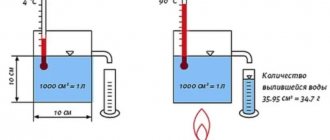
A single-circuit or double-circuit gas boiler is equipment that makes our life in a house or apartment more comfortable. Manufacturers now produce a huge range of gas appliances, differing in power, functionality, and installation method. However, even the most expensive and reliable models can fail. Agree, it’s not very pleasant to be left on a winter evening without heat and hot water.
Having analyzed the possible causes of breakdowns of gas equipment, we came to the conclusion that most often malfunctions occur due to the fact that the pressure in the expansion tank of a gas boiler or water heater is incorrectly adjusted. In this article we will figure out why an expansion tank is needed, how to pump air into it yourself and set the optimal pressure.
Is an additional expansion tank needed for a double-circuit wall-mounted boiler?
When replacing a boiler or upgrading a heating system, the owner often has the question “Do I need to install an additional expansion tank?” Let's consider some points.
The expansion tank of a heating system is a capacitive equipment designed to compensate for the expansion of the coolant due to its heating. When water is heated from 10℃ to 100℃, water increases in volume by 4.34%. If there is nowhere for it to expand and the safety valve jams, there will be an uncontrolled increase in pressure and the elements of the heating system may fail. The expansion tank receives excess coolant volume when heating and returns it back to the system when cooling. In addition to compensating for coolant expansion, expansion tanks also:
- soften pressure fluctuations within certain limits;
- protect against air entering the coolant due to pressure drop at the highest point;
- protect pumps, valves, drives from cavitation damage;
- compensate for the missing volume of coolant when removing air from the system
Diaphragm expansion tanks are needed only for closed heating systems. In an open system, the cistern is installed at a high point (often in the attic).
Standardized indicators
To understand how much the indicators deviate from the norm, you need to know the maximum permissible values for a certain type of network. In autonomous systems, the value should not exceed 1.5-2 atm. If the normalized values are exceeded, for example, up to three atmospheres, heating devices and pipelines may depressurize. All this can lead to failure of various important components and equipment.
As a rule, in autonomous circuits the pressure is maintained within 1.5 atm. When the coolant is heated, it expands. This will help increase the readings on the pressure gauge to operating values of 2 atmospheres.
To prevent the pressure from rising to critical levels during the expansion of the coolant, an expansion tank is installed in the circuit. When operating parameters are reached, excess expanded liquid enters this container. When the temperature of water decreases, it contracts. As a result, the lack of coolant is replenished by the liquid that flows back from the tank into pipelines and devices.
Expansion tank for boiler
Expansion tanks for boilers can be external or built-in.
As a rule, manufacturers build tanks into boilers with a power of up to 30-35 kW at the factory. Factory installation ensures greater reliability and compactness of the boiler unit. Usually the built-in expansion tank for a boiler is non-separable, flat, round or rectangular.
The external expansion tank is selected using special formulas (see below). They are floor-mounted and wall-mounted. As a rule, expansion machines with a volume of more than 35 liters are produced only in a floor-standing version.
Do you need an additional tank?
Modern gas wall-mounted boilers are “plug and play” equipment. They are already equipped with an expansion tank, circulation pump, three-way valve, heat exchanger, and safety group. Connect the heating, water supply, gas pipes and start the system. However, there are nuances regarding the additional expansion tank.
The factory membrane expansion tank is selected for the average parameters of a modern system. Yours may be different.
That is, you need to compare the capacity of the factory tank with the calculated value and determine whether an additional expansion tank is needed for heating.
How to calculate the required volume of the expansion tank?
The volume of the expansion tank for heating depends on three parameters:
- heating system volume
- safety valve response pressure
- minimum operating pressure
In this article we will present the easiest way to quickly select an expansion tank without complex calculations for the average one-, two-, three-story house using the REFLEX table. To determine the required volume of the tank, you need to know the volume of the heating system, the preliminary minimum operating pressure, and the response pressure of the safety valve.
The minimum operating pressure in the heating system (P0) is equal to the static pressure plus 0.2 Bar. It should not be less than 1 Bar. Static pressure can be calculated by knowing the height between the top point of the heating system and the mounting point of the expansion tank. For houses up to three floors with ceiling heights up to three meters, the static pressure will not exceed one bar. The minimum operating pressure can be taken equal to 1.2 Bar.
The response pressure of the safety valve for wall-mounted boilers in private houses is usually set at 2.5-3 Bar. Usually they focus on the maximum operating pressure of the boiler.
The volume of a heating system can be determined by summing the volumes of all its components: pipes, heat accumulator, radiators, convectors. All these parameters are indicated in product passports. If the characteristics of the system elements are unknown, but the power and type of devices are known, you can assume 8.5 l/kW for panel radiators, 13.5 l/kW for heating devices of other types. Some manufacturers recommend an average of 15 l/kW for any system.
Knowing the three above parameters from the REFLEX table, you can select the required volume of the expansion tank and understand whether you need an additional one. The volume of the built-in expansion tank can be found in the instructions for the boiler.
An example of the selection and recommendations of the REFLEX manufacturer can be seen below:
Also, many manufacturers indicate in the passport for a wall-mounted gas boiler the maximum volume of the heating system. If the volume of your system is larger, you need to calculate the required volume of the membrane tank for your system and install an additional one. The total volume of built-in and additional volumes must be no less than the calculated volume.
How to determine the required expander volume?
The volume of the expander must exceed the value of the required volume, which represents the maximum amount of coolant entering the tank as a result of its heating.
First of all, the total volume of coolant in the system is determined. By summing the internal volume of pipes and cavities of all system elements (boiler, heating radiators, shut-off valves), we obtain the total volume. The amount of liquid in pipelines can be calculated depending on the size of the pipe, using the data in Table 1. The volume of equipment cavities is indicated in the documentation (passport or manufacturer’s catalog) for the product.
Table 1 - Determination of the volume of coolant in 1 linear meter of pipeline.
Next, knowing the total amount of liquid, determine the required volume of the expander using the data in Table 2. This value is selected depending on the pressure in the system. If the previously calculated value is between two tabular ones, the required tank volume is determined by the larger of the values.
Table 2 - Determination of the required volume of the expansion tank.
The data in Table 2 is valid if water is used as a coolant. For liquids with a coefficient of thermal expansion different from water, the tabulated value of the total volume is multiplied by a correction factor equal to the ratio of the density of water and the liquid used.
Expansion tanks for gas boilers: design and pressure regulation
- Peculiarities
- How is the system structured and how does it work?
- How to control the system and work with it?
- Possible problems
- Additional Information
Heating equipment is always designed for a certain pressure and pressure in the system. Gas boilers are no exception to this rule. Expansion tanks for gas boilers help them maintain the stability of their parameters.
Peculiarities
The question of how these tanks should normally operate is related either to operational irregularities or to the need for maintenance. The main purpose of using a tank is to eliminate the expansion effect of heating water. It is getting larger, but the volume of pipes, radiators and storage tanks is finite. In closed heating circuits, 100% filling is required, and this means that the excess coolant mass must be dumped somewhere. The tank becomes a suitable place.
If suddenly there is no way out, the liquid will certainly find a path through which the excess will escape. Safety valves usually become such a place, but still this is rather an emergency equipment. Even if they work exactly as they are supposed to, you will have to remove the spilled water and refill (top up) the system. Installing tanks in advance helps prevent this from happening. And even when the coolant boils, keep everything in perfect order.
How is the system structured and how does it work?
Expansion tanks are tightly closed vessels, which are divided into two fragments using rubber membranes. This is not simple rubber, since it must withstand significant heat while remaining elastic and without losing strength.
Important: the pressure must be determined inside the air cavity entering the empty container, strictly at a temperature of 20 degrees. It is equal to the static pressure of a heating system filled to capacity. This condition makes it possible to achieve an equilibrium state of the membrane and compensate for the pressure exerted by the coolant.
That is, by the time it is put into operation, the tank will be completely empty, and its entire volume can be used to correct the thermal expansion of water or antifreeze. If the gas boiler sensor detects that the pressure in the heating system has dropped to 0.7 bar or less, it gives a command to turn off the heater. And the average value that ensures normal operation is 1.2 bar. Since moving from a non-equilibrium position to an equilibrium one, the membrane can increase the pressure further, its initial level for an empty tank is taken to be 0.3 bar (on average) higher than the standard for a heating system.
Conclusion: with a closed heating circuit with a gas boiler, the pressure should be from 0.8 to 1 bar; the parameters of any system deviating from the standards are calculated individually, taking into account:
- expected volume of water or antifreeze;
- Tank efficiency;
- its required value;
- initial pressure at start-up.
Tanks on Baxi double-circuit boilers, as follows from the instructions, must operate at a pressure of 0.5 bar. However, in reality this figure is minimal, and the same pressure of 0.8 - 1 bar allows you to guarantee the normal functioning of the device. The built-in expander with a capacity of 6 liters works stably with heating systems with a capacity of 75 liters (on water). Or 50 l (with antifreeze).
Whether it is necessary to use an additional expansion tank, or whether standard equipment is enough, is decided only by specialists at the time of preparation of the project.
Working with a storage boiler
A storage boiler is a container inside which a coil with hot coolant passes. The difference from a standard heat exchanger is in the volume and method of heating - here the liquid is static, it receives thermal energy in a constant mode.
As water is drawn, the water is replenished and heated again. At the same time, the temperature of the hot water supply is much more even, and the amount of hot water with stable parameters is much greater than that of designs with plate heat exchangers.
Most often, external drives are used, but there are dual-circuit units with built-in capacities . They are efficient, have maximum capabilities and service life.
Experts and ordinary users speak of such designs as the most preferable options.
Possible problems
It is not always possible to pump the expansion tank to the required number of atmospheres. People who strictly monitor the health of their equipment rarely encounter problems, of course. But carelessness or an irresponsible approach can lead to a number of troubles. Often the pressure gradually decreases, and after a series of boiler top-ups, the tank fails. It even goes so far that the membrane is deformed by the spool when pressed against the wall.
In this case, repair is impossible; the expander can only be replaced completely. It also happens otherwise: the pressure in the heating circuit is at the maximum permissible level, but the tank has not been serviced and remains without pressure. As soon as the heating system stops and begins to cool, the liquid will compress, making it impossible to correct the change in pressure. As a result, the boiler gets into an “accident”. Problems of this kind can be caused by prolonged use of a hot water heater or power outages.
Another likely scenario is that new water has to be supplied systematically and for no apparent reason. For example, the hot water supply circuit is working, and the pressure gauge shows a drop in pressure, the boiler stops working. Since thermal expansion is not compensated, heating of the coolant leads to the release of its excess by safety valves. If you do not notice this situation in time, you can face serious troubles. Therefore, it is necessary to pay maximum attention to the condition of the expansion tank and regularly measure the pressure inside it.
Pressure jumps - finding the causes and troubleshooting
During operation of the boiler, both surges and drops in pressure in the heating circuit may occur. Why does the water pressure fluctuate, how to fix this problem?
A fall and rise can occur for the following reasons:
- if it falls slowly over a long period of time, microcracks in the heat exchanger of the unit are most likely to blame. They appear after washing the heat exchanger to remove scale, wear, or poor quality of the metal from which it is made. It is not easy to identify microcracks, since they may not be visible externally due to the high temperature on its surface and the evaporation of escaping moisture.
If soldering is not possible or does not give a positive result, the heat exchanger will have to be replaced. In bithermic heat exchangers, cracks can occur due to water hammer when pressure rises sharply after accidents on the main line. It is almost impossible to solder it, due to its specific design, replacement is necessary.
open or leaking feed tap. In a situation where the pressure in the water supply system is higher than in the boiler, water flowing through the make-up tap increases the pressure in the system to a critical point.
Balancing (make-up) tap of the heating system
Until excess pressure is released through the safety valve. Then, when the pressure decreases, the liquid from the heating circuit pushes the water out of the water supply, and the pressure in the heating circuit Close or replace the tap.
three-way valve malfunction. The liquid to produce hot water enters the heating circuit, increasing the pressure. The valve may become clogged; if cleaning does not work, it needs to be replaced. A malfunction of the pressure gauge can cause the pressure on the gas boiler to jump. This happens when debris gets into the pipe that connects the pressure gauge to the unit.
Additional Information
The expander helps to absorb hydraulic shocks created by air pockets and sudden closure of the valve. Tanks can perform this function if they are placed on the return flow of the coolant directly in front of the boiler. Do not assume that the pressure set at the factory will be ideal for practical needs. It is reconfigured using a spool valve.
Important: any pressure gauge, when measuring pressure in the expander, registers only an excess value; to obtain an absolute figure, add 1 bar.
A pumped tank does not work well, since the air will push the coolant out. If everything is configured correctly, but the fuses continue to periodically discharge water, most likely the problem is in the expander being too small. Therefore, it is worth choosing tanks that hold 10% of the total coolant circulating in the system, or even more. Since the tank does not have fittings for pressure gauges, they must be connected to the nipple. It is located on the side opposite to the coolant-filling circuit.
Since car and bicycle pressure gauges measure pressure in MPa, you need to compare their readings with the pressure in the heating system (expressed in bar or kgf/sq. cm). One bar is equal to 100 kPa. When using a car meter, it is recommended to wait 10 minutes after turning off the boiler for the circulation to stop. When the tank is built into the boiler itself, it is necessary to shut off not only the shut-off valves, but also the coolant supply and its return. By following these recommendations, you can significantly simplify your life.
To learn how to check the serviceability of the expansion tank, see the following video.
Useful tips
It was already mentioned above that the volume of the expansion tank is equal to 10% of the volume of the entire coolant in the heating system of the house. Of course, this is an approximate figure. To accurately determine it, it is necessary to take into account a large number of various coefficients that are included in a complex formula. It will be difficult to make such a calculation on your own, if you are not a specialist. Therefore, take the above ratio as a basis.
By the way, if the safety valve trips very often, you know that you missed the volume. Most likely, you incorrectly calculated the total volume of coolant. In this case, do not rush to replace the installed expansion tank with a new one with a larger volume. You can simply insert another one next to it so that it compensates for the missing liters.
When the question arises of how to install the piping of the expansion tank, there are only two points to consider:
- The coolant must enter it from the top point.
- And leave from the very bottom.
Expansion tanks of open and closed type
This is how you can avoid mixing air with water inside the tank.
Very often, ordinary people ask why the expansion tank is boiling? There are two reasons:
- The diameter of the contour pipe is incorrectly selected. Usually a reduced diameter leads to boiling, so experts advise using pipes of at least 32 mm. But also take into account the fact of correct installation of heating radiators. They should not rupture the pipe system, but crash into it.
- Lack of slope of the contours, which we have already discussed above. Therefore, you will have to redo the heating system or install a circulation pump in it.
A few words about the pump. It was already mentioned above that open-type heating and a circulation pump are not always compatible. If you increase the volume of coolant, then a low-power pump can be inserted into the circuit. And this will solve the problem. By the way, they install it on the return circuit near the boiler. How to increase the volume of coolant? Option one is to increase the diameter of the distribution pipes. You can also increase the sections of heating radiators. In general, everything will need to be calculated and thought through. You shouldn't make hasty decisions.
Why do you need an expansion tank in a heating system?
To understand why an expansion tank is needed, you should familiarize yourself with the operating principle and main functions of such a tank. Without this information, you may mistakenly think that the item is not of particular value and is simply taking up space in the room. However, in practice, it performs a lot of important tasks and is an indispensable component of the heating system.
- 1 Expansion tank in an open system 1.1 Operating principle
- 1.2 Where to place
- 1.3 What tank volume is required
- 2.1 Design and principle of operation
Expansion tank in an open system
Due to ease of installation, affordable cost and high efficiency, the expansion tank in an open-type heating system is very popular.
The advantages of open options are as follows:
- Simplicity of design. In some cases, you do not need to purchase additional materials to install heating, and the working tank can be stored in the garage.
- Open systems do not have the problem of excess pressure, since they are connected to the atmosphere. This eliminates the need to purchase a safety valve.
- Other advantages include the ability to use a tank for air removal.
In addition to the advantages, an open system also has disadvantages. First of all, this is the need to install the tank at the highest point. To do this, it is important to take care of good insulation of the attic floor, otherwise the liquid in the tank will freeze at subzero temperatures.
Principle of operation
To understand why an expansion tank is needed, you should evaluate its performance characteristics, the specifics of its operation and the subtleties of self-installation. In liquid heating systems, water plays the role of coolant.
With the help of special equipment, it moves over long distances and provides full heating of buildings with different number of floors and area. This contributes to an increase in demand for the installation of water systems.
The key advantage of open systems is the ability to operate without pumping devices. The movement of the coolant is carried out according to thermodynamic principles, since hot and cold water have different densities, and the pipes are located at an angle.
The purpose of the expansion tank for heating is to automatically stabilize the liquid pressure and store the remaining heated water.
The tank is mounted above the other components, and the principle of its operation consists of the following stages:
- innings. The heated coolant moves from the electric, solid fuel or gas boiler to the radiators;
- return The remaining warm water enters the tank, begins to cool and returns back to the boiler unit. As a result, the cycle repeats.
If the system is equipped with a single-pipe line, both procedures occur in one pipe. In two-pipe types they are independent.
Where to place
Since the circuit of an open heating system is closed, but not isolated from outside air and not sealed, the problem of excess pressure is eliminated. In this case, the expansion tank must be installed in the correct place - above all other components. If you do not take this rule into account, the coolant will simply pour out.
An even higher placement promotes efficient air removal. The liquid always contains dissolved air, which can turn into a gas and enter into a chemical reaction with metal surfaces in pipes and the heat exchanger.
In some cases, open tanks are combined with a return line, which is due to design features or other layout considerations.
However, they remain at the highest point of the circuit to which the pipe is connected. With this installation, you will need to install special valves for venting gases.
Operating principle of a boiler with a flow-through heater
In this case, we mean a plate heat exchanger, although the bithermal design is flow-through. The plate heat exchanger has high efficiency, but relatively low productivity.
The principle of its operation is to pass two flows in a perpendicular direction between a pack of metal plates connected in such a way that the flows do not mix. The large area of the plates ensures high heat transfer efficiency, which allows you to prepare hot water in flow mode, i.e. on the run.
With its small size, this device raises the cold water temperature to 50° and above, which only a highly efficient device can do.
At the exit from the primary heat exchanger, the hot coolant is passed through a secondary heat exchanger . At the same time, a stream of water flows through it, which receives a given temperature and enters the water tapping devices.
IMPORTANT!
The only disadvantages of such devices are the instability of the heating mode, which depends on the speed of water passage, and the need for periodic cleaning of lime deposits.
Expansion tank for closed heating
The main advantage of a tank for a closed heating system is its compact size and the ability to be installed on any part of the circuit.
When installed in accordance with approved standards, there are no clear restrictions on the choice of installation location. However, in many designs the reservoir is located near the pump.
Due to the tightness of the tank, the pressure inside the circuits can increase to a high level. To protect the structure, it is important to provide a “safety group”.
It consists of the following nodes:
- Safety valve with a specified upper pressure threshold.
- Air vent with automation support.
- Pressure gauge or pressure gauge with thermometer for performing control and measurement tasks.
However, the need to organize a “security group” is not a minus, since it is explained by the specifics of the system.
Design and principle of operation
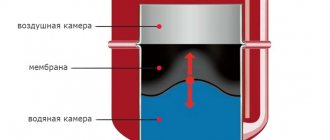
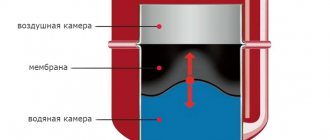
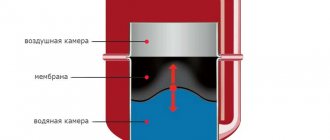
To determine which expansion tank is needed for heating, you should study the structure and operating principle of structures for a closed heating system. The design of such a tank is quite simple. Depending on the model, it may differ slightly, but the specifics of the operation remain the same. It involves separating a hermetically sealed liquid into 2 chambers using a special elastic partition. One part is connected via a pipe to the system circuit and is called the water part. The second (air) is intended to organize optimal pressure.
The design of the tank provides for the following components:
- Tank body.
- Threaded pipe.
- Nipple or spool.
- Membrane.
- Water and air chambers.
In most cases, a prefabricated stamped cylindrical structure is used as the body (other options are available on the market).
The inner surface of the walls has a protective coating against corrosion and an enamel layer. The body color is red, since stores also offer hydraulic accumulator tanks, which are distinguished by their blue color, indicating the impossibility of working with hot liquid.
On the tank there is a threaded pipe for connecting the tank to the heating circuit. Leading manufacturers supply fittings and an American union nut complete with the tank, which simplifies the installation process.
On the opposite side of the body there is a nipple or spool, reminiscent of a bicycle valve. It is used to pump up the pressure in the air chamber.
The next important component is the membrane, which divides the internal volume of the tank into 2 separate parts. In some cases, an additional membrane tank is installed, which is activated when the main membrane fails. According to this principle, an expansion membrane tank is required.
To manufacture this part, elastic materials with a minimum diffusion rate are used. For a long time, rubber played their role, but due to its fragility, it lost its popularity. In modern devices, it is customary to fix ethylene-propylene or butyl elements.
The role of the air chamber is to create excess pressure, which pushes the membrane down and ensures the minimum volume of the water chamber until it is completely filled.
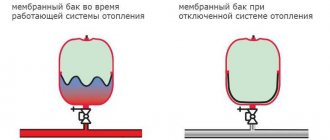
When the system is filled with liquid and put into operation, the circuit builds up pressure, and the surface of the membrane begins to bend - this indicates an increase in the volume of the water chamber.
Depending on the heating intensity, the degree of expansion may vary. Excess coolant moves into the water chamber of the tank, where it cools down, acquires its previous volume, and the membrane is pressed down. As a result of such actions, an optimal pressure balance is ensured.
Often the membrane may have an unconventional shape. Thus, balloon-type tanks are available for sale, where it is an elastic cylinder with hermetically sealed edges.
This tank acts as a water chamber, and the remaining space is used as an air chamber with a given pressure. If the liquid expands, the walls of the membrane begin to stretch, and it becomes like a pear. In this case, the volume of the air chambers decreases, and the pressure values continue to increase.
What volume should the expansion tank have in a closed heating system?
On the market you can find whole series of tanks with different working volumes. To find the most optimal option, you need to carry out some calculations using the following formula: Vb = Vc × k / D.
The value Vb indicates the minimum volume of the tank, Vc indicates the total volume of the heating system, and k is an indicator of the coefficient of expansion of the liquid.
D is the tank efficiency coefficient, which can be determined using the following formula: D = (1m - Qb)/(Qm + 1).
Qm is the upper indicator of the permissible pressure in the heating system and determines the actuation force of the valve from the “safety group”.
Qb indicates the pre-created pressure in the air-type chamber. If there is built-in paging, a similar indicator will be indicated in the technical documentation. Sometimes the pressure level is regulated by a car pump with a pressure gauge.
To simplify the process of calculating volume, you can use special online calculators.
Signs that your blood pressure needs to be increased
During operation, the boiler must be under a certain excess pressure in the expansion tank. The user of this equipment is required to monitor this pressure, shown on the pressure gauge, which is located on the boiler itself. If the equipment is assembled correctly and there are no leaks, the pressure indicator should not drop. But sometimes, after a year or two years of operation of the boiler, the pressure in the boiler may drop or even the pressure may jump during the operation of the boiler when the burner starts working. Most often, in the absence of a visible leak, the cause of this behavior is an empty expansion tank.
A typical expansion tank used in boilers. Installed either at the back or side of the boiler
The pressure in the tank refers to the initial coefficient showing the pressure of the chamber with air in an empty tank at the temperature in the room. This pressure must fully correspond to the degree of static heating pressure after it is filled with coolant. This will provide the membrane with a state of equilibrium. The pressure level in the coolant will be compensated due to the gas pressure in the air chamber. In this case, the volume of the tank is not completely filled, so this volume will be sufficient to cover the liquid level, depending on thermal expansion.
The static pressure of 1 m of water column is approximately 0.1 atmospheres. It follows from this that the indicator of this pressure in the heating of an apartment or house will be less than 1 atmosphere.
In order for a gas boiler to operate stably and correctly, it is necessary that the coolant pressure level in a closed system is not less than the value specified in the boiler’s operating instructions.
During operation, it is necessary to check the pressure of the expansion tank and set its value corresponding to that specified in the instructions for use. One of the indicators of a devastated bank will be pressure surges. During operation of the boiler, the pressure begins to increase, and the boiler safety valve is triggered. A reset occurs and after the burner turns off, the pressure begins to drop to almost zero. When you try to fill or refuel the boiler, the pressure readings on the pressure gauge return to normal. But the next time the burner is turned on, when heating begins to occur, the pressure readings jump again. As a result, the safety valve is triggered again.
When checking the pressure in the tank, it is necessary to drain the water from the boiler. The heating circuit should be closed and the cold water supply should be closed. Water must be discharged through a special discharge device, using some kind of container for this. Connect the hose to the drain fitting. Using a 13mm wrench, unscrew the nut that secures the fitting. After this, the water gradually begins to drain from the boiler, as a result of which the pressure begins to decrease. Drain the water completely until the needle on the pressure gauge drops to 0.
To check the pressure in the expansion tank, you can use a tire pressure gauge, which is used to check the tire pressure in a car. Usually in boilers the expansion tank is installed in such a way that it is not even necessary to remove the lid from the boiler in order to pump it up. The tank is most often located behind the combustion chamber and installed on the rear wall of the boiler. In order to get to it, we find the Schrader valve, closed with a cap, and remove it. Using a tire pressure gauge, we check the pressure in the expansion tank. The lack of pressure in the expansion tank explains the jumps in pressure readings in the boiler. Therefore, it is necessary to pump up the pressure in the expansion tank
Heating expansion tank
The expansion tank in double-circuit gas boilers has a volume of 6-8 liters. As a rule, this is enough for its operation under normal conditions. But if you have a large heated area, there are a lot of radiators, and they are also non-standard; more liquid is required to fill them. It happens that the volume of the tank installed in a gas heater may not be enough.
In this case, excess heated water will fill the expansion tank completely, but the pressure in the batteries will still increase, since there is a lot of liquid. Then there will be an emergency release from the boiler until the pressure in the radiators stabilizes.
Then, when the temperature drops and the liquid cools, it will come out of the tank. But since an emergency release has occurred, the pressure will drop to a level at which the boiler will not be able to automatically start working. If you do not replenish the heating system with water in time, and the outside temperature is low, it may defrost and be destroyed.
To prevent such a negative scenario from happening, an additional expansion tank for heating is installed in the system. In the event that water fills a standard tank installed in the boiler, there will be no emergency discharge; now the liquid will go into an additional container and then return to the radiators. Thus, the volume of liquid in the system will be constant.
EXPANSION TANK FOR HEATING
1. Turn off the double-circuit boiler from the network.
2. Close the water supply taps to the heating device.
3. Let's drain the water from the batteries.
4. Let's prepare the expansion tank for heating for operation. Our system is assembled from polypropylene pipes. Accordingly, to connect it, you will need a device for soldering them and several corners, couplings and fittings. So that later you can remove the container for repair or replacement, we use a special fitting, the so-called “American”.
5. Having made sure that there is no water in the heating system, we proceed to the installation of polypropylene pipes.
Let's turn on the polypropylene soldering machine and set it to the desired temperature.
6. Connect the tank by screwing the “American” on it. We will install it on the floor, in a corner, near a wall, so that there is easy access to it.
7. While there is no liquid in the pipes, unscrew the coarse water filter and rinse it.
8. At the same time, we will replace the cartridge in the main filter, which is installed immediately after the water supply pumping station.
9. Having installed everything in place, open the liquid supply taps and fill the radiators until the pressure is 1.2-1.3 kPa.
10. Let's bleed the air from the pipes and close the Mayevsky taps.
11. Turn on the boiler and heat the room.
The tank is set to a working pressure of 1.8 kPa. If it increases in the system and exceeds the value of 1.8, the tank valve will open and excess water will flow into it, and, conversely, when the pressure decreases, water will flow into the batteries. Thus, we ensured stable operation of the system by installing an additional expansion tank for heating.
Checking the operation of the tank is very simple. Let's pump it up with air to a pressure of 1.6 atm and provide access to the nipple. Let's turn on the gas boiler. Let's bring the pressure in the heating system to 1.5 Atm. Using the nipple, we will begin to bleed air from the tank. As soon as it drops below 1.5 Atm, water from the system will begin to flow into the tank, and the needle on the boiler pressure gauge will begin to fall. This means that the expansion tank is working and connected correctly.
If you liked the article, share it on social networks.
Setting principles
When the hydraulic tank is properly pumped, the pressure gauge needle shows smooth development. If jumps appear, additional adjustment is needed. Without this, the network will not work productively.
The gas pressure in the expansion tank is calculated using any of these methods:
- The pressure gauge is located on the outside of the unit. The device displays the required data. You can verify their objectivity by first blocking the valves (this will disconnect the tank from the water supply network). After 10 minutes, air is released into it and immediately released. At this moment, watch the pressure gauge needle. It should move smoothly - this is a sign of correct settings.
- There is no pressure gauge on the tank. A portable version with a similar connector to the container outlet valve in the upper sector is used, put on and tightly secured here. The valve opens and the pressure gauge synchronizes with the hydraulic tank and displays the current pressure in it.
In the case of extremely high pressure levels in the tank, its compensating characteristics do not work, and the integrity of the system components is on the verge of failure. Excess air appears, and pipes and radiators are under enormous stress.
If its parameters are low, the water level displaces the membrane, and the entire tank is filled with HP and gradually expands here. The safety valve reacts to this and the DHW mechanism is turned off.
To avoid these difficulties, optimal parameters are determined and excess air is removed. All actions are performed with a cold network, and 0.2 atm is added to the initial figure.
The statistical head is determined by dividing by 10 from the height of the building. For example, it is 9 m in a house, then the arithmetic turns out like this: 9: 10 + 0.2 atm. To correct these data, air is systematically introduced into the hydraulic tank (to raise the parameter) or removed from it (to lower the number) through a special spool.