The change in pressure during thermal expansion without taking into account the deformation of the system elements can be calculated using the formula: Δp = βt · Δt / βv, where βt is the coefficient of thermal expansion of water, 1/°C; Δt – change in water temperature, °C; βv – coefficient of volumetric compression of water, 1/Pa. Calculations show that in a rigid closed system, the pressure change is about 3 bar/°C. If we take into account pipe deformations, the results will be as follows:
|
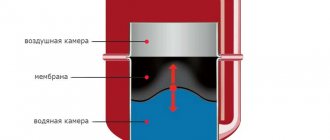
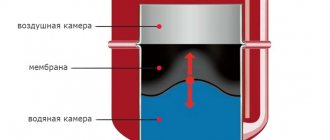
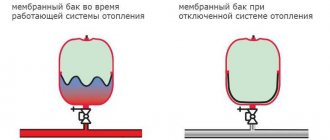
How does the VALTEC expansion tank work? The expansion membrane tank contains a diaphragm that divides it into two parts, one of which contains nitrogen, which is under initial excess pressure, and the other part receives excess coolant from the system.
Initially, the entire volume of the expansion tank is completely occupied by nitrogen; When the coolant is heated, its volume increases, which leads to nitrogen compression. The pressure of the nitrogen blanket increases and equalizes the pressure in the heating system at a given static level. When the temperature of the coolant and, accordingly, its volume decreases, the pressure of the nitrogen blanket returns the coolant back into the system, preventing the pressure in the system from falling below the set level.
| Under operating conditions, the inner surface of the membrane expansion tank body is often an area of possible condensation. If there is oxygen in the gas cushion, intense corrosion of the metal of the tank body will inevitably begin. That is why manufacturers pump neutral nitrogen into the tank, and not atmospheric air containing water vapor and oxygen. By pumping air into the gas cavity, the user unwittingly shortens the service life of the membrane tank. |
Connection point of the VALTEC expansion membrane tank to the heating system
The pressure at the point of connection of the membrane tank to the system is always equal to the static pressure at a given point at given temperature parameters.
| Proving the above statement is very simple. If we assume that the pressure at the tank connection point changes, then we will have to admit that the volume of coolant in the tank has also changed. But this cannot be, because... There was nowhere for excess coolant to come from in a closed system, and there was no way it could disappear without a trace either. It should be noted that this rule only applies to a system with one expansion tank. |
Thus, the operating parameters of all other elements of the heating system, the required initial pressure in the expansion tank and the volume of the tank itself depend on the location of the expansion tank.
| When choosing the location for connecting the expansion tank, remember that the higher the pressure in the heating system, the less likely it is to become airborne. |
| If the membrane tank is connected to the system directly after the circulation pump, you should check that an anti-cavitation pressure reserve is maintained in front of the pump. |
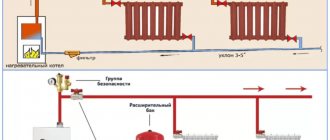
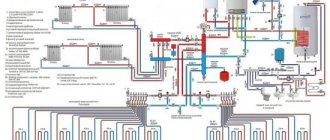
In Fig. 1 shows several options for connecting a membrane tank to a heating system with the following height parameters:
- excess of the top point of the system over the bottom (H) – 10 m;
- the heat generator and safety valve are located 2 m above the lowest point of the system (h1);
- the expansion tank is placed 1 m above the point of its connection to the system (h2);
- static pressure at the lowest point of the system is 15 m of water. Art.
Rice. 1. Options for connecting the membrane tank to the heating system
At the remote flags in Fig. 1 indicates the calculated values of operating pressure at characteristic points of each system (in m of water column).
The safety valve setting value is assumed to be 33 m water. Art., pump pressure – 6 m water. Art., system capacity – 200 l. The difference between the maximum and minimum temperatures of the coolant is 80 ºС.
In table 1 shows the calculated characteristics of membrane tanks for circuits with their different connections.
Table 1. Calculated data for systems in Figure 1
| Scheme in Fig. 1 | Estimated preliminary pressure in the tank, m water. Art. | Estimated tank capacity, l | Brand of selected tank VALTEC |
| A | 13 | 14,9 | VRV18 |
| b | 13 | 14,9 | VRV18 |
| c | 11 | 14,2 | VRV18 |
| d | 11 | 14,2 | VRV18 |
| e | 3 | 11,5 | VRV12 |
| f | 3 | 11,5 | VRV12 |
| When installing a membrane tank in a gravity heating system on the upper line, it should be shifted from the main riser towards the heating risers in order to eliminate the parasitic effect on the circulation of the coolant cooling in the tank. The main riser must be equipped with an air vent and a safety valve (Fig. 1f). |
The coolant must enter the membrane tank from above. In this case, there is no chance of air getting into the liquid compartment of the tank. If this requirement cannot be met, it is recommended to follow these rules:
Rice. 2. Options for organizing the release of air from a system with a membrane tank |
Design and principle of operation of a membrane tank
An expansion tank with a rubber membrane inside to accumulate excess water when heated.
The expansion tank is a sealed metal container, the inside of which is divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. One compartment is filled with air, the second will receive water as it expands. The tank body is made of steel. Powder coating protects the metal from corrosion. Based on the type of heating networks, devices are divided into two groups:
- open;
- closed.
The open type expansion tank must be located at the highest point of the circuit. It is made of steel, the most common being a rectangular shape. The tank serves to remove excess liquid and air dissolved in it. Its design is very simple - two pipes are cut into a metal container with a lid - for inlet and outlet of water. The tank is often installed in the attic. In a cold room it must be insulated with polystyrene foam. The advantage of the open design is simple operation and low cost.
Membrane expansion tanks for closed heating systems must be sealed. The steel tank is designed for long-term use. Its working part is an elastic membrane. It is made of special heat-resistant rubber. Depending on the type of tank, a balloon or diaphragm type membrane is used.
Principle of operation
In water heating systems, a coolant fluid circulates. When heated, it expands. The excess flows through the connecting pipe into the membrane tank. Elastic rubber stretches, one compartment is filled with liquid, and air is compressed in the second. After cooling the water in the circuit, the pressure decreases. Under the influence of compressed air, the membrane straightens and pushes the liquid back into the system.
During movement, the liquid does not come into contact with air. This reduces the likelihood of corrosion development.
Installation of an open type hydraulic tank
An open-type device is used less and less often, as it requires constant user intervention in its operation. An open expansion tank is an unsealed container that serves to generate pressure in the water supply system, accumulate water, and also serves as an expansion chamber.
The tank is connected to: a drain tap, pipes for the recirculation and supply pipes, a control and overflow pipe
The tank is installed above the highest plumbing point, for example, in the attic, water enters the system by gravity. Every meter the device rises increases the pressure in the water supply by 0.1 atmospheres.
To automate the process of providing water, the tank is equipped with a float switch and an automatic relay is installed that will turn the pump on and off.
The container is mounted in a frost-free room, covered with a lid to prevent dust and debris, and the walls are wrapped in mineral wool or other insulation.
This method of organizing water supply requires regular monitoring by the user, otherwise the water may freeze at subzero temperatures (if the room is not heated). The liquid will evaporate, so you will have to constantly add it.
In addition, such a container is bulky and not aesthetically pleasing; it requires an attic space in the house. But the main drawback of the device is that the tank is not designed to work under conditions of high water pressure in the system.
Types of membrane tanks
Tank with a fixed membrane - no replacement of rubber required
In order for the heating system to operate at maximum efficiency, it is important to choose the right membrane tank.
Fixed
The fixed membrane design is recommended for small heating systems. In such circuits, the pressure is relatively stable and there are no sudden jumps. The flexible element is rigidly fixed and cannot be removed for replacement in the event of a malfunction. The advantage of this option is the low price.
Flange with replaceable diaphragm
A special feature of the tank design is the fixation of the balloon-type membrane on the neck using a flange. Bolt fastening allows you to securely hold the rubber part during operation. If it breaks, you can remove the part and replace it with a new one. The ability to repair extends the life of an expensive tank.
For protection against water hammer
Such a load represents a sharp jump in the speed of water flow, which occurs when the pipeline is unexpectedly blocked. A change in the number of atmospheres, in turn, can cause damage to pipes. In such a situation, the expansion tank acts as a damper: the membrane-partition stretches, which leads to an increase in the volume of the corresponding compartment of the tank, and the pressure decreases.
Advantages and disadvantages
The rubber is hermetically sealed, so air does not enter the system.
The main advantage of the equipment is the prevention of leaks and other emergency situations that occur during pressure surges. Tanks are necessary in long circuits. They contain a significant volume of water, which, when expanded, creates an increased load on joints, radiators and pipes.
Advantages of the equipment:
- prevents air from entering the line;
- the equipment is designed for water of any quality;
- there is no evaporation of liquid;
- emergency pressure rise is prevented;
- installation possible anywhere;
- Maintenance of the system is simplified; regular refilling of coolant is not required.
The disadvantages include heat loss and the rather high cost of membrane tanks compared to open-type tanks.
Design features
In residential and industrial premises, heating networks are installed according to open and closed schemes. The first option is more suitable for centralized systems, which allows the liquid to be collected directly for hot supply. In this case, the tank is installed in the upper zone of the circuit. The container makes it possible to control the process of pressure surges by removing air pockets from the pipes.
The second type of installation involves the use of tanks with a membrane. They are distinguished by their comparative simplicity of design. They consist of an expansion tank and a membrane-plate, which, in turn, can be:
- Balloon. This means that the heat carrier is placed inside a rubber cylinder, and on the outside there is nitrogen or air. If this element breaks down, it’s easy to replace; you don’t have to buy a whole new device.
- Diaphragm. Made in the form of a permanent partition made of metal or polymer material. This part has a compact capacity and can neutralize only small pressure surges in the network. If it fails, it is impossible to replace it, as a result of which you will have to purchase another tank. Of course, the cost of this membrane is slightly lower than the above option.
Volume calculation
The expansion tank by volume should contain 10% of the total coolant in the system.
The parameters of the tank should prevent pressure from rising when the coolant is heated. For an approximate calculation of a system with a capacity of up to 150 liters, you can use the formula: tank volume - 10% of the system volume. If antifreeze is used, the parameter increases to 15%. For calculations you will need loop capacity. You can find out the parameter using the water meter during the process of filling the system. It is also calculated by adding up the volume of all components, pipes, radiators and boiler. There are online calculators for calculations.
A more accurate value will be obtained by calculating using the formula: V = V1 x Bt/(1-(Pmin/Pmax)), where:
- V – volume of the tank;
- V1 – volume of liquid in the circuit;
- Bt – coefficient of thermal expansion of the coolant, found from the table;
- Pmin – factory pressure in the tank;
- Pmax is the maximum pressure in the system, determined at the moment the safety valve is activated.
The correctly selected volume of the expansion tank helps extend the life of the heating system.
Use as a hydraulic accumulator
Thus, the expander is used in water supply systems. Thanks to the unit, it is possible to accumulate a certain amount of liquid and then use it for its intended purpose. It is noteworthy that to organize the supply, the accumulated liquid medium under pressure is used without taking into account the operation of the pumping station. The pump does not have to be turned on too often, which significantly extends its service life.
In addition, the membrane cistern replenishes the expansion of H2O in the hot water supply.
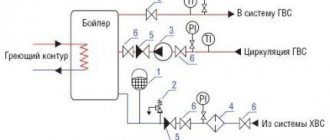
Requirements and recommendations for installing a membrane tank
Small volume tanks are mounted on the wall.
You can install the equipment yourself, following the instructions. When working, adhere to the installation requirements:
- The first stage is choosing a location. It is necessary to ensure free access to the tank for maintenance. A good place is considered to be the section of the return line between the pump and the boiler.
- To ensure the safety of a closed circuit, you will need to install a safety valve, an air vent, a pressure gauge and a thermometer.
- A drain valve is installed in front of the inlet pipe to drain water from the tank.
- Filters must not be installed in the area connecting the tank and the heating system.
- Before connecting the equipment, check the pressure of the gas space. If necessary, pump up air.
- The tank should not be located in a room with sub-zero temperatures.
The tank is securely mounted on the wall, and no additional load should be placed on it. Large volume models are mounted on the floor. A connection diagram with the inlet pipe located at the bottom is recommended. Experts advise making a detachable connection between the pipe and the drain valve in front of it. If necessary, the expansion tank can be easily dismantled.
The manufacturer specifies the requirements for the amount of antifreeze in the coolant. The stated proportions must not be exceeded.
The difference between a tank and a hydraulic accumulator
Despite the similarity in design characteristics, the purpose of the devices is still not the same. The expansion tank compensates for the increase in liquid volume due to heating. A similar device accumulates a liquid medium under pressure, minimizing the number of starts of the pumping station, thereby prolonging its performance.
Also inside the hydraulic accumulator structure there is a special rubber bulb container, thanks to which it is possible to avoid contact of H2O with the walls of the tank. The expander, in contrast, is manufactured together with a membrane designed to divide the body into two compartments. In this case, there is interaction of the coolant with the tank.
Equipment selection rules
It is important to choose the right tank volume in order to adjust the pressure in the system.
The main characteristics of a membrane tank, which are oriented towards when purchasing:
- volume;
- maximum pressure;
- membrane and housing material;
- working temperature.
These criteria will ensure reliable heating operation. Insufficient or excessive tank volume will not allow normal pressure to be established in the circuit. The type and material of the membrane and housing affect the service life of the equipment. High-quality rubber can withstand a large number of expansion and compression cycles. To prevent the body from corroding, it must have a protective coating. It is worth considering the dimensions of the product and considering the installation location. Experts advise buying products from well-known manufacturers. Low product costs are often an indicator of the use of low-grade materials.
Restrictions
Manufacturers impose certain restrictions on the use of membrane expansion tanks, which depend on the design and materials used in the manufacture of the device. Manufacturers have clear requirements for the properties and composition of the liquid in the heating system. The content of, for example, ethylene glycol in an antifreeze solution is limited. The use of a membrane expansion tank at pressures exceeding permissible standards is prohibited. It is mandatory to install a safety group that controls and limits the pressure in the tank. The heating systems of autonomous heating apartments and private houses use equipment with an operating pressure of at least 3 bar.
Possible breakdowns
With prolonged use, the membrane may burst.
During operation of the equipment, owners are advised to inspect the housing for leaks and damage every six months. It is also necessary to measure the pressure in the gas chamber. The condition of the membrane is checked once every 2 years. If there is no use for a long time, the water is drained from the tank.
Common faults:
- Pressure drop in the gas compartment - it is necessary to pump air through the nipple using a pump.
- Damage to the housing - mechanical stress or corrosion can cause a crack to appear. The seal of the container can be restored at a service center.
- Leaking from the air valve - due to high loads and hot water, the rubber may crack. It is better to replace the damaged part in a timely manner.
You can repair the equipment yourself. To replace the membrane, you will need to drain the water, remove the container and relieve the pressure. Then unscrew the flange bolts holding the rubber part. The old membrane is removed and replaced with a new one. All procedures are carried out in reverse order.
Common faults
Typically, most problems are not related to the container itself. Not so often there are cases when the tank itself cracks and begins to leak for no obvious reason. However, even taking into account the simple design, the problem part may well be the cap of the expansion tank of the engine cooling system.
The valve built into the lid may fail. Insufficient sealing may also occur due to deformation of the rubber ring. As a result of such malfunctions, the cap may begin to leak antifreeze, the system may become airy, etc.
If the valve in the cover begins to work incorrectly, then in such a case deviations in the operation of the internal combustion engine cooling system are inevitable. In addition to the formation of air locks, this situation in some cases leads to a critical increase in pressure and rupture of the expansion tank. In such a situation, the tank needs to be replaced with a new one. It is not recommended to attempt to restore a damaged container by sealing cracks.
If we talk about the cover, its damage and defects, as well as malfunctions of the valves due to clogging or deterioration, are a reason to replace the cover. In some cases, the lid is cleaned in an attempt to restore functionality, but this method does not always work. Given the low cost, it is better to replace the element immediately.
Popular models
Expansion tanks of the Wester brand for hot water supply and heating are painted red.
The Russian brand Wester produces membrane tanks for cold and hot water supply, as well as heating. The WRV series is designed to compensate for the expansion of the coolant. It includes models of various capacities - from 8 to 10,000 liters. The body of the products is painted red.
Wester WRV 50
The device is used in closed heating systems. Its volume is 50 l. The housing is positioned vertically, installation is floor-mounted. The model is made from durable carbon steel. The membrane is made of food-grade synthetic rubber. It is replaceable; a flange on the neck of the tank allows you to install and fix a new elastic part. The design is designed for pressures up to 5 bar.
Wester WRV 200 top
Membrane tanks for heating Wester wrv200 top are made of complex drawn steel. Heat-resistant elastic EPDM rubber is used to separate the inner chamber. The part is replaceable. Operating temperature range from -10 to +100°C. The design can withstand pressure up to 10 bar, its volume is 200 liters. Floor placement.
The expansion tank is a simple in design, but functional part of the heating system. Prevents breakdowns caused by sudden increases in pressure. Its installation will ensure safe and stable operation of all working units.