Of all the heating methods that exist today, air heating is considered the rarest. Despite the fact that 50-70 years ago these heating systems were popular and were installed en masse, today it is quite difficult to find such objects. The exceptions are fireplaces and traditional Russian stoves, which are not full-fledged air heating systems.
Of all the equipment and devices that work on the same principle, we are most familiar with heat guns, fan heaters and convectors. Heating, where the main emphasis is on solid fuel boilers, provides air heating today and is used in rare cases. Let's look at the reasons why air heating today is not as popular as other types of heating. Let's understand the principle of operation of an air heating device that runs on solid fuel.
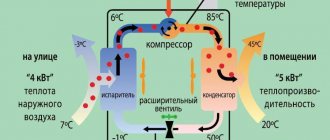
Application of ducted air conditioners and heat pumps
Electric air heating is often supplemented with such elements as:
- multifunctional air conditioners that can both cool and dry the air and operate for heating;
- anti-dust filters;
- ultraviolet radiation filters that disinfect incoming air;
- supply and exhaust ventilation systems.
In such systems, it is electricity that is used as a heat source. Judging by numerous reviews, heating with air conditioning is easy to use and can provide comfortable living conditions. Control is carried out by one block, which sets all the necessary parameters.
If we compare this scheme with a system that includes a gas boiler for air heating, a whole network of air ducts and ventilation fans, then the first one looks more modern and thoughtful.
Due to the fact that the installation of visible heating devices (radiators and pipelines) is not required, air heating does not create obstacles to interior design. Nothing will be visible anywhere except the ventilation grilles.
Among the disadvantages of the described air heating scheme is the high cost of the equipment. Duct air conditioners, even of low power, will be quite expensive.
In addition, there are some restrictions on the operating conditions of the external unit of the air conditioner - it is not designed for temperatures below -15 ℃ - -25 ℃, otherwise the efficiency of the equipment is reduced.
An alternative solution for use in particularly cold regions could be a geothermal heat pump. Whatever the ambient temperature, below the freezing level, the soil temperature always remains at 8-12 ℃. If you deepen a heat exchanger of sufficient area into the ground, you can obtain a constant source of thermal energy and use it to heat your house.
Air heating options
So, our task is to heat the air masses and supply them to the premises of a country cottage or apartment. How to organize air heating:
- From the fireplace, wood stove.
- Use VRF systems using freon. Simply put, inverter air conditioners, air source heat pumps.
- Install a combined boiler + chiller + fan coil air conditioning system.
- Organize centralized air heating (abbreviated as VO), combined with ventilation of a private house. Use an electric heater or a gas air-heating furnace as a heat source.
A veranda with a large glass area can be conveniently heated with hot air supplied from the floor
Reference. The latter option is often implemented in American and Canadian cottages built using frame technology. The heater is a gas oven.
For heating/cooling large production workshops, a slightly different scheme is implemented. There are 2 networks of air ducts built in the premises - supply and exhaust. Both converge to a ventilation unit - a central air conditioner, consisting of the following blocks:
- 2-3-stage filters purify air masses before being supplied inside the building and emitted outside;
- heat exchanger-heater No. 1 heats the flow using hot water from the boiler room;
- heat exchanger No. 2 serves to cool the air and works in conjunction with a chiller;
- a plate cross (or rotary) recuperator removes heat from the exhaust flow and transfers it to the supply flow, saving 50...80% of energy;
- humidification unit;
- Centrifugal fans force flows through sections of the central air conditioner and further along the air ducts.
Why did we describe the design of an industrial climate control system? So that you immediately understand: installing full-fledged air heating + ventilation + cooling is not an easy and expensive task. But, as the owner of a country house, you can consider all heating methods, choose the simplest and cheapest, or return to the water scheme - heated floors, radiators.
Industrial series heating system running on natural gas
Direct air heaters
Direct air heaters are based on the principle of heating a room with red-hot porous ceramic tiles emitting infrared radiation, in the depths of which natural gas is burned. These are nothing more than gas fireplaces, near which it is pleasant to spend time, basking in the flow of radiant energy. Usually these are relatively inexpensive devices with a power of 3-4 kW, the production of which has been mastered by some manufacturers of heating devices (about the selection and placement of heating devices).
The biggest disadvantage of heating devices of this type is that oxygen “burns out” in heated rooms, and gas combustion products remain in the room. Therefore, such devices serve more for decorative purposes and cannot be recommended as the main source of heat.
Indirect air heaters
The above disadvantages can be partially or completely avoided by using indirect air heaters. This equipment is a convective-radial heat exchanger and heat exchangers with a built-in combustion chamber. When heated, the air becomes lighter and rises, and in its place comes cold air, which heats up, etc. (picture 1). Thus, the idea of a convector that warms a room without using forced air circulation devices arose.
Figure 1. Convector air exchange in the room: 1 - convector; (+) - warm air; (+/-) — cooling air; (-) - cold air.
Gas convectors and heaters
Gas convectors are independent heating equipment that represents a real alternative to traditional heating devices. They provide not only the ability to maintain a set temperature in the range from 8 to 33°C in a heated room, but also allow you to set different temperatures in different rooms.
We recommend: Do-it-yourself biogas plant: diagrams, projects, 130 photos and video description of the operating principle
Convectors operate on the principle of burning natural gas in a metal heat exchanger, which ensures highly efficient heat transfer to the room. At the same time, combustion products are removed outside and combustion air is taken in. This ensures the environmental cleanliness of the room and its effective ventilation. Compared to a traditional heating system, which requires boilers, radiators, room piping, fittings, pumps and other components, when using convectors, all this equipment is not required, since there is no water circuit. It is this feature of gas convectors that allows them to be used for efficient heating of country houses, cottages, garages, greenhouses, etc. The gas-air mixture in these devices is ignited either by a spark from the electronic unit or by the wick of the pilot burner, which, in turn, ignites when the button of the built-in “piezo lighter” is pressed. In the latter case, no electrical energy supply is required.
Duct air heating
In the practice of cottage construction in regions with cold and temperate climates, ducted air heating systems have been widely used (Figure 2). This system allows you to heat the premises of the house with warm air supplied through special channels without traditional pipelines and radiators. The advantages of this method over traditional ones are the low inversion of the system, which allows you to raise the temperature in the house from -10 to +22°C in 35 - 40 minutes.
Figure 2. Scheme of air heating of a house: 1 - stove; 2 - filters; 3 - air intake pipe from the premises; 4 — fresh air intake; 5 — fresh air supply pipe; 6 — supply of warm air to the premises; 7 - air intake from premises; 8 - chimney.
After quickly warming up the premises, the automation switches on, allowing you to maintain the temperature at a given level. The advantages of air heating systems include:
- uniform heating of the room throughout the entire volume with a slight “pressure” of air, which completely eliminates drafts and the possibility of penetration of street dust;
- the ability to ventilate rooms, filter heated air to eliminate odors, germs and other foreign matter;
- low operating costs, allowing to increase efficiency up to 93%;
- ability to work in economical mode.
Gas or liquid heaters with safety automatics are used as heat generators. If the house is well thermally insulated, the heater is turned on 3-4 times a day to maintain the set temperature, which saves fuel and, consequently, money for heating residential premises. For example, to heat a small country house, one cylinder of liquefied gas is enough for about 8 - 12 days.
In almost all heating systems, the heat generated by the heat generator is transferred to the consumer by air. Even in a water heating system, water acts only as an intermediate coolant, and the final distribution of heat from the radiators still remains with the air. The only exceptions are heating devices from which heat is transferred by radiation - open fireplaces, infrared emitters, etc. But they play a limited role in heating residential buildings in our country.
The air is heated on heat-releasing surfaces (the surfaces of water heating radiators, convective-type electric heaters, “mirrors” of stoves, etc.) and enters the heated room, where it cools, giving off heat to walls, ceilings, and pieces of furniture. After this, the air should heat up again. This air circulation can occur under the influence of natural forces (warm air is lighter and therefore rises) or forcefully - due to a fan. In the future, we will use the term convection heating (by the way, here is general information about heating) for systems with natural air circulation and air heating (AH) for systems with forced air circulation.
This definition of VO is not generally accepted. A heating system is often called air-based if there is a system of air ducts for distributing heated air from a heat generator (without a fan). Wood-burning stoves such as “Buleryan” and “Professor Butakov” also fall under this definition, since they have the ability to connect air ducts and distribute warm air to other rooms due to convection.
Based on our definitions, these ovens should be classified as convection-type systems.
VO systems can be divided into two types - channel and local. Ducted systems require a system of air ducts, both supply and return. For local systems, air ducts are usually not needed. The simplest local heating systems are fan heaters and heat guns.
Figure 3. Direct heating heat exchanger: 1-hot air; 2- heat exchanger; 3-fan; 4-cold air; 5-burner; 6-chimney.
Figure 4. Indirect heating heat exchanger: 1 - hot air; 2 - heat exchanger; 3 - fan; 4 - cold air; 5 - burner; 6 - intermediate coolant circuit; 7-chimney.
How to organize stove heating
An important advantage of any stove: it simultaneously heats the air and surrounding surfaces with intense infrared radiation. No batteries or coolant pipes are needed.
Clarification. Stoves or fireplace inserts with a water circuit can be used to heat 2-3 small rooms. The coil is connected to a gravity or closed system with a pump.
How to use a stove for pure air heating:
- For 1 room it is enough to install a cast iron or steel potbelly stove.
- To heat 2–3 rooms with a total area of up to 40 m², place a brick stove of a suitable design in the wall between the rooms.
- It is not easy to build a stove in a lived-in house. If there are no high aesthetic requirements, we install a potbelly stove, attach convection casings to the firebox and connect air ducts.
Cast iron stove with air pipes and a ceramic heat accumulator on the chimney
Option No. 3 involves laying air ducts into adjacent rooms and installing duct fans that can withstand the temperature of the moving medium 100–150 °C. Air can move through the pipes on its own, but too slowly, and the ventilation duct must slope upward. How such an air heating system works, see the video below.
The first two options are well known, but not always applicable:
- It is generally unrealistic to install a stove in an apartment;
- even a large Russian stove is not able to cover an area of more than 50 square meters (on one floor), so it is suitable for heating a dacha or a small house;
- the foundation plus a brick stove-fireplace is erected during the construction or major renovation of the building;
- a metal potbelly stove takes up space and is dangerous for small children (in terms of burns).
You can install an iron stove with your own hands - this is a tangible plus. But you will also have to heat it, which results in a lot of inconveniences: frequent loading, the smell of firewood and smoke in living rooms, dust. The author of the video acted wisely by placing the potbelly stove in a separate furnace room. We do not recommend repeating one thing after the home craftsman - installing air ducts made of aluminum corrugations. Such pipes create high aerodynamic resistance and greatly slow down the flow. It is better to use galvanized boxes.
We recommend: Pandora's Box - Engine on water or What is Brown's gas?
Preliminary conclusion. Solid fuel stoves are a budget option for air heating with their own advantages and disadvantages. Suitable for small buildings - country houses, garages, greenhouses.
Application of air conditioners and heat pumps
As you know, modern split systems are able to operate in heating mode, consuming three times less electricity than a conventional electric boiler of the same power. Hence, a completely workable solution is to buy and install an inverter air conditioner in each room.
Reference. Why an inverter? The compressor in such “splits” does not stop, and therefore does not freeze in the cold. The air conditioner successfully heats the air down to -5 °C outside, after which the efficiency noticeably decreases.
The advantages of this scheme are obvious:
- lack of batteries, pipes, boilers and other heating equipment;
- relative ease of installation;
- aesthetic appearance of the indoor unit;
- cooling mode in summer;
- Possibility of installation in apartments.
The air-conditioned heating method is viable in the southern regions, where the temperature rarely drops below -15 °C. To the north, “splits” are used only during the transition period – in spring and autumn.
Other disadvantages of heating with a split system:
- Air conditioners will have to be installed in all rooms, which is unacceptable for cottages of 2–3 floors. A multi-split VRF system will cost more than the same number of single coolers/heaters.
- The device “can” clean, dry and change the temperature of the air flow. Rare models are designed to mix in outside air. This means that you will have to do separate ventilation.
- When the external unit of the air conditioner is operating, the distinct noise of the fan and the hum of the compressor can be heard from behind the wall.
The problem of efficiency at low temperatures is solved by an “air vent” heat pump, whose performance remains intact down to -30 degrees below zero. The design and operating principle are identical to the split system, the differences being the larger size and price. If the external unit is installed on the ground and carried 2-3 m from the building, the noise of the unit will become inaudible.
Brief conclusion. VRF systems are good for apartments and small houses located in the southern regions. Heat pumps can also be installed in northern latitudes, but the cost of the equipment plays a role here. If desired, you can install the air conditioner yourself.
Combined multi-zone systems
In this case, the coolant is still used, which is why the system is called combined. How this equipment works:
- Each room has an air heating/cooling unit - a four-pipe fan coil unit that looks like an indoor air conditioner unit.
- One pair of pipes supplies the units with coolant from the boiler. Hot water passes through a heat exchanger blown by a fan, causing the room air to heat up.
- When it is necessary to switch to cooling, the automation switches the fan coil to the second pair of pipes supplying cold water from the chiller.
- Users in rooms can set different air temperatures, but they cannot turn on cooling and heating at the same time. Hence the second name of the air conditioning system – multi-zone.
Note. Chiller is a type of refrigeration machine designed to cool liquid. Usually located on the street under a canopy or in an open place (depending on the design).
Various fan coil units are used inside the building - wall-mounted, duct-mounted, floor-mounted, ceiling-mounted. It all depends on the wishes of the homeowner and aesthetic requirements. Duct-type units can be built inside ventilation ducts to heat/cool the supply air.
Connection diagram of a cassette, duct and floor fan coil to a chiller and boiler
Advantages of multi-zone air systems:
- applicable in large buildings with 20 or more rooms - administrative and residential buildings, warehouses, and so on;
- can work in conjunction with forced ventilation of the cottage;
- any heat generator is used for air heating - a boiler using solid fuel, gas, electricity, diesel fuel;
- pipes with coolant (coolant) take up little space, air units are easily built into the ceiling, hung on the wall or hidden behind the cladding;
- closed terraces with stained-glass windows covering the entire wall are heated by in-floor convectors or wall-mounted fan coil units;
- possibility of adjusting the temperature in individual rooms, remote control.
We believe that the boiler + fan coil + chiller scheme is the most universal and successful from the point of view of aesthetics and operation. Of course, you can’t do this type of air heating yourself; this is a minus. It is necessary to make calculations, select equipment, install, adjust... without knowing the basics, it is extremely difficult to carry out these works.
Let's list other negative points:
- high price of air conditioning units;
- the boiler and chiller are quite large devices, occupying 2–3 m² of area;
- the operation of the system depends entirely on electricity; when the lights are turned off, the heat supply will stop.
Conclusion. A multi-zone combined scheme is the best way to air-heat a home. But implementation will require significant investments.
Heating combined with ventilation
This is a classic method of heating buildings with air, used in enterprises since the last century. Subsequently, manufacturers began to produce small-sized analogues of industrial ventilation units installed in private homes. Thanks to less stringent requirements for air purity, the treatment scheme has also been simplified.
Let us explain the principle of operation of the “ventilation + heating” system step by step:
- The heat source is a stove, usually a gas one. A burner, an air heat exchanger, a fan and an electronic control unit are installed inside.
- The first network of ducts radiates from the furnace, distributing heated air throughout the rooms. With the help of diffusers, grilles and other supply devices, jets are supplied to the premises (usually to the upper zone).
- The second network of channels collects polluted/cooled air from the lower zone of the rooms into a common collector connected to the stove from below.
- Having passed through the collector, the exhaust air masses are cleaned in a mesh or cell filter, then sent to a heat exchanger, where they are heated by a burner.
- Electronics monitor the safe operation of the gas air heater, maintain the outlet temperature, and signal when the filters are dirty.
Typical air heating circuit with recirculation. The heater is a furnace and an air conditioner with a ducted indoor unit
Addition. Since the heater dries the air, an automatic humidifier with an electronic hygrometer is usually installed on the supply duct. The latter is located on the return air duct to measure the humidity of the flow.
The air heating stove is a rather noisy unit, so it is installed in a separate room. Combustion products are removed through a conventional or coaxial chimney (depending on the design of the heater). Air ducts made of galvanized steel are laid in several ways:
- in the basement or ground floor;
- hide in floors and wooden ceilings;
- in the attic;
- vertical channels run along the walls and are covered with facing materials.
Large ventilation ducts are laid under plasterboard finishing
The supply air temperature reaches 40...45 °C, the speed of movement through the ventilation ducts is 4-5 m/s. You can't go any faster; there will be additional noise. In this situation, the diameter of the main collector reaches 300 mm, we took a typical flow rate of 1000 m³/h, although it can be more.
We recommend: Geothermal heating: what is it, the principle of operation of the system and options for a private home using the heat of the earth, reviews from owners
A logical question: why heat air masses to 40 °C if 22 degrees is sufficient in the house? We answer: the heating system must compensate for 2 types of heat loss - through building structures and energy consumption for heating the inflow, since ventilation is needed in any case. Accordingly, we bring the air to a temperature of 20–24 °C (compensating for losses at home), then overheat it to 40…45 °C.
Conclusion. The “ventilation + heating” scheme is the most cumbersome and expensive. The building must be prepared in advance - even at the design stage, otherwise the air ducts will go directly through the rooms. Operating efficiency is highly dependent on the way the building is ventilated, which we will discuss next.
Features of carrying out competent calculations
Despite the assurances of would-be experts, it is very difficult to independently calculate air heating. Only specialists can do this task.
The customer can only check the availability of all project items, which include:
- Determination of heat losses for each heated room.
- Type of heating equipment indicating the required power, which should be calculated based on actual heat loss.
- The required amount of heated air, taking into account the power of the selected heating device.
- Required cross-section of air ducts, their length, etc.
These are the main points for calculating the heating system. It would be right to order a project from specialists. As a result, the customer will receive several calculation options from which he can choose and implement the solution he likes best.
An air heating system is a complex structure consisting of many elements. To calculate it, it is better to involve professionals; to familiarize yourself with the components, it is worth studying the diagram in detail (+)
Installation standards
The installation conditions for VK are simple, but for specialists, there are many nuances that need to be known so that the user is not disappointed in choosing an air-heating boiler.
Features of VK installation:
- The boiler is installed indoors during the construction of the building.
- Specialists must first complete an installation project, taking into account the actual heating and structural characteristics of the building, in accordance with which the main and auxiliary equipment will be selected.
- The system must be equipped with a backup power source.
- To increase efficiency, the boiler should be installed in a room with well-insulated walls.
- The combustion room must have a good ventilation system for ventilation.
- Air ducts make sense if you are installing them in multi-level houses with an area of more than 100 m2.
To select a VC you will need the following data:
- AC power taking into account heat losses in the building;
- the rate at which heated air enters the room;
- technical data of the air duct system;
- VK installation location.
If installing a boiler seems to be a difficult and impossible task for consumers, it is better to entrust it to a company that will perform the entire set of installation and adjustment work for the home heating system; in this case, inconsistencies can be avoided and reliable and safe operation of the equipment can be ensured for many years.
Furnace structure
Today, the most popular among consumers are the air-heating boilers of Professor Butakov, which have a wide range of applications: private residential sector, garages, greenhouses, industrial warehouses and basements.
What units does the boiler consist of? Photo source: paliwadrzewne.pl
The main structural parts of a typical hot water boiler:
- Lower drawer for collecting ash and regulating the amount of air entering the firebox.
- The door with a handle located above the ash pan may have a heat-resistant glass window.
- The combustion chamber and its volume affect the amount of loaded fuel and operating time.
- A cast iron grate is located under the chamber. The sides of the chamber are covered with convection pipes crossing at the top.
- A chimney with a damper to regulate the speed of flue gases and the intensity of draft.
- In some VK models, an additional afterburner chamber with two nozzles for supplying oxygen is located at the top. It burns the gas that is formed during smoldering.
The long-burning air-heating boiler is equipped with all the necessary automation devices, complete with temperature sensors and electronic control units. An automated fuel supply system and an increased volume of the combustion chamber allow the boiler to operate practically without human presence.
Advantages of an air heating system
The undeniable advantages of a system using boilers of the described type include:
- Low rate of inertia of the system - heating of the premises to a comfortable temperature occurs within an hour. It is also possible to use “standby” heating - when there are no people in the premises, the temperature decreases. This makes it possible to save up to half of all energy resources;
- The combination of several functions in one system - heating, air conditioning, ventilation, air humidification and air purification;
- The fact that there is no water in the system as an intermediate coolant allows us to say that the system is not afraid of defrosting under any circumstances;
- Cost-effectiveness of the system - capital cost savings occur due to reduced costs for the system installation process. Air systems are much less metal intensive than water systems, for example. Operating costs are saved due to the rational operation of the system (low inertia and “standby” heating mode).
Design Features
Gas-generating stoves can be installed in residential premises.
Long-burning gas generator stoves will heat a solid fuel boiler with the same operating principle. However, the first ones are distinguished by a simple design that vaguely resembles potbelly stoves. At the same time, unlike a potbelly stove, the operation of the stove is easy to control. The basis of any gas-generating heating equipment is the pyrolysis process.
In this case, we are talking about the release of gas from the fuel with a large percentage of heat capacity. When it is burned, several times more thermal energy is released compared to conventional wood burning. As a result, with one stack of wood, relying on the pyrolysis effect, it is possible to heat a significantly larger area of the room. The release of gas from the energy carrier occurs in a special chamber at high temperatures and in conditions of insufficient oxygen. The resulting fuel was previously discharged along with combustion products outside. Now it enters the upper chamber of the equipment, where its oxidation ends, followed by the release of a large amount of heat.
Long-burning air-heating furnaces have the following schematic structure:
- body made of thick steel or cast iron;
- convection jacket;
- combustion or primary chamber;
- secondary chamber or gas afterburning chamber;
- ash pan;
- chimney;
- draft regulator;
- secondary air supply pipe.
Long-burning air-heating stoves can change their appearance and structure depending on the configuration and model. However, they all have a similar operating principle. So, first comes the laying of the energy carrier. This can be regular firewood, pellets, seed husks, straw and other solid organic products. They also read about types of fuel for long-burning stoves.
Coal and coke are not suitable for long-burning steel furnaces. As a result of their combustion, the temperature of the heating equipment rises to a critical limit. This may lead to an accident.
Next, the usual combustion reaction occurs in the primary chamber with a sufficient amount of oxygen. Then the equipment goes into long-term combustion mode, that is, the temperature in the chamber drops. Oxygen is not supplied there in full. As a result, the firewood stops burning and simply smolders. Of them
A gas generator stove can be installed anywhere, as long as there is a chimney.
gas is released. It enters the secondary chamber. Secondary, heated air is supplied there. The gas ignites, releasing a large amount of heat.
Economical long-burning stoves heat the room as follows:
- infrared radiation from a hot body;
- warm air currents that pass through the convection jacket;
- distribution of thermal air into adjacent rooms through air ducts connected to the stove.
Today you can find equipment on sale that can service the DHW circuit and allow you to cook food. In the first case, the device is additionally equipped with a heat exchanger, in the second - with a frying surface.
Advantages and disadvantages of equipment
Economical long-burning stoves have received special attention from consumers due to a number of positive characteristics:
- The efficiency of the device can reach 80-85%;
- one stack of firewood burns for 8-10 hours;
- it is possible to purchase completely energy-independent models;
- modern devices are equipped with a combustion control function;
- multifunctionality;
- durability;
- ease of use;
- affordable price;
- depending on the power, you can heat a room with an area of 40 sq. m. - 500 sq. m.
There are also disadvantages:
- You can only use fuel with a low percentage of moisture content, up to 20%;
- condensation formation;
- non-compliance with the operating rules of the equipment leads to the formation of soot accumulations on the chimney, which makes it difficult to clean;
- regular chimney cleaning;
- condensation leaking onto the floor.
If you strictly follow the rules for operating the equipment specified in the instructions, using the stoves will not create much trouble.
How much time and money do you need to spend to make solid fuel heating boilers with your own hands at home?
What components are needed to install a solid fuel boiler for water heating? The answers are here.
Air heating boilers
Hot air heating using boilers combined with furnaces and duct systems is a more common option. Thus, fuel combustion is ensured not by a coolant, but by air, which is blown through a heat exchanger. Hot air travels through the house through a duct system. To reduce unnecessary heat losses, ventilation and heating systems are laid with heat-insulated sleeves, placed under the finished floor between the joists, hidden in the walls and installed above the suspended ceiling.
Air heating boilers
The cold air that is displaced from the room goes outside completely or partially. Some of this air can be used again for heating.
Note that it would seem more logical to supply warm air through the grilles, which are located as close as possible to the floor. So, due to convection, the air will evenly heat the room. But not in this case. Typically, the ventilation system supplies air heated by the boiler from above, then the cold air masses are forced out into those exhaust grilles that are located below.
Installation diagram and device
Below are the components of air heating of a private house with your own hands:
- Bake;
- Filter elements;
- A pipe that takes air from the room;
- Hood;
- A pipe that supplies fresh air;
- Supplying warm air to the room;
- A system that removes cooled air from the house;
- Chimney.
Composition of the complex system
A liquid or gas heater equipped with a programmable controller is ideal as a heat generator. After the house is completely warmed up, the automation immediately works and maintains the temperature according to the specified parameters.
Note! The heater should turn on automatically a maximum of 4 times a day, provided that the thermal insulation is of good quality. This mode helps save energy resources.
Compact natural gas heat generators
Operating principle of air boilers
Heating of residential, industrial or public premises is carried out with warm air heated using an air heater. The heater is connected to a system of air ducts that are routed to each room of the building. Low-temperature (160 degrees or less) combustion gases are discharged outside.
Using an air heater allows you not only to quickly warm up a room, but also to do so throughout the entire volume of the room, that is, evenly. After cooling, the air flows back into the heat generator through return air ducts. Thus, the operating principle of the system is based on the recirculation of air masses, to which fresh street air is mixed.
To maintain the desired temperature in the rooms, a thermostat (thermostat) is used. A special additional electronic unit allows you to very finely tune any climatic air parameters. The main electronic unit (processor) is used to control the air heater. It tracks the following parameters:
- Availability and pressure of gas in the system;
- State of security elements;
- Power options.
In addition, the processor is involved in controlling the humidifier, air conditioner, electronic filter and other equipment. All of the above functions can be added modularly to the basic heating system if desired by the user.
Disadvantages of long-burning stoves
The disadvantages of such furnaces include:
The need to install a metal chimney that must be thoroughly insulated
This requirement is usually silent from equipment sellers. Meanwhile, it is very important, since operation without compliance with this condition is simply impossible. Previously, it was said about incomplete combustion of flue gases during gas generation mode. Getting into a cold pipe, they instantly form soot and condensation, similar to tar, foul-smelling and flowing down the walls of the pipe.
- This publication is devoted to the use of fireplace stoves with a water circuit.
- Review material about Bavaria fireplace stoves is waiting for you at this link.
If you use a prefabricated pipe, then the upper assembly part must be inserted into the lower one, and not vice versa. The pipe must be at least 1.5 meters above the roof ridge, since this combustion mode produces a large amount of soot that pollutes the roof.
The need to install such a pipe, taking into account the ceiling cuts, passage through the roof, umbrella, etc., often more than doubles the cost of the stove itself.
This will have to be done at least once every 3 months when the furnace is constantly operating. Signs of the need for cleaning are smoke coming out when the firebox is opened, the absence of a hum when the stove is ignited, and increased wood consumption. That is why it is better to make the chimney dismountable - this will make it much easier to clean it from tar and soot.
Use only in premises with temporary occupancy
Manufacturers, as a rule, are silent about the negative impact of metal stoves on health. It is explained by dust in the air and burning on stove surfaces. Combustion products are easily spread throughout the room, and inhaling them is unsafe for health.
In Soviet times, regulatory documents regulated the surface area of stoves with a temperature of 120 degrees or more (in residential premises it was prohibited to operate stoves with 5% or more of this area). This norm has not been canceled since then, but it is not customary to mention it among manufacturers of furnace equipment. Such stoves should not be installed in bedrooms and rooms where children stay for long periods of time.
Incomplete combustion of fuel has a harmful effect on the environment
In damp, windless weather, chimney smoke falls down, enveloping nearby houses. And a gas generator stove, unlike a brick stove, has to be fired constantly.
The choice of a stove for a summer house or country house should be approached individually, taking into account the characteristics of the home, the time spent in it, the availability of sufficient fuel and other factors. If possible, the classic, time-tested brick oven remains the preferred option. A long-burning furnace can be considered as an auxiliary one. As the main one, it should be used only when there is a periodic need for heating the home.
Scheme for heating a private house with air
The main unit of the system is usually installed in the basement of the house in its center and includes all the main equipment:
- air heater (heat generator);
- fan;
- filter and purifier;
- humidifier;
- indoor air conditioner unit;
- various sensors.
Not all listed types of equipment are required to be installed. The minimum set will not include a fan, purifier, humidifier, air conditioner and sensors. From the main node of the system, often in the center of the house, the main, main air duct runs upward. It supplies heated air to all levels of the building.
Photo 1. Scheme of air heating of a two-story private house. The arrows indicate parts of the heating structure.
Horizontal levels of heating ducts are typically located under the floor of each floor, as well as in the ceiling of the upper level, thus covering the building from both below and above. An air collection system is installed separately inside and outside the house. Internal air is cleaned and humidified in the main unit, and external air is used for additional ventilation and renewal.
How to install
There are jobs in installing a system like this that require a professional, and some that some homeowners do themselves. The first include:
- calculation and design of the system;
- installation of gas equipment.
The second category includes the installation of some parts of the system (air ducts, sensors). This makes it possible to reduce the cost of organizing heating. It is optimal to start designing and installing such heating together with planning the house, since it is better to hide all parts in the floors and ceilings, and also immediately allocate a place for installing the main unit.
The sequence of installing air heating at home:
- system design;
- equipment purchase;
- installation of main unit equipment;
- installation of the main air duct;
- installation of other air ducts and grilles;
- installation of additional equipment (temperature, humidity sensors);
- commissioning works;
- finishing work, as a result of which the components of the heating system are closed.
Self-installation
You can do air heating yourself, which will help you save money. It is best to do this during the construction stage. Installation of an air heating system consists of the following steps:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=QO2mryOkg6E
Carrying out calculations
This is one of the most difficult and lengthy stages, requiring knowledge, skills and careful work. You need to consider several important factors:
- calculate heat loss separately for each room;
- choose the type of air heater and its power depending on the heat loss indicators;
- based on the heater power indicators, calculate the amount of warm air;
- perform an aerodynamic calculation of the entire system;
- calculate the required diameter of the air channels.
Purchase of equipment
You should start by purchasing the most important part - the heat generator. It should be selected based on the size of the heated area and fuel consumption indicators.
It is better to purchase air ducts, tie-ins and throttle valves from a special enterprise that produces ventilation equipment.
Everything else, namely aluminum tape, screws, mounting tape, insulation, etc., can be found on any decent market.
Installation features
During the installation of this heating system, the main air duct is first installed. Usually it is made of galvanized steel, after which it is covered with foil insulation with a thickness of about 3-5 mm.
After this, a system of smaller air ducts is installed, which branch off from the main one. To make the system easily adjustable, a throttle valve must be installed in each supply duct.
At the end of the main air duct, it is better to leave a section 50 cm long, in which there will be no insertion of thin air ducts. This way there will be uniform pressure along the entire length of the device and equal volumes of air will enter the side branches.
All this is followed by the installation of the air heater itself. It provides all mounting holes for additional equipment (filters, air conditioning, air sterilizer) and a fastening system. Assembly of the complex will take no more than an hour. However, connecting all this equipment will take time.
From all this we can conclude that air heating of a cottage is a modern and effective option that has long been used abroad and is slowly being introduced into Russian homes.
System Design Principles
When designing air heating systems, many important factors are taken into account. First of all, this is the heat demand of each individual room, as well as the heat loss for each room. Doors, windows, vents and other objects allow precious kilojoules of heat energy to escape.
The Buleryan stove is an economical heater option that can be used to organize air heating. A long-burning wood stove can also be an excellent solution.
The most important point is the presence of high-quality insulation of the building. If the house has plastic windows, good doors, and its facade is reliably insulated, there will be less heat loss, and heating costs can be significantly reduced. If we are talking about the reconstruction of a building, we should start with the design of insulation.
After the need for thermal energy and its costs are correlated, the power of the heating equipment is calculated and its type is selected. Then the hot air flow parameters are calculated. Special aerodynamic calculations are performed to calculate the required dimensions of the air ducts.
A diffuser grille is installed at the outlet of the air duct. Its size and configuration may affect the speed of air flow
You can preliminarily calculate the power of the equipment based on the following figures: for heating every 10 sq. meters of room you will need about 0.7-0.8 kW of heat. This is provided that the house is well insulated, otherwise more powerful equipment will be needed. But it is better to entrust complete design and detailed calculations to an experienced engineer.
Incorrect calculations can have a very bad effect on the state of the finished system. An unprofessionally designed air heating system is characterized by such problems as frequent equipment breakdowns, overheating of indoor air, overheating of equipment, drafts, and increased noise levels.
Simultaneously with designing an air heating system, it makes sense to think about the placement of stationary pieces of furniture in the house. Supply and exhaust grilles should be located in places away from the constant presence of people.
They also should not be hidden under cabinets, cabinets or other objects that impede the free movement of air masses.
In a multi-storey private house, it is recommended to place exhaust grilles in such a way that on the upper floors the cooled air is taken into the system from above, and on the lower floors - from below. This will ensure a more even distribution of heat throughout all rooms. Read more about how to correctly calculate air heating in this material.
Image gallery
Photo from
Inclined airflow direction
Scheme of operation of inclined warm air supply
Horizontal direction of heat supply
Vertical supply of warm air flow
Air duct routing
Such air ducts are temperature resistant and provide excellent thermal insulation.
On the other hand, a ducted air conditioner can use conventional ventilation ducts made of plastic.
How to install air ducts depends on the layout of the premises and the materials used. If space under the floor allows, then between the joists; if you plan to have a suspended ceiling, then above it. Drywall walls can also hide ductwork. The main line itself uses forced air injection, and circulation from top to bottom is possible. But the ventilation grilles, through which heated air enters the rooms, are located strictly below: only in this case will the air masses in the room be mixed by convective currents.
Warm air should be blown as close to the floor as possible