Home / Heating
Back
Published: December 16, 2020
Reading time: 3 min
0
12206
Stable operation of the heating system in private homes is vitally important; the question of what pressure should be in the expansion tank needs to be studied thoroughly. After all, such indicators directly affect the functionality and wear of all equipment.
At low values, the boiler will not start, and high numbers will lead to unpleasant consequences after some time. To understand all the small details, you need to approach the topic as seriously as possible. I consider the design of the expansion tank to be simple, I will try to explain everything as clearly as possible in detail and consistently.
- 1 Why is an expansion tank needed?
- 2 What pressure should be in the heating expansion tank
- 3 Why does the pressure in the heating system drop?
- 4 How to check pressure
- 5 How to adjust the optimal pressure
- 6 Rules for maintaining a membrane tank
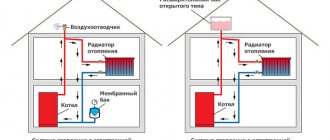
Types of heating systems
There are two schemes for building heating networks - open and closed. An open (gravity) heating system is used in centralized heating networks and allows water to be directly withdrawn for hot water supply needs, which is impossible in private housing construction. Such a device is located at the top point of the heating system circuit. In addition to leveling pressure drops, the heating expansion tank performs the function of natural separation of air from the system, since it has the ability to communicate with the outside atmosphere.
Thus, structurally, such a device is a compensation tank of the heating system, not under pressure. Sometimes a system with gravitational (natural) circulation of a heat-carrying fluid may be mistakenly called open, which is fundamentally incorrect.
With a more modern closed circuit, an expansion tank of a closed-type heating system with a built-in internal membrane is used.
Sometimes such a device can be called a vacuum expansion tank for heating, which is also true. Such a system provides for forced circulation of the coolant; air is removed from the circuit through special taps (valves) installed on the heating devices and at the top of the system pipelines.
Gas boiler baxi eco four 24
A very popular series among all others in the BAXI line. The 4th generation boiler with a capacity of 24 kilowatts is available in various versions: with an open and closed combustion chamber. Boilers with a closed combustion chamber and forced smoke removal are designated by the letter “F” in the name. Baxi turbocharged boilers are the most popular and are often used when organizing apartment heating, so we will consider the use of an expansion tank in the heating system using this boiler model as an example.
What are the advantages of a closed heating system
Despite the fact that many modern devices and systems for space heating have appeared recently, the principle of heat transfer through a liquid with high heat capacity circulating through pipes undoubtedly remains the most common. Water is most often used as a carrier of thermal energy, although in some circumstances it is necessary to use other liquids with a low freezing point (antifreeze).
Water heating is the leader in prevalence
The coolant receives heat from the boiler (furnace with a water circuit) and transfers heat to heating devices (radiators, convectors, “warm floor” circuits) installed in the premises in the required quantity.
How to decide on the type and number of heating radiators?
Even the most powerful boiler will not be able to create a comfortable atmosphere in the premises if the parameters of the heat exchange points do not correspond to the conditions of a particular room. How to correctly calculate the required number of heating radiators is in a special publication on our portal.
But any liquid has general physical properties. Firstly, when heated, it increases significantly in volume. And secondly, unlike gases, this is an incompressible substance; its thermal expansion must be compensated in some way by providing free volume for this. And at the same time, it is necessary to ensure that as it cools and decreases in volume, air does not enter the pipe contours from the outside, which will create a “plug” that prevents the normal circulation of the coolant.
These are the functions that the expansion tank performs.
Not yet in private construction, there was no particular alternative - an open expansion tank was installed at the highest point of the system, which completely coped with the tasks.
Schematic diagram of an open type system
1 – heating boiler;
2 – supply riser;
3 – open expansion tank;
4 – heating radiator;
5 – optional – circulation pump. In this case, a pumping unit with a bypass loop and a valve system is shown. If desired or if the need arises, you can switch forced circulation to natural circulation, and vice versa.
Prices for circulation pumps
A closed system is completely isolated from the atmosphere. A certain pressure is maintained in it, and the thermal expansion of the liquid is compensated by installing a sealed tank of a special design.
Differences between a closed heating system
The tank in the diagram is shown pos. 6, embedded in the return pipe (item 7).
It would seem - why “fence the garden”? A regular open expansion tank, if it fully copes with its functions, seems to be a simpler and less expensive solution. It probably doesn’t cost much, and besides, with certain skills, it’s easy to make it yourself - weld it from steel sheets, use an unnecessary metal container, for example, an old can, etc. Moreover, you can find examples of the use of old plastic canisters.
Open expansion tank
Does it make sense to spend money on purchasing a sealed expansion tank? It turns out that there is, since a closed heating system has many advantages:
- Complete tightness absolutely eliminates the process of evaporation of the coolant. This opens up the possibility of using, in addition to water, special antifreezes. The measure is more than necessary if the country house is not used constantly in the winter, but only occasionally, from time to time.
- In an open heating system, the expansion tank, as already mentioned, must be mounted at the highest point. Very often, an unheated attic becomes such a place. And this entails additional efforts to thermally insulate the container so that even in the most severe frosts the coolant in it does not freeze.
The expansion tank can be placed in an inconspicuous corner
And in a closed system, the expansion tank can be installed in almost any area. The most appropriate installation location is the return pipe directly in front of the boiler entrance - here the tank parts will be less exposed to temperature effects from the heated coolant. But this is by no means a dogma, and it can be mounted in such a way that it does not create interference or disharmonize its appearance with the interior of the room, if, say, the system uses a wall-mounted boiler installed in the hallway or in the kitchen.
- In an open expansion tank, the coolant is always in contact with the atmosphere. This leads to constant saturation of the liquid with dissolved air, which causes increased corrosion in the circuit pipes and radiators, and increased gas formation during the heating process. Aluminum radiators are especially intolerant of this.
- A closed heating system with forced circulation is less inert - it warms up much faster when starting up, and is much more sensitive to adjustments. Completely unjustified losses in the area of the open expansion tank are eliminated.
- The temperature difference in the supply and return pipes in the connection currents with the boiler is less than in an open system. This is important for the safety and longevity of heating equipment.
- A closed circuit with forced circulation to create circuits will require pipes of a smaller diameter - there is a benefit both in the cost of materials and in simplifying installation work.
- An open type expansion tank requires control to prevent overflow when filling, and to prevent the liquid level in it from falling below a critical level during operation. Of course, all this can be solved by installing additional devices, for example, float valves, overflow pipes, etc., but these are unnecessary complications. In a closed heating system, such problems do not arise.
- And finally, such a system is the most universal, as it is suitable for any type of battery and allows you to connect underfloor heating circuits, convectors, and heat curtains. In addition, if desired, you can organize hot heat supply by installing an indirect heating boiler into the system.
Of the serious shortcomings, only one can be mentioned. This is a requirement of the “safety group”, which includes control and measuring instruments (pressure gauge, thermometer), a safety valve and an automatic air vent. However, this is most likely not a disadvantage, but a technological cost that ensures the safe operation of the heating system.
In a word, the advantages of a closed system clearly outweigh, and spending on a special sealed expansion tank looks completely justified.
Circulation pump
The circulation pump ensures the operation of the closed heating system. Its power depends on many factors: the material and diameter of the pipes, the number and type of radiators, the presence of shut-off and thermostatic valves, the length of the pipes, the operating mode of the equipment, etc. In order not to go into the intricacies of calculating power, the circulation pump can be selected according to the table. Select the nearest larger value for the heated area or the planned thermal power of the system, and find the required characteristics in the corresponding line in the first columns.
You can select the parameters of the circulation pump from the table
In the second column we find the power (how much coolant it can pump in an hour), in the third - the pressure (system resistance) that it is able to overcome.
When choosing a circulation pump in a store, it is advisable not to save money. The entire system depends on its performance. Therefore, it is better not to save money and choose a trusted manufacturer. If you decide to buy unknown equipment, you need to somehow check it for noise levels. This indicator is especially critical if the heating unit is installed in a residential area.
Strapping scheme
As mentioned earlier, circulation pumps are installed mainly on the return pipeline. Previously, this requirement was mandatory, today it is only a wish. The materials used in production can withstand heating up to 90°C, but it’s still better not to take risks.
In systems that can also operate with natural circulation, during installation it is necessary to provide for the ability to remove or replace the pump without the need to drain the coolant, as well as for the possibility of operation without a pump. To do this, a bypass is installed - a workaround through which coolant can flow if necessary. The installation diagram of the circulation pump in this case is shown in the photo below.
Installation of a circulation pump with bypass
In closed systems with forced circulation, a bypass is not needed - without a pump it is inoperative. But two ball valves on both sides and a filter at the inlet are needed. Ball valves make it possible, if necessary, to remove the device for maintenance, repair or replacement. The dirt filter prevents clogging. Sometimes, as an additional element of reliability, a check valve is also installed between the filter and the ball valve, which will prevent the coolant from moving in the opposite direction.
Connection diagram (piping) of a circulation pump to a closed-type heating system
Why do you need pressure in a closed heating system?
Standard pressure values contribute to the efficient and smooth operation of the entire heating system.
It guarantees a high production coefficient and uniform distribution of the coolant through the pipes in all rooms.
The pressure level sets the water pressure speed parameter. The heat exchange process in the system, its intensity and its final efficiency directly depend on this.
Pressure stabilization reduces the rate of heat loss, and the liquid entering all elements of the heating system retains the same temperature as it received as a result of heating.
How does an expansion tank for closed heating work and how does it work?
The design of an expansion tank for a closed type system is not very complicated:
Diagram of the device and operation of a sealed expansion tank
Usually the entire structure is housed in a stamped steel body (item 1) of a cylindrical shape (there are tanks in the shape of a “tablet”). For production, high-quality metal with an anti-corrosion coating is used. The outside of the tank is covered with enamel. Products with a red body are used for heating. (There are blue tanks - but these are water batteries for the water supply system. They are not designed for elevated temperatures, and all their parts are subject to increased sanitary and hygienic requirements).
On one side of the tank there is a threaded pipe (item 2) for insertion into the heating system. Sometimes fittings are included in the package to facilitate installation work.
On the opposite side there is a nipple valve (item 3), which serves to pre-create the required pressure in the air chamber.
Inside, the entire cavity of the tank is divided by a membrane (item 6) into two chambers. On the side of the pipe there is a chamber for coolant (item 4), on the opposite side there is an air chamber (item 5)
The membrane is made of elastic material with a low diffusion rate. It is given a special shape, which ensures “orderly” deformation when the pressure in the chambers changes.
The principle of operation is simple.
- In the initial position, when the tank is connected to the system and filled with coolant, a certain volume of liquid enters the water chamber through the pipe. The pressure in the chambers is equalized, and this closed system acquires a static position.
- As the temperature rises, the volume of coolant in the heating system expands, accompanied by an increase in pressure. Excess fluid enters the expansion tank (red arrow), and its pressure bends the membrane (yellow arrow). In this case, the volume of the coolant chamber increases, and the air chamber correspondingly decreases, and the air pressure in it increases.
- As the temperature decreases and the total volume of the coolant decreases, excess pressure in the air chamber causes the membrane to move backward (green arrow), and the coolant moves back into the pipes of the heating system (blue arrow).
If the pressure in the heating system reaches a critical threshold, then the valve in the “safety group” should operate, which will release excess liquid. Some expansion tank models have their own safety valve.
Expansion tank on a special bracket
Different tank models may have their own design features. So, they can be non-separable or with the ability to replace the membrane (a special flange is provided for this). The kit may include brackets or clamps for mounting the tank on the wall, or it can be provided with stands - legs for placing it on the floor.
In addition, they may differ in the design of the membrane itself.
Differences in the design of expansion tanks with diaphragm (left) and balloon type membranes
On the left is an expansion tank with a membrane diaphragm (it has already been discussed above). As a rule, these are non-separable models. A balloon-type membrane (picture on the right), made of elastic material, is often used. In fact, it itself is a water chamber. As pressure increases, such a membrane stretches, increasing in volume. It is these tanks that are equipped with a collapsible flange, which allows you to independently replace the membrane in the event of its failure. But this does not change the basic principle of operation.
Air pressure in the expansion tank
The air or nitrogen pressure in the expansion tank will not be the same for different gas boilers; it all depends on the type of equipment and design features. The standards are indicated by the manufacturer in the product passport.
Typically, the pressure in a new damper tank is 1.5 atm. But this setting may not be suitable for a specific heating system. Factory settings are easy to reset. For these purposes, there is a special fitting in the expansion tank housing (for some manufacturers this is a spool valve for pumping), through which the air pressure is adjusted.
The nipple is located on the side of the air chamber of the cylinder. With its help you can release excess pressure or, conversely, pump up the tank
For the normal functioning of a gas boiler, it is necessary that the pressure in the membrane tank be 0.2 atm less than in the system itself. Otherwise, the heated water that has increased in volume will not be able to enter the container.
In small houses and apartments for closed heating systems, the pressure in the expansion tank is usually acceptable in the range of 0.8-1.0 bar (atm). But not less than 0.7 bar, since many gas boilers have protection and the device simply will not turn on.
The tank pressure level should be checked annually. If pressure surges are noticed in the heating system, it means that air has come out of the damper tank and needs to be pumped up.
Features of adjusting the hydraulic accumulator
Expansion tanks for water supply are sold with standard manufacturer settings - often the pressure in the air compartment is already set at 1.5 bar. The permissible pressure is always indicated on the label and the manufacturer does not recommend deviating from the specified parameters, especially in the direction of increasing it.
Before proceeding with the adjustment, the system is disconnected from the power supply and the shut-off valves are closed. The membrane tank is completely emptied by draining the water - an accurate pressure indicator can only be measured when the water compartment is empty.
Next, pressure readings are taken using an accurate pressure gauge. To do this, remove the decorative cap from the spool and bring the device. If the pressure differs from the required one, it is brought into compliance by pumping or bleeding excess air.
When adjusting the pressure in the gas compartment of the tank, the manufacturer fills it with an inert gas, for example, dry nitrogen. This prevents corrosion of the inner surface. Therefore, users are also recommended to use technical nitrogen to increase pressure.
Setting the tank pressure in the water supply system
The pressure in a closed tank is always set slightly lower (by 10%) than the pressure level when starting the pump. By adjusting the pressure in the device, you can adjust the water pressure. The lower the gas pressure in the hydraulic tank (but not less than 1 bar), the more water it will hold.
In this case, the pressure will become uneven - strong when the tank is full and increasingly weak when it is empty. To ensure a strong and even flow of water, set the pressure in the chamber with air or gas to within 1.5 bar.
Adjusting the hydraulic tank in the water heater trim
The expansion tank, which is used for hot water supply, should initially not contain water. The pressure in the device is set at a value that is 0.2 greater than the upper pump shutdown threshold. For example, if the relay is configured to turn off the equipment at a pressure of 4 bar, then the pressure in the gas compartment of the expansion tank should be set to 4.2 bar.
Installed in the water heater piping, the tank does not serve to maintain pressure. It is designed to compensate for expansion when water is heated. If you set the pressure in it to a lower value, then there will always be water in the tank.
Characteristics of closed expansion tanks
The main task of expansion tanks is to maintain pressure within specified limits.
Sealed metal containers are used, which contain a reserve of coolant in case of thermal compression of the liquid. This solves the problem of pipeline airing. If the coolant, expanding when heated, creates too much pressure, the hydraulic tank compensates for the difference.
Despite the apparent simplicity of the design, expansion tanks differ from each other, and different models have different operating parameters. Structurally, the following types of hydraulic tanks differ:
- Reservoirs providing for replacement of pears.
- Tanks with a permanently installed membrane.
- Containers that do not have a membrane in their design.
In the first case, the pear acts as a membrane. It is into it that air is pumped, which changes the volume of the working chamber with a thermal increase in the volume of liquid in the system. The air pressure in the expansion tank must be such as to squeeze water into the pipes when the temperature in the radiators drops.
Where to put it in the system
The expansion tank in a closed system is placed after the boiler before the pump, that is, so that it creates a flow in the opposite direction. This way the system works more reliably. So the specific installation location depends on where you have the circulation pump.
It is connected to the system via a tee. You cut a tee into the pipe, direct the perpendicular outlet upward, and screw the tank onto it. If the wall does not allow you to place a container, you will have to make an elbow, but the tank will be turned upward. Now we can assume that the expansion tank is installed.
But for the convenience of checking, it is advisable to install another tee after the tank, and install a shut-off valve on the free outlet of it. This makes it possible to check the membrane tank without draining the entire system - it cuts off the tank. Turn off the tap and bleed water from the boiler. Check the pressure on the disconnected branch (in the boiler). It must be zero. Afterwards, you can carry out all other setup work.
Expansion tank for closed heating: do-it-yourself installation
For a person who has skills in plumbing work, installing an expansion tank yourself will not be difficult. The principle of its insertion into the system is shown in the diagram:
Recommended scheme for inserting an expansion tank into a closed heating system
On the return pipe (item 1), in the area as close as possible to the entrance to the heating boiler (item 2), but usually in front of the circulation pump (item 3), a cut is made into which the tee (item 4) is packed. The installation method may be different - it all depends on the type of pipes used - metal, polypropylene or metal-plastic.
A ball valve (pos. 7) is packed onto the branch pipe (pos. 6) of the expansion tank itself (pos. 5). It is necessary to ensure the possibility of turning off the expansion tank in case of need for repair or maintenance work. For the same purposes, it makes sense to place a connection with a union nut - “American” (pos. 8) between the tap and the tank. In the operating position, the valve must be constantly open.
From the tap there is a connecting section of the pipe (item 9) to the tee. Its length and configuration (number of bends or turns) do not matter much - but it is usually done along the shortest and most convenient path from the location of the tank to the return pipe.
Now let's see what needs to be done on the tank itself.
Brief description of the operation performed
| The tank was taken out of its original packaging and the necessary tools and accessories were prepared for work. |
| If necessary, an adapter is packed onto the threaded pipe of the expansion tank. It is important to achieve extremely reliable sealing of the connections. It is best to pack tow using Unipack paste or using a special thread-sealing thread (cord) impregnated with a sealing compound (as shown in the figure).. |
| The adapter is tightened, and you can proceed to installing the tap. It is worth noting right away that in the example shown there was a flaw - the master did not install a detachable connection - “American” between the tap and the tank. That is, if it is necessary to dismantle the tank with the tap closed, this will be very difficult to do. A recommendation to all installers is not to forget about this point. |
| The thread is wound to wrap the tap,... |
| ... the tap is put in place and tightened tightly. You should immediately ensure that the “lamb” is in a position convenient for use after placing the tank on the wall. |
| A transition is mounted from the tap to a pipe of the required configuration, in accordance with the drawn up diagram of the general installation of the expansion tank. Essentially, this part of the work is finished. |
| Now you can check the pressure in the air chamber of the expansion tank. On its opposite side there is a nipple - almost exactly the same as on car wheels. In many models it is covered with a special plastic cap, which, if necessary, access to the valve is simply unscrewed. |
| You can check the pressure with a car pressure gauge. If it exceeds the values that were used when calculating the system, then it can be released to the required level by pressing the valve stem. If there is insufficient supply, you will have to pump it up - a car pump is quite suitable for this. |
| In the variant under consideration, the tank already has devices for its placement, even in two versions - legs for installation on a horizontal surface (blue arrows) and a mounting panel for hanging on the wall (yellow arrow). The tank is mounted in the chosen location, and then connected by a section of pipe to a tee embedded in the return line. At this point the installation can be considered complete. |
| Another version of the tank, on the body of which there are no structural elements for fastening at the installation site. But they are usually included as separate parts in the delivery kit. |
| Usually this is a bracket - a mounting pad for fastening to the wall, and a long screw band clamp. |
| The collar of the clamp is straightened and threaded through the slots of the mounting area. |
| All this is done in such a way that the protruding side of the tank falls into a special groove in the mounting platform (shown by arrows), and the clamp is higher than the side. |
| After installing the tank in the mounting area, the ends of the clamp are connected, first tightened by hand... |
| .. and then - all the way, using a screwdriver or wrench. |
| In this form, the tank will be ready to hang on the wall. |
| Installation of plumbing fittings to the cistern pipe is carried out in the same order as mentioned above. |
| The nipple can be located openly, only with a dustproof plastic cap. Checking the pressure and pumping, if necessary, is no different from the previously considered option. |
| By the way, tanks usually come from the factory with a preset pressure in the air chamber, and you can immediately select the required parameter. It is indicated on the packaging and in the technical documentation of the product. Further installation of the tank is carried out in the already known order - installation on the wall in the selected location and connection with a pipe with a tee. |
After final installation, be sure to open the tap and fill the system with coolant. If no leaks are detected in the connecting nodes, the installation of the expansion tank can be considered complete.
Step-by-step instruction. Different connection methods
Expanzomat is another name for an expansion membrane tank. It makes more sense if a specialist does the installation. If you decide to install it yourself, then in unclear moments, contact him and get advice. The tank can be installed both on the supply side of the line and on the return side.
Installation sequence and features:
- location of the expansion tank in space. In principle, as already mentioned, the tank can be positioned in any way you like. But from a rational point of view, the air chamber should be located at the top so as not to be affected by gravity. This will increase the already significant impact on the membrane from the coolant and air. Replacement or repair will be required after a shorter period of time than specified in the warranty;
- On the installed diagram of the heating system, select a place free from turbulence. This is usually the section of pipe in front of the recirculation pump. This is the best option;
- attach the tank to the wall and connect it to the system with a flexible hose.
It doesn’t matter where you place the tank: for supply or return, it is important that it is located at a minimum distance from the suction side of the centrifugal pump
Pressure in the heating expansion tank - how to calculate?
The initial pressure in the heating expansion tank is the second important parameter, along with the volume of the tank (the choice of volume was discussed in the previous article). At the factory, a pressure of 0.75 atm is created in the tanks. But this is not enough; you also need to take into account the conditions in which the tank will operate.
I won’t bore you with calculations here, but will immediately give you the main numbers. But first, I’ll explain why it’s important to know the initial pressure in the expansion tank. Here's why:
— after filling the system with coolant, the expansion tank itself must be filled by 25% (0.25 of the tank volume), under this condition there is another 75% of the tank volume that can be compressed, and, conversely, there is 25% of water that can leave the tank. This condition must be ensured by the initial pressure in the tank.
Why is the latter also important and what happens if the tank is completely empty? With any drop in temperature or slight leak of coolant, the pressure in the system immediately drops to zero. It is unacceptable!
Another extreme case is that the tank is completely full. If the temperature in the system rises further, the coolant has nowhere to go. The pressure will increase until either the relief valve trips or the system ruptures.
Therefore, it is necessary that when filling the system at room temperature, the pressure in it is set (usually 1.5 atm, since most wall-mounted boilers are designed for this to start working). If such pressure is not created, the wall-mounted boiler simply will not start. In general, at this initial system pressure, the tank should be 25% full.
In the future, when the coolant heats up and expands, in the expansion tank and, accordingly, in the entire system, the pressure should not exceed 3 atm.
If the volume in the tank “walks” from 20% to a certain value, but the pressure does not exceed 3 atm, then the system works well.
To fill the tank by 25% when initially filling the system, it is necessary that the initial pressure in the heating expansion tank be 80% of the pressure in the system that we will create. If at 20 degrees a pressure of 1.5 atm should be created in the system, then:
Initial Tank Pressure = 1.5 x 0.8 = 1.2 Bar.
I hope that in all this verbosity you have not missed the main point. Here it is: the pressure in the heating expansion tank before installing it (or before filling the system) should be 80% of the pressure at which the boiler starts.
Calculating pressure in two ways
Before you buy a tank, you need to calculate its volume. In practice, decisions are made in the following order:
- design. At this stage, a decision is made about which rooms will be heated and which will not, diagrams are drawn and the volume of the system in liters is calculated;
- boiler selection. Based on the volume of the system and the area of the heated premises, a heater is selected. For 15 liters of coolant, one kilowatt of heater power is required;
- determining the required volume of the expansion tank.
Now let's look at several different methods for calculating the pressure in the expansion tank of a sealed heating system.
Option #1.
For this we need the following quantities:
- system volume (OS);
- tank volume (VT);
- the maximum permissible value of the pressure gauge scale for a given system (DM);
- water expansion – 5%.
By the time you have to make calculations, you already know how many liters the system holds. The required volume of the tank is calculated by dividing the capacity of the circuit in liters by ten. Although this is an approximate calculation, it is very working.
There is another way to calculate the air pressure in the expansion tank of the heating system:
Air vent
Option #2.
It's good that we live in a world of fierce competition. To ensure that the client is satisfied with the purchase and does not have any problems with operation, boiler manufacturers indicate the required pressure of the heating expansion tank in the product data sheet. If for some reason this cannot be found out, then you can calculate this value, knowing what the pressure gauge readings should be in the operating mode of the system.
The latter can be found with one hundred percent probability in the technical documentation or on the boiler. Then 0.2-0.3 atmospheres should be subtracted from the working pressure. What is it for? If the pressure in the tank is greater than the working pressure in the system, the coolant will not be squeezed into the tank. He simply cannot do this, as an even greater force acts on him from the side of the tank. And if there is not enough air in the tank, then there will be difficulties with returning the coolant to the system.
Basic rules for heating a private home
Heating in a private home is a very complex and capacious concept. Therefore, the first rule is that the development of the system and its installation should be carried out only by professionals. You need to remember this and not engage in amateur performances.
Only a heating engineer with the necessary knowledge and practical experience is able to correctly and competently create a heating project, taking into account the architectural features of the building, the functional purpose of the premises, the requirements and wishes of the customer, and his financial capabilities.
If you need to order high-quality installation of engineering systems (heating, water supply), please contact DESIGN PRESTIGE by phone +7 , and we will install the system at a professional level in accordance with high quality standards.
Therefore, it is necessary to perform a thermal engineering calculation, calculate heat losses, select the equipment correctly, know the specifics and features of its use, select the installation location, and carry out the installation.
Only in this case will the heating system in a private house be as efficient and economical as possible, and the costs of its installation and maintenance will be minimal. The purpose of this article is to outline the basic parameters based on which a contractor can develop the optimal heating plan for a home. Rule two is “cheaper in bulk.” To save on heating installation, you need to contact companies that provide comprehensive services.
That is:
- draw up design documentation based on the requirements and wishes of the customer, architectural features of the building, functionality of individual rooms, operating mode, climatic and many other factors, performing thermal, hydraulic, thermal calculations, calculation of heat losses, establish the thermal load and determine many other parameters;
- select the optimal equipment configuration, install it, start up the heating system, check its performance with further warranty and post-warranty service;
- are engaged in the sale of everything necessary, and even better, they are dealers of manufacturers, this allows you to avoid additional trade markups, and the installation technicians thoroughly know the features of all models, even those that are not listed in the manufacturer’s technical documentation and identified during installation and operation.
Only with this approach will a heating system in a private house be installed quickly, at the lowest possible cost, without headaches for the person and work as efficiently as possible.
What pressure should be in the damper
An important characteristic of the hydraulic tank is the working volume of the device, proportional to P and not exceeding the discharge of network water, at the maximum permissible temperature conditions. Before determining what pressure should be in the expansion tank of the heating system, technical data of the heating system is collected.
Initial data for determining the operating parameters of the damper:
- Total volume of coolant, liter;
- water volume of pipes of the intra-house system, liter;
- battery volume, liter;
- boiler water volume, liter.
The resulting total volume is multiplied by the correction factor established for the specific liquid. In this way, they determine what pressure should be in the expansion tank of the heating system.
So for a pipe system with a volume of 100 liters you will need a hydraulic tank with the volume:
- for water coolant: 100x0.2 = 20 l;
- for antifreeze: 100x0.15 = 15 l.
The initial P in the hydraulic tank is set at the manufacturer - 0.75 atm, but this is not enough for trouble-free operation of the networks. The conditions of equipment manufacturers determine the maximum pressure at which it is permissible to operate a solid fuel boiler and auxiliary devices - no higher than 3 atm.
If the volume of coolant in the damper “walks” from 20% to 80%, despite the fact that P in the vessel = 3 atm, then this is considered a normal operating mode. Calculation of the pressure in the expansion tank of a gas boiler depends on the actual indicator in the pipes. If P = 1.4 atm, then the damper should be filled at a coolant temperature of 18-20 C:
Damper P = 1.4 × 0.8 = 1.12 atmospheres.
This will be the operating parameter for the hydraulic tank, which will ensure trouble-free operation when starting the heating of the house.
Malfunctions of expansion tanks
Checking the pressure of the expansion tank is included in the list of annual maintenance procedures and if it is followed there will be no problems, but if neglected it can give the owner unpleasant surprises:
- the pressure in the air chamber gradually decreases and with each refill of the boiler the tank fills more and more with water and gradually ceases to perform its function. In this case, the membrane is so pressed against the wall of the air part of the tank that it can be damaged by the valve spool and the tank will have to be replaced.
- The heating circuit pressure is at the permissible limit, the expansion tank has not been serviced - there is no pressure in it. When the heating system cools down, the volume of liquid decreases, the pressure drop is not compensated for by anything - the boiler stops due to an emergency. This situation can arise, for example, when the boiler operates for a long time in DHW mode or when there is a power outage.
- the owner of the boiler often has to top up the boiler for no apparent reason, for example, while hot water is being used - the pressure on the pressure gauge drops and the boiler stops by mistake - the owner tops up. Since thermal expansion is not compensated by anything, with further heating of the coolant, excess pressure is released through the safety valve. Some users set the reset and simply do not notice this situation. Frequently refilling the boiler with untreated water is detrimental to the heat exchanger!
Advantages and disadvantages
Closed expansion tanks have a number of advantages over open ones:
- Closed analogues do not necessarily need to be installed in the attic; they can be installed near the boiler itself. And open ones must be installed at the highest point of the system.
- In closed tanks, water does not have access to contact with air, which means that oxygen will not dissolve in the water and interfere with the movement of the coolant.
- Most people have converted the attics of their homes into living spaces, so using closed tanks saves space as they can be installed anywhere.
The disadvantages of closed tanks are as follows:
- High price.
- It is necessary to pump air into the device from time to time.
The procedure for setting pressure - what it should be and how to set it
The coolant pressure in the heating system tank is an adjustable parameter. You can perform all setup steps yourself.
To do this you need:
- Make calculations and understand what pressure should be in the expansion tank. It should be made 0.2 atmospheres less than in the heating system.
- This indicator is set before placing the container by releasing air or pumping it in through a nipple. But first you need to know how to pump up the heating expansion tank correctly.
- The container is connected to the pipeline and the system is filled with water, doing it slowly, observing the pressure indicators. The liquid is pumped until the pressure levels are equal.
- Then connect the pump and continue to pump liquid until the pressure in the tank reaches the operating values, which are calculated before installing the network. As a result, a reserve volume of coolant will enter the housing.
- The system must be started at maximum temperature, and then the volume of the working medium increases by the specific increment. This ensures that water enters the device, the volume of which is equal to the capacity of the tank. As a result, the pressure reaches maximum values.
To know what the pressure should be in the expansion tank of a double-circuit boiler, you should look at the instructions for it. You can set all parameters yourself using a pressure gauge and a car compressor.
Control methods
You can control the pressure in the system using a sensor
For monitoring, water pressure sensors are installed in the heating system. These are pressure gauges with a Bredan tube, which is a measuring device with a scale and pointer. It shows excess pressure. It is installed at control nodes defined by regulatory documents. Using a heating system pressure sensor, you can determine not only a quantitative indicator, but also areas with possible leaks and other problems.
The flow of the working medium does not pass directly through the pressure gauge, since the measuring device is installed using three-way valves. They allow you to purge the pressure gauge or reset the readings. This tap also allows you to replace the pressure gauge with simple manipulations.
Pressure gauges are installed before and after elements that can affect pressure losses and pressure increases in the heating system. It can also be used to determine the serviceability of a particular unit.