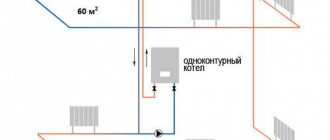
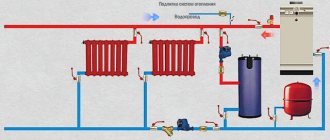
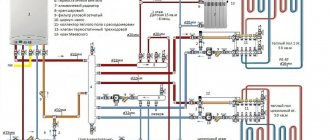
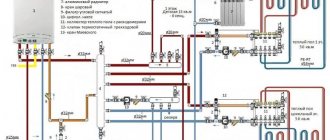
Until recently, the most popular and affordable type of material from which heating pipelines were made was metal-plastic. Such pipes are a structure of two polymer layers with aluminum foil between them.
However, the complexity of installation and repair of damaged sections of metal-plastic mains have become key factors why most buyers increasingly prefer cross-linked polyethylene pipes, such as PEX and PE-RT.
Features of cross-linked polyethylene pipes
These types of pipelines are made from the same raw material - polyethylene, however, PEX and PE-RT pipes differ in production technology.
PEX – products made of cross-linked polyethylene with varying degrees of cross-linking, which is achieved through the formation of cross-links between polymer macromolecules under chemical or physical influence. The following types of crosslinking are distinguished:
- PEX-a (peroxide 75%),
- PEX-b (silane 65%),
- PEX-s (radiation 60%).
The percentage of crosslinking indicates the degree of strength and resistance of the pipeline to high temperatures and aggressive environments, although this does not affect the quality and reliability in any way. However, it is believed that the higher the degree of cross-linking of polypropylene pipes, the higher the likelihood of creases and damage during their installation.
PE-RT is a polyethylene with increased heat resistance, in which crosslinking is carried out due to the strong interweaving of the branches of macromolecules of a copolymer such as octylene. There are PE-RT pipes of types 1 and 2, the second can withstand pressure 20% more than the first. This characteristic indicates its increased wear resistance.
What is PEX
Cross-linked polyethylene, or PEX, is polyethylene that has a high molecular weight. To do this, they take as a basis ordinary low-density polyethylene, which becomes stronger by cross-linking linear molecules with the help of ionizing radiation and a set of certain substances at high pressure. The additional bonds formed between molecules directly strengthen the PEX pipe.
Thanks to this procedure, PEX retains all the positive qualities of ordinary polyethylene, while acquiring additional characteristics: strength, heat resistance, heat resistance. PEX shows itself to be the best analogue type of reinforced polyethylene.
Comparison of PEX and PE-RT pipes
Despite the fact that these types of pipes have similar features and advantages, such as:
- UV resistant.
- Resistant to aggressive substances and corrosion.
- Long service life (up to 50 years).
- Safety and environmental friendliness of the material.
However, PEX and PE-RT products have a number of distinctive properties. In the video below, Valtec experts make a visual comparison of different types of polyethylene pipes:
Heat resistance and service life
Most manufacturers claim that polyethylene pipes of these two types will not lose their performance properties during 50 years of service. However, such a duration is achieved only if certain temperature parameters of the coolant are observed.
PERT pipes are considered products of increased heat resistance, however, when the liquid temperature in the line is more than 70 degrees, their service life is sharply reduced (this characteristic applies to a greater extent to PERT pipeline type 1).
For PEX pipes, the durability is determined by the operating class of the polyethylene heat pipe. The construction is made of class 5 cross-linked polyethylene and can withstand coolant temperatures up to 90 degrees. In this case, the service life directly depends on the operating pressure in the heating system. For example, at a pressure of 8 bar and a water temperature of 90 degrees, the PEX pipeline will last a maximum of 8 years.
It is worth noting that fluctuations in temperature and pressure in the heating system directly affect the durability of all types of polyethylene products: the higher the temperature, the shorter the service life of the pipeline.
Rigidity
If we compare PEX and PERT pipes, the latter are slightly softer in properties than the former. This allows them to accept the smallest bending radius without breaking the heat pipe during its installation, which is especially important when installing a water-heated floor.
The flexibility of PEX piping depends on its degree of crosslinking. PEXa pipes are the most rigid in comparison with PEXb and PEXc, however, this type of product is characterized by good repairability. In the event of a break, PEX pipes return to their original shape under the influence of high temperature; to do this, it is enough to heat the damaged section of the pipeline with a hot hairdryer.
Please note that PE-RT pipes can be welded during installation and ensure good tightness of the pipeline. This cannot be done with PEX heat duct.
Price
Another distinctive feature of pipelines made of cross-linked and heat-stabilized polyethylene is their price. There is a wide range of polyethylene pipes on the market and often PEX products will cost 1.5 times more than PE RT analogues.
How is PErt material obtained?
Pert heat-resistant polyethylene has similar characteristics to the material that is formed during cross-linking. Pert does not use a crosslinking process, which speeds up and reduces the cost of polyethylene production. The technology involves control over the introduction of co-monomer into the hexyl branch of the polymer.
- The molecular chain of polyethylene has a linear structure.
- With the addition of co-monomer, changes occur in the chain. Transverse mechanical connections appear. The co-monomer is 1-octane.
- During cross-linking, cross-chains are formed between the molecules. When producing Pert with the addition of a co-monomer, an octane branch is formed that is large in size and closely bonded.
- A new crystal lattice appears, which is located across linear molecular chains and is connected to it using amorphous segments.
- Transverse chains increase the rigidity of the material, increase its strength, and resistance to external influences.
The technology has been developed. Metal-plastic pipes for hot and cold water supply, for liquid heating systems and for underfloor heating are made from heat-resistant polyethylene. Resistance to chemicals and biological microorganisms makes it possible to produce utility lines for wastewater and sewer systems from polyethylene. The technology has been approved in a number of countries: Germany, the Netherlands, and the USA.
We recommend: Instructions for laying heated floors
PEX and PE-RT pipes: which is better for heating and underfloor heating?
It is worth remembering that the pipes are selected taking into account the characteristics of the heating system. According to established standards, each pipeline indicates its operation class, which indicates the operating pressure, temperature and maximum service life of the product subject to the specified temperature indicators.
Taking into account that pressure surges and hydraulic shocks are possible in a central heating system, in such a system it is more rational to use PEX pipes or heat-resistant heat pipes of type 2 with class 5 operation. However, when using cross-linked polyethylene products in centralized heating, it is not recommended to recess them into the wall.
In terms of price-quality ratio for underfloor heating, the best solution is the PE-RT pipeline. The maximum operating temperature for them should not exceed 70 degrees, which is acceptable when installing a water heated floor.
In an autonomous heating system, where it is possible to regulate the temperature of the system, both PEX and PERT pipelines can be used. Here the main factor in making a decision can only be its price.
How to connect the pipeline?
For heated floors, a multilayer pipe is used. The presence of layers does not affect the elasticity of the material or other characteristics of PE. For systems with high loads, products that consist of 5 layers are chosen. The top shell is protective from UV rays and mechanical influences.
- 1 layer – heat-resistant polyethylene.
- 2nd layer – adhesive base.
- 3 layer – oxide barrier; aluminum layer;
- 4th layer – glue.
- 5th layer – PE.
- 6 – protective, “EVOH”.
We recommend: How to connect a mixing valve for underfloor heating?
The connection of individual sections of pipes for underfloor heating is carried out using soldering. To do this you will need a special soldering iron with attachments. The pipes are connected using fittings made of heat-resistant polyethylene.
- Select a nozzle for the fitting and pipe, insert it into the soldering iron.
- Heat the equipment to 260 0C.
- Place the fitting and pipe onto the nozzle. Hold for 4 seconds.
- Remove the plastic products and make the connection. The edges of the fitting and pipe expand and become soft when exposed to high temperatures.
- After 120 sec. check the reliability of the connection.
For a pipe of a certain diameter, a specific soldering time is maintained. A pipe for underfloor heating with a diameter of 16-32 mm requires 4 seconds. Products 40-50 m – 5 sec. 63-75 mm – 6 sec. If you overheat the plastic, both the pipe and the fitting will become deformed. The seams will not be sealed.
Another way to connect the Pert floor line is by pressing. It is necessary to prepare an expander with nozzles and pressing pliers. Cut off the edge of the pipe with pruning shears so that the fitting can be installed on a flat surface. How is pressing carried out?
- The edges of the pipe must be aligned using pruning shears. Place a crimp ring on it.
- A nozzle is inserted into the expander, which corresponds to a certain pipe diameter.
- Insert the nozzle into the product, turn it 1200, hold for 1-3 seconds.
- The expander is removed and the fitting is inserted into the pipe.
- Using pressing pliers, grip the crimp ring and fitting and connect the elements.
- Wait 1-2 seconds. During this time, the plastic will take its original shape. The seams are sealed. It will be impossible to disturb the connection point.
Laying of the underfloor heating line from Pert pipe is carried out on a flat surface; use the “snail” or “snake” technique. It is recommended to install it on a contour coating. The circuit securely holds the line. Cover the pipes with a deep screed.
As floor covering, a material is used that matches the design of the room. Heat-resistant polyethylene is purchased in Moscow and St. Petersburg. Specialists will help you calculate the footage of the main line and the step at which the water pipeline is installed.
We recommend: What characteristics does Caleo underfloor heating have?
YouTube responded with an error: The request cannot be completed because you have exceeded your quota.
- Related Posts
- How to install a heated floor in a toilet?
- How to choose a thermostatic valve for underfloor heating?
- Features of Legrand heated floors
- What should be the height of the heated floor?
- What kind of warm floor to lay under a parquet board?
- How to install Grand Meyer underfloor heating?
Conclusion
When choosing cross-linked polyethylene pipes, you should be guided by their performance characteristics and select a pipeline depending on the type and features of the heating system. Any polyethylene line has three main parameters: operating temperature and pressure, as well as service life. The higher the pressure or temperature in the system, the lower its service life.
It is important to choose high-quality products from trusted manufacturers in order to avoid unexpected problems in the future.
Have you had experience using cross-linked polyethylene pipes for radiator heating or water heated floor systems? Share your stories and impressions in the comments!
Requirements for pipes
In most cases, the contours of a water-heated floor are filled with a heavy concrete screed, closed with a finishing finish. Even after removing tiles or removing part of the laminate, it will be impossible to visually inspect the system for leaks or any other malfunctions.
Therefore, any pipe that is part of a water-heated floor system must meet strict requirements stipulated by the special conditions of its operation.
Dimensions of polyethylene pipe coils
- The pipe for water systems must be made of materials that are not subject to corrosion. It must have a special structure of the internal cavity, which does not become overgrown when the coolant is in it for a long time. The material, like PE-RT polyethylene, must be resistant to high temperatures and chemicals.
- Each water circuit must consist of a single section, excluding the use of welded technologies. For this reason, the pipe cannot be made of steel, galvanized or stainless metal. When arranging systems, they can be used, but only on the segment leading from the heating boiler to the manifold cabinet.
Connecting a water heated floor - The material must have a large bending radius so that kinks do not form on it during laying. And given that the pipeline is laid out according to a certain pattern, the pipe must maintain its given shape.
- Pipe for water heated floor systems is always supplied in a coil. Therefore, when purchasing, you should take into account that its length must correspond to the length of the pipeline and have some margin.
The main element of water heated floor systems has a standard diameter, which can correspond to the following values:
- 16 mm;
- 20 mm;
- 25 mm. Characteristics of pipes for heated floors
It should be noted that when using consumables of a smaller diameter, heat transfer decreases, which leads to a reduction in the distance between the loops of the circuit and, accordingly, to an increase in material consumption. In addition, the small diameter of the pipe leads to overloads of the pumping equipment. It is also inadvisable to use pipes of too large a diameter, since in this case the thickness of the concrete screed will increase and, as a result, the load on the floor.
DIY water heated floor
[ads-mob-1][ads-pc-1]
Temperature
The maximum temperature in heated floors can be any - as the customer wishes. But do not forget about common sense and limiting the heating of screeds (for anhydrite screed - 55 ⁰С, and for cement screed - 60 ⁰С). And also by choosing the type of flooring - this is relevant for wooden and laminated floors, where the heating limit, don’t forget, is up to 29 ⁰C. And also the presence of a temperature guard, which simply will not allow the floor to heat above 60 ⁰C.
In fact, consumers usually set the temperature in the range of 28-29 degrees, due to personal comfort, this is exactly the range of indicators at which the coating feels warm (and not the sands of the Sahara Desert). Of course, this is always a subjective question, but still.