When installing a heating system yourself, heating batteries are connected to the boiler, making one-pipe or two-pipe wiring and choosing their connection diagram. One of the most popular options is the diagonal connection of heating radiators, which has a number of significant advantages over other schemes, as well as some disadvantages.
It should be noted that the correct choice of method for connecting heat exchangers depends on the efficiency of the entire heating system and, accordingly, the expenditure of funds for heating the coolant. Therefore, before making a decision on choosing a heating scheme, it is useful to familiarize yourself with the various options for connecting batteries, compare their advantages and disadvantages, and decide on the type of heat exchange devices to purchase.
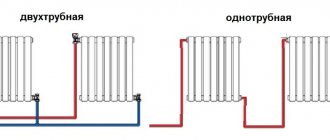
Rice. 1 One-pipe diagonal connection
Pros and cons of diagonal connection of heating radiators
A distinctive feature of the diagonal scheme is the pipeline supply to the radiators. In order for heating to be as efficient as possible, you need to familiarize yourself with the positive and negative sides of such a connection.
The diagonal scheme is distinguished by a special pipeline supply to the radiators
Pros:
- The scheme is highly efficient and is considered the optimal choice for a private home. Heating efficiency exceeds 90%.
- With the diagonal connection method, you can install a large number of sections on the heating heating device - optimally up to 24 pieces.
- As the coolant circulates through the sections, a gradient contour is formed.
Minuses:
- Heating efficiency is achieved when the connection is made diagonally in a two-pipe system. This option is not suitable for a single-pipe scheme.
- The supply of two pipes to the heating heating device from different sides does not look aesthetically pleasing indoors.
- With a diagonal scheme, the pipes are supplied to the heating device from two sides. In the future, if it is necessary to add or reduce the number of sections, the pipeline will have to be cut.
- For apartments, the diagonal scheme is rarely used, and in some cases it is not available at all.
- Installing a heating circuit in a diagonal pattern is expensive, as it requires more materials and work.
To have a clear idea of the diagonal connection method, you need to understand its features and nuances.
Useful tips
- Despite the simplicity of a communication network of this type, it is necessary to draw up a detailed project with preliminary calculations before carrying out the main work;
- To place conductive elements in arbitrary locations, it is imperative to install a circulation pump, which will forcibly move the coolant in a closed loop;
- The polypropylene pipelines themselves must be secured to the side surface using compensating supports. They allow you to fix products in one position, but at the same time linear movement remains possible;
- If instead of polypropylene elements metal analogues are used, then the joining is carried out using special connecting parts or welding;
- If desired, pipelines can be laid in the wall, which will have a positive effect on the aesthetic perception of the room. You can also make a decorative box that will hide conductive products;
- To reduce heat losses, it is not recommended to place radiators of the heating system in a niche or any openings, especially if the efficiency of the entire network is not very high;
- If you have a circulation device, it is advisable to acquire a backup power source, since if the electricity is turned off, the heating will not function;
- It is recommended to fix batteries using floor holders if the walls are made of lightweight materials. In other cases, special hooks should be installed.
Features of connecting a radiator diagonally
Thanks to the connection of supply pipes on both sides, the heated coolant is evenly distributed across all sections. The most effective scheme is considered to be when the supply is connected at the top and the outflow at the bottom. After all, according to the laws of physics, hot liquid is always located above cold liquid. However, there is a diagonal connection of heating radiators with a lower coolant supply. The efficiency of such a system is less. This is due to the fact that, according to the same laws of physics, it is more difficult for the cooling coolant in the lower part of the sections to flow upward to the outlet pipeline.
A system in which the supply pipe is connected to the upper manifold of the heating device has greater efficiency.
An increased number of pipe lines spoils the appearance, but in a private house aesthetics fade into the background. Connecting heating devices diagonally with top supply has high efficiency, and this is the main thing for the consumer.
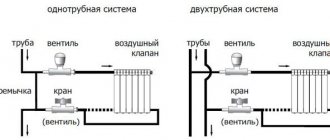
The layout of the heating device with a diagonal connection method is also different. The battery must be equipped with a Mayevsky crane. Install it on the upper manifold, free from the pipeline. The tap helps to bleed the air, otherwise, when aired, some of the sections will not warm up.
Important! The design of Mayevsky cranes is varied. There are models with levers, handles, for a screwdriver or a key.
Regardless of whether the diagonal connection of radiators has a supply from below or from above, the outlet pipe is always suitable. If necessary, it is impossible to remove the battery without cutting the pipeline. To avoid such inconveniences, connections are made using detachable couplings. Previously, so-called threaded fittings were used. Their disadvantage is that the metal quickly corrodes. In a couple of years, it will be difficult to promote such a drive. Modern heating systems use “American” ones. The coupling consists of two parts, between which there is an o-ring. “American” is easily unscrewed with keys, after which you can freely dismantle the heating device.
Together with the “American” ones, shut-off valves are installed on each pipe. If the radiator leaks in winter, it is turned off with taps and dismantled for repairs. The rest of the system continues to function.
In heating with a diagonal connection method, it is important to correctly position the radiator on the wall. According to established standards, the following distance is observed:
- from the bottom surface of the window sill to the top of the sections 5-10 cm;
- from the floor to the bottom of the sections 8-12 cm;
- from the wall to the sections of the back side of the heating device 2-5 cm.
Maintaining the gaps ensures optimal conditions for the convection of air masses around the battery.
Important! Radiators are installed strictly horizontally in order to reduce the likelihood of airing sections and the formation of calcium deposits.
Types of diagonal battery connections
There are several types of schemes for diagonally connecting heating devices in the heating system. What they have in common is that in any option the pipeline is supplied from two sides. With a double-sided connection, the efficiency of the radiator is greater than with a one-sided connection.
Double-sided connection of pipes increases heat transfer compared to one-sided connection
An important difference between the diagonal system is the supply and outlet pipes. A scheme is considered effective where the supply is connected to the upper collector of the battery, and the return comes from below. This option is suitable for gravity-fed autonomous heating systems where a circulation pump is not provided. With a reverse supply (supply from below and return from above), the efficiency decreases. The scheme is suitable for a closed type of heating, where a circulation pump pumps the coolant.
Another difference is that heating devices can be connected diagonally in a single-pipe or two-pipe heating circuit.
Diagonal connection of a heating radiator with a single-pipe system
The scheme involves the use of one pipe in the circuit. A ring is formed from it. In other words, one looped line plays the role of supply and return. The battery is connected diagonally to it with outlet pipes.
Diagonal connection of radiators in a two-pipe heating system
In a two-pipe system, the circuit is similarly made as a ring, but there are two pipes. The coolant heated by the boiler is directed through the supply pipeline. The coolant is removed from the radiators through the return pipe (return pipe) and sent to the boiler for heating. The heating device in a two-pipe system is connected by outlet pipes to both lines of the common circuit.
Varieties of methods for connecting heat exchangers
When the optimal option for installing the heating system has been chosen, and radiators have been installed, you need to decide how to supply coolant to the batteries. There are different options for this:
- lower;
- lateral.
Depending on the locations of the supply and return connections, the following types of connections are distinguished:
- Diagonal.
- One-sided.
- Lower.
Depending on the version of the selected system (one-pipe or two-pipe), the connection will not only have a different design. This will also affect the efficiency of the radiators and the entire heating system as a whole.
Bottom connection
The bottom connection method depends on the type of radiator used. Such products have corresponding holes in the lower part into which the coolant enters and exits. Which hole to connect the supply to, and where to return, must be indicated in the instructions for the radiator.
Radiators are connected to both single-pipe and two-pipe systems with bottom supply.
Side connection method
Heat exchangers with a side connection method are the most common, as they allow insertion into the battery from any side. Installing such batteries allows you to save on material and also try out different options.
The best option is a lateral connection, made using a two-pipe or one-pipe scheme.
Side radiators are connected in three ways: diagonal, side and bottom.
Diagonal connection
The diagonal method of connecting heating radiators has minimal heat loss. When connected according to this scheme, the following occurs:
- The coolant enters the device from the supply pipeline.
- It is carried out through all sections of the battery, releasing heat into the room.
- Exited through a hole on the other side.
Experts call this method, such as diagonal connection of heating radiators, the most effective.
It is used for one- and two-pipe heating networks. The diagonal connection of heating radiators can be implemented using the following options:
- Coolant flows into the radiator through the top hole, and flows out from the bottom on the other side.
- The coolant is supplied to the lower hole and exits from the upper hole on the other side.
How to properly connect heating radiators with a two-pipe heating system is shown in the photo below.
This connection method is effective and allows you to connect long batteries with a total number of more than 12 batteries in the network.
The diagonal connection functions not only with the injection method of coolant circulation, but also in a gravity system. In addition to the diagonal connection, bottom and side connections are also known.
Where to place the diagonal radiator connection system
The system is used in autonomous and centralized heating. It is more suitable for private houses than apartments. Autonomous heating is of open and closed type.
In an open type of heating, the coolant circulates by gravity
If a diagonal connection is chosen for a gravity system, the pipeline is laid at a slope. The supply always goes up, and the return goes down. The absence of a circulation pump does not allow the coolant to be evenly distributed. Radiators further along the ring will always be colder than those located closer to the boiler. The problem is solved by a parallel two-pipe connection. The supply pipe from the boiler and expansion tank fits with pipes to the upper manifold of each battery. Similarly, from the lower manifold of each heating device, a pipe extends to the return pipe connected to the lower part of the boiler. The heating device itself is installed in a pit so that the main circuit is higher in level.
Important! A gravity flow system can be installed in a building with a maximum of two floors. In addition, the length of the circuit and the number of batteries are limited. The downside is the inability to connect a “warm floor”.
Forced heating equipped with a circulation pump
Centralized and autonomous heating of a closed type involves the use of a circulation pump. The coolant is supplied under pressure. There is no need to observe slopes or bring a large expansion tank to the top point. In forced heating, the diagonal is suitable for one-pipe and two-pipe systems. In addition, the supply pipeline can be connected to the upper or lower manifold of the heating device.
The video shows more information about connecting radiators:
Master Class. We connect the radiator from the floor using L-shaped tubes
L-shaped tube
Step 1. Installation begins with the installation of the nipple.
Nipple installation
Step 2. Then the block of ball valves is installed.
Installation of ball valve block
Step 3. Place the threaded clamp onto the L-shaped tube.
Threaded clamp connection is put on
Step 4: Now the L-shaped tube is flared using a tool.
The L-shaped tube is flared using a tool
As a result, the rubber seal no longer slips off the tube into the Eurocone.
Now the seal does not slip off the tube
Step 5. The tubes are installed in the fixing angle.
Installation of tubes in the fixing angle
Step 6. Next, the tubes are inserted into the block of ball valves and baited.
Baiting tubes
Step 7. A hole is marked for attaching the fixing angle, after which the tubes are dismantled.
The future hole is marked
Removing tubes
Step 8. A hole is drilled in the floor according to the markings.
A hole is drilled in the floor
The kit with a fixing angle includes a dowel and a self-tapping screw. The dowel is driven into the hole made.
Dowel and self-tapping screw
The dowel is driven into the hole
Step 9. The L-shaped connecting tubes are installed back and fixed to the ceiling.
Fixing L-shaped tubes
Step 10. Take the pipe and connect it to the L-shaped connecting tubes. The thermal insulation on the pipe is moved back at least 2 lengths of the sliding sleeve. Then the sleeve is fixed.
Pipe for heating system
Thermal insulation is moved back by 2 sleeve lengths
Fixing the sleeve
Step 11: The connection is made. The end of the pipe is flared.
Note! In this example, a metal-polymer pipe is used, which is why the nozzle on the tool is green.
Green nozzle is used
Pipe flaring
The pipes are connected
Step 12. The pipes are attached to the ceiling using dowel hooks in increments of 50 cm. Thanks to this, the pipes will not float up when pouring the screed.
The pipes are attached to the floor with dowel hooks
Schemes for diagonal connection of heating radiators
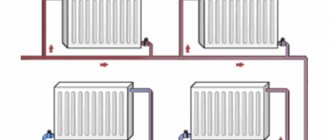
The two-pipe scheme is considered the most effective and correct when it comes to the diagonal connection method. It is better to connect the supply branch to the upper collector on one side, and the return branch to the lower collector on the other side of the radiator. The two-pipe scheme works perfectly in gravity and forced systems. However, it is important to position the supply and discharge lines correctly.
If the circulation is forced, two pipes can be located at the bottom of the radiator
Since during forced circulation the coolant is supplied under pressure, the supply and return lines can be located on the floor below the radiator. The scheme benefits from aesthetics, since only the pipes suitable for the manifold are visible on the wall.
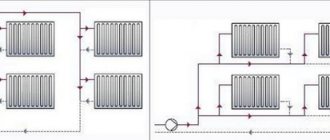
If the circulation is natural, the supply pipe is located above the heating devices
With natural circulation, the two-pipe scheme does not look aesthetically pleasing, since the supply branch runs along the wall above the radiators. From it there are outlet pipes to the upper collectors of each battery. The return line runs along the floor. It still remains less noticeable.
The single-pipe scheme involves laying only one pipe along the floor, from which pipes are connected to the lower and opposite upper manifold
In terms of efficiency, the single-pipe scheme loses in everything, but there is one plus. With lower wiring, the diagonal connection method allows you to increase heat transfer by 15% than in other systems, for example, “Leningradka”, where both supply pipes from one pipe are connected only to the plugs of the lower oppositely located collectors.
How to install a radiator diagonally
Before proceeding with installation, it is necessary to accurately determine the scheme. It will differ depending on the type of heating. An important nuance is the type of housing: a private house or an apartment in a multi-story building.
Diagonal connection of heating radiators in an apartment
For apartments, it is rarely customary to connect batteries diagonally. In apartment buildings, side supply is more common. That is, in a one-pipe and two-pipe system, the outlet pipes from the risers are connected to the upper and lower collectors on one side.
For apartments, lateral supply from risers is acceptable
The disadvantage is the inability to warm up long batteries. If there are 12 or more sections, then each subsequent element will be colder than the previous one. For this reason alone, experts recommend using a diagonal connection of heating radiators in an apartment building. Even if the battery has more than 12 sections, the coolant will circulate evenly through each of them.
Diagonal connection of heating radiators in a private house
The situation is completely different with a private house. The heating circuit here is usually small. The coolant circulates perfectly throughout all sections in one-pipe and two-pipe circuits. However, it is optimal to give preference to the second option.
Installation technology requires the use of additional parts
Installation occurs in the following order:
- Markings are applied to the wall and brackets are installed. The section of the wall adjacent to the rear sections is covered with foil material. The reflective screen will increase the heat transfer of the heating device by 30%.
- The next step is to assemble the battery. A Mayevsky tap is installed on one upper manifold. A supply pipe will be connected to the opposite upper manifold. Here they install an “American” and a shut-off valve. A similar kit is placed on the lower manifold on the opposite side. The return line will come in here. The remaining free second collector from below is closed with a plug.
- The completed battery is hung on brackets and connected to the common circuit. The connection method depends on the selected pipes (plastic, metal).
All radiators are installed using a similar principle. At the end of the work, pump in coolant and check for leaks.
Single-pipe circuit with jumper (apartment version)
This option is slightly better than the previous one, since the goal is to heat all the radiators in the apartments, along the riser, evenly.
By reducing the resistance created by the radiators with such a jumper, the coolant passes through the entire riser, partially entering (mixing) into the radiator, thereby heating all floors evenly.
The main thing here is to make sure that none of the residents put a tap on the lintel (and close it), otherwise this whole “undertaking” of the engineers with the lintel will be covered with a “copper basin”. In some houses, knowing about such cases, they simply reduce the diameter of the lintel.
The tap on the jumper is needed in case of an accident or repair - if the radiator “leaks” (breaks), it is removed for replacement. Then the jumper serves as a bypass between the apartments so that the flow of coolant stops.
Advice from professionals
Several useful recommendations will help you more accurately decide on the choice of scheme:
- For apartments, a diagonal connection is beneficial if the heating device has 12 or more sections;
- it is optimal to give preference to the diagonal if the wiring is two-pipe;
- You should always try to bring the supply to the upper manifold, and the return to the lower.
In heating with forced circulation, you can give preference to a diagonal with a single-pipe system, and the supply pipe should be connected to the lower collector. However, heating efficiency decreases.
The main mistakes made during installation work
When trying to install a heating unit without the help of professionals, novice craftsmen make mistakes. Let's name the most common ones:
- The decision to save money and the purchase of low-quality, cheap communications.
- The type of pipes is incorrectly selected - it is best to buy copper alloy pipes for this purpose. They have high strength, resistance to corrosion, and serve for a long time. The only drawback is the high cost. If the amount does not allow, give preference to metal-plastic or polypropylene.
- The radiators themselves are incorrectly selected, or more precisely, their power - the power of the heater strictly corresponds to the size (area) of the heated room.
- Installing decorative screens, buying window curtains that are too long and too thick, preferring a “standard design”, that is, protruding window sills - all this leads to a decrease in thermal efficiency.
- Incorrect location of the thermostat head - if it is not placed at a right angle, the device will operate unstably.
- The absence of air valves is the cause of uneven heating and corrosion.