The heat loss of sawdust-based insulation is slightly higher than that of modern materials.
However, in terms of the totality of their characteristics, they are not inferior to either mineral wool or polystyrene foam.
Next we will talk about:
- main characteristics of sawdust;
- their advantages and disadvantages compared to other insulating materials;
- methods of their use;
- using sawdust to insulate various parts of the house;
- choosing the most suitable binder for a given situation;
- reviews about insulation with sawdust.
Main characteristics of sawdust
There are several characteristics that help you compare different insulation materials and choose the one that best suits your specific situation.
These are the characteristics:
- cost (excluding delivery);
- thermal conductivity;
- vapor permeability;
- resistance to high humidity and condensation;
- life time.
Cost is one of the most important parameters, especially if you have to insulate a large area . After all, the cost of 1m2 of the cheapest modern material, even without taking into account delivery costs, exceeds 150 rubles.
Therefore, when insulating a large house, the cost of purchasing insulation alone amounts to hundreds of thousands of rubles . Sawdust is much cheaper.
You can read more about their costs here.
Thermal conductivity is another important parameter on which the thickness of the layer required to reduce heat loss to a given level depends.
In this parameter, sawdust is inferior to all modern insulation materials, but you can slightly increase the thickness of the layer and bring heat loss to a given level.
In terms of thermal conductivity, 10 cm of wood sawing waste corresponds to a layer of mineral wool 8–9 cm thick and a layer of polystyrene foam 7 cm thick.
Vapor permeability is the ability of a material to pass water vapor through itself. This characteristic is very important for materials that are used to reduce heat loss in breathable houses built from wood or hollow clay bricks.
The main advantage of such houses is that the humidity in them is the same at any time of the year, because their walls remove excess moisture outside and into the atmosphere.
In terms of this parameter, sawdust leaves any other materials far behind, because of all modern insulation materials, only mineral wool allows steam to pass through at least a little. The rest of the materials completely block this process , which is why the microclimate in the house changes not for the better.
Resistance to high humidity and condensation is important for any insulating material, because humidity is always present in the air, and condensation occurs when temperatures change.
Sawdust absorbs excess moisture, and after a while, when air humidity drops, it releases steam. Therefore, humidity cannot harm them , which cannot be said about mineral wool, which, even if it gets a little wet, sharply loses its thermal insulation properties.
The actual service life of a material can only be determined by its condition after some time.
Polystyrene foam, polystyrene and polyurethane foam rarely withstand 30 years, because they are destroyed by oxygen and ultraviolet radiation , mineral wool can withstand 50–70 years, and sawdust can easily withstand a service life of 150 years.
In Russia and other countries there are houses built in the early and mid-19th century and insulated with sawdust. Despite such a considerable age, the sawdust insulation is in excellent condition and does not require either repair or replacement.
All this allows us to draw an unambiguous conclusion - in terms of the totality of its characteristics, sawdust is in no way inferior to any modern insulating material, and when used correctly, it is noticeably superior to them .
Recommendations and common mistakes
Often owners of private houses and households try to simplify the work and perform insulation with granules made from pressed sawdust. The thermal insulation turns out to be weak; it is necessary to increase the layer of sawdust granules and accordingly change the height of the floors in the house. Today you can buy ready-made material from sawdust and straw, pressed at high temperatures without binders. These are usually large blocks that can be easily cut in any direction. Such blocks cannot insulate the floor, only the walls and ceiling of the house.
Another problem is the self-compaction of the poured mixture. Often the layer of sawdust poured between the heaped joists sags by almost half. The reason for this can only be moisture that has got on the material. Therefore, sawdust is always dried under pressure, often tamped and compacted. If there is no opportunity and time in a private house for the natural shrinkage of sawdust insulation, then you can sew mats from fabric and fill them with small sawdust and straw, which are used to insulate the floor. Approximately according to the same scheme as is done when laying rolls of mineral fiber.
Methods of using sawdust
There are 4 methods for insulating with sawdust:
- backfill;
- fill;
- plastering;
- use of slabs.
To backfill, wood sawing waste is mixed with lime, which prevents the appearance of rot or mold even with increased humidity and protects the insulation from rodents and various beetles.
After backfilling, the insulation must be compacted, adding new sawdust, until a layer of the same density is obtained over the entire height.
After 2–3 years, and sometimes earlier, you have to add additional sawdust, because the lower rows are caked and compacted .
To fill, wood sawing waste is mixed with various binders in different proportions.
Then the finished composition is poured into voids or cavities prepared for it , where it turns into a fairly strong and hard material with low thermal conductivity.
By changing the amount of sawdust and binder, the thermal conductivity and strength of the insulating material are regulated.
For plastering, the same compositions are used as for pouring, only more suitable proportions are selected . In addition, before plastering, the walls are lined with chain-link mesh or its plastic equivalent, this improves the adhesion of the insulating layer to the wall.
Insulating boards are made from the same compounds that are used for pouring and plastering, only by selecting the most suitable binder.
After manufacturing, the slabs are stacked in a dry, ventilated area, then secured to the walls or ceiling using the same mortar and anchor nails or bolts.
In addition, they can be laid in floor cavities formed by floor joists and the lining or ceiling of the lower floor.
The following are used as binders:
- cement;
- gypsum;
- clay;
- PVA.
Read more about these insulation methods, as well as about choosing the optimal binder and the correct proportions here.
Criteria for choosing insulation material
The first thing you should pay attention to is the size of the chips. The smaller the fraction, the higher their thermal insulation properties, but the heavier they are and the more they scatter during operation. Large sawdust has lower insulating properties, but it is more convenient to work with them. It is recommended to use shavings from carpentry waste, since they use already dried wood.
When installing thermal insulation, it is recommended to choose coniferous wood shavings. Due to the presence of resin in them, they will perfectly protect the insulation from rodents.
To prepare sawdust, antiseptic agents are used, they are dried, and then mixed with lime. It is recommended to use at least 10% lime of the total volume of material in the finished mixture.
Using sawdust to insulate various parts of the house
For each part of the house, the most suitable technology is selected , ensuring not only an acceptable level of heat loss, but also ease of work.
After all, the simpler the method, the better the result, and the more complex, the higher the likelihood of error.
Moreover, often errors do not appear immediately after the completion of work , but only in winter, when it is no longer possible to change anything and you have to patiently wait for spring.
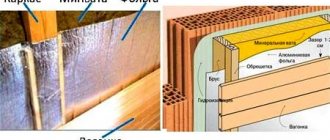
Walls
The method of insulating walls primarily depends on their design. If the walls are brick/concrete and empty inside, then most often they are either covered with a mixture of lime and sawdust.
Indeed, in such conditions it is difficult not only to lay the slab inside, but even to pour the solution. this method is not very effective in the walls of frame houses , so you have to use ready-made slabs.
For external insulation of walls without voids, pouring using the sliding formwork method is most often used; this ensures not only a uniform layer over the entire area of the walls, but also a beautiful appearance of the insulating layer.
In most cases, insulation made by pouring must be protected from precipitation, because cement, clay and gypsum lose their properties when exposed to water .
The exception is PVA, which after polymerization does not lose its ability to transmit water vapor and is not afraid of even long-term contact with water. The same applies to insulation using the plastering method.
Walls built from wood and brick, especially hollow brick, have very high vapor permeability , due to which the inside of such a house always has a dry and cozy microclimate.
Insulating such a house with foam plastic and other vapor-proof materials deprives it of its main advantage - a dry microclimate in the rooms , and the use of mineral wool is undesirable due to its high sensitivity to humidity and condensation.
Therefore, it is best to insulate such walls with sawdust.
After all, even when mixed with cement, they provide good vapor permeability and reduce heat loss without harming the microclimate.
Read more about wall insulation, choosing the most suitable method, choosing the optimal binder and the correct proportions of the mixture here.
Floor
Insulating the floor on the lower floor reduces the impact of a cold basement, basement or foundation .
On higher floors, especially if there is heating everywhere, it is less important, but even here, reducing heat loss through the floor has a beneficial effect on the microclimate of the room. After all, the colder the floor, the less comfortable the room is, because the feet are very sensitive to a decrease in temperature .
The method of insulation directly depends on the design of the ceiling.
Any method is suitable for wooden floors; the limitation arises only due to the strength of the ceiling cladding of the lower floor, because it bears the entire load.
If the strength of the sheathing is insufficient , then install a lining that can withstand the weight of the insulating layer with any type of binder. If the thickness of the layer, taking into account the lining, is not enough, then another insulating layer is laid on top of the subfloor.
The same method is also used on concrete floors, only instead of load-bearing joists, logs from bars of the required thickness are laid, after which the space between them and the floor is filled with insulating mortar.
Read more about floor insulation in this article (Floor insulation).
Ceiling
The method of insulating the ceiling directly depends on the design of the floors .
If they are made of concrete, then it can only be plastered with a thin layer (this will only slightly reduce the level of heat loss) or sheathed with ready-made slabs.
However, working with slabs of sufficient thickness is complicated by their large weight , so it is much easier to carry out insulation from the floor of the next floor, although this is not always possible.
The ceiling of wooden floors can be insulated in any way , including pouring, but to do this you will have to completely remove and then put back the ceiling lining.
In some cases, the sheathing will have to be cut into pieces of small width or replaced with boards, because without this it will not be possible to properly fill the space between the joists with an insulating mixture.
In most cases, PVA-based mixtures are used to insulate the ceiling, because the specific gravity of the frozen composition is slightly less than that of solutions based on other binders. This reduces the load on the ceiling lining.
In addition, this type of binder is not afraid of water, so it will not be damaged by condensation that occurs on the ceilings of the upper floor.
Read more about choosing a method and selecting a binder for ceiling insulation here.
Roof
The main problem that arises when insulating a roof is a large amount of condensation caused by a significant temperature difference on the inner surface of the roof.
This is due to the small thickness of the roofing material , as well as insufficient thermal insulation properties.
During the day, cold air enters the attic from the street and heats up, and at night, when the roof cools, moisture falls on its inner surface. The situation is the same with a heated attic - if insulation is insufficient, it greatly heats up the attic space , so cooling the roof leads to condensation.
Roof insulation can be divided into 3 stages, that is, reducing heat loss:
- roofs;
- attics;
- attic.
To reduce heat loss from each part of the roof, our own technology is used , which takes into account all important factors. In addition, it is necessary to ensure the correct ventilation mode and select the optimal type of binder.
After all, the wrong choice of binder can not only reduce the effectiveness of insulation, but also lead to damage to the rafter system or ceiling.
You will find more detailed information on all issues related to roof insulation here (Roof insulation).
Selecting the optimal composition of the insulating mixture
For each area of the house, it is necessary to select the most suitable composition of the insulating mixture, in which not only the type of binder is important, but also its percentage.
After all, on the outside of the walls it is necessary to use the most durable composition , and the binder should easily withstand the effects of precipitation, and on the ceiling a mass with minimal strength and a lower specific gravity is better suited.
The correct choice of binder and the proportions of its mixture with sawdust more effectively reduces heat loss in various sections of the walls and better resists aggressive factors.
Therefore, in many cases, proper insulation with sawdust is at least as good as proper insulation with other materials at significantly lower costs, or even surpasses it in terms of a combination of factors.
Moreover, any modern material has not only advantages, but also disadvantages.
In addition, any good sawdust insulation composition that you can make yourself always includes slaked lime . After all, thanks to it, mice and rats do not grow in the insulation, and other pests and diseases do not appear.
More detailed information about the correct use of binders in certain areas of the house, as well as the effect of their percentage on the characteristics of the insulating composition, can be found here (What can sawdust be used with as insulation).
Ceiling preparation
Before starting work, the surface must first be prepared:
- Hem the plane with a board 2.5-3 cm thick, the width depends on the pitch of the beams. The boards selected are tongue and groove, planed, and dry.
- The plank flooring is laid on top of the laid vapor barrier layer, in a continuous order. Fix with nails 100 mm long, screws with a stem length of 50-60 mm. Two hardware is enough for each fastening point.
Impregnate all wooden elements with antiseptic and fire retardants, and it is best to do this before starting work. If the hemming boards are not sufficiently dried, dry them, then process them and dry them again.
Reviews about sawdust insulation
On the Internet you can find many different reviews about sawdust as an insulating material, but most of them are custom-made material, the purpose of which is to advertise some products or services.
the most authoritative RuNet forums as a source of reviews , where both ordinary residents and experienced builders or engineers share their opinions.
Here are links to such forums and their threads related to the discussion of the use of sawdust as insulation:
- Forumgrad.
- Artisan.
- We are building a house.
- Mastergrad.
- Forumhouse.