12.01.2021
Timber made from natural wood is a popular building material on the market, which customers and construction companies choose for the construction of private homes and commercial real estate. This article will be useful to those who want to understand how to insulate a home. It should be taken into account that a house made of laminated veneer lumber, due to the low thermal conductivity of the material, does not require additional thermal insulation. Houses made from many other building materials (including ordinary profiled timber) require proper insulation. Glued laminated timber is one of the few wood building materials that do not require internal and external thermal insulation of the house. Therefore, if you are going to build a house from any other material other than laminated timber, you will have to take care of its insulation in order to maintain a comfortable temperature even in cold winters.
Heat transfer resistance of timber of different sections
Insulation of profiled timber with natural humidity:
A beam with a cross-section of 100 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 0.73 R, (m2 °C)/W
A beam with a cross-section of 150 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 1.1 R, (m2 °C)/W
A beam with a cross section of 200 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 1.29 R, (m2 °C)/W
A beam with a cross section of 250 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 1.85 R, (m2 °C)/W
That is, even timber with a cross-section of 250 mm does not meet the standards. By the way, this is a fact reflected in the old SNIPs, according to which the thickness of the timber for the North-West of Russia should be at least 500 mm! Which, of course, is not realistic - if you just look for thick forest around the world.
But let's see what happens if we insulate a house from timber. Fortunately, modern materials are relatively safe and accessible:
Profiled timber of natural humidity with external insulation (basalt or mineral wool)
A beam with a cross section of 100 mm + mineral wool 50 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 1.9 R, (m2 °C)/W
A beam with a cross section of 100 mm + mineral wool 100 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 3.25 R, (m2 °C)/W
A beam with a cross section of 150 mm + mineral wool 50 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 2.35 R, (m2 °C)/W
A beam with a cross section of 150 mm + mineral wool 100 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 3.56 R, (m2 °C)/W
A beam with a cross section of 200 mm + mineral wool 50 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 2.55 R, (m2 °C)/W
A beam with a cross section of 200 mm + mineral wool 100 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 3.82 R, (m2 °C)/W
Timber chamber or atmospheric drying (importance no more than 20%, GOST):
At the same time, it is interesting that the timber with a cross section of 140x140 mm is chamber or atmospheric drying!!! (namely, this kind of timber is subject to external insulation) has a heat transfer resistance = 1.9363 R, (m2 ° C)/W - which is significantly greater than that of its counterpart with natural humidity. Bearing in mind that we ultimately need to obtain walls whose heat transfer resistance will be equal to = 3.16 R, (m2 ° C)/W, we must insulate the facade of the house with a layer of basalt slabs equal to only 50 mm!
Conclusion: the optimal solution for a warm house suitable for permanent residence would be the following pie: a wall made of dry timber 140 mm thick + 50 mm basalt slab + windproof film + external cladding imitation timber/block house.
As you can see, the problem of energy saving can be easily solved by insulating the facade of a wooden house made of timber.
In our next article we will tell you how to insulate a house?
Video description
Caulking timber: how it happens is shown in the video:
To understand how to properly caulk a house made of timber, we will consider in detail the methods of caulking with various materials.
Caulking technology with fiber insulation:
Moss or flax tow is applied to the gap with fibers across it, then, holding the material, it is pressed deep with force with a special spatula.
Caulk of towSource fasad-exp.ru
- The remaining material should be carefully rolled up into a tight roller, pushed into the gap, leaving the tip out.
- Then the next strand needs to be woven into the remaining “tail” and the same actions must be performed again. It is necessary to ensure that the formed roller is not interrupted along the length of the wall.
Technology of caulking with rolled material:
- The tape is rolled out along the wall of the log house, but not stretched. Place it on the ground. They don't cut it.
- Starting from the corner, the edge of the tape is applied to the seam with fibers across and the middle is pushed into the gap. At this stage, the edges remain hanging down by 5-6 cm. This is how the seam is initially caulked along its entire length.
- The remaining material is carefully pushed between the beams, ensuring that the seams are filled as tightly as possible.
Attic, doors and windows
The technology for insulating the attic of a wooden house is as follows:
- a vapor barrier layer is laid on the false ceiling of the attic;
- insulation is laid on top - mineral wool or expanded polystyrene;
- A layer of waterproofing is laid on the insulator and a sheathing of boards is installed.
The ideal option for installing doors and windows is the use of double-chamber metal-plastic or wooden double-glazed windows and double doors, as well as the mandatory presence of an entrance vestibule. Finally, before choosing a method of thermal insulation for a log house, it would be correct to make sure that such a procedure is necessary in principle.
07.05.2017 21:25
Profiled timber attracts many Russians with its affordability and excellent thermal characteristics. However, most of them mistakenly believe that such a house will not have to be insulated. Of course, you want to preserve the unique wooden flavor of the interior and exterior of the building, but comfortable living is more important. There are some nuances when it comes to insulating a house made from profiled timber. We will tell you about them today.
Video description
Caulking with rolled material: you will see how to do it correctly in the video:
The corners of the timber are caulked using the same technology:
- If the gaps are wide, a cord is formed from the insulation tape. Roll it into a ball.
- Unwind part of the cord and weave loops from it. Then each loop is pushed inside the seam.
- Hammer the loops with a spatula, first from above the joint, then from below.
- After sealing the seams, final caulking is carried out if necessary. It involves residual filling of joints and is carried out if necessary.
- The density of the caulk is checked with a kitchen knife. The knife blade should not extend into the joint more than 1.5 cm. If this condition is met, caulking is done correctly. If not, then additional caulking is required.
Checking the density of caulk Source 24aul.ru
Caulking of corners is carried out using the same technologies using roll insulation, for this they move along the seam from the bottom up. To ensure uniform laying of the material, it is constantly tensioned and straightened.
Insulating a house made of timber: pros and cons
Today, more and more people are beginning to understand that they are a part of nature. And, realizing this simple truth, they refuse to live in houses made of brick and concrete, preferring life in a wooden house. And they are absolutely right, because living in such a house is an incomparable pleasure. And all because wood is a living, breathing material that creates its own special microclimate in the house. Wooden walls can remove all unpleasant odors and excess moisture in the air from rooms. The air in such a house is always clean, saturated with the smells of pine forests, which have a beneficial effect on the well-being of people living in the house, especially those who have heart problems or blood pressure.
Heat loss from a house made of timber usually occurs at various cracks and joints.
But life does not stand still, and neither do construction technologies. Today, more and more often you can find houses built from timber - wood processed using special modern technology, which ultimately results in an excellent building material, durable, beautiful in appearance, low cost, easy and quick to install. But a house built from this material has one significant drawback - it is necessary to insulate the timber house.
Although this question is not so clear-cut, because the thickness of the walls of a wooden house under construction is usually selected taking into account the thermal conductivity of the wood and the characteristics of the local climate. Typically, the thickness of timber walls is sufficient to maintain a comfortable temperature inside the house. The standard thickness of a timber wall is 30-32 cm, which is comparable to the effect of a 10-15 cm ball of insulation, such as mineral wool or fiberglass. And the consideration that any insulation will lead to a change in the external appearance of the facade of the house forces many owners of houses built from timber to abandon their insulation.
Heat loss of laminated veneer lumber and rounding.
But to all these arguments there is one very significant counterargument. If you do not insulate a house built from timber, this can lead to the appearance of cracks in the beams, gaps between them, as well as to distortion and depressurization of windows. After all, there is no guarantee that the seal located between the beams will provide high-quality permanent protection for the entire period of operation of the house. And poor thermal insulation will lead to the fact that due to blowing and freezing, the temperature regime of the walls is disrupted, and the wood will rot, significantly reducing the life of the house.
Do I need to insulate the seams?
To ensure that a house made of laminated timber does not heat the surrounding air, it is necessary to carefully seal all the cracks and cracks. In particular, insulate inter-crown connections, or seams.
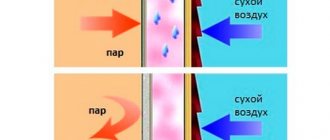
Fig.4. Seam insulation for different profiles
Laying thermal insulation tapes is required only for material with a “Finnish” profile. “German” timber has multiple teeth and grooves for them, which, when laid, form a tight connection. Therefore, the use of inter-crown insulation is not required; only the bowls are sealed. If laminated timber with a small number of teeth is used in the construction of a house, then insulation can also be used to reduce the ventilation of the joints.
Yes and no
Wood has very low thermal conductivity - on average 3.5 times lower than that of brick. Thus, where a half-meter thick brick wall is needed, you can get by with 150 x 150 mm timber.
If we are talking about a building not intended for permanent residence (a country house), or during construction in a warm region, a house made of profiled timber does not need additional insulation. The thermal insulation properties of the material itself will be sufficient to provide a comfortable microclimate even in the event of some frosts. Provided, of course, that the thickness of the timber is selected correctly.
If construction is carried out in a region with a harsh climate, and permanent residence in the house is also implied, then insulation can be considered quite appropriate, if not necessary. Insulation will solve the following problems:
- Maintaining a comfortable microclimate even at extreme temperatures;
- Increasing energy efficiency of heating by reducing heat losses;
- Reduced wear of wall structures.
It is also strongly recommended to insulate when building baths, regardless of the region.
Insulation methods
The preferred method of insulating a log house largely depends on the specific project.
The main feature of using profiled timber compared to log materials is that there is no need to insulate the inter-crown space. The reason is obvious - it is practically non-existent, since the timber has a square (rectangular) cross-sectional shape.
Otherwise, the insulation of houses made of timber is carried out using standard prims.
Traditionally, they are divided into external and internal. External insulation of wooden houses is practiced only if you did not expect to maintain a “traditional” appearance. Typically, the insulation procedure is not much different from similar actions in relation to a brick house.
The only thing worth noting is the need for high-quality ventilation of the space between the wall and the insulation (this can be achieved by installing the insulation on the frame with some indentation). Otherwise, the wall structures will be negatively affected by excess moisture.
Before starting external insulation, you should decide on further finishing. For example, if you plan to use siding or lining, then one frame can be used both for laying insulation and for installing finishing.
Internal insulation also implies a loss of colorful design, but there are a number of other subtle points:
- Internal insulation reduces the usable area of the premises, so it is advisable to use panels no thicker than 30 mm;
- One of the key points when choosing insulation is the ability of the material to transmit excess moisture;
- The insulation should be unattractive to rodents;
- Since we are talking about a wooden building, the insulation must be chosen completely non-flammable.
Otherwise, the insulation technology is standard and depends on the subsequent finishing technique.
Shrinkage of a house made of profiled timber with natural moisture Glued laminated timber - pros and cons
Insulation from outside
The best option for insulating a wooden house would be to create a ventilated facade system with an air gap - the rising currents themselves will remove unnecessary moisture.
This system has high heat-protective qualities and ensures dry walls. It is necessary to pay attention to the sealing of windows and doors, floors, installation of interfloor ceilings and attics. Floor insulation is carried out by laying a layer of waterproofing and heat insulation, on top of which a layer of vapor barrier is placed
Beginning of work
To begin with, the entire surface of the walls is well treated with antiseptics and fire retardants. After processing, gaps and cracks are eliminated at all joints and between the timber. Gaps are eliminated with polyurethane foam or sealants, which are used when laying a log house. More often it is flax batting, jute fiber or tape tow.
After sealing all the gaps, vertical load-bearing slats are placed on the walls. The distance between them is left slightly smaller than the width of the future insulation material. This is done for easier and tighter entry into the structure.
Laying
Between the supporting rails, starting from the underside of the wall, sealing plates are laid. The slabs are secured using anchor fasteners, with the joints located close to each other and to the edges of the sheathing.
The second frame row of beams is attached in a horizontal direction. Mineral wool slabs are installed in the gaps between them. In this case, the upper slabs must overlap the joints of the underlying layer. The second layer of heat insulation is also strengthened with anchors. In addition, the densely elastic structure of the fiber boards itself contributes to a fairly reliable installation of the material between the sheathing beams.
A diffusion membrane is fixed to the surface of the insulation, permeable from the inside to steam and air, but completely closed from the outside to wind and external moisture. This layer will perfectly protect the insulator and the wood underneath from adverse weather conditions.
Ventilation layer and finishing
The frame for exterior finishing must be fixed so that there is an air gap between the finishing layer and the heat insulator for ventilation of water vapor. After all, external moisture will inevitably condense on the surface of the insulation, which should be able to evaporate.
External facade finishing is mounted on the frame. This can be lining, siding or panels made of polymers. You can decorate the building with a block house - a polymer that imitates wood with its texture and pattern
It is important to prevent heat loss through other areas - roof, floor, foundation, windows, doors
Stages of insulating a house made of profiled timber
All elements of the house need insulation. Therefore, it is worth taking each of them responsibly. Otherwise, the event will be useless.
Foundation
There are two ways to insulate the foundation:
Internal insulation is extremely undesirable and is recommended only if for some reason external insulation is impossible.
External insulation has a number of advantages:
- materials for it are cheaper than for internal insulation;
- allows you to avoid freezing and, as a result, sudden changes in temperature, which lead to the destruction of the structure;
- allows you to save the internal space of the basement.
The most preferred material for foundation insulation is polyurethane foam.
It is more expensive than polystyrene foam, and has the following advantages:
- its installation does not take much time;
- no seams or gaps;
- there are no cold bridges.
Special equipment is used to lay such material. The thickness of the insulation layer should not be less than 5 centimeters.
A little less often they use insulation - extruded polystyrene foam. It only has a couple of advantages:
- low price;
- absolute immunity to moisture.
A floor laid with boards will sooner or later become covered with gaps and cracks. This means that the thermal insulation of the room will drop sharply. To prevent this from happening, the floor is also insulated. Moreover, it is advisable to do this at the stage of building a house in order to avoid problems with relaying boards in the future.
Thermal insulation of the floor covering involves not only laying insulation, but also hydro- and vapor barrier. It is best to agree on what materials are required with a specialist, since the choice depends on many factors, such as the material of the boards, the ventilation system in the house, etc.
In order to insulate the floor, logs are installed in the foundation. Then the panels are nailed to the timber and hydro- and vapor barriers, insulation and both insulations are installed again.
This method is not the only one, but is more common in its implementation.
Walls
There are only three options for wall insulation:
The last option is for those who care about the aesthetics of the room.
As a rule, the following materials are used for thermal insulation of walls:
- natural insulation materials: flax, sheep wool, flax wool, etc. Such materials are suitable for inter-crown installation;
- polystyrene foam or any cotton material is ideal for external insulation;
- for the interior - exclusively cotton insulation.
In addition to thermal insulation materials, a vapor barrier will also be required, which will prevent the insulation from absorbing moisture.
Also, do not forget about the ventilation system.
In order to avoid misunderstandings related to the thermal insulation of the room in the future, it is better to immediately familiarize yourself with all the rules for laying materials. If you do not have sufficient experience in this area or are not confident in your abilities, then it is better to turn to specialists.
The peculiarities of the Russian climate - strong winds, heat and frost, rain - one way or another, require home insulation. Let's consider how to insulate a house made of timber in accordance with regulations and heat saving standards.
In general, insulation should begin during the manufacture of the log house, laying the inter-crown seal after each row of logs. Wood is a natural material that dries out and shrinks over time. Therefore, a year later, after the walls of the log house have dried and settled, repeated work on window sealing and thermal insulation is carried out.
What elements need thermal insulation?
Among the structures that require improved thermal insulation properties:
- Base.
- Floors.
- Roof.
- Floors.
- Partitions.
- Fountains (if there is an attic).
Work on the plinth is carried out during construction, with additional thermal insulation of the plinth floors. At the same stage, cold bridges are eliminated. The best thermal insulation for floors is polymer materials or mineral wool. Mineral wool is also used for floors above the basement or attic.
Types of insulated laminated timber
There are several types of insulated timber, which differ in the type of heat-insulating material, as well as in the type of timber structure itself.
Thermal insulation material
Polyurethane foam (PPU insulation).
This material has a good set of positive properties. For example, a fairly low thermal conductivity coefficient. When using it, the entire volume of the timber frame is filled, and the possibility of the formation of cold bridges is also reduced. But along with the advantages, there is also a disadvantage. This material has low vapor permeability, because of this, when designing a building, you need to take care of having an effective ventilation system.
Ecowool (cellulose).
The advantages of this insulation lie in its fairly high thermal insulation characteristics, as well as in its relative cheapness, which affects the cost of the insulated timber itself. But when using this material, the possibility of exposure to rodents increases. It is also necessary to use special equipment, which increases the construction time.
Construction of insulated profiled timber
Single chamber timber
The design of such a beam consists of two boards, which are connected by jumpers every 500 mm. A frame of this type is in most cases filled with polyurethane foam, which ensures the “solidity” of the timber used.
Photo of a single-chamber beam
Batch timber
This type of construction is in many ways similar to the design of a single-chamber beam
But there is an important difference. Its frame is divided by longitudinal jumpers, in addition to horizontal ones, which form separate honeycombs closed on all sides
They are filled with the selected insulation. This type of construction device significantly increases the characteristics of single-chamber timber, but at the same time the cost of such material increases.
Batch timber
An example of assembling a box from profile insulated timber
Having selected and installed the foundation according to the project, we install anchor bolts at a given distance.
For a foundation made of screw piles, anchor bolts are attached as shown in the diagram:
Type of fastening to the foundation on screw piles.
If a strip foundation filled with concrete is used, the anchor bolts are attached as follows:
Method of attachment to a strip foundation.
- Having installed the anchor bolts, we lay insulating material on the foundation.
- Then we screw a coupling onto the anchor into which the pin is screwed.
- The next step is to install the bottom layer of profiled backing boards, which are placed on the studs.
- The timber with grooves lies on the board, with the pin acting as a guide.
- The next one is installed across the installed beam, then the box is assembled in the same way.
- The upper beam of the box is also covered with a profile board, after which it is tightened with a nut and washer.
Assembly diagram of a box made of profile insulated timber
On our website you can learn about insulating a loggia (also find out how to insulate the roof of a house).
Briefly about the main thing
Caulking involves sealing cracks in a log house with insulating material. It is necessary to caulk the house after the timber shrinks. This must be done twice, and in the absence of outer cladding - three times.
Caulking is done using various materials. The main thing is that they meet the requirements of heat conservation, are environmentally friendly and durable in use. Traditional materials are represented by moss, tow and hemp. Modern ones - jute and linen felt.
Depending on the width of the gaps that appear after shrinkage, they can be caulked in two different ways using rolled or fibrous materials: the “stretch” method or the “set-up” method.
Wet mechanical method of spraying ecowool
The area of the insulated space is calculated, and based on these measurements, a sheathing is made from a wooden beam or metal profile.
Then it is sprayed with moistened ecowool into the cells of the sheathing onto the open wall space. It is wetted at the outlet of the nozzle with a special built-in device.
After drying, ecowool becomes elastic and plastic, forming a continuous layer that is not subject to deformation.
Excess material is cut off and dried before being returned to the spraying equipment. Thus, there is virtually no ecowool waste.
Wet-glue mechanical method of spraying ecowool
The thermal insulation technique is practically no different from the wet method, only in this case adhesives are added along with water to increase the adhesive properties of ecowool. This makes it possible to apply a layer of insulation to complex surfaces, thin walls, and hanging structures.
You can build a device for spraying ecowool yourself. To do this you need to purchase:
Thus, a homemade device will cost approximately 18,000 - 32,000 Russian rubles.
A factory-made device will cost 180,000 - 600,000 Russian rubles, and their productivity will be much higher. But for one-time work such expenses are impractical. Be that as it may, using ecowool as insulation will cost much less than laying other thermal insulation material.
Prices for materials are approximately as follows:
Features of the procedure
Many users choose houses made of timber.
The popularity of such buildings is explained by their attractive and natural appearance, the use of natural materials in construction, as well as the comfortable microclimate that is maintained in such environments. The timber itself is a warm material, so houses made from it are considered cozy and hospitable. They are not cold in winter, but not hot in summer either. However, such buildings still need to be additionally insulated, otherwise during the frosty seasons they will not be so comfortable. Insulation is primarily required for timber houses in which the building material is not of sufficient thickness. If the section is incorrect, complete freezing can occur inside a wooden house. This fact suggests that the floors in such a structure are unable to retain heat efficiently and it is impossible to do without insulation. If the beam in the house has a cross-section of 150x150 mm, then it is not necessary to provide additional finishing, especially if the building is located in areas with a warm and temperate climate. Timber with a section of 180x180 mm is also popular - very warm and reliable houses are built from it, for which additional finishing is also optional. However, it is worth considering that if the cross-section of the beam of the house is correct, the building material will still dry out over time, and this will also cause significant heat loss.
If you decide to insulate a log house, then you should note that this can be done both outside and inside. The following features are typical for insulating a house from the inside:
The following features are typical for insulating a house from the inside:
- with such work, a certain part of the useful living space will inevitably be lost due to the installation of a frame structure under the insulation;
- a layer of thermal insulation material hides wooden floors underneath, which affects the design of the rooms in the house;
- Due to the inevitable winter cooling of wooden walls, the dew point moves directly into the internal insulation. After this, condensation and mold appear. It is worth considering that monitoring the condition of the timber in such circumstances is not an easy task.
Insulation of a log house from the outside is considered more common. It includes the following features:
- with such insulation, the useful area of the living space does not undergo major changes and does not become smaller;
- external work is good because it does not in any way affect the internal routine of the household;
- with this method of insulation, the facade of a wooden house is reliably protected from destructive temperature fluctuations, and this significantly extends the service life of the building;
- if you correctly select suitable and high-quality insulation, then the comfortable microclimate in the interior of the house will not be disturbed;
- most owners turn to this method of insulation to make the house cozy and “breathe”;
- with external insulation, you can update the facade if it naturally darkens;
- Using external insulation materials, you can protect the timber from damage.
At the moment, there are several main options for insulating walls in a house made of timber. A curtained ventilated façade is a technology developed as an additional decoration for the façade of a building.
It is worth considering in more detail what advantages are typical for this option for insulating a log house:
- ventilated facades have a long service life, which can reach 50 years;
- This insulation option is characterized by excellent heat and sound insulation, which is noted by many users;
- installation of a suspended ventilated facade is considered simple and affordable;
- This method of insulation allows the use of a variety of facing materials;
- with such insulation, the dew point moves outward, which avoids the accumulation of condensation in the material.
The technology for insulating a timber house under siding largely replicates a hinged ventilated façade. In this case, the insulation is also installed from the outside, and is supplemented with a decorative coating on top. Polyurethane technology will be clear to every craftsman who has at least once encountered work involving polyurethane foam. The main difference between this method lies only in the volume of materials required to form a thermal insulation cushion, because much more is needed. That is why, when choosing this technology, it is necessary to stock up on a high-quality spray gun.
Installation features
The insulation technology primarily depends on the selected heat insulator. If a rolled or slab material is chosen, then the ventilated facade for a house made of timber in the form of a multilayer system is equipped with ventilation gaps. In the case of using sprayed materials, the technology is simplified.
Spray insulation
Sprayed polyurethane foam and ecowool are applied directly to the walls, which does not allow for a ventilation gap to be created between the wooden structure and the heat insulator. In the case of ecowool, this is not important - such insulation is vapor permeable. But if the outside of the house is covered with a layer of polyurethane foam under the siding, the walls stop “breathing”, and you need to be very careful about arranging ventilation in order to avoid dampness in the rooms and the appearance of mold.
Thermal insulation of external walls with sprayed polyurethane foam
Before spraying the material, the walls are cleaned and vertical lathing is stuffed onto them, forming cells for filling with heat insulator. The size of the slats is selected in accordance with the calculated thickness of the heat-insulating layer.
Using special equipment, polyurethane foam is sprayed into open cells, and in the case of using ecowool, the technology depends on the thickness of the layer. If the size exceeds 70 mm, a vapor-permeable windproof membrane is attached to the sheathing. Holes are made in it (one per cell), through which the gaps between the slats are filled. The holes are sealed hermetically.
A windproof film is installed on top of the polyurethane foam layer, as well as ecowool, applied using the open method, a counter-lattice is stuffed, and the external finish is attached. If it is made of wood, the counter-lattice will provide a ventilation gap to prevent rotting of the material.
Arrangement of a traditional ventilated façade
If there is a task to preserve the unique microclimate of a wooden building, it is important to figure out how to properly insulate a house made of timber from the outside. When thermally insulating external walls, the provision of a ventilation gap between the wooden wall structure and the insulation is often neglected.
This leads to the fact that a wooden house does not remove excess moisture through the walls and the wood accumulates moisture. The result is the development of mold, rotting of the walls of the house.
To avoid negative consequences, you cannot install polymer insulation materials or a vapor barrier membrane for a mineral wool heat insulator directly on the wall.
Thermal insulation diagram of a timber house from the outside
First stage. To properly insulate a house made of timber, first of all, a vertical sheathing of edged boards 40–50 mm thick is placed on the walls. A vapor barrier is attached to it. The resulting gap allows air to circulate, removing excess moisture. It is necessary to leave a ventilation gap at the top, covering it with a canopy made of wooden slats to prevent the penetration of precipitation.
It is recommended to level the sheathing to a strictly vertical plane to make it easier to insulate a log house from the outside. All lumber used in the “pie” is pre-treated with an antiseptic and fire retardant.
Second phase. During the insulation of a log house, sheathing slats are attached to the boards of the installed sheathing under the slab insulation. The width of the slats must correspond to the thickness of the heat insulator. The end posts should be at the corner of the wall. The installation step depends on what material it was decided to insulate the house with:
- if it is polystyrene foam or sheet extruded polystyrene foam, then the gap between the slats should be equal to the width of the sheet;
- if the building is thermally insulated from the outside with mineral wool, then the gap should be 10–15 mm less than the width of the slab material.
Third stage. Thermal insulation of walls from the outside requires proper installation of insulation:
- polymer boards are inserted into the cells, all joints are filled with polyurethane foam;
- Stone wool slabs are installed by surprise.
Additional insulation of corners is usually not done, but when installing heat insulation along the edges of the walls, it is necessary to ensure that cold bridges do not arise.
Fourth stage. A windproof film is attached over the sheathing. If the heat insulator is a polymer material, you can use a regular film, but it is better if it is a material that protects from UV rays. When insulating the walls of a log house with a fibrous heat insulator (mineral wool), it is recommended to use membranes that allow steam to escape but do not allow moisture to enter.
Fifth stage. The facade finishing can be done using siding, lining, block house and other materials that are relatively light in weight. The walls should be sheathed using 40mm thick counter battens on top of the wind barrier. This will provide ventilation to the system.
Diesel boilers
This type of boiler runs exclusively on liquid diesel fuel (diesel fuel). Diesel combustion fuel releases heat that heats the coolant (water or a special liquid) that circulates in the heating system. The boiler itself includes a diesel burner, a fuel filter and a pump, and an automatic control system. Diesel boilers are also divided into:
- single-circuit (the coolant circulating in the heating system is heated)
- dual-circuit (There is a second heating circuit for tap water)
Advantages of diesel boilers:
+ High efficiency + Large selection of models for any need + High safety. + Low energy consumption + Availability of fuel in any region of the country + Easy to install + No permits required + Long-term battery life possible
Disadvantages of diesel boilers:
— High cost of operation — High cost of equipment — An additional tank for diesel fuel is required — A high-quality chimney and its careful installation are required. — Diesel fuel combustion products pose a danger to the body. — Additional heating of the fuel tank is required (In severe frost, diesel fuel thickens and the pump cannot pump it) — The diesel boiler is noisy during operation — Unpleasant smell in the boiler room — Dependence on the quality of the fuel
Properties of mineral wool
The fibers of the material are made from basalt, a particularly strong rock. The big advantages of mineral wool are its resistance to mold, fungi, insects, and the ability to withstand temperatures above 1000°C.
In addition, mineral wool fibers have good vapor permeability, which allows vapors to evaporate rather than accumulate in the walls. An important quality of mineral wool is the absence of toxic substances in its composition.
The thickness of the applied insulation slabs depends on the width of the walls of the house itself. For example, for a 150 mm beam it would be correct to use only 5 cm of mineral wool. Thinner slabs are mounted in two continuous layers. The joints must be covered to enhance the heat-saving effect.
Types of mineral wool
URSA mineral wool is a mixture of dolomite (mineral) with quartz sand. Its main advantages are high elasticity and flexibility (facilitate installation) and excellent thermal insulation characteristics (the thermal conductivity coefficient of such insulation is 0.032 W/mK).
For the walls of ventilated facades, the Ursa FACADE material is used in the form of semi-rigid fiberglass slabs, covered with black high-density fiberglass. Additionally, the boards are treated with water-repellent agents. Thanks to all these qualities, there is no need to install windproof films.
ROCKWOOL mineral wool is made from basalt rocks impregnated with a hydrophobic mixture - the chaotic arrangement of mineral fibers ensures high strength. Such material contains a minimal amount of binders. ROCKWOOL is not subject to deformation during operation. It is produced in a variety of forms - rolls, slabs, mats of various thicknesses and areas, which also differ in the degree of rigidity.
ISOVER mineral wool is made from glass fiber and is characterized by excellent heat saving properties, dimensional stability and durability. The upper surface of such plates is covered with fiberglass, so they do not require the use of diffuse membranes. When carrying out two-layer insulation, such material acts as the top layer.