Home |Blocks and floors |Wall blocks with cladding and insulation for construction
Date: October 25, 2018
Comments: 0
Increasingly, residents of the private sector are faced with the question: how best to insulate their home? They know from their own experience how damp and uncomfortable it is in a cold room.
Traditionally, during the construction and thermal insulation of buildings, insulation was carried out in three stages:
- a main wall was erected;
- insulation was installed;
- exterior finishing was carried out.
It was important to choose the right characteristics of the heat-protective composition. A frivolous attitude to solving this problem led to significant heat losses, and, consequently, an increase in the cost of heating the house. For developers, this was a serious problem, which was solved by modern material - blocks with cladding and insulation. They harmoniously combine a power array, a heat-insulating gasket and decorative finishing. More recently, builders dreamed of such a product, but today the dream has become a reality.
Would you like to learn in detail what veneer composites are? Let's consider the structure, characteristics, properties, scope of application of this promising building composite.
Manufacturers offer new materials that simplify the process of building an insulated house
Practical thermal blocks
Thanks to the layer-by-layer organization of products, the properties and performance indicators of the product are formed. Thermal insulation building blocks consist of several layers:
- load-bearing made of expanded clay concrete;
- internal made of polystyrene foam;
- monolithic from concrete-sand mixture.
Each layer is connected using basalt-plastic or reinforcing bars, which makes insulated blocks for construction the most popular in the building materials market.
Slag and ash are also raw materials for products that reduce the cost of producing goods. Prices for insulated blocks for building a house are determined by the method and features of their production.
When building from ergonomic materials, it should be noted that there are significant savings in material resources due to the optimization of labor costs. Since the warmest blocks for building a house involve laying them in one row.
Area of use
Modular composites are widely used in the construction of small buildings where it is important to provide effective thermal insulation, quickly complete the work and achieve savings. At the same time, blocks are in demand for the construction of multi-story buildings. It is not advisable to use them for main walls and load-bearing structures.
Three-layer composites are used for frame construction of a house. The main forces are absorbed by the frame, and a wall of modular elements is erected nearby. Due to the fact that walls made of sandwich blocks have a smaller width than brickwork, the interior space of the room increases with the same external contour.
General device
Three-layer modular elements are a universal material used for insulation. Let's look at how the product works:
- The basis of the structure is a load-bearing strength layer, usually made of expanded clay-filled porous concrete.
- The thermal insulation layer is made of high-quality compounds intended for thermal insulation.
- Textured textured concrete is the base for decorative finishing, having a thickness of 20-30 mm. The facade surfaces of the composites are different - they imitate the texture of stone and differ in color.
Such material is necessary for the construction of a building with high strength, increased thermal insulation coefficient, and attractive appearance.
Let us consider in detail what compositions can be used for a three-layer module.
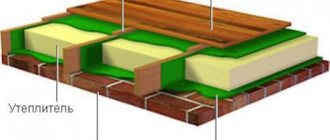
Heat block design
The usual dimensions of warm blocks (thermally efficient wall blocks) are shown in the figure. With a total width of 300 - 400 mm, the thickness of the layers can be different. The inner concrete layer is the widest, 120 - 200 mm, and has the greatest impact on the strength of the wall.
The outer layer is narrower, finishing, can be painted, and equipped with a relief, textured surface.
The insulation is most often foamed polystyrene foam (EPS), and the more expensive extruded polystyrene foam XPS is also less common. The thickness of the insulation varies between 100 - 160 mm.
To connect the layers, plastic anchors are most often used in addition to glue. Or the strength of the connection of the layers is increased due to the comb shape of the connection, which prevents tensile forces.
Power section
It absorbs the main forces and is made of the following materials:
- concrete with expanded clay filler;
- gas-filled composition;
- foamed concrete;
- a composite to which perlite, polystyrene, and slag are added;
- clay massif.
The load-bearing part absorbs significant loads and has high strength.
Such materials have a three-layer structure: the thickest load-bearing layer, an internal heat-efficient layer and a protective decorative layer.
Thermal insulation layer
It is the central layer of the module, located between the façade cladding and the force-receiving layer. Manufacturers use various compositions for thermal insulation. Possible use:
- Foam plastic – has increased density, increased thermal insulation properties and has an affordable price.
- Dense mineral wool.
- Polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam are cellular varieties of gas-filled plastic.
Facade part
The outer layer is a decorative cladding that protects the insulation from the effects of precipitation, wind and ultraviolet radiation. The retail chain offers many options for wall blocks with decorative finishes that provide an attractive and aesthetically pleasing appearance to the facade of your building.
The following are used as decorative layers:
- polypropylene and polyvinyl chloride;
- glass fiber reinforced concrete;
The total thickness of the multilayer block can be 30-350 mm
- decorated plastic;
- wood fiber panels;
- architectural concrete;
- acrylic resin.
The use of special dyes allows the finished product to imitate the texture of natural stone or brick. Such coatings are popular among developers.
Technical characteristics of warm blocks
The dimensional error in the manufacture of blocks is often no more than 2 mm. This allows you to lay blocks on a thin layer of glue - 3 - 5 mm. If the dimensional accuracy of the blocks is more than 2 mm, then the masonry is made using ordinary cement-sand mortar with a joint thickness of 10 mm.
An important characteristic of heat blocks is the resistance to heat transfer of the finished wall. First of all, it will depend on the thickness of the insulation layer. And also from his appearance.
Polystyrene foam is “colder” than extruded polystyrene foam. In addition, the foam can be moistened. At the same time, it significantly increases its thermal conductivity. While extruded polystyrene foam does not absorb water and does not change its thermal conductivity when the wall is saturated with moisture.
Heat transfer resistance
The table provides information about the heat transfer resistance of heat blocks depending on the insulation material, layer thickness, and humidity.
For blocks in the wall, the maximum humidity value should be taken.
Heat blocks, even with a small thickness of extruded polystyrene foam (XPS), have satisfactory heat transfer resistance for many regions according to SNiP.
Before choosing a heat block, you need to find out more precisely what heat transfer resistance should be at the walls of a house in a specific climate zone according to the standards.
The wall design itself practically does not increase thermal conductivity. The coefficient of thermal heterogeneity of a wall made of this material when laid on glue with thermal break of seams on foam plastic is 0.92. The thermal insulation characteristics of the wall will depend mainly on the correctness of the masonry; it is necessary to prevent cold bridges.
Strength of heat blocks and walls made from them
The strength characteristics of warm blocks are the most important. In a conventional three-layer wall, only the inner layer is the load-bearing layer. And the outer one creates façade finishing and protection for the insulation; it does not take the load from the overlying structures. How three-layer walls are insulated and finished
In a wall made of three-layer warm blocks (thermal block, polyblock, porcelain stoneware, thermal...) both the inner and outer layers are load-bearing.
Characteristics of thermal insulation composites
Three-layer blocks have a number of advantages compared to traditional materials used for construction:
- a significant reduction in financial and labor costs compared to the construction of a brick building and the subsequent application of additional thermal insulation composition;
- reducing the time required for construction activities, since masonry, façade insulation, and exterior finishing are carried out simultaneously. The increased dimensions compared to brick allow the construction time of walls to be halved;
- increased thermal insulation characteristics due to the fact that buildings made of three-layer composites do not require special thermal insulation;
As a rule, the role of the supporting layer is played by porous expanded clay concrete, and dense concrete is used as the front layer, and you can choose colored or textured one that imitates natural material
- improved sound insulation provides effective noise suppression, which contributes to the acoustic comfort of the room;
- increased strength of structures due to reliable connection of element layers using steel reinforcement;
- increased degree of protection against moisture;
- aesthetics, since wall blocks with insulation and a decorative layer imitate various textures - marble, wood, natural stone or brick;
- high fire resistance;
- resistance to fungal formations, putrefactive deposits.
Advantages of single-layer walls made of Porotherm 44 and 51
● Cheap - if you take materials of comparable quality, then a single-layer wall is cheaper than multi-layer ones. Of course, the larger the blocks, the more expensive they are (per piece). But it takes much more money to purchase high-quality insulation than to buy a large block.
● Fast - a square meter of a wall made of Porotherm 44 blocks is erected on average in an hour, and a square meter of a multilayer structure (blocks + insulation + brick cladding) is built in about 3 hours.
● Angry - a joke. Single-layer structures are less susceptible to moisture. For example, deformation of mineral wool or expanded polystyrene leads to moisture entering the blocks. This is a sure path to loss of strength. You will have to dismantle the cladding and replace the insulation. On a single-layer wall, it is enough to apply a leveling layer of plaster.
Warmth not only in the blocks, but also between them
An important feature for creating a masonry of Porotherm blocks is the use of a heat-saving mortar. It is applied only to horizontal seams, while filling the vertical spaces between the blocks with mortar is completely eliminated. The design of the block provides vertical grooves-ridges. They fit into each other like a puzzle, so over-plastering the mortar will result in heat loss.
Don't worry that all the solution will settle into the voids and the blocks won't stick together. This is wrong. It is to avoid this that a warm solution is prepared: heated water (but not boiling water) is poured into the dry mixture. Warm solution has a lighter texture and improved binding properties.
Particularly sized ceramic blocks are built on a thin layer of glue or adhesive foam.
The heat-saving properties of Porotherm ceramic blocks are reduced if you use conventional cement-sand mortar. During the hardening process, horizontal cold bridges are formed, which allow most of the heat to pass out.
An additional method of insulation is to minimize additional elements
Elements of Porotherm blocks that require vertical filling with mortar are considered additional components. This can be the junction of corners, bends of walls and partitions. That is, where the ribbed surface of one block meets the flat side of another.
Vertical laying of the solution brings additional heat loss. Therefore, it is important to reduce the number of additional elements to a minimum. To do this, it is important to comply with the dimensions of the house, calculated according to the drawings and projects. The area and length of the walls of houses made from Porotherm blocks are specially planned so that only whole elements fit in one wall. Additional parts remain only in the corners of the building.
Definition of need
Calculation of the amount of materials required for thermal insulation and construction of walls is simple and is carried out using the following algorithm:
- count the total length of the walls and partitions of the building;
- multiply the figure by the height of the future ceiling;
- divide the resulting value by the area of the multilayer composite.
The need for materials is easy to determine. Using blocks with insulation and cladding, the process of constructing thermal insulation of buildings will turn into simple activities that do not require professional skills.
Types of insulation
Mineral wool: type - rigid slabs. Choose a density of 125 kg/m3 or more.
The technology is to stick it on the blocks using a special glue and apply a thin layer of vapor-permeable plaster.
Mineral wool: type - flexible slabs. Suitable for insulating ceramic blocks with a density of 45-80 kg/m3.
Technology - place flexible mineral wool between the facade sheathing, cover with a breathable membrane and attach with dowels. Cover with facing material: brick, siding, tiles or decorative stone.
Aerated concrete slabs with a density of 100-200 kg/m3.
Technology - glue the slabs onto Porotherm blocks, placing them on a load-bearing base - the foundation. Plaster or cover with facing bricks.
Ceramic brick is self-supporting; it also rests on the foundation. It is important to leave gaps between the insulation boards and the brick wall. This promotes improved ventilation. This is how the wall becomes three-layered.
The main criterion for choosing insulation is the durability of the material. High-quality mineral wool from well-known manufacturers will last 35 years or more, and aerated concrete slabs - 50 years. The higher the density of mineral wool, the longer its service life will be. Over time, the material begins to settle and become thinner. Therefore, mineral wool with a density below 45 kg/m3 will last less than 25 years.
Aerated concrete slabs are foamed stone. In the absence of waterlogging of the material, its durability is comparable to that of brick and dense concrete.
Decorative layer
The final outer layer on the front surface is decorative. The variety of design options for the outside of a multilayer block allows you to decorate walls in various styles, creating your own unique compositions that are in harmony with the overall architectural design. The thickness of this layer usually does not exceed 3 cm.
In addition to a purely aesthetic function, external finishing allows you to protect the inner layer from mechanical damage, thereby significantly increasing the service life of the entire building. The front side can be multi-colored or textured, and also imitate noble natural materials - such as granite, marble and others.
We build houses from thermal blocks
Do you want to build a stone house cheaply and immediately with exterior decoration in the style of an ancient castle or a modern stone cottage?
Then choose a heat block. This is the case when cheap means warm, reliable, fast, and beautiful! The heat block is also called teplosten, warm block, polyblock, three-layer block, four-layer block.
Our task is to offer the best balance of strength, thermal insulation and wall thickness at low construction costs.
What is a heat block?
This is a multilayer block, the load-bearing basis of which is an expanded clay concrete block. Then there is a layer of insulation that does not absorb moisture. And the third facing concrete layer is 5-8 cm thick. All three layers are molded into a single block, the layers of which are connected inside by basalt rods.
This turns out to be what all builders strive for. Namely:
- create a strong stone wall;
- create a warm, frost-free wall;
- create a strong and durable external wall covering that is not subject to atmospheric and physical influences;
- simplify the process of laying walls;
- and at the same time reduce the cost of stone construction.
Reference. Inventors of building blocks usually seek to increase the thermal resistance of walls by adding air to the block in pores or voids, or materials with low thermal conductivity.
This is how expanded clay concrete blocks, arbolite blocks, expanded polystyrene concrete blocks and even warm ceramics turned out. At the same time, the exterior finishing and insulation of the blocks remained a separate stage of construction and a significant cost item in the estimate.
Monolithic concrete construction with permanent formwork solved the problem of strength and insulation in one process, but still requires the next stage of expensive exterior finishing.
And only the heat block solves all problems at once in one stage of wall laying.
Differences between heat blocks
1. By size and thickness of layers
- In a block measuring 400x200x400 mm (thickness/height/length), the expanded clay concrete layer (sometimes sand concrete layer) has a thickness of 160-190 mm, which is enough for the construction of mansions up to 3 floors. The insulation has a thickness from 130 to 160 mm. Outer concrete layer up to 80 mm thick.
- In a block measuring 300x200x400, the thickness of the expanded clay concrete layer is 130-160 mm, which is enough for the construction of cottages up to 2 floors. The insulation has a thickness from 100 to 140 mm. Outer concrete layer with a thickness of 50 to 80 mm.
- Some manufacturers began to produce a block measuring 230x200x400 mm for light one-story buildings such as a guest house, garage or bathhouse. The thickness of the expanded clay concrete layer is 80-100 mm. The insulation has a thickness of about 80 mm. The outer concrete layer is no more than 50-80 mm thick.
- The length of the heat blocks is a multiple of 400 and 200 mm. They can be cut or sawed to size if needed.
2. There are 2 types of blocks based on external cladding and color
- Blocks with a ready-made reinforced facing layer, painted to a depth of 2-3 cm. I.e. out of 8 cm of concrete facing layer, 2-3 cm are made of reinforced concrete. The decor can be ordered for different types of stone and brick. Any colors, because... painting is done in production. Sometimes body-colored silica granite is used.
- blocks with a concrete facing layer are intended for painting or hydrophobization. The block color is grey. The decor can be ordered for different types of stone and brick. Any façade paints for concrete can be used. Apply with a roller or spray gun. The service life of the paint is at least 20 years. If you want to leave the façade gray, it is recommended to coat the blocks with a conventional water-soluble water repellent to increase weather resistance and improve the properties of the facing layer. Polymer-silicate water repellent with work costs from 50 rubles. per m² of wall and lasts from 10 years.
3. By type of insulation
- In the production of a heat block, granules of high-quality polystyrene foam (density not lower than 25) are usually used, which is pressed between two concrete layers. Thus, in the masonry, polystyrene foam is located in a completely sealed concrete box and does not absorb moisture or steam, therefore cannot be exposed to any atmospheric influences and is absolutely harmless and safe even in the event of a fire. Under such conditions, the service life of modern polystyrene foam exceeds 50 years (longer studies have not been conducted).
- If you want to replace polystyrene foam with a more advanced insulation material, then use extruded polystyrene foam (EPS), which is better in all respects.
4. According to the constructive applicability of the blocks
Thermal blocks are intended only for the construction of walls. Since the walls of a house have window and door openings, internal and external corners, the manufacturer produces special blocks for these applications.
The ceilings of the first floor are mounted on the load-bearing concrete part of the block and covered with an additional two-layer block (insulation + facing part).
How are the warm properties of the wall preserved when laying heat blocks?
The blocks are laid in a checkerboard pattern. The masonry mixture is placed only on the concrete parts of the block in a horizontal and vertical seam. A thin layer of masonry adhesive can be applied to the vertical seam. Polyurethane foam should be applied to the insulation layer.
This creates a gap in the cold bridge that forms in the seams of any masonry. Some builders, violating technology, fill the entire joint with warm masonry mixture to simplify the masonry process. But a warm mixture, for example, perlite, is only 15-25% warmer than usual. This is not at all enough to eliminate cold bridges in the seams between blocks. Such seams become conductors not only of cold, but also of moisture.
Why do we recommend thermal blocks for construction?
The advantages of houses made of thermal blocks (thermal walls) are enormous for the construction of country houses, dachas, cottages, garages:
- The lowest cost of walls is in stone construction, when both the load-bearing and facing parts are stone.
- The high structural strength of the expanded clay concrete layer of the block and the absence of shrinkage make it possible to use blocks with a thickness of 160-190 mm and not worry about the reliability of a structure up to 3 floors high.
- Improved thermal insulation characteristics compared to conventional blocks provide savings on heating costs, since the thermal resistance exceeds the required building standards.
- The size, weight and geometry of thermal blocks speed up the construction process compared to brick and make it more technologically advanced and simpler.
- The concrete part of the blocks consists of cement, sand and expanded clay. High quality polystyrene foam insulation, enclosed in a sealed concrete box, is not accessible to ultraviolet radiation, air, or heat. All components of the block in the wall do not emit anything into the air even when heated. They don't rot. They don't burn. Absolutely non-toxic and safe for people and the environment.
- The rough cement-porous surface of the blocks is absolutely suitable for further interior wall finishing and plastering.
- The use of blocks for load-bearing walls with a thickness of 400 mm and especially 300 mm significantly increases the internal usable area of the house. Compared to a brick wall (1.5 bricks 380 mm + insulation 100 mm + air gap + face brick 120 mm) with a thickness of 640 mm, a wall made of 400 mm thermal blocks will be 230 mm thinner. For a house 10*10 m in two full floors, an additional area of more than 18 m² arises. And this is an entire bedroom or living room.
- The heat blocks are bulletproof.
- It is easy to apply any fastening elements that can withstand heavy loads to the block.
- The heat block uses multi-layer wall technology, when a non-moisture-absorbing insulation is placed between the outer facing layer and the load-bearing wall. High water absorption and vapor permeability are harmful to load-bearing walls if they are not protected from moisture, vapor permeation and freezing. There is no such problem in the heat block, because The dew point (the temperature of moisture condensation from saturated steam on the surface) is removed from the load-bearing concrete layer of the wall into the insulation. Therefore, the frost resistance of the blocks and the service life of the walls are greatly increased.
The basis
The thickest part of the heat block is the load-bearing part. It is usually based on expanded clay concrete, polystyrene concrete and other types of lightweight concrete. The main filler in lightweight concrete is porous materials with small cells and voids. This feature of the filler allows the production of a load-bearing part with different density and volumetric mass options. This is an advantageous building material with reduced material consumption and significantly reduces the cost of the finished block.
In addition, the low density ensures low weight of the finished blocks. These factors greatly facilitate the process of transportation, laying walls and increase the speed of construction of the finished building.
Walls built from such lightweight blocks are comfortable, safe from an environmental point of view and provide a high level of sound insulation.
Types of external insulation of buildings
Since multilayer blocks have not yet taken root in the construction market, most specialists and home craftsmen use traditional materials when insulating a house from aerated block or brick. And in most cases, the building is insulated from the outside, even if you insulate the loggia. One way or another, any type of such thermal insulation implies the same three layers that are present in the facade multilayer block.
Let's look at the most popular types of facade insulation.
- Creation of a plaster facade or wet type of insulation. It involves the creation of a multilayer structure on the outside of the building.
- Using dowels, we attach thermal insulation to the load-bearing partition, for example Technoblock Standard insulation or Euroblock insulation.
We apply finishing material to the reinforced insulation layer
- Next, we reinforce the surface with fiberglass mesh.
- Apply the finishing material in one or two layers.
Advice! Most often, plaster is used as a finish, which should be applied in two layers: first we lay the starting layer, and after it dries, the finishing layer should be laid.
- After finishing, the surface is covered with special facade paint.
- Well masonry (another name is “three-layer system”). The wall is erected in two layers: load-bearing, after which a small gap is left and a half-brick layer is laid out. In the gap, ecowool insulation (spray foam, etc.) should be placed.
Insulation of well brickwork - photo
- Ventilated facade. The design assumes the presence of a sheathing, which is made of metal or wood. Insulation is placed in the sheathing, and facing material (most often siding) is mounted on top.
Advice! Wooden sheathing beams must be treated with protective compounds.
Schematic representation of a ventilated facade using metal profiles.
Product sizes
The blocks for thermal insulation of your building and decorative finishing of the facade are standardized and have the following dimensions:
- Length 40 cm.
- Width 25–40 cm (the most popular products are 30 cm wide).
- Height 20 cm.
The products do not differ in increased dimensions, which makes installation easier. The composite does not create increased forces on the base of the building. Laying is carried out in the same way as installing bricks.
Laying a wall from multilayer building blocks
Painting walls made of heat blocks
Before you start painting the walls, you need to treat the seams with sealant, we already talked about this a little higher. The sealant will provide effective waterproofing and also serve as part of the decorative finish.
When the walls of the house are erected, all that remains is to paint them. The appearance of the house is limited only by your imagination.
Thermal blocks do not require cladding; after construction they can simply be painted. Painting external walls occurs in stages:
- First the walls are primed. The primer is needed to improve adhesion (adhesion of the paint element to the wall). For example, VERNOV VD-AK-0110 deep penetration primer is quite suitable.
- then you can start painting. You can choose any color - pastel colors, shades of beige and peach look good on heat blocks. For example, you can use facade acrylic paint on a water-dispersion basis VERNOV VD-AK-103.
- Many owners of thermal block houses paint corner blocks in contrasting colors to create the illusion of complex geometry and a more interesting look.
An example of a finished house made of heat blocks
We talked about the stages of building houses from thermal blocks, the features of laying thermal blocks and the basic rules that must be followed during construction. Let's summarize:
- When laying heat blocks on glue or cement mortar, try to ensure that the binder does not get on areas with foam plastic.
- The foam joints are foamed with polyurethane foam.
- Every 2 or 3 rows of masonry heat blocks you need to lay a reinforcing mesh.
- When constructing buildings higher than one floor, it is recommended to install a monolithic reinforcing belt.
- Iron lintel corners for openings are preferable to other types of lintels.
Laying heat blocks:
Features of masonry
It is recommended to use special solutions for laying such blocks . Since there will be no insulation in the future, it is better to use compounds with thermal insulation characteristics. They can also use reinforcing additives.
It is better if the stone is produced with a tongue-and-groove fastening, then the connection of two adjacent expanded clay blocks is simplified.
Since the facade block is the only material and nothing is used after it, it is important to maintain the exact evenness of the masonry . To do this, be sure to pull the string, plumb line, and after laying each stone, check the evenness with a building level. A laser level will provide the greatest accuracy.
At the end of the laying, it is necessary to check all the stones for cleanliness. It is possible that during the work some of the solution got onto the front side, which will spoil the appearance. To eliminate errors, it is better to immediately remove excess glue.
Ventilated facade
Another method of external insulation, although practically not used in cottages, is the installation of a system of ventilated curtain walls . This technology is called dry. It involves a ventilated air layer between the insulation and the cladding. Insulation (mineral wool slabs) is attached to load-bearing walls using dowels or anchors. A small gap is left between the insulation and the cladding due to the supporting profiles (15-60 mm) and a decorative layer of metal, plastic, or cement-sand coating is installed.
Construction of a system of ventilated curtain facades
Due to the air gap, moisture is removed and does not accumulate in the insulation. This eliminates the problem of cold bridges. Ventilated facades can be installed at any time of the year, since the technology does not involve wet processes.
Ventilated curtain facade system
The main thing is that the materials used for insulation are not only durable, but also resistant to wind loads, otherwise the insulation will change geometry and collapse. If you manage to choose the right insulation system for your home, in the future you will save on heating the premises, and also protect your home from dampness and drafts.
These articles may also be of interest to you:
- Multilayer blocks. Insulation and finishing of the facade
- Installation of facade blocks
- Can vertical gardening of the facade harm the house?
- Insulation of external walls with mineral wool. Step-by-step instruction
A little about quality
There are no problems with building a house from polystyrene concrete blocks - this is a common building material. To determine the quality of products, you must remember:
- High-quality products are equipped with a certificate that lists the characteristics of the material.
- The choice of product brand depends on the type of structure (residential building or outbuilding). The standard size of a regular PSB block is 188x300x588, a large one is 380x300x588 mm.
Low-quality polystyrene concrete blocks break with one blow Source beton-house.com
- The durable PSB block can withstand a fall from a height of 3-4 m or several blows with a sledgehammer.
- The granules on the cut of the material are clearly distinguishable, have the same size and are evenly spaced, adjacent to each other.
- The material must not have voids.
Production methods
Polystyrene concrete products are produced in two ways:
- Handicraft (foundry). Popular among home craftsmen due to the availability of components and simple technology. The process is reminiscent of the production of non-autoclaved aerated concrete - the necessary components are mixed, the mixture is poured into molds and kept there until hardening (3-7 days). Injection molding technology is unprofitable in production (many labor-intensive operations for preparing and servicing molds).
- Vibrocompression (vibroforming). In industrial production, the mixture is mixed more concentrated (more cement, less water). It is loaded into molds and sent to a vibropress, where it is kept until semi-dry. When stripping, blocks with a clear geometry are obtained, which are then sent for final drying.
Polystyrene concrete with different densities is obtained by changing the ratio of components and the type of polystyrene granules (the larger the diameter of the polymer balls, the lower the specific gravity and strength of the material).
Pouring polystyrene concrete into molds Source beton-house.com
Disadvantages of homemade blocks
The presence of a concrete mixer and molds allows you to set up home production of PSB blocks. There are several comments regarding such products:
- Homemade production reduces the construction budget, but stretches the time.
- It is unknown what parameters the blocks will have, since the production process is poorly controlled.
- Homemade products will have low density.
- Inaccurate dosing will result in blocks that vary in quality.
- The products will have poor geometry, which will increase material consumption during laying.
The quality of the blocks will inevitably affect the quality of construction and durability of the house.
Polystyrene concrete: getting to know the material
Polystyrene concrete is a composite (complex in composition) material belonging to the class of lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete has a reduced density, which allows solving several construction problems:
- reduce the weight of the building;
- increase its thermal insulation characteristics;
- reduce the cost of construction (by reducing labor costs and increasing the productivity of builders).
For the production of polystyrene concrete the following is used:
- Portland cement (a type of cement);
- water;
- polystyrene, filler in the form of granules of various fractions with heat-insulating properties (polystyrene is a polymer with a wide range of uses);
- quartz sand;
- plasticizers - various additives (for example, resin) that improve the plasticity of the mixture; Thanks to this, the blocks do not crack during hardening and drying.
Polymer granules (very similar to foam balls) create the lightweight structure of polystyrene concrete. The low density of foam and aerated concrete is ensured by air pores resulting from a chemical reaction.
Polystyrene granules Source archidea.com.ua
Why does foam plastic need to be insulated?
Well, first of all, because you are unlikely to find something more effective. Polystyrene foam does not shrink, does not deform, does not absorb water - what, it would seem, could be better?
Plus, polystyrene foam is now produced in such interesting versions that you can insulate a facade with it without additional finishing.
PHOTO: tiu.ru Take, for example, foam boards covered with ceramic tiles - these are thermal panels that look like brickwork from the outside
Composition and classification
Certain components are added to the solution for making blocks:
- slag or Portland cement;
- water;
- additives that promote rapid hardening and the inclusion of air bubbles;
- polystyrene Its granules reduce the thermal conductivity value of blocks;
- quartz sand.
Factories for the production of polystyrene concrete blocks must produce material that fully meets the parameters of state standards.
In the final version, the blocks differ in the following sizes:
| options | size, mm |
| length | 288 — 598 |
| height | 88 — 298 |
| thickness | 195 — 300 |
The most popular are:
| block name | parameters, mm | weight, kg |
| wall | 588 x 300 x 188 or 588 x 380 x 300 | 5 – 30 |
| septal | 588 x 600 x 92 | 5 – 15 |
| jumper | 380 x 300 x 1300 |