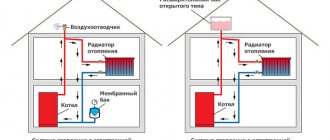
For heating networks in private houses and apartments, it is advisable to use boilers with closed coolant circulation, i.e. double-circuit. This design allows you to increase the pressure of the working fluid in the circuit.
High pressure in the heating system ensures safety and a higher boiling point of the coolant, therefore, the economic effect of the installation increases, and a decrease in pressure leads to problems in the system. Therefore, let’s look at why the pressure in the heating system of a double-circuit boiler drops and how to raise it.
The parameters of the boiler unit are monitored by measuring instruments - pressure gauges, main and additional. If a pressure gauge should be included in instrumentation and control measures, then choose models with electronic sensors.
Factors that affect the pressure inside the circuit:
- The impact of the coolant on the walls of the heating network elements;
- Height of laying pipes, hanging radiators and boiler unit;
- Design of main pipeline sections.
The pressure value for autonomous heating is not standardized. Acceptable values of network parameters are calculated based on the data of a specific object:
- Boiler type, pipe characteristics (diameter, presence of reinforcement, etc.), type and number of radiators;
- Equipment installation location, circuit length;
- Number of floors of the house;
- Parameters and condition of the external water pipeline.
Reasons for pressure drop in the circuit:
- Presence of leaks in the pipeline;
- Malfunction of the boiler, cracks on the surface of the heat exchanger;
- Malfunction of the membrane valve responsible for the safety of boiler equipment;
- Failure of the expansion tank membrane;
- Depressurization of the hot water supply circuit.
Leaks
Gaps are determined visually by pumping water into the pipeline to a predetermined level, and the cycle is stopped. The most susceptible to leaks are the joints of pipes, shut-off valves, radiator connections and the boiler itself.
One of the reasons for the pressure drop is a leak at the junction of the pipe and the radiator
- The presence of corrosion on metal pipes and connections;
- Poor quality pipeline installation;
- Weakening of joints;
- Damage to the pipe due to mechanical impact.
Troubleshooting
If the connection is damaged, replace the fitting or the connection itself. If a leak is detected (by a special scanner) in a pipe behind a decorative partition, wall or under the floor, it is necessary to dismantle the surfaces and make repairs.
Preventing the formation of air jams
Preventative measures against the occurrence of air locks are as follows:
- Pay attention to the correct installation of pipes and connections of heating devices. Many problems are caused precisely by mistakes made at this initial stage.
- To prevent air locks, proper commissioning of the equipment is necessary, before which it is important to first check all components and connections.
- Before putting devices into operation, check them for functionality. Using a compressor, you need to apply a pressure level that is ¼ higher than its normal operating value. If it does not weaken within 30 minutes, then everything is in order and the system is ready for operation. If the pressure drops sharply, then leaks are possible, which should be promptly identified and repaired before starting operation.
Expansion tank and its bleeding
In a closed-type system, the cause of a drop in pressure in the circuit may be the failure of the expansion tank.
- Frequent recharge of the system. If there is a need to additionally introduce coolant into the system at least once a week, without visible leaks, then the problem lies in the incorrect operation of the expansion tank;
- Dispersion of pressure gauge readings for different operating modes of the system. A sharp drop in coolant pressure in the system when using hot water supply also indicates a malfunction in the RB.
Pressure inside the expansion tank
To check its functionality, it is necessary to pump the tank and check that the pressure in it corresponds to the pressure in the heating system.
Sequence of pumping actions:
- Close the shut-off valves (direct and return water supply);
- Open the fitting, drain the water until the pressure in the boiler becomes zero;
- Take readings on the expansion tank in the “open” position. The presence of condensation on the RB should not be observed;
- Pump air into the RB until liquid stops flowing from the fitting. Allow the water to drain completely from the tank;
- Release the air;
- Repeat the procedure, keeping the pressure in the RB at 1.1...1.3 bar;
- Open the shut-off valve;
- Connect the coolant to the network. Set the pressure level to 1…1.1 bar.
Air injection
If there is no special pump for RB, you can use a regular bicycle pump.
Make-up tap
A common cause of pressure drop is a malfunction of the make-up valve. Causes:
- Loose tap connections. When opened, water will constantly flow into the drain, causing a voltage drop;
- The additional make-up tap is open. This position of the shut-off valves causes constant fluctuations in coolant pressure.
To ensure heat supply and water heating in an individual residential building, owners most often install gas boilers with closed coolant circulation. To install and operate a gas boiler, it is necessary that a gas pipeline runs nearby. If there are no gas supply networks nearby, bottled liquefied petroleum gas can be used for heating.
The dual-circuit design allows you to increase the pressure of the working medium in the system circuit. A decrease in pressure contributes to problems during the operation of the heating system. Let's take a closer look at what the causes are and what methods can be used to eliminate this unpleasant problem.
If there is no expansion tank
The expansion tank for a home heating network is the second most important element (after the boiler). Water, when temperature changes, changes in volume. The volume inside the circuit is always constant, so an expansion tank is additionally connected to the circuit, where excess coolant can be diverted, i.e. acts as a compensator. Consequently, the RB is a safety device that prevents emergency situations - increased pressure, depressurization of pipes, etc.
The use of boiler equipment without an expansion tank is highly not recommended.
For stable operation, the pressure of the RB must correspond to the system volume, because when replacing radiators with pipes, the volume of coolant must be increased. At the same time, a too large RB will not maintain the operating pressure in the circuit.
The standard is an expansion tank designed for 120 liters of coolant in the circuit (typical two-room apartment). If the tank is too small, then the water will be discharged when heating and expanding the volume through a safety valve. When the boiler is turned off, when the liquid temperature decreases, starting the boiler will be impossible, because its volume, and, consequently, the pressure will be insufficient. In such cases, additional network feeding is necessary.
Conclusions and necessary video on the topic
Video #1. How to implement balancing of heating radiators in a home heating system. Note that without valves on each heating radiator it will not be possible to balance the system.
Video #2. Tips from a heating engineer for restoring operating pressure in closed-type heating circuits. The video also explains the procedure for pumping an expansion tank that has lost its “factory” gas:
A properly balanced heating system will perform its functions for many years. But somehow the characteristics of the coolant will change or critical parts of the thermal circuit will break. Due to this, monitoring the indicators of the coolant using instruments for determining the pressure value must be carried out regularly in order to respond to pressure changes in a timely manner.
Please write comments if you have questions about the topic of the publication. We are waiting for your stories about your experience in normalizing pressure in the heating circuit. We and site visitors are ready to discuss controversial issues in the block located under the text of the publication.
Competent calculation of the heating system
In private homes, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to the choice of expansion tank. If the volume is insufficient and the system does not start, there is a high probability of pipes freezing.
Variety of expansion tanks
The installed equipment should be checked twice - immediately after installation and upon the onset of the cold season (at higher heating intensity).
Causes of drop in pressure
The reasons for the pressure drop in a gas boiler are as follows:
- Water is leaking from the heating system.
- The electricity was cut off for a long period.
- Malfunctions of the main expansion tank.
- Incorrect boiler selection.
Due to low pressure the boiler stops working. When the water pressure in the heating network reaches a minimum level, water does not flow into the main heating system. When the gas pressure in the boiler drops, it immediately turns off automatically. To avoid such difficulties, you need to regularly carry out maintenance of such devices. To do this, you need to invite specialists from the service department.
Norm and control
We have already said that in a gas boiler the pressure should be within 1.5-2 atmospheres - this is the norm for a system that is put into operation and is in a heated state. In multi-storey buildings heated by centralized boiler houses, this figure is higher. Here, pipes and batteries must withstand not only high pressure, but also water hammer - this is an abrupt increase in pressure.
If drops are typical for centralized systems, then for autonomous heating they are rare - the volume of coolant here is not so large that serious jumps can be observed. In a cold state, the normal indicator is 1-1.2 atm., and in a warm state - slightly higher.
In private households, autonomous heating systems are used, powered by single-circuit and double-circuit boilers. The latter are becoming increasingly widespread. In addition to heating, they solve the problem of preparing hot water. One circuit in them heats the coolant circulating through the pipes, and the other ensures the operation of the hot water supply system.
Types of pressure
The pressure in a 2-circuit (double-circuit) boiler is divided into the following types:
- static, formed under the influence of gravity, with an increase in height for every meter it becomes higher by 0.1 Bar;
- dynamic, created by pump operation (the greater the pump power, the higher the dynamic pressure) or by increasing temperature;
- working, is obtained by adding two types of pressure - static and dynamic;
- the excess, which is recorded by the pressure gauge, is the difference between the atmospheric and the measured;
- nominal, set in accordance with the physical parameters of the materials from which the gas boiler blocks are made; when operating in this range, the service life declared by the manufacturer is guaranteed;
- maximum, maximum permissible, guaranteeing the exclusion of emergency situations and malfunctions;
- crimping, this pressure is used to test the parts of the unit in production; it can exceed the working pressure by 1.5 times.
Control devices
To control the water pressure in the heating boiler and heating system, pressure gauges and thermomanometers are used. The latter are combined devices for monitoring two parameters at once. After starting the circuit, it is necessary to monitor the indicators so that they do not go beyond normal limits.
Some double-circuit floor-standing and wall-mounted boilers do not have traditional dial pressure gauges. Instead, electronic sensors are installed here, information from which is transmitted to the electronic unit, after which it is processed and displayed on the display. Another approach is also possible - if the heating unit does not have a pressure gauge, it is provided by the safety group.
The security group itself includes the following nodes:
- Pressure gauge or thermomanometer - for monitoring temperature and pressure in the heating circuit;
- Automatic air bleeder – prevents the circuit from becoming airy;
- Safety valve - relieves coolant pressure when it increases excessively.
Be sure to provide this unit in a closed heating system.
Operating principles of gas boilers
In gas boilers (GC), the coolant is heated as natural gas is burned. This process produces a lot of heat. And it goes through a heat exchanger to the heat carrier (TH). The heated heating element disperses throughout the heating network.
A model with two circuits supplies hot water to all plumbing fixtures in the house and for the “warm floor” system.
If you notice a drop in pressure in the blood pressure, and the low reading lasts for quite a long time, you need to contact a specialist.
In order for the heating network to function correctly, boilers must maintain stable pressure. This way the heated heating element will circulate normally throughout the entire network.
A decrease in pressure can disrupt the operation of the entire network. As a result, the house will lose heat.
Various devices for its control are integrated into the design of the main body. They collect data on the condition of the heating network. And this data is displayed to the user.
For example, the normal pressure in a private house is considered to be 1.5-2 atm. A reading lower or higher indicates a malfunction of the device.
Difficulties with pressure in the heating network of a house arise only in technologies where there is forced circulation.
It is almost impossible to eliminate pressure drops with your own efforts. You should definitely invite a professional in the field of civil repair.
Pressure drop and causes
In this section you will learn why the pressure in the heating system drops and how to deal with it. The reasons can be very different, so a comprehensive check of the entire circuit is practiced.
The pressure in the system drops when hot water is turned on
This problem is widespread, such complaints are received from many users. The bottom line is this: you open a hot water tap, and at the same time the pressure in the heating system drops. There is nothing wrong with this, since this phenomenon is associated with the design features of some double-circuit boilers. Experts say that in fact it does not fall, and the pressure gauge shows the wrong value.
When the pressure in a gas boiler drops, it goes into error and does not turn on - this scheme is implemented in many double-circuit units. If you open a hot water tap, and then the heating does not restore its operation, therefore, the pressure still drops - you need to deal with the reasons. For example, this may be caused by air leaks into the circuit or improper operation of the three-way valve.
Pressure drops due to leaks
A problem such as a coolant leak leads to a constant drop in pressure in the circuit. The user's task is to inspect the entire heating system - water can come out through literally every node. For example, leaks are often caused by poorly clamped connections, leaky heat exchangers, cracks in pipes and radiators. Typically, the tightness is checked during the initial startup of the circuit, but it can be broken later.
Let's look at what needs to be inspected and checked if the pressure in a closed heating system drops:
- Connecting fittings - the more connections, the less reliable the system;
- Heating batteries - even the smallest crack can cause coolant to leak out of it;
- Expansion tanks - make sure that their tightness is not broken;
- Double-circuit boilers - if the pressure drops due to a leak, puddles of water may form under them.
Any faults found are corrected, after which the system is refilled with water until normal pressure is restored.
Air jams
Cracks and lack of sealing in the heating system lead not only to leaks, but also to the opposite phenomenon - air being sucked into the circuit. As a result, air bubbles form in it. Some of them are eliminated by air bleeders, but they are not present in all systems. If the pressure in the system drops, there is probably a strong airing of the heating.
Air bubbles can also form as a result of improper filling of the circuit - air pockets form in it, due to which the pressure in the heating system drops. Airing causes many other phenomena:
- Gurgling and murmurs traveling through pipes are sound effects caused by air bubbles;
- Cold batteries and pipe sections - not only the pressure drops, but also the heating efficiency;
- Metal corrosion – the presence of air in the heating system leads to the thinning of metal components.
Thus, banal deaeration of the system will help to increase the pressure in the boiler.
Problem with expansion tank
The pressure drops in the Baxi boiler or in the Arderia boiler - quite common problems that plague users. This is usually caused by leaks in pipes and radiators, improper operation of the make-up tap, and leaky heat exchangers. But sometimes the problem lies in membrane expansion tanks. Somehow they cannot maintain the nominal pressure in the heating system - it drops.
How to solve the pressure problem?
The very first thing to do in such cases is to check the valve. Before starting the test, make sure that the make-up valve is closed as tightly as possible. Check what happens when the gas boiler is turned off. To do this, disconnect it from the power supply. The same thing happens even when it is turned off - there is only one solution - call a service center that will replace the faucet for you. It is not recommended to replace the faucet yourself at home, as this work may require special equipment.
How to increase the pressure in the boiler
If the pressure drops due to the expansion tank, it means that its volume is incorrectly calculated or the internal membrane is damaged. The situation can be corrected by more accurately calculating the required volume or by replacing the tank.
If the pressure in the heating system drops immediately after it is first started, then this is normal. The newly filled circuit, if it was filled with ordinary tap water, is full of air. As soon as it is converted into bubbles and removed from the pipes, the circuit parameters are normalized. You can also try removing the bubbles manually by using a manual air release.
The worst thing is if the pressure in the system laid inside the walls and floors has dropped - the pipes are often masked and completely recessed in building structures. If something happens to them, you will have to suffer thoroughly to localize the problem. The situation can be prevented by more careful selection of materials for the construction of the heating circuit.
Before increasing the pressure, it is necessary to check the tightness of the system. To do this you need to inspect:
- All heating devices - often leaks form where they connect to the pipes. Leaks between individual sections are also possible;
- Pipes - microcracks often lead to leakage of coolant, due to which the pressure gradually drops;
- Fittings are another common place for coolant leaks to occur;
- Boilers - double-circuit models have a complex internal structure; it is necessary to inspect the circulation pump, three-way valve and heat exchanger.
It is best if a specialist inspects the double-circuit boiler.
Increased pressure in the heating system causes unbalanced operation of the equipment and frequent boiler blockages. As a result, individual elements are subjected to increased load, which leads to circuit breakdowns and equipment failure. Why does the pressure in the heating system increase? There are several reasons for this phenomenon, most often these are leaks, unbalanced operation of individual elements, failure of automation or incorrect settings.
The pressure in the heating system in a wall-mounted boiler increases
The presence of a stable operating pressure in the heating system (1 - 2 bar) is the key to the safe operation of a double-circuit gas boiler. The boiler will not start if the system pressure is less than 0.6 bar; if more than 3 bar, an emergency water discharge occurs.
- There are two reasons why the pressure in a double-circuit gas boiler can gradually but constantly increase:
- does not hold the make-up valve (most likely);
- The secondary heat exchanger is faulty.
This usually happens like this: the pressure slowly increases (sometimes you may not notice this and leave for a few days) until the safety valve is activated (usually at 3 bar). And so several times, in a cycle. As a result, the floor in the kitchen is flooded, the furniture and mood are ruined.
The heating system is autonomous (not connected to the water supply). This is essentially a closed circuit that can be heated by a gas burner. But to fill this heating circuit with water, there is a make-up tap, and if it leaks, then water from the water supply will leak into the heating system (increasing the pressure there).
Well, the second (unlikely) option is that in the secondary heat exchanger the water supply and heating pipes are located side by side, literally through a thin wall. And if a fistula has formed there, then there may be leakage from the water supply system into the heating system (until the pressure is equalized). And if the pressure in the cold water supply is more than 3 bar, the same pressure will eventually be in the heating system. Which will trigger the emergency valve (and release some of the water).
How to fill the heating system of a double-circuit boiler
- The heating system of a double-circuit gas boiler is filled through a make-up tap, which is included in the basic configuration of any boiler:
- open all air vents;
- open the feed tap and fill the system;
- As the circuit fills, close the air vents;
- we achieve pressure (specified in the boiler passport);
- after the pressure in the heating system has reached the required level, the make-up valve closes.
Why do you need a feed tap on a gas boiler?
The make-up valve serves to initially fill the heating circuit with coolant (water) and compensate for the loss of coolant.
- But the loss of coolant itself is possible for several reasons:
- banal coolant leaks at the joints of pipes and radiators;
- when the operating conditions are critically exceeded, the pressure in the heating system may increase, which leads to the activation of the emergency valve, which discharges part of the coolant;
- automatic air vents release air, but some coolant still comes out in the form of steam.
How does the boiler feed tap work?
The filling and make-up valve for compact boilers is usually located at the bottom of the body, next to the cold water supply pipe. And it is a manual valve that connects this line with the heating return line.
Double-circuit gas boiler does not hold the make-up tap
- There are only two reasons why the make-up valve may not hold (podtivate):
- the sealing rubber on the rod has become hard over time;
- the rubber band has broken, for example from over-tightening the make-up tap.
How to tighten the feed tap correctly: select the free movement of the rod (the tap rotates with almost no effort) and when you feel that the rubber band has rested against the cone, tighten it another half turn.
Boiler feed tap repair
In most cases, it is not at all necessary to change the make-up tap; it is enough to relieve the water pressure in the boiler through the valve, unscrew the turntable from the tap and replace the small rubber ring on it.
The main reasons for increased pressure
Most often, the reason why the pressure in the heating circuit increases in a closed heating system is equipment failure due to which the indicators either jump up or drop sharply down. But apart from this, the reasons also include the following:
- A sharp increase in coolant pressure due to blocked shut-off valves. An increase in pressure is observed in the system, after which the boiler is blocked and the system stops. To fix the problem, you need to check the fittings for leaks, open valves and taps to relieve pressure.
- The reason for the increase in pressure in the heating system may be contamination of the dirt filter. Rust particles, debris, sand and slag accumulate on the surface of such a filter. As a result, the pressure increases greatly in the area between the boiler and the filter. To eliminate the cause, it is necessary to regularly clean the filters, at least 3-4 times a year. Also, a good solution would be to replace conventional mud filters with magnetic or flush filters. They cost more, but their maintenance is much easier.
- The operating pressure of the system may increase due to a malfunction of the heating boiler automation. This is a manufacturing defect, incorrect system settings, or a breakdown of the control board. All these problems require boiler repair, which can only be carried out by a master.
- There are leaks in the make-up tap, that is, water will constantly penetrate into the general circuit, which causes a pressure surge. The repair is usually quite simple, you just need to replace the rubber gaskets. But if there is a defect, the crane or equipment should be completely replaced.
Why does the pressure drop in a double-circuit or conventional boiler? This situation most often occurs when the expansion tank breaks down or the air valve leaks. To fix the problem, you may need to repair or completely replace the tank.
Types of pressure in heating systems
Depending on the current principle of movement of the coolant in the heat pipeline of the circuit, static or dynamic pressure plays a key role in heating systems.
Static pressure, also called gravitational pressure, develops due to the gravitational force of our planet. The higher the water rises along the contour, the stronger its weight presses on the walls of the pipes.
When the coolant rises to a height of 10 meters, the static pressure will be 1 bar (0.981 atmosphere). An open heating system is designed for static pressure, its largest value is about 1.52 bar (1.5 atmospheres).
Dynamic pressure in the heating circuit is developed artificially - using an electric pump. Basically, closed heating systems are designed for dynamic pressure, the contour of which is formed by pipes of much smaller diameter than in open heating systems.
The usual value of dynamic pressure in a closed heating system is 2.4 bar or 2.36 atmospheres.
Air lock as a cause of pressure increase in closed systems
When operating a closed system, it is not uncommon for the pressure to increase, which may be accompanied by a decrease in the overall coolant temperature and blocking of the boiler. All this leads to imbalance in the operation of the circuit and failure of its individual elements.
Why does the pressure increase in the system or is there a sharp increase in it? Typically, in closed heating circuits using gas equipment or other types of boilers, such changes occur due to airing. Air locks are a fairly common cause of pressure drop. Typically, the presence of such problems is determined in the following cases:
- equipment breakdown;
- incorrect system startup;
- automation malfunctions;
- presence of cracks in the boiler heat exchanger.
There are several reasons for such system failures:
- the contour is filled from the top point;
- upon startup, there is a very rapid filling of water in the system;
- Mayevsky valves or air vents are faulty;
- the heating radiators were not vented after their repair;
- The impeller of the circulation pump is loose, that is, air pumping occurs with disturbances.
Results of instability in circuits
Insufficient or very high pressure in the heating circuit is equally bad. In the first option, some of the heating devices will not heat the rooms well, in the other, the integrity of the heating system will be compromised, and some of its parts will break.
An increase in dynamic pressure in the heating pipeline occurs if:
- the coolant is excessively overheated;
- the pipe cross-section is insufficient;
- the boiler and pipe wires are overgrown with scale;
- air pockets in the system;
- an overly powerful booster pump was installed;
- water replenishment occurs.
Also, high pressure in a closed circuit is caused by incorrect balancing of the taps (the system is over-regulated) or breakdown of some regulator valves.
To control operating parameters in closed heating circuits and for their automatic adjustment, a safety group is set:
The pressure in the heating pipeline drops for the following reasons:
- leakage of coolant;
- pump breakdown;
- breakthrough of the membrane tissue of the expansion tank, cracks in the walls of an ordinary expansion tank;
- breakdown of the security unit;
- water leakage from the heating system into the feed circuit.
The dynamic pressure will be very high if the voids of pipes and heating devices are clogged, if the catch filters are dirty. In such situations, the pump does not stop working at a very high load, and the efficiency of the heating circuit decreases. A typical result of increasing pressure values is leaks in connections and even pipe ruptures.
The pressure parameters will be less than required for normal functionality if a pump of insufficient power is inserted into the line. It will not be able to move the coolant at the required speed, which means that a somewhat cooled working medium will be supplied to the device.
The second obvious example of a drop in pressure is when the flow is blocked by a tap. A sign of such problems is the loss of pressure in an individual segment of the pipeline located after the obstacle to the coolant.
Since all thermal circuits have devices that protect against excessive pressure (at least a safety valve), the problem of low pressure occurs much more often. Let's consider the reasons for the drop and ways to increase the pressure, and this means improving the movement of water along a closed circuit, in closed and open heating systems.
Optimal value for a private house or cottage
Any boiler operates at certain system settings, in particular, it is necessary to correctly calculate the water pressure. This value is influenced by the number of floors of the building, the type of system, the number of radiators and the total length of the pipes. Usually for a private house the pressure level is 1.5-2 atm, but for a five-story apartment building this value is 2-4 atm, and for a ten-story building it is 5-7 atm. For higher buildings, the pressure level is 7-10 atm, the maximum value is achieved in heating mains, here it is 12 atm.
For radiators that operate at different heights and at quite a decent distance from the boiler, constant pressure adjustment is required. In this case, special regulators are used to reduce it, and pumps to increase it. But the regulator must always be in good working order, otherwise sharp fluctuations and drops in coolant temperature will be observed in certain areas. The system must be adjusted so that the shut-off valves are never completely closed.
What to do when gas pressure disappears?
A drop in gas pressure may occur for the following reasons:
- Increasing the load on the gas main during severe frosts and holidays, connecting additional consumers to the main. Contact the gas service with a request to increase the gas pressure.
- The gas filter is clogged - clean the filter.
- The gas hose is clogged, replace it with a new one.
- The injectors are clogged, clean them with a brush.
- Gas valve is faulty. If after disassembling and cleaning it the situation does not change, replace it with a new one.
- The old pipes on the gas main are rusty, there is a leak - notify the gas service.
What to do if the problem with the gas supply occurs constantly - some users connect a gas cylinder between the gas pipe and the boiler, using it as a receiver. In this case, when the unit is turned on, gas will flow directly from the cylinder, without creating a vacuum in the gas pipeline.
There are models of units, for example, Buderus, Bosch, Deo (Daewoo), which operate at reduced pressure; when buying a boiler, you should pay attention to this.
Another solution to the problem is replacing the gas boiler with an electric boiler. Using it will undoubtedly be more expensive, but you will always have heat and hot water. Below are the gas supply pressure values for some models.
Pressure drop
An increase in pressure in closed heating systems is not the only problem; in some cases there is a sharp drop in operating pressure, and among the reasons why the pressure level drops, the following should be highlighted:
- hidden system leaks, corrosion, loose connections, leaking fittings;
- rupture of the tank membrane, which requires replacement or repair of equipment;
- pressure drops in the system are observed, if the nipple poisons, such an air leak leads to deflation of the tank, and this causes damage to the membrane;
- there are cracks on the boiler heat exchanger, which leads to coolant leakage;
- pressure drops associated with the appearance of air bubbles lead to a decrease in the overall temperature in the system and its shutdown;
- One of the reasons for the decrease in pressure may be a soured or slightly open tap used to discharge water into the sewer system.
Increase in pressure
The reasons for a spontaneous increase in pressure in the heating circuit, which leads to the activation of the safety valve, may be as follows:
- There is a problem with the valve on the jumper with the cold water supply system. Screw valves and plug valves have one common problem - they cannot provide complete tightness when closed tightly. In most cases, leaks occur due to wear of the screw valve linings or scale trapped between it and the seat. This can also cause scratches on the faucet body and plug. When the pressure in a closed heating system exceeds a cold one (this happens quite often), water gradually leaks into the circuit. It is subsequently discharged into the drainage system using a safety valve.
- There is not enough expansion tank volume. Heating of the coolant and further increase in its volume will not be able to be fully compensated due to the lack of space in the tank. Signs of this difficulty are considered to be an increase in pressure specifically when lighting or turning on the boiler.
To remove the first breakdown, it is better to replace the valve with a modern swivel valve. This type of shut-off valve is characterized by stable tightness in the “Closed” position and a very long service life. Frequent maintenance is also not required here. In most cases, it comes down to tightening the gland nut under the handle after several hundred closing cycles.
In order to solve the second problem, you will need to change the expansion tank, choosing a more spacious tank. There is also an option to equip the circuit with an additional expansion tank. In order for the system to operate without failures, the volume of the expansion tank should be approximately 1/10 of the total amount of coolant.
Sometimes it happens that an increase in pressure provokes a circular pump. This is typical for the filling area after the impeller if the pipe wire has high hydraulic resistance. The usual reason is undersized diameter. There is no need to worry in such a situation: this problem can be solved by easily installing a safety group (at a sufficient distance from the pump). Replacing the filling with a larger pipe is justified only if there is a large temperature difference between the first heating devices from the boiler and the last ones in the direction of circulation of the coolant.
Causes of problems
Let's take a closer look at what affects the level of pressure indicators in the system:
- installation height of a wall-mounted boiler, height and length of the pipe system/circuit;
- material of pipes and elements, as well as the effect of liquid on them;
- correctness and integrity of the design of main tracks.
The standards for monitoring pressure level indicators are slightly different in an autonomous heating system. You should pay attention to the model and technical parameters of the boiler, the pipeline network and pipe characteristics, installation locations and the number of floors in the building.
Why did the water pressure drop?
What affects the indicators in the circuit:
- The installation height of the housing, as a result - the height and length of the pipes.
- The effect of liquid on pipes and other elements.
- Construction of main tracks.
If your home has autonomous heating, then the standards depend on:
- Boiler models, pipeline paths.
- Installation locations.
- Number of floors in the building.
- Characteristics of the outer pipe.
Next we'll look at non-installation related reasons. If the device releases and does not gain pressure, this may be an internal failure or external factors.
Leak in the system
You add coolant to the circuit, but the pressure is still low. If the batteries heat up well, the moisture evaporates quickly, making the leak difficult to detect. Take a dry cloth and go over all pipe joints and connections. Look, there may be puddles accumulating under the radiators.
If the leak cannot be detected, use a compressor.
- Disconnect the radiators from the heating device.
- Drain off all liquid.
- Connect a compressor to the taps.
- Bleed the circuit with air.
- You will hear extraneous sounds in places where there is damage.
- To seal, use plumber's tow or sealant.
Are your radiators built into the wall? Then contact the specialists. They will conduct a thermal imaging check. All you have to do is open up the damaged area and carry out repairs.
Incorrectly selected boiler - the power does not correspond to the established parameters of the pipeline. Therefore, the pressure constantly drops and does not hold.
If the values drop quickly, the cause may be the expansion tank . At the same time, you fill in the coolant every week, but it is becoming less and less, although no leaks have been detected. There is also a pressure drop in the mixers.
How to gain and improve performance:
- Turn off the water supply valves.
- Drain the circuit completely.
- Open the fitting on the expansion tank (RB) and record the numbers.
- Pump air until all the water comes out.
- Bleed the air and repeat the steps. Make sure that the needle on the pressure gauge does not exceed 1.3 bar.
- Open the taps and fill in the liquid.
If after the procedure the pressure drops and does not rise, inspect the membrane for damage. Replace if necessary.
Heat exchanger malfunction . After checking the pipes and connections, were there any violations found? Inspect the radiator for damage. A large accumulation of scale on the tubes leads to frequent flushing with reagents. This causes the material to quickly wear out and cracks to appear.
The bithermic unit cannot be repaired due to its design. Will need replacement. If a tubular radiator is installed, remove it. Fistulas can be detected by green spots on the surface. Dry the device and clean the damaged area with sandpaper. Then carry out soldering with a soldering iron or torch.
Unfortunately, after repair the unit will not last long. Therefore, sooner or later you will have to change it.
Problems with the water supply valve . When a faucet leaks, it leads to a constant drop in pressure. How to add coolant to the system? Only replacing the part will help.