Despite the promotion of alternative methods of heating rooms, in the vast majority of cases the main heat source is a liquid heating circuit. Due to its economy and efficiency, it is optimal in the long winters typical of our latitudes.
The downside is that the water can freeze. Therefore, in addition to it, a non-freezing coolant is also used for heating systems, replacing water. In this article, we will take a closer look at its main varieties, consider their significant advantages and main disadvantages.
We will also provide an algorithm for calculating the required volume of coolant for a specific system and recommendations for choosing the type of fluid for heating circuits.
When is antifreeze necessary?
Before you start considering alternative liquids, don't discount water. If heating is installed in a house where residents live permanently, then water will be one of the safest and most reliable options.
As a coolant, it has optimal parameters for circulation through the circuits of heating systems.
However, at the peak of winter frosts, the slightest crystallization of water can cause a serious accident with the destruction of the pipeline and heating equipment components.
If we are talking about a country house, which is periodically visited, or when on weekends the family often leaves their abode, leaving the heating unattended, then the coolant used must be resistant to the low temperature range characteristic of the area.
Only for the use of chemical compounds as a carrier of thermal energy, it is necessary to prepare the heating circuits. The system must be completely sealed, because the liquid is toxic and flammable to varying degrees.
Antifreeze cannot be used “in its pure form” in heating circuits. Since undiluted anti-freeze compositions are aggressive and tend to stimulate the development of corrosion, they are diluted with water
The owner must take into account that the antifreeze liquid needs to be changed periodically, which is fraught with additional costs.
Some models of boiler equipment have specific recommendations for the use of a certain brand of coolant. If you use a liquid of a different composition, you may lose the warranty on the boiler.
Water as a coolant for the heating system of a private house
Water is the most accessible coolant, but it cannot always be used. In terms of technical parameters, it is superior to any antifreeze, but for many homeowners its disadvantages cancel out all its advantages.
Advantages of water as a coolant
- Compatible with heating equipment. Condensing boilers are designed to operate on water. All parameters are valid only when working with this coolant. Boiler heat exchangers have a small tube diameter, so when using antifreeze, over time they can become clogged with additives and other decomposition products of liquid components. For this reason, adding antifreeze will void the equipment warranty of most boiler manufacturers.
Some boiler manufacturers allow the use of antifreeze while maintaining warranty service, but in this case only recommended brands of coolants can be used.
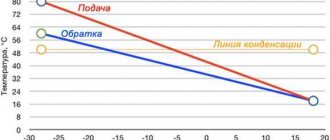
- Power of heating devices. For radiators, this parameter depends on the heat capacity of the coolant. With water it turns out to be 15 - 20% higher compared to antifreeze.
The power of the radiator can be calculated using the formula W=c*Q*(t2-t1), where c is the heat capacity of the medium, Q is the liquid flow rate in liters per hour, t2 and t1 are the temperature difference. Also, when calculating the number of radiators per room, it is important to take into account that the power parameter of the device on the packaging is indicated for operation on water.
- Water does not require replacement. Non-freezing coolants require replacement every 5 years. Some manufacturers produce compounds that can last up to 10 years. Replacing antifreeze and flushing the system is a labor-intensive procedure that will require the involvement of specialists and significant costs. At the same time, it is almost impossible to completely remove the antifreeze carrier.
This fragility of antifreeze is due to the additives that are present in their composition. These additives reduce corrosiveness so that substances do not harm heating equipment. Over time, the additives decompose and precipitate, after which ethylene glycol and propylene glycol begin to react with the metal.
- Water cannot be faked. The likelihood of purchasing counterfeit products when using water tends to zero. There is only a possibility of purchasing ordinary water under the guise of distilled. When using antifreeze, the possibility of filling with counterfeit liquid is higher.
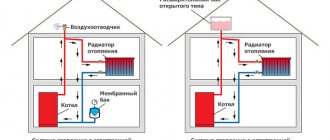
- Safety. Water does not belong to the group of toxic substances, does not emit harmful fumes and is disposed of without great expense. Its harmlessness to humans makes water the only possible coolant for open gravity flow systems.
Disadvantages of water
The main disadvantage of water is that it freezes at 0 degrees. When the liquid turns to ice, it increases in volume by 10% and can burst pipes. This means that in any building where the temperature drops below freezing, water cannot be used as a heating medium. Such buildings include dachas, tourist centers, campsites, etc. There are many situations when the owner is not at home and he cannot control the operation of his heating system.
Also, improperly prepared water can lead to damage to heating equipment: corrosion, salt deposits.
What kind of water can be used for heating systems?
Water for heating systems must meet the requirements for two parameters: hardness and acidity, and it must not contain sand or other large particles. The pH indicator is responsible for acidity; normally it should be 7 units. Values from 1 to 6 correspond to acid, and from 8 to 13 to alkali. An acidic or weakly acidic liquid in a closed system tends to increase its pH to normal, for this it absorbs metals from the environment. This leads to destruction of pipes and boiler elements.
Hardness reflects the amount of salts dissolved in the liquid and is expressed by the total mineralization of the solution. When the temperature rises, these substances precipitate in the form of scale. The accumulation of deposits on the internal parts of the equipment can cause equipment failure.
If the heating system is closed and no new liquid enters it, then the initial amount of water will contain too few salts to clog the heat exchanger.
- Tap water – has a normal pH, but in some regions contains high levels of salts. Over several cycles of passage through the heating system, the hardness decreases, as some of the salts precipitate and are deposited on the heat exchanger. This will not cause any harm during startup, but it is not recommended to add water from a water supply or well to such a system, as there may be more deposits.
- Boiled water differs from ordinary tap water in the lower mineralization of the solution. At the same time, boiling large volumes is problematic.
- Bottled drinking water has normal acidity and a level of mineralization acceptable for humans. Thanks to this, it does not leave scale and is safe when topping up the system.
- Distilled water does not contain mineral impurities, but has a pH level of 5.4 to 6.6, which is not normal acidity. Some boiler manufacturers do not recommend using distilled water due to the potential for corrosion.
Recommendations for choosing a product
It is necessary to take into account not only the characteristics of the coolant for the heating system, but also the configuration of the equipment in order to make heating safe and efficient.
If you decide to use antifreeze, let's look at the conditions under which its use is excluded:
- lack of a heating temperature regulator in the boiler;
- when using oil-treated flax seals;
- the heating circuit uses pipes, radiators, shut-off valves with a galvanized surface; - open type heating system
Evaporation of water from an antifreeze liquid can change properties, and ethylene glycol vapor is toxic.
Compliance with the following rules will allow owners to get rid of a number of troubles due to incorrect use of antifreeze liquids:
- in places of sealing, flax tow must be coated with sealing paste;
- sectional radiators need to be sorted out to replace the seal with Teflon or paronite gaskets;
- do not use automatic air vents (to bleed off excess air, it is better to install Mayevsky valves for manual adjustment);
- radiators and pipes must have increased volume and diameter;
- the presence of a high-power circulation pump;
- install a membrane expansion tank with increased volume.
Antifreeze is poured into the heating system only after proper flushing of the heating circuit, for which it is better to use special compounds. For the safety of all residents, experts recommend using propylene glycol.
The boiler cannot be brought to peak power immediately after filling the system with coolant. It is necessary to increase the temperature in steps. This is necessary for the antifreeze to gain optimal performance characteristics and expand within normal limits.
To select a suitable coolant, it is necessary to take into account the properties of pipes, boiler equipment and other factors.
When diluting a liquid with water, concentrations should not be allowed higher than -20 degrees. Excess water will cause scale deposits and change the performance properties of the glycol. Can only be diluted with distilled water.
Application of coolants
There are usually no special difficulties when choosing antifreeze. But when using it, some peculiarities arise.
When preparing a solution of coolant and concentrates, the proportion requirements must be met.
Antifreeze must be replaced as needed or as part of the maintenance schedule unless replacement is required during engine repair. Do not mix coolants of different properties and types, as malfunctions of the cooling system may occur.
If the brand of antifreeze poured into the engine is unknown, then it is better to drain it all and purchase new antifreeze. It is undesirable to mix different brands of antifreeze, since different sets of additives have different properties, and as a result of chemical reactions they will become unbalanced. When mixing different reagents, malfunctions and ballast sediment may occur, water pump failure, engine overheating, clogging of the cooling system, and major repairs of the power unit. You should not save on buying antifreeze, as engine repairs will cost much more.
Antifreeze for car engines is sold in finished or concentrated form. Many car enthusiasts are accustomed to purchasing concentrate in order to make the solution themselves in the required proportion. But we must not forget that to dilute the solution, only distilled water is needed, and the proportion should be determined by the freezing temperature. Each time you need to use only the concentrate manufacturer’s instructions.
How to determine the volume of coolant?
The easiest way is to use a water meter or water flow meter. There is one in almost every house or apartment with a centralized water supply.
Before starting measurements, the heating circuit must be completely emptied. Then readings are taken on the meter, and the system begins to be filled with a small pressure of water. This is necessary to avoid air pockets that distort the readings.
As soon as the heating pipeline is filled with water, you need to take the water meter readings again. You need to remember that 1 cubic meter is 1000 liters, and purchase the appropriate amount of liquid.
The second method is less convenient, but effective when there is no counter. The filled system is emptied through a measuring container (tank or bucket of a certain volume). The main thing is not to go astray with the number of buckets.
Another method is mathematical. The values of the volumes of radiators and expansion tank, pipe diameters, and the volume of the boiler heat exchanger are taken as initial data. Using simple geometric and arithmetic formulas, you can calculate the final volume.
We looked at detailed examples of calculating each of the elements of the heating system in our following articles:
- Calculation of pipe volume: principles of calculations and rules for making calculations in liters and cubic meters
- Expansion tank for open type heating: device, purpose, main types + tips for calculating the tank