It’s not for nothing that they say that the most important thing is the weather in the house. Or rather the microclimate. After all, no one wants to spend extra money on heating, freeze, or fight mold and mildew in the house. Therefore, you need to correctly select the insulation and its characteristics. Today we are talking about the density of mineral wool for wall insulation.
In general, mineral wool, or simply mineral wool, has several varieties. The most popular type of insulation is basalt. They are often perceived as synonyms. I don't see anything terrible in this.
The material received different ratings from consumers. It also happens that a person carries out insulation himself. But eventually the wall begins to collapse, or the room is still cold. Because of this, a person thinks that the reason is the low quality of mineral wool, as well as its unsuitability for use.
Such situations cannot be called rare. Moreover, the reason is usually not that the laying technology was violated, or the wall was not properly prepared. The issue is precisely the incorrect choice of characteristics. We are talking about density and thickness.
Density options
Basalt wool is used for insulation of private houses. It is widespread due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and easy installation. It is made from gabbro-basalt rocks by drawing out thin threads.
Fibers obtained during hot production are laid out in a chaotic manner and pressed. Thanks to this arrangement, basalt wool retains heat well.
When insulating ventilated facades, mineral insulation of varying densities and thicknesses is used. To obtain products of different densities, manufacturers adjust the compaction density of the strips. They are then cut into the required sizes. In construction stores you can find mineral insulation materials with a density of 35 to 200 kg/m3.
Features and benefits
Mineral wool is a fibrous slab with dimensions of 60x120 and 50x100 cm. The thickness of the products is 5, 10 and 15 cm. Ten-centimeter slabs are the most in demand. This thickness is sufficient for using the material in harsh climatic conditions, under the influence of negative temperatures and large amounts of precipitation.
The fiber density of facade slabs is slightly higher than that of the material intended for interior decoration and corresponds to 130 kg/m3. The high density and elasticity of mineral wool are necessary conditions for its installation under plaster. The slabs must withstand the weight of the applied solution and retain their original qualities when it dries.
Due to the fact that most of the country is located in a cold climate zone, mineral wool is in high demand in the domestic building materials market.
The popularity of the material is due to a number of undeniable advantages:
- The excellent heat and sound insulation properties of wool guarantee heat retention at temperatures below 30 degrees, and reliably protect the home from street noise;
- High fire resistance and non-flammability of the material guarantee complete fire safety of the slabs, which begin to melt only at a temperature of 1000 degrees;
- Rodents, insects and other pests do not show interest in mineral wool, so their appearance in it is excluded;
- Excellent vapor permeability promotes moisture removal and rapid elimination of condensation;
- Resistance to moderate mechanical stress significantly increases the service life of the facade, and makes the use of cotton wool preferable to the use of polystyrene foam;
- The absence of the need for additional thermal insulation of interpanel seams solves the problem of heat loss in large-panel buildings;
- The low cost and availability of the material make it possible to finish large areas at minimal cost.
The disadvantages of mineral wool include the presence of formaldehydes in its composition, which have a negative impact on the health and well-being of others. When purchasing, you need to make sure that you have a certificate of conformity and markings from the regulatory authority. This will help avoid purchasing low-quality products and will guarantee the safety of raw materials.
Mineral wool installation work must be carried out using personal protective equipment. The disadvantages include the need to treat the slabs with a hydrophobic compound. If this is not done, the cotton wool will absorb moisture and lose its thermal insulation qualities.
Mineral wool is produced in three modifications, which differ in composition, purpose and performance characteristics.
- Glass wool. Made from sand, soda, borax, dolomite and limestone. The fiber density corresponds to 130 kg per cubic meter. The material is able to withstand heavy loads, has a thermal resistance limit of 450 degrees and thermal conductivity of up to 0.05 W/m3.
Areas of application of insulation based on basalt fiber
Basalt slabs are used for insulation of building facades, partition structures, floors, roofs and other building structures. In addition to residential buildings, basalt insulation is used on industrial sites. Most often used for insulating frame houses.
Having studied the technical characteristics, it is easy to come to the conclusion that mineral insulation can be used in almost all areas of construction. Due to its fire resistance, it is recommended to be used when insulating a building that requires a high degree of fire safety.
Low water absorption makes it possible to use insulation when insulating a bathhouse or sauna. When choosing, remember that the weight of basalt insulation exceeds the weight of polystyrene foam or mineral wool.
Installation technology
Before you begin cladding the facade, you need to prepare the wall surface. To do this, it is necessary to clean it from oil contaminants and dismantle the metal elements. If it is not possible to remove them, then they should be provided with a constant flow of air, which will prevent their premature corrosion and destruction. In such a situation, you should refrain from using acrylic plaster due to its poor ventilation. Old plaster and remaining paint must also be removed.
The next step should be hanging the wall. To do this, you need to drive in reinforcing pins and stretch nylon cords between them. The use of sags will help to evaluate the geometry of the surface and correctly calculate the required amount of material. Next, you can begin installing the guide profile. You need to start with the installation of the base element, which will serve as a supporting guide for the first row of slabs and will allow you to control the distance between the bottom row and the wall surface.
After installing the guide profile, you should begin cladding the facade with mineral wool. When fixing the slabs, you can use driven dowels or special glue. Then the mineral wool is reinforced with a metal mesh, the lower edge of which should be folded under the profile. The mesh must be secured with adhesive-reinforcing plaster.
The final stage will be covering the mineral wool with decorative plaster. For finishing work, you can use silicate, mineral, acrylic and silicone plaster mixtures. It is recommended to paint the plastered surface.
Mineral wool allows you to quickly and effectively solve the problem of facade cladding, significantly reduce heat loss and significantly save your budget. And the ease of installation and accessibility ensure the material’s growing popularity and high consumer demand.
See video instructions for installing mineral wool below.
In the process of building houses and cottages, various types of insulation are used.
And if you are building or reconstructing your home yourself, then sooner or later you will be faced with the question of which insulation to choose?
Today, the building materials market has a huge selection of manufacturers and brands of insulation.
All of them are designed for insulation of walls, roofs, facades, floor coverings and much more.
Insulation properties
Among the advantages of thermal insulation fiber, the following should be highlighted:
- Basalt is a non-combustible material, which makes it possible to install it on fire-hazardous buildings.
- The heat and sound insulation qualities of the mats also have a sufficient level. This quality gives an advantage when installing residential buildings.
- Due to their moisture resistance, basalt slabs are used in the construction of baths and saunas.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient is low.
- Withstands temperature fluctuations and is resistant to frost.
What's the news: insulation with a cached layer
Using windproof fabric over a thermal insulation layer is not always convenient. Affixed at significant intervals over a large area, it can peel and tear. Insulation with a cached layer solves the problem. In this capacity, fiberglass acts, securely glued during the manufacturing process to the outer surface of the mineral wool slab. It does not allow air flows to penetrate into the material, which increases its service life. The installation process of a ventilated facade with such insulation is simplified and accelerated.
Characteristics of the heat insulator
The main indicators of basalt wool include its density. Material of one density or another is selected depending on the area of its use. Low-density basalt wool used when installing partitions will settle over time, which will lead to a decrease in the quality of thermal insulation.
For horizontal insulation, you can use wool with a low density level, while when installing vertical structures, use a product with a sufficient level of density.
In the production of basalt fiber, adhesives are used that allow the threads to be arranged in a chaotic manner, forming air spaces between each other. Due to the high air saturation, the material has low thermal conductivity.
Hydrophobicity can also be considered another positive property of insulation. This parameter is characterized by poor moisture absorption. The space between the fibers allows air vapor to easily penetrate through the mineral mats. This quality prevents condensation from accumulating inside the material.
Basalt can withstand temperatures up to +500°C, and some specially designed ones up to +1000°C.
Types of insulation of ventilation facades: which can and cannot be used in the system
Only non-combustible materials should be used as a thermal insulation layer. Otherwise, the presence of a ventilated gap in the event of a fire can lead to the rapid spread of fire throughout the entire area of the facade. Polystyrene foam is not used when installing ventilation facades. It burns with the release of toxic gases, does not allow water vapor to pass through it, preventing the house from “breathing,” and crumbles over time.
The most effective insulation for ventilated facades is stone wool or fiberglass slabs. They are made from environmentally friendly natural materials using heat treatment and fully comply with the requirements. Mineral insulation has a wide temperature range of application, is resistant to moisture, is not susceptible to the spread of mold and perfectly absorbs noise. They can be used separately and in combination with each other. In this case, the fiberglass layer should be internal, and the basalt fiber layer should be external.
Cotton wool in the form of rectangular slabs that are elastic and capable of maintaining their shape throughout the entire period of operation, is easy to install and durable. Rolled thermal insulation materials do not have these qualities. They have low density, quickly deform and are subject to weathering of the fibers. They are not used when creating ventilated facades.
Thermal conductivity of basalt mats
The thermal conductivity coefficient of basalt wool is in the range of 0.032-0.048 W/mK. The same indicators characterize polystyrene foam, polystyrene, cork and foam rubber.
Important! Mineral mats have replaced asbestos, which is harmful to health, as a fire-resistant material.
Before you go shopping for insulation, consult with friends or knowledgeable people about trusted retail outlets known for the quality of the product. Only this approach guarantees the purchase of good material that meets the standards.
Heat transfer resistance coefficient
When everything is clear about the scope of application of each thermal insulation material, the most effective possible option for this design is determined.
Heat loss through the structural elements of buildings is affected by the thickness of the material used and its heat transfer resistance coefficient - the ability to transmit heat. The lower the thermal conductivity coefficient and the thicker the layer of building material, the better the heat is retained.
To visually represent the required thickness of walls made of a homogeneous material that meets the requirement for heat transfer resistance, we made a calculation that takes into account the thermal characteristics of the building materials used. See the results obtained in the graph:
- Expanded polystyrene
- Mineral wool
- Gas silicate block
- Solid wood
- Expanded clay concrete
- Brick
To choose the most economical option, you should pay attention to the thermal conductivity coefficient of building materials in the thickness of the enclosing structures: external walls, flat or pitched roofs, attic roofs, attic floors, windows, foundations, wooden and concrete floors (see table 2). The lower this indicator, the smaller the thickness of the thermal insulation layer will be required.
Table 2 - thermal conductivity coefficient of building materials
| Name | Density, kg/m3 | Thermal conductivity* λ W/(m °С) under operating conditions**: | |
| A (dry mode) | B (normal mode) | ||
| Construction materials | |||
| Reinforced concrete | 2500 | 1,92 | 2,04 |
| Foam and aerated concrete | 1000-300 | 0,36-0,09 | 0,37-0,10 |
| Foam and gas silicate blocks | 1000-300 | 0,36-0,09 | 0,37-0,10 |
| Ceramic brickwork | 1800 | 0,70 | 0,81 |
| Lime-lime brick masonry | 2000-1600 | 1,36-0,69 | 1,63-0,81 |
| Masonry of hollow ceramic bricks (gross brick density 1400 kg/m3) | 1600 | 0,63 | 0,78 |
| Pine, spruce across (along) the grain | 500 | 0,14 (0,29) | 0,18 (0,35) |
| Regular glass | 2500 | 0.76 | |
| Double-glazed window 32 4M—10—4M—10-4M | 0,47 | ||
| Single-chamber double-glazed window 24 mm 4M—16—4M | 0,32 | ||
| Ruberoid (GOST 10923-82) | 600 | 0.17 | |
| Clay tiles | 1900 | 0.85 | |
| Gypsum plaster | 800 | 0.3 | |
| Insulating plaster | 500 | 0.2 | |
| Steel | 52 | ||
Table 3 - Comparison of thermal conductivity characteristics of insulation materials
| Name | Density, kg/m3 | Thermal conductivity* λ W/(m °С) under operating conditions**: | |
| A (dry mode) | B (normal mode) | ||
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 26-60 | 0,034-0,036 | 0,034-0,036 |
| Polyurethane foam | 80-40 | 0,05-0,04 | 0,05-0,04 |
| Stitched mineral wool mats | 125-50 | 0,046-0,042 | 0,051-0,045 |
| Mineral wool slabs with synthetic binder | 250-75 | 0,061-0,047 | 0,069-0,051 |
| Slab polystyrene (foam) | 50 | 0,043 | 0,052 |
| 35 | 0,041 | 0,05 | |
| 25 | 0,043 | 0,052 | |
| 15 | 0,045 | 0,054 | |
| Polystyrene concrete slabs | 300-230 | 0,092-0,075 | 0,10-0,085 |
| Expanded clay | 800-200 | 0,21-0,11 | 0,23-0,12 |
| Ecowool | 35-60 | 0.032-0.041 | |
*coefficient values were taken from Appendix A of TKP 45-2.04-43-2006, technical characteristics from thermal insulation manufacturers;
**in residential buildings, external enclosing structures refer to operating conditions B, and internal walls, partitions, attic and basement floors - to operating conditions A.
Thermal calculation of the thickness of thermal insulation and checking for the non-formation of condensation in the thickness of the structure is carried out by designers individually for each case according to approved standards for Belarus. The methodology and reference values are given in TKP 45-2.04-43-2006 with current amendments and additions.
Description of slabs with different density levels
There are basalt slabs of various density levels. This is reflected in the following properties of insulation: vapor permeability, moisture resistance, resistance to high loads and response to compression of the material.
Table of parameters of basalt insulation
Based on density, slabs are divided into the following categories:
- Up to 35 kg/m3 – used for vertical and inclined insulation without load.
- Up to 50 kg/m3 - with the help of such insulation they increase the level of thermal insulation of interior partitions, attics or attics. Where there is no load on the surface.
- Up to 75 kg/m3 – lightly loaded surfaces, under floors when placed between joists.
- Up to 100 kg/m3 – external insulation of industrial and residential buildings.
- Up to 125 kg/m3 – arrangement of ventilated facades.
- Up to 150 kg/m3 – single-layer insulation of reinforced concrete or metal building frames.
- Up to 175 kg/m3 – insulation of heavy buildings with further plastering of the facade. Or it is located inside a three-layer cake.
- Up to 200 kg/m3 - insulation with such a density can withstand the highest loads. The soundproofing qualities of the material are significantly higher than analogues with a lower density level.
Features of installation of mineral wool
To install fiber insulation, a frame (sheathing) is first installed. The distance between its guides is made 1-2 cm less than the width of the slab, so that the latter is installed at random. The basalt insulation is fixed with dowels with wide plastic washers at the ends.
A wind barrier is placed on top of the fixed fiber insulation. Its adjacent strips overlap (up to 10 cm). The purpose of the additional layer is to protect against unwanted penetration of moisture onto the surface of the insulation, as well as weathering of individual fibers of the material during operation.
The final stage of installation is the fastening of the facing material, the most popular of which is vinyl siding. Ease of installation, coupled with durability, efficiency and reliability are the key advantages of using mineral wool as insulation for a ventilated façade.
Operational period of mineral insulation
Recently, the construction of private houses has become popular. They, like other buildings in our climate, need insulation. To feel confident that the thermal insulation of a private home is at the required level for a long time, it is necessary to select materials that meet these standards.
Mineral wool based on basalt fiber is ideally suited for this task. The service life of this heat insulator, subject to installation rules, is 50 years or more. The advantage of basalt wool over other insulation materials is not only in chemical and physical indicators, but also in price. The quality of the products is also excellent.
Rating of the best insulation for home
| Nomination | place | Name of product | price |
| The best basalt insulation | 1 | Rockwool | 695 ₽ |
| 2 | Hotrock Smart | 302 ₽ | |
| The best polystyrene foam insulation | 1 | Technicol XPS Technoplex | 1 100 ₽ |
| 2 | Penoplex Comfort | 980 ₽ | |
| The best foam insulation | 1 | Knauf Therm House | 890 ₽ |
| 2 | PSB S 15-O | 1 688 ₽ | |
| The best fiberglass insulation | 1 | Isover Warm House | 660 ₽ |
| 2 | Ursa Geo | 800 ₽ | |
| The best polyester fiber insulation | 1 | Shelter EcoStroy ShES Arctic | 1 780 ₽ |
Technology of wall insulation with basalt
Inside with sheathing
Refers to the simplest option for insulating a private home and industrial structures. The essence of the method is to create a sheathing frame. Assembly is made from wooden beams or metal profiles. The width of the mats is first measured and, subtracting 5-7 cm from the obtained values, the sheathing is assembled.
Next, mineral wool is tightly inserted into the cells of the frame, filling the entire space. A vapor barrier membrane must be attached on top of the insulation.
Lathing
Insulation of walls using the “well” method
If the house design involves laying facing bricks, then the best insulation option would be “well”.
Consider the composition of the “well” pie:
- Bearing wall. As a rule, it is brickwork laid out in one row. Although other materials are also used for load-bearing structures. Depending on the required load-bearing capacity, the walls are laid out in half a brick, a brick and a half or two.
- Insulation. In this case, basalt wool is used. Fastening to the surface is done using umbrella dowels.
- Facing wall. Masonry begins after complete installation of the insulation or as the inner layer builds up. Ceramic or silicate brick is used as the outer layer. The usual installation method is half a brick. A prerequisite for laying facing bricks is the presence of a concrete base.
- Ventilation gap. Since the appearance of condensation on the inside of the insulation is undesirable, a ventilation gap is created for this purpose to ensure sufficient ventilation.
Well method
Attention! If for some reason it is not possible to create a ventilation gap, then it is better to abandon the well method of insulation altogether. This applies to mineral wool.
Wet insulation of walls
The method is used for plastering, because with the “wet” method of insulation, lathing is not provided. Since a high load will be applied to the mineral wool, it is recommended to use high-density mineral wool.
Wet method
Basalt wool fastening technology:
- Following the instructions supplied by the manufacturer on bags of glue, we prepare a liquid solution.
- Apply the prepared mixture onto the mineral coating with a notched trowel. The glue is applied in a continuous layer without coating the end part, which can lead to a decrease in the level of thermal insulation.
- We install mineral mats on the basement of the building and press them against the wall. To increase adhesion, it is necessary to smooth the surface using pressing movements, applying little force. Installation of basalt wool is done from bottom to top. The next row is laid with an offset of half the mat. The same applies to places near window and door openings.
- External and internal corners are reinforced with plaster corner plates.
- We fix the mineral wool with umbrella dowels - 5 fasteners per sheet.
- Using an adhesive solution, we attach the reinforced fiberglass mesh. Make sure that the material overlaps each other by 15-20 cm.
- At the final stage, plastering is carried out.
Frameless method of insulation from the inside
The frameless installation method refers to the wet fastening method. To complete this task you will need an adhesive solution and a cleaned wall surface. The mortar is applied directly to the wall using a notched trowel. Next, a mat of stone wool is applied. To improve the quality of adhesion, umbrella fasteners or self-tapping screws are used, depending on the type of coating.
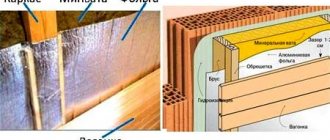
Installation of mineral wool on a ventilated facade
This method requires the assembly of the sheathing, as it involves the installation of facing material.
Ventilated facade
Warming process:
- The sheathing structure is assembled taking into account the width of the mats.
- Mineral mats are laid at random.
- Next we move on to attaching the windproof membrane.
- For further fastening of the cladding, a counter-lattice is assembled from 50x50 mm slats.
At the final stage, façade finishing work is carried out.
Insulation of the wall of a frame house
Thermal insulation of a frame house differs in that it involves the installation of slabs inside the walls, and on the inside and outside of the building. As a rule, manufacturers of frame buildings create walls with a thickness of about 15 cm, which allows you to place 3 mats of 5 cm each. It is also possible to combine wool of different thicknesses - 10 cm and 5 cm. If it is necessary to carry out finishing work on the facade of the building, lathing is assembled on top of the insulation.
Thermal insulation of a frame building
Choosing plaster for the facade
Insulation of the facade using mineral wool is carried out using the “wet facade” technology - all stages are carried out using aqueous solutions, and plastering is used as a finishing touch.
There are 4 types of facade plaster mixtures; the properties of the resulting coating depend on the components included in the material.
Mineral
For the manufacture of mineral plaster, cement and various additives are used, which increase the ductility and adhesion of the product.
To increase strength, microfiber fibers are added to the mixture; Some formulations contain components that increase moisture resistance. Cement mortar has increased strength, but is inferior to other types in ductility, and therefore it is not recommended for use on walls that may be subject to serious mechanical stress.
Supplied dry. Popular brands: Knauf, Bolars, Ceresit, Baumit.
Acrylic
Acrylic plaster is a ready-to-use mixture based on acrylic resins with a small addition of mineral components.
The coating is characterized by plasticity, durability and resistance to temperature changes. Among the advantages are:
- moisture resistance, which is especially important for coatings used for external walls;
- high adhesion;
- large selection of shades;
- ease of application;
- quick drying;
Examples of manufacturers: Ceresit, Knauf, Bolars, Weber, Technodecor.
Silicate
This type of plaster consists of potassium silicate and acrylic resins.
Thanks to this combination, the finished coating is durable, vapor-permeable, and at the same time plastic and durable. Excellent for mineral wool. Among the disadvantages:
- Application requires experience;
- work must be done quickly;
- Before applying plaster, the surfaces must be treated with a silicate primer.
Available in finished form, in plastic containers of various sizes.
Manufacturers: Baumit, Caparol, Ceresit, Kema.
Silicone
It has all the positive properties of compositions on other bases - it is plastic, vapor-permeable, non-toxic, adheres well to the surface and does not attract dust and dirt.
The finished coating is resistant to fading, mold or mildew. Disadvantages: quite high cost; it is advisable to use a silicone primer as a base.
Supplied ready-made. Produced by: Ceresit, Weber, Baumit.
Of the types of plaster considered, all types are suitable for constructing a wet facade.
Often, in order to save money, builders use a mineral cement composition, but it requires subsequent painting or coating with a decorative layer.
Insulating the facade with foam plastic
It is polymeric materials that have become insulation materials with the longest periods of successful operation in difficult climatic conditions. Research and special testing were carried out, which confirmed excellent results: the foam does not lose its original technical characteristics even under conditions simulating 80 cycles of temperature changes.
What are the unique performance characteristics of foam? After all, almost all builders know: foam type insulation cannot boast of serious resistance to external influences. They do not tolerate the influence of ultraviolet rays well, they can dry out quite quickly, lose their original structure and even completely collapse. But the façade of the building is directly exposed to ultraviolet rays.
Insulation of facades with foam plastic
It turns out that the main secret to the effectiveness and practicality of polystyrene foam as insulation is its combination with a layer of plaster. The material must be plastered in full accordance with technological principles. Then it will acquire excellent performance characteristics.
- A layer of plaster will protect the foam from the negative effects of moisture. The insulation itself takes a long time to dry, and when left in a humid environment for a long time, it becomes too fragile, completely losing its performance properties. Plaster completely eliminates this negative factor, turning polystyrene foam into durable insulation that is resistant to atmospheric influences.
- Polystyrene foam is a rather fragile material. A layer of plaster prevents the formation of dents, scratches, cracks and other damage to the insulating layer. Together with plaster, the foam is already quite reliably protected from mechanical influences.
- When plastering polystyrene foam, the fire safety level of the facility increases. The foam insulation catches fire on its own, and the plaster prevents the spread of fire. However, builders note that the professionalism of the plasterer will matter here: the layer must be even, continuous, and of sufficient thickness.
- Exposure to sunlight is detrimental to polystyrene foam, since ultraviolet radiation destroys it and makes it brittle. But the foam + plaster option completely solves this problem.
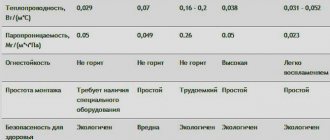
Advantages of insulating facades with foam plastic and mineral wool
We provided a table, examined the advantages of both materials as an insulating layer for a facade, and made some comparisons.
Important! One conclusion can be drawn: when providing insulation for the walls of buildings made of natural wood, mineral wool is of greater interest. Due to its ability to maintain air exchange and moisture evaporation, it is ahead of foam. At the same time, it is with polystyrene foam that you can install insulation efficiently, as quickly as possible, with minimal time costs.
Table - technical characteristics of mineral wool
In general, it can be noted that both materials have good performance, are modern insulation materials, popular and in demand in the construction market.
Polystyrene foam size chart
Well-known manufacturers of mineral wool
Mineral wool for wet facades is a popular material, and therefore is produced by many companies. Not all of them were able to widely present their products, or did not achieve the required quality. Among the well-known Russian manufacturers are: Rockwool, TechnoNIKOL, Izorok and Ecover. These enterprises were able to show the advantages of their wet façade mini-slabs not only to Russian consumers, but also sell their products abroad. The products of such foreign companies as Paroc, Nobasil and others are in high demand.
Advice! The best imported mineral wool is German, since no other country has stricter certification.