 + 20) x 2 = 180 °C.
- According to the standards, the calculated difference in coolant temperatures between the supply and return lines should be 20 degrees. This means that the water coming from the boiler needs to be heated to 100 °C, the return water will cool to 80 °C.
- The 100/80 °C operating mode is not available for domestic heating installations; the maximum heating is 80 degrees. In addition, maintaining the specified coolant temperature is not economically profitable (remember, we took the average value of 65 °C).
Conclusion. In real conditions, the battery will give off much less heat than specified in the operating instructions. The reason is the lower value of ΔT - the temperature difference between water and ambient air. According to our initial data, the ΔT indicator is 130 / 2 - 22 = 43 degrees, almost half the declared norm.
Calculation of the power of batteries, heating radiators
The first thing you need to know is that when calculating the type of heating device, it does not matter whether it is cast iron, aluminum, steel or made of bimetal. The main indicator is the power of the unit. All manufacturing companies must indicate the thermal power of radiators. In case of emergency, knowing the model of the unit, you can always find technical data on the Internet. A little advice: some manufacturers may significantly inflate this figure.
The second thing you need to know is the area of the room that you need to heat. It is important to remember that calculating battery power
must be performed not for the total area of a private house, cottage or apartment, but for each room separately.
Third, the formula for calculating the power of heating batteries
It is extremely simple and anyone can use it. According to SNiP, per 1 square meter of a room with an average ceiling height (2.7 meters) there is 100 W of thermal power. Therefore:
- K – number of sections
- S – area
- P – radiator power
Example: calculating radiator power
for a room of 30 square meters with a standard ceiling height of 2.7 meters. The average power of one section is 180 W. We use the calculation formula: K = 30 * 100 / 180 = 16.7 pieces. Round up to 17, that is, you need 17 sections.
Bottom line
Steel panel heating radiators have an attractive appearance and laconic design. Such devices are characterized by high thermal power and can be connected both from the side and from below.
When choosing, it is important to correctly calculate the required heat transfer and select the appropriate standard size of heating equipment.
Contact us for qualified help! We will help you with calculations and answer all your questions.
What kind of radiators are in your house or apartment? Write in the comments!
How to calculate the power of a panel radiator
P (radiator) = V * 41
- P – radiator power
- V – room volume (height * length * width)
- 41 is 41 W of thermal power required to heat 1 cubic meter of standard construction
For example: a room 6 * 7 meters, with a ceiling height of 3.5 meters. First, we calculate the volume of the room V = 6 * 7 * 3.5 = 147. We use the calculation formula: P (radiator) = 147 * 41 = 6027 W.
We received a figure that means how much heat needs to be given to the battery to warm up a given room. That is, in this case it is necessary to use two 2500 W radiators and one 1000 W radiator. Calculating the number of sections is very simple; just divide the resulting power by the power of one section.
General provisions and algorithm for thermal calculation of heating devices
The calculation of heating devices is carried out after the hydraulic calculation of the heating system pipelines using the following method. The required heat transfer of the heating device is determined by the formula:
, (3.1)
where is the heat loss of the room, W; when installing several heating devices in a room, the heat loss of the room is distributed equally between the devices;
— useful heat transfer of heating pipelines, W; determined by the formula:
, (3.2)
where is the specific heat transfer of 1 m of openly laid vertical/horizontal/ pipelines, W/m; is accepted according to the data in Table. 3 Appendix 9 depending on the temperature difference between the pipeline and the air;
— total length of vertical/horizontal/ pipelines in the room, m.
Actual heat output of the heating device:
, (3.4)
where is the nominal heat flow of the heating device (one section), W. Accepted according to the data in the table. 1 appendix 9;
- temperature pressure equal to the difference between half the sum of the coolant temperatures at the inlet and outlet of the heating device and the room air temperature:
, °C; (3.5)
where is the coolant flow through the heating device, kg/s;
— empirical coefficients. The parameter values, depending on the type of heating devices, coolant flow rate and flow pattern, are given in Table. 2 applications 9;
— correction factor, method of installing the device; is accepted according to the data in Table. 5 appendices 9.
The average water temperature in a heating device of a single-pipe heating system is generally determined by the expression:
, (3.6)
where is the water temperature in the hot main, °C;
— cooling of water in the supply line, °C;
— correction factors adopted according to table. 4 and table. 7 appendix 9;
- the sum of heat losses of the premises located upstream of the premises in question, counting along the movement of water in the riser, W;
— water flow in the riser, kg/s /determined at the stage of hydraulic calculation of the heating system/;
— heat capacity of water equal to 4187 J/(kg deg);
— coefficient of water flow into the heating device. Accepted according to the table. 8 appendices 9.
The coolant flow through the heating device is determined by the formula:
, (3.7)
The cooling of water in the supply line is found according to the approximate relationship:
, (3.8)
where is the length of the main line from the individual heating point to the design riser, m.
The actual heat transfer of the heating device must be no less than the required heat transfer, that is. The opposite relationship is allowed if the discrepancy does not exceed 5%.