In a heating system, a very important element is the heating expansion tank. Such a device serves to accept excess coolant at the moment when it expands, thus preventing rupture of the pipeline and taps.
Heating expansion tank
The principle of operation of an expansion tank for heating is as follows: when the temperature of the coolant rises by 10 degrees, its volume increases by about 0.3%. Since the liquid is not burned, excess pressure appears that needs to be compensated. This is precisely why an expansion tank is installed.
Purpose of expansion tank
The cooling systems of various cars contain from 5 to 20 or more liters of non-freezing liquid - antifreeze (antifreeze). During operation, the engine, and along with it the antifreeze, heats up from low temperatures in winter to high temperatures in summer.
The temperature difference can reach 100 °C or more. For example, when operating a car in northern regions, where engine warm-up starts at minus 20 °C and ends at an operating temperature of 90 °C, this difference will be 110 °C.
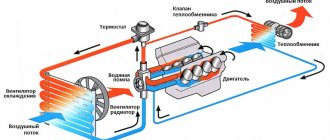
During engine operation, a pressure of about 1 bar arises in the expansion tank
Since any liquid expands in volume when heated, excess is formed in the cooling circuit of the car, which needs to be directed somewhere. Antifreeze is an incompressible medium, so when it expands, it will create high pressure in the system, which can rupture the pipes and radiator honeycombs. Conversely, when cooled, the liquid will decrease in volume and create a vacuum (vacuum), which acts with the same force.
To ensure normal operation of the power unit cooling system and avoid pressure surges, an expansion tank is integrated into it. Its functions are as follows:
- absorb additional volume of antifreeze that expands when heated;
- release excess pressure through a plug with a built-in safety valve;
- release the fluid back into the system when the engine cools, preventing the formation of air locks.
Large expansion tanks are used on trucks
Antifreeze, which is a mixture of distilled water with ethylene glycol (sometimes propylene glycol), adds about 5% in volume when heated from zero to 100 °C. In a circuit designed for 10 liters of antifreeze, after complete warming up, as much as 500 ml is formed, which goes into the expansion tank.
Video: why do you need an expansion tank?
Open type
Open type expansion tanks are installed at the highest point of the system. Often the location of the tank is chosen to be in the attic.
In addition to the fact that the device prevents the expansion of the coolant in the pipes, it also serves to prevent boiling of the coolant, and also replenishes its reserves in cases of leaks.
Design and principle of operation
Modern expansion tanks for cars are a reservoir made of durable thick-walled plastic with a filler neck and fittings for connection to the elements of the cooling system. The shape of the tank does not matter functionally, so manufacturers customize it to fit the location of the tank.
The shape of the tank depends on the location of its installation and can be different - round, rectangular or flat
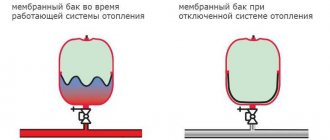
The capacity of the container for expanding antifreeze is calculated for each car model and depends on the total volume of liquid in the pipes and units. Moreover, in a cold state, the tank is only half filled with antifreeze, the rest of the space is occupied by air that can compress under pressure. The neck of the tank is closed with a plug with a built-in air valve. The principle of operation of the container is as follows:
- When the engine is “cold,” the tank is half empty—the antifreeze level is between the minimum and maximum marks on the body.
- After starting the engine, the antifreeze begins to expand and its level in the vessel rises, and the air gap contracts. The lid valve remains sealed.
- When the liquid reaches an operating temperature of 90–95 °C and a maximum increase in volume, the pressure in the tank reaches the air valve response threshold (1–1.2 Bar or 120 kPa). It opens and releases air into the atmosphere.
- As the engine cools down, the opposite picture is observed - the valve allows air to flow in the opposite direction until the amount of antifreeze stops decreasing. This prevents air locks in hoses and radiators.
The design of the container is quite simple - the tank body is closed with a stopper with a built-in valve
In an emergency situation, when antifreeze or water begins to boil for various reasons, the safety valve releases not only air, but also steam.
The built-in sensor sends a signal about insufficient fluid level to the instrument panel
In some car models, for example, VAZ 2110-2115, the container is equipped with a second neck into which the coolant level sensor is screwed. If, due to a breakdown or leakage of a component, antifreeze begins to leak out and its level in the container drops to a minimum, the sensor will operate and warn the driver with a signal from the corresponding light on the instrument panel.
There are cars (both domestically produced and imported) in which the expansion tank is closed with a simple plug, not equipped with a valve and communicating with the atmosphere. In such systems, the function of releasing pressure and re-injecting air is performed by the main radiator cap, and the reservoir only compensates for the expansion of the liquid.
The radiator cap is equipped with a bypass valve that directs excess antifreeze into the expansion tank
Circulation
The tank can be installed in systems with natural or forced circulation.
- With natural circulation, the device should be built into the main line, thanks to which it will additionally serve as an air collector;
- With forced circulation, the device is connected to the return pipe so that the water does not boil in the system.
Place of the reservoir in the cooling system
A container to compensate for expanding antifreeze can be installed in different places, the location depends on the make of the car. The reservoir is attached to body parts - side members and the interior partition using a rubber clamp or a special bracket. As a rule, the tank is placed on the side where the upper radiator pipe for its connection is located.
Typically the container is installed closer to the radiator pipe
There are containers with 2 and 3 fittings. The latter are connected by three hoses to the following units:
- A thick pipe connected to the lower fitting of the vessel connects it to the main line of the cooling circuit - a small circle of liquid circulation that is always open. The antifreeze, which increases in volume, enters the tank through this hose.
- A thin tube running from the radiator to the upper fitting. Designed to discharge liquid and steam from the radiator directly.
- The second thin pipe, connected to the middle fitting, comes from the interior heater radiator. Its task is the same - to drain excess antifreeze and steam into the container.
Excess antifreeze from three units enters the reservoir with 3 fittings.
The tanks, equipped with two fittings, are connected to the small circulation circuit and the main cooling radiator; there is no connection to the stove.
The expansion tank is the highest point of the engine cooling system. This is done so that the liquid from the tank can flow into the circuit according to the law of communicating vessels. When the antifreeze level in the container is 3-4 cm above the Min mark on the body, all pipes and units are filled with antifreeze. Including the highest of them - the throttle cooling circuit.
Remaining air from the system is removed through the throttle heating pipes
When pouring liquid into the water jacket of the power unit through the expansion tank, it is recommended to remove the throttle cooling pipe. This allows air pockets to be pushed out of the lines and the heater radiator.
How to make a calculation?
As mentioned above, any expansion tank used for open heating is characterized by simplicity of design and manufacture. And calculating the dimensions of such a product is no more complicated.
For this purpose, you can use formulas or a method that involves approximate calculation of the working volume of the tank.
An example of using a formula to calculate the required tank volume. Based on the actual volume of water circulating in the circuit, only its increase when heated to a certain temperature is calculated, rounding up. Then add the result obtained to the volume of coolant in the heating system and add an arbitrary number of liters “in reserve”
In reality, to determine the required capacity of the tank, the owners of a small country house use formulas extremely rarely. Most often, the approximate volume of the expansion tank is calculated, to which any number of liters can be added for insurance.
Reason: in the case of open tanks, the extra volume does not significantly affect the cost, and in some cases does not lead to an increase in price at all.
As a result, the entire calculation of capacity comes down to determining 10% of the volume of the entire coolant, which should be its minimum value for the expansion tank.
The easiest way to do this is at the time of designing and creating a heating system, when all the parameters of radiators, pipes and other structural elements are known or can be easily found out by taking measurements. And then simply adding up the volumes of all components.
Although open expansion tanks and the systems for which they are intended have long since become obsolete, their availability and, most importantly, high autonomy make them in demand in conditions that are far from ideal. For example, if there is a problem with stable electricity supplies or the owners of the premises do not live there permanently
If the source data is unknown, then the most practical method of calculation is experimental. Why do you need to drain all the water from the system and then refill it with coolant?
In this case, measurements must be made, which can be done using a meter or using containers of known volume. After that, all that remains is to find out the required 10% of the coolant volume, which serves as a guideline when making or purchasing a tank.
Liquids for filling into the tank
Today's cars, built with the widespread use of new technologies, are very demanding of all process fluids, including coolant. The list of requirements is as follows:
- the liquid must boil at a temperature not lower than 110 ° C;
- freezing threshold - from minus 20 to -60 ° C depending on environmental conditions;
- no foaming upon contact with the pump impeller, minimal viscosity;
- the liquid must contain non-aggressive additives that prevent the appearance of scale on metal parts;
- the chemical composition should not change for 3 years or 60 thousand kilometers.
Antifreeze is a purely domestic product, synthesized during the USSR
All of the above requirements are met by antifreeze or antifreeze, which is the same thing. The name antifreeze comes from the English word antifreeze, which means “non-freezing”. Antifreeze is a substance created on the same basis from ethylene glycol in the former USSR. The word consists of the abbreviation TOS (technology of organic synthesis) and the ending “ol”, inherent in the names of chemical preparations.
The base of antifreeze and antifreeze is the same - water + ethylene glycol in different ratios. Differences between products from different manufacturers may lie in the package of inhibitory additives, so it is not advisable to confuse liquids. There will be no fatal consequences, but some substances can neutralize the effect of others and the anti-freeze properties will deteriorate. In this case, the color of the liquid does not matter - it is just a dye.
You can use distilled water to fill the tank in the following situations:
- to dilute antifreeze concentrate to the desired freezing temperature;
- in case of an emergency - complete or partial loss of coolant en route;
- for the purpose of washing.
The color of antifreeze does not affect its properties; the additive package is important
Distilled (desalted) water does not meet the above requirements: it freezes at zero temperature and boils at 100 °C. Therefore, it is poured temporarily or as a solvent for antifreeze.
It is unacceptable to pour tap water saturated with salts into the expansion tank. An exception is the breakdown and loss of antifreeze on the way and the absence of a car shop nearby. Fix the leak, fill the cooling system with tap water and get to a garage or service station, then drain it immediately. Otherwise, deposits will form on the inner walls of the water jacket of the engine and other units, impairing heat transfer.
Video: liquids for pouring into the car cooling circuit
Closed type
The membrane expansion tank does not have all the disadvantages inherent in the system described above.
However, installing it requires some additions and rules:
- Requires a pressure gauge;
- A device for manual pressure adjustment is required, otherwise the pressure may exceed all standard tolerances;
- The tank should be installed as close to the boiler as possible and with a connection to the return pipe. This is necessary to prevent the water from boiling.
You should not ignore the reliability of the fasteners, since during operation the weight of the expansion tank can increase significantly.
About malfunctions and tank repairs
During operation of the machine, the following breakdowns of the expansion tank may occur;
- contamination or failure of the bypass valve of the plug;
- rupture of the tank body;
The tank wall ruptures when the internal pressure is too high
- Antifreeze leaking from under the cap.
The leakage of the lid is characterized by the appearance of multi-colored streaks on the body
Most car enthusiasts, when a valve or body breaks down, simply replace the part with a new one. This is justified by the lack of time for repairs and the low cost of these spare parts. Although, if desired, the burst plastic of the tank can be soldered, and the lid can be disassembled and cleaned.
Leaks from under the cork occur when the seal is not tight or due to the design features of the container. For example, on VAZ 2110 cars, a stream from the upper small fitting connected to the radiator hits directly into the neck, causing a leak. The solution is to install a more advanced tank from Priora.
DIY connection
A closed type system is more common, so it is better to familiarize yourself with the process of connecting the tank, just this option.
- First you need to decide on the capacity. It should be about a tenth of the total volume of the coolant.
- Make correct technical calculations. Particular attention should be paid to the overall volume of the heating system.
- Disconnect the boiler from the heating source. Shut off the coolant supply using the valve to connect the expansion tank.
- Completely empty the circuit of liquid.
- To connect the container to the system, you will need a special soldering iron, fasteners, and a set of tees and fittings.
It is recommended to install the tank in a place with the lowest pressure. But you need to calculate so that the expansion tank does not interfere. Despite the ease of installation, it is advisable to entrust the connection of the expansion tank and boiler to a specialist.
An expansion tank of a simple design is not that difficult to install yourself. This procedure does not require special skills or special tools.
However, it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations relating to the characteristics of the heating system in which installation work is carried out.
Results
Initially, it is necessary to determine the volume of the tank for expansion, and only after that decide what type to purchase, open or closed. Installation of the entire system must be carried out by qualified specialists. Self-connection is not allowed. During the work, the installation team will make sure that all components and assemblies of the system are installed in accordance with safety requirements and correct installation. In addition, the home owner will be provided with a guarantee on materials and work performed. Therefore, if problems arise, the homeowner can seek help from the place where he ordered the project.