In modern conditions, to ensure efficient operation of an autonomous heating system, it must be equipped with a high-quality circulation pump. The presence of such a device allows you to provide the premises in the house with a large amount of thermal energy.
Considering that there are many models of pumping units of different brands on the market, it is very difficult to make the right decision. When choosing, you should correctly calculate the parameters for the pump and take into account some important points.
Features of heating systems equipped with a pump
Country houses equipped with a separate heating system may be heated unevenly due to the heat energy being distributed across all rooms. The least amount of heat will reach those rooms that are located further from the boiler. To solve this problem, you can not only focus on creating new heating systems with a large-diameter pipeline, but also insert a pump into the heating system. currently present.
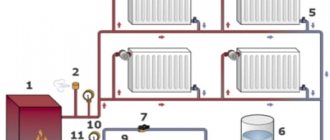
Typical circulation pump installation diagram: 1 - boiler, 2 - air vent, 3 - thermostatic valve, 4 - radiator, 5 - balancing valve; 6 - membrane tank, 7 - ball valve, 8 - filter, 9 - circulation pump, 10 - thermomanometer, 11 - safety valve.
Connecting a pump to a heating system is not as expensive a procedure as connecting a new pipeline.
At the same time, in this case, a dismantling procedure is applied to old heating systems, which cannot be a simple task. Installing a pump is much cheaper, especially since you can always do it yourself. The pump avoids the formation of air plugs inside the pipes, ensuring its normal circulation through the pipeline. With the help of a pump, temperature stabilization is achieved in each room of the house. The device as a whole serves to optimize the operation of the heating system of any residential premises.
Circulation pump wiring diagram.
The type of sealed throttleless pump for heating systems is the most common due to their simple operation and convenient design. The body of this type of pump is made of cast iron. In this case, it is possible to use plastic or steel as a material for a part such as a rotor. The operation of such devices is silent. In this case, there will be no need to replace gaskets in the heating system, which will be filled not with a cooling element and lubricant, but with water. During its entire service life, the unit will be characterized by high reliability. The main condition for this is the correct connection of the pump to the heating system.
Harness
There are two types of heating systems - forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump; systems with natural circulation work, but in this mode they have lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is installed into it. This gives high heating efficiency and reliability. It is clear that the installation of a circulation pump in these systems is different.
All heating systems with heated floors are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
Forced circulation
Since a forced circulation heating system without a pump is inoperative, it is installed directly into the gap in the supply or return pipe (of your choice).
Most problems with the circulation pump arise due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They can jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a mesh dirt filter must be placed in front of the unit.
Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
It is also advisable to install ball valves on both sides. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps and remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
Natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not working. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed the entire time the pumping is running. In this mode, the system operates as forced.
Installation diagram of a circulation pump in a system with natural circulation
When the electricity goes out or the unit fails, the valve on the jumper is opened, the valve leading to the pump is closed, and the system operates as a gravity system.
Installation features
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require rework: it is necessary to rotate the rotor so that it is directed horizontally. The second point is the direction of flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating which direction the coolant should flow. This is how you turn the unit so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, just when selecting a model, make sure that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (pressure created) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.
What is a circulation pump and why is it needed?
A circulation pump is a device that changes the speed of movement of a liquid medium without changing pressure. In heating systems it is installed for more efficient heating. In systems with forced circulation it is a mandatory element, in gravity systems it can be installed if it is necessary to increase the thermal power. Installing a circulation pump with several speeds makes it possible to change the amount of heat transferred depending on the outside temperature, thus maintaining a stable temperature in the room.
Cross-section of a circulation pump with a wet rotor
There are two types of such units - with a dry and wet rotor. Devices with a dry rotor have a high efficiency (about 80%), but are very noisy and require regular maintenance. Units with a wet rotor operate almost silently; with normal coolant quality, they can pump water without failure for more than 10 years. They have a lower efficiency (about 50%), but their characteristics are more than sufficient for heating any private home.
Plumbers Forum - Water Supply and Heating 2
Good day!
Please help me with one question regarding heated floors!
After looking at your materials, I realized that the heating system was made for me by non-professionals and at a primitive level.
In the future I plan to install heated floors in another house, I will follow your recommendations!
Question about existing water heated floors: There is a circulation pump in the distribution manifold, it has 3 speeds, which speed should be set to. Is it more effective for fluid circulation to be slower or faster?
Question about existing water heated floors: There is a circulation pump in the distribution manifold, it has 3 speeds, which speed should be set to. Is it more effective for fluid circulation to be slower or faster?
Here it comes down to system performance in terms of costs. The heavier the heating system in terms of hydraulic resistance. The greater the speed. This needs to be sorted out by numbers. Take into account hydraulic resistance, performance at a certain heat removal rate, and so on. To get a specific answer to your question, you need to get to know your heating system completely. It is not possible to advise by eye.
You need to know: 1. Pump parameters 2. Hydraulic characteristics of the circuits. 3. It is necessary to know the entire circuit in general or provide hydraulics.
Therefore, you are required to provide a photo of the heating system diagram. Diagram in axonometry indicating the lengths and diameters of pipes. Pump parameters, etc.
Don't be afraid of my answer. If you want, I will solve your problem! To solve a problem you need to have a dialogue.
And now there is only one question: at what speed should the pump be set. The building has 2 floors, on the first there are 2 pumps, and on the second there is one. Is this correct, if not, then how should it be done?
Yes and no! Not enough information. Here it comes down to system performance in terms of costs. The heavier the heating system in terms of hydraulic resistance. The greater the speed. This needs to be sorted out by numbers. Take into account hydraulic resistance, performance at a certain heat removal rate, and so on.
Turn on the pump at low speed and check operation. Since you don’t have flow meters, you won’t be able to adjust the circuits according to flow rates. If at the first speed it does not warm up normally, then increase the speed until the floor heating operates comfortably.
And how does the speed of liquid passage through the pipes affect the temperature in the room?
The faster the speed, the greater the consumption and heating occurs faster, and the greater the consumption, the higher the heating of the floor in terms of thermal output. Increasing the speed may cause the pump to cavitate. and a lot of things. need to be understood.
Cavitation is determined by ear (gurgling small bubbles and there are a lot of them, and the sound is more like not a glug-glug, but more like: bsrrrsrsrsrrrsrssssrrrrrrrsrsrsr, that is, the noise of a large number of small bubbles.). If the noise does not stop within 24 hours, then you need to increase the pressure of the heating system. If the pressure is ok and you don’t want to increase it, then it means you have a hydraulic accumulator installed in the circuit - not correctly! However, there may still be some kind of snag...
Hello! As I understand it, there is a pump with flow switching. For such a pump, you need to install a bypass on the manifold, with a pressure bypass valve. In case all circuits are closed, the pump will work through this bypass, otherwise it will burn out. Or don’t forget to turn off the pump in time. Still, the mixing unit is not visible, to save fuel on the boiler. And the remote control of the collector, it seems to me, is too small; it may not allow enough flow to flow for 6 circuits. In addition, as you can see from the photo, the pipe on the contours of the TP is like metal-plastic, but it is better to attach it to polystyrene foam and cover it with a MAC mesh on top.
In addition, as you can see from the photo, the pipe on the contours of the TP is like metal-plastic, but it is better to attach it to polystyrene foam and cover it with a MAC mesh on top.
I wonder why?
Please don't judge me too harshly; I'm a beginner myself. So, I decided to be smart. . Well, as far as I understand, MAC mesh is an anti-shrink mesh. Its direct purpose is to hold the surface of the screed and provide an iron frame to the concrete to form a slab. And being under the pipes, at the bottom its significance decreases.
Well, as far as I understand, MAC mesh is an anti-shrink mesh. Its direct purpose is to hold the surface of the screed and provide an iron frame to the concrete to form a slab. And being under the pipes, at the bottom its significance decreases.
If you had studied the strength of materials, there would be no doubt that the mesh should be located at the very bottom of the concrete slab. The mesh is more needed to prevent the concrete slab from bending downward under pressure from above. With pressure from above, the steel mesh rod stretches, which prevents the concrete slab from bending.
Hello! The funny thing is that I actually studied strength of strength and was one of the best in the course! But the obvious inertia of consciousness from which stereotypical thinking takes its roots in this case let me down. Thank you, you opened my eyes. PS By the way, this is not strength of material, but theoretical mechanics
I noticed that almost no one installs a bypass for the pump on the mixing unit, in case all circuits are completely closed. Maybe it’s really not advisable to install it? Yes, and pressure-regulated bypass valves are not visible in stores. Only before. valve with a certain pressure from 1.5 to 6 bar. Do you think it is possible to do without such a bypass at the mixing unit?
Recommendations for proper pump installation
To ensure convenient access for servicing the pump, the unit must be connected correctly. In practice, when installing a pump, the following basic installation rules should be taken into account:
After installing the circulation pump, it should always be accessible so that in the event of a breakdown, it can be easily repaired or replaced.
- Both sides of the pumping unit must be equipped with special ball valves, which are necessary when carrying out maintenance of the entire heating system or during the dismantling of the unit.
- It is necessary to equip the entire system with a filter in order to protect the device from exposure to small particles that lead to damage to the installation and its components.
- Since the water passing through the heating system is far from ideal, additional protection will be required for the pumps to function properly. Therefore, the heating bypass on top must be equipped with a valve, which must be installed. You can choose any valve: automatic or manual. Its purpose is to release air pockets formed in the pipes; its terminals should be directed clearly upward.
- Belonging to the type of wet models, the pump must be installed in a horizontal position so that it is completely immersed in water, and not just a separate part. Incorrect installation can cause damage to the working surface of the unit, and the installation will be pointless.
- To increase the operating potential of the structure, it is necessary to specially treat all fasteners and connections in the system with a sealing agent.
- It is necessary to ensure that the sequence is observed when connecting the pump and fasteners.
High-tech control system
AUTOadapt function is an automatic adaptation technology developed and patented by Grundfos. The pump constantly analyzes the system in which it is installed and, depending on the coolant flow rate, adapts to it, for example, selects the minimum possible pressure that meets the requirements of the system. Pumps of the Grundfos Alpha2 L and Grundfos Alpha2 series themselves find an operating point that provides an optimal level of comfort with minimal energy consumption. They do not need to reach the maximum of the performance curve to adapt to the requirements of the heating system, which allows the pump to adjust the performance curve either up or down.
The Alpha2 L and Alpha2 circulation pumps allow you to not worry about complex pump settings. It is enough to install the pump and leave the factory settings using the AUTOadapt mode. It will automatically analyze the heating system, find the optimal parameters and continue to adjust its operation depending on the required changes.
The function became a real breakthrough and a kind of standard for subsequent generations of circulation pumps. The AUTOADAPT mode makes it possible to automatically change equipment settings when the needs of people living in the house change, or, for example. Changes of seasons. Using complex software algorithms, the equipment electronics constantly analyzes the processes and, depending on the indicators, selects the optimal pressure. This significantly saves heating system resources and consumer money.
Now more than 3 million ALPHA series pumps are successfully operating around the world. GRUNDFOS has released an updated model, which has an even higher energy efficiency class and meets the high requirements of the European EuP standard. The average energy efficiency index (EEI) for ALPHA2 pumps is 0.15. At the moment this is the best indicator. ALPHA2 can use as little as 3 watts in constant speed mode and 4 watts in AUTOADAPT mode. This means that the pump requires 87% less energy than most analogues on the world market. The pump has a built-in electronic flow meter to simplify balancing and diagnostics of the heating system. It is also capable of operating at temperatures from 2 to 40 °C and even in an environment that forms condensation.
The MAGNA3 series are the most efficient circulation pumps available on the market today. Its Energy Efficiency Index (EEI), even lower than required by the EuP directive, allows you to save up to 75% of energy compared to a conventional circulator and pay for the purchase of a new model in an amazingly short time. The new FLOWLIMIT function and FLOWADAPT control mode allow you to set the maximum flow limit for the MAGNA3 pump. The pump continuously monitors changes in flow rate and helps prevent it from exceeding it. This eliminates the need for throttling valves and thus improves the overall energy efficiency of the system. In order to comply with system flow restrictions, the pump will regulate output to the set value, which will significantly reduce energy costs.
The MAGNA3 circulation pump is ideal for heating and air conditioning systems, as well as domestic hot water systems. It is designed to handle liquids down to -10°C, making it suitable for both demanding industrial applications and ground source heat pump (GSHP) applications. Moreover, the liquid temperature (from -10°C to +110°C) is now independent of the ambient temperature (from 0°C to +40°C).
In order not to make a mistake when choosing a pump for a heating system, you need to know many parameters. But the main ones are two: how much thermal energy does the house need, and what are the hydraulic resistance indicators? For an ordinary person, all this is difficult. And in order not to make a mistake, it is better to trust professionals who will select the optimal equipment model. You can contact Proffinstal engineers by calling 8 (495) 580-29-99 or at the nearest engineering center.
How the unit works
The principle of operation of the circulation unit is very similar to the operation of a drainage pump. If this device is installed in a heating system, it will cause movement of the coolant by capturing liquid on one side and pumping it into the pipeline on the other side
The principle of operation of the circulation unit is very similar to the operation of a drainage pump. If this device is installed in a heating system, it will cause the movement of the coolant by capturing liquid on one side and pumping it into the pipeline on the other side. All this happens due to the centrifugal force, which is formed during the rotation of the wheel with blades. During operation of the device, the pressure in the expansion tank does not change. If it is necessary to increase the coolant level in the heating system, install a booster pump. The circulation unit only helps water overcome the resistance force.
The device installation diagram looks like this:
- A circulation pump is installed on the pipeline with hot water coming from the heater.
- A bypass valve is installed on the section of the line between the pumping equipment and the heater.
- The pipeline between the bypass valve and the circulation pump is connected by a bypass to the return pipeline.
This installation scheme involves the release of coolant from the device only if the unit is filled with water. To keep the liquid in the wheel for a long time, a receiver equipped with a check valve is built at the end of the pipeline.
Circulation pumps used for domestic purposes can develop a coolant speed of up to 2 m/s, and units used in the industrial field accelerate the coolant up to 8 m/s.
It’s worth knowing: any type of circulation pump operates from the mains. This is quite economical equipment, since the motor power for large industrial pumps is 0.3 kW, and for household appliances it is only 85 W.
Types of open heating schemes
In an open heating system, the coolant moves in two different ways. The first option is natural or gravitational circulation, the second is forced or artificial stimulation from a pump. The choice of scheme depends on the number of floors and area of the building, as well as on the expected thermal conditions.
Natural circulation in heating
The gravitational system does not have any mechanism to ensure the movement of the coolant. The process is carried out solely by the expansion of hot water. For the operation of the circuit, an accelerating riser is provided, the height of which is at least 3.5 m.
If you neglect to install a vertical transit riser, then there is a high probability that the coolant coming from the boiler will not develop a sufficient speed
The natural circulation heating system is optimal for buildings with an area of up to 60 square meters. m. The maximum length of the circuit capable of providing heat is considered to be a 30 m mainline. An important factor is the height of the building and the number of storeys of the house, which allows the installation of an accelerating riser. The natural circulation scheme is not suitable for low-temperature applications. Insufficient expansion of the coolant will not create the proper pressure in the system.
Possibilities of the gravity circuit:
- Connection to heated floors. A circulation pump is mounted on the water circuit leading to the floor. The rest of the system operates as usual. If the power goes out, the house will continue to be heated.
- Working with a boiler. The heating device is mounted at the top of the system - slightly below the expansion tank.
To ensure uninterrupted operation, a pump can be installed on the boiler. Then the heat supply and hot water production scheme automatically becomes a forced option. Additionally, a check valve is installed to prevent recirculation of the coolant.
Forced system with pump
In order to increase the speed of the coolant and reduce the time for heating the room, a pump is built in. The movement of water flow increases to 0.3-0.7 m/s. The intensity of heat transfer increases, and the branches of the main heat up evenly.
Pumping circuits are constructed of both open and closed types. In open circuits, the expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the system. The presence of the pump allows you to increase the pipeline between the heating boiler and the batteries, both in height and in length (+)
- The circuit with a built-in pump is volatile. To ensure that the heating of the room does not stop during a power outage, the pumping equipment is placed on the bypass.
- The pump is installed in front of the boiler inlet on the return pipe. The distance to the boiler is 1.5 m.
- When installing the pump, the direction of water movement is taken into account.
Two shut-off valves and a bypass elbow with a circulation pump are mounted on the return line. If there is current in the network, the taps close - the coolant moves through the pump. If there is no voltage, then the valves must be opened - the system will switch to natural circulation.
A check valve must be installed on the supply pipeline. The element is placed immediately after the boiler and prevents recirculation of the coolant during pump operation
Principles of installation and connection of the pump
To prepare the heating system for pump installation, first drain the heating fluid and clean the entire system if it is dirty. The system is filled with water only after the pipes are secured, after which they are carefully checked for any malfunctions for their further elimination. Using the central screw, excess air is removed from the system.
In order for the installed pump to interact with the cooled coolant and to extend its service life, the unit is mounted in the return line pipeline. When installed in a forced circulation system, the connection of the expansion tank should be made not to the main riser, but to the return pipeline.
Having positioned the pump strictly horizontally, it is attached to the pipes. As an additional device, the circulation pump can be installed in a natural circulation system. In this case, the pump must be equipped with a filter and a split thread. The diameter of the filter must match the diameter of the pump. Pressure operation of the system must be maintained by a conventional valve corresponding to the thread diameter of the unit. If you are using an open system, it will not be required.
After the pump is installed, a valve should be installed on the main and return pipelines. So that air can be discharged from the system, a special device is installed on the bypass.
Where it is planned to install the pump, a pipe is cut off and a special connection for shut-off valves is welded to it; it is installed before and after the pump unit. This must be done for ease of removal, cleaning and repair of the device. Having turned off the taps on the outlet and inlet pipes of the pump, turn off the heating boiler, then unscrew the nuts that secure the pump to the pipes.
The pump must be connected after starting the entire system and filling the pipes with water. There should be no air remaining in the pipes, so it is released each time before starting the pumping unit. To bleed air manually, use special valves installed on both sides of the pumping unit.
Grundfos pump - is it capable of passing coolant without electricity?
The house has both an electric boiler and a solid fuel boiler. The electric one will work to maintain the desired temperature in the absence of the owners in the house, and the solid fuel one will work as the main one during their presence. The system has a built-in pump connected to both boilers.
The question is this. If for some reason there is no electricity in the house, but the solid fuel boiler is working, will the coolant be able to pass through the pump freely?
Igor Iofchu wrote: will the coolant be able to pass through the pump without hindrance?
Yes. Any hydraulic centrifugal pump with a locked rotor creates insignificant hydraulic resistance.
Vladimir_Vas wrote: Yes. Any hydraulic centrifugal pump with a locked rotor creates insignificant hydraulic resistance.
That is, there is no need to make a special arc to bypass the pump? I'm afraid that the solid fuel boiler might boil if something happens.
Igor Iofchu wrote: I’m afraid that the solid fuel boiler might boil if something happens.
Maybe. But not because of the resistance of the de-energized pump. You take any circulation pump from the shelf and just blow into the pipe - the questions will disappear on their own.
Vladimir_Vas wrote: Maybe. But not because of the resistance of the de-energized pump. You take any circulation pump from the shelf and just blow into the pipe - the questions will disappear on their own.
OK. Thanks a lot. They calmed me down.
Igor Iofchu wrote: If for some reason there is no electricity in the house, but the solid fuel boiler is working, will the coolant be able to pass through the pump unhindered?
With a normal EC, it will be able to pass, but not entirely unhindered.
Igor Iofchu wrote: So there is no need to make a special arc to bypass the pump?
With EC, the pump is switched to bypass and the return valve, with a ball of positive buoyancy, the valve or, especially, the shut-off valve on the main line should not be installed at all, since the check valve may stick, the shut-off valve may not be switched at the right time and the hydraulic resistance will be greater than just pump located on the main line.
With an EC with a pump, so that without electricity there is the minimum possible hydraulic resistance, the bypass with the pump must be connected to the main line at the minimum possible angle, without a check valve and, even more so, without a shut-off valve on the main line between the pump connection points.
Igor Iofchu wrote: I’m afraid that the solid fuel boiler might boil if something happens.
To do this, you need an EC and RB on the boiler return, but in any case, measures must be taken to forcibly reduce the critical temperature of the coolant.
Power connection
The circulation pumps operate from a 220 V network. The connection is standard; a separate power supply line with a circuit breaker is desirable. The connection requires three wires - phase, neutral and ground.
Circulation pump electrical connection diagram
The connection to the network itself can be organized using a three-pin socket and plug. This connection method is used if the pump comes with a connected power wire. It can also be connected via a terminal block or directly with a cable to the terminals.
The terminals are located under a plastic cover. We remove it by unscrewing several bolts and find three connectors. They are usually labeled (the pictograms are N - neutral wire, L - phase, and “ground” has an international designation), so it’s hard to make a mistake.
Where to connect the power cable
Since the entire system depends on the performance of the circulation pump, it makes sense to make a backup power supply - install a stabilizer with connected batteries. With such a power supply system, everything will work for several days, since the pump itself and the boiler automation “pulls” electricity to a maximum of 250-300 W. But when organizing, you need to calculate everything and select the battery capacity. The disadvantage of such a system is the need to ensure that the batteries do not discharge.
How to connect a circulator to electricity through a stabilizer
Hello. My situation, a 25 x 60 pump is located immediately after a 6 kW electric boiler, then the line from a 40 mm pipe goes to the bathhouse (there are three steel radiators) and returns to the boiler; after the pump, a branch goes up, then 4 m, down, rings a house of 50 sq. m. m. through the kitchen, then through the bedroom, where it doubles, then the hall, where it triples and flows into the boiler return; in the bathhouse there is a branch 40 mm up, it leaves the bathhouse and enters the 2nd floor of a house of 40 sq. m. m. (there are two cast-iron radiators) and returns to the bathhouse in the return line; there was no heat on the second floor; the idea of installing a second pump in the bathhouse for supply after the branch; the total length of the pipeline is 125 m. How correct is the solution?
The idea is correct - the route is too long for one pump.
Types of circulation pumps, design
The devices in question are similar to the same products for pumping water for other purposes, the operating principle is similar, but in this case the device is created taking into account the nuances of heating: for high temperatures, their differences, as well as for the characteristics of the system, the need to regulate pressure, speed in a wide range range. The product is manufactured for insertion specifically into pipes and bypass (a whole unit with it and taps is often sold), taking into account their specifics.
There are 2 types used: with a wet and dry rotor. The latter are more productive, but are less often used for home and domestic use, since they are noisy, with noticeable vibration, and more expensive.
The main disadvantage of all pumps is their dependence on electricity. If the facility has frequent power outages, then backup batteries are installed; a stabilizer is recommended to level out voltage surges.
As standard for a heating pump, for all types, manufacturers provide stepwise speed settings: you can select the optimal mode and control energy consumption.
A brief description of the disadvantages and advantages of the varieties is as follows. Dry type products are noisier, create vibration, are expensive, but more productive, the purity of the pumped resource is not significant. Wet - quiet, cheaper, more compact, but limited in pressure, the transported substance must be free of impurities.
There are dual models on the market used for backup in emergency situations.
What indicators to consider when choosing a pump
The correct choice of pump is based on the hydraulic resistance that the device itself overcomes in the process of creating the required pressure and force of water flow. For an optimally selected pump, the recommended power should be lower than the calculated one, by 10-15% of the calculated power. If the required power level is exceeded, the device may have a shorter service life, which will lead to its rapid wear. The noise level in the heating system may increase. If the power of the unit is less, then under these conditions the required amount of coolant will not be provided.
Diagram of the circulation pump.
The calculation of the pump power indicator is based on the diameter and length of the pipeline, the level of water temperature and coolant pressure. Ten meters of the heating system should be provided with half a meter of pressure using a pump. During the calculations, the coolant flow rate is compared with the level of water flow used in the boiler, the power of which is known. You should have data for calculations about how much water is needed for the normal operation of each of the rings of the heating system. Calculation of heat losses of a building can be made on the basis of tables of thermal conductivity of materials. The length of the heat pipeline and the number of heating radiators are also taken into account. The power of the battery is determined by the required amount of water per minute to ensure optimal heating of the room.
The circulation pump can be equipped with either an electronic or manual speed controller. If the pump shaft speed is set to the highest level, then the maximum operating coefficient of the device should be obtained.
A change in temperature outside is a reason to turn on a different speed
The presence of several modes in the heating pump will allow you to adjust the heating level in a particular room . This function is important when there is a sharp change in temperature outside. In this case, the device can be manually switched to the required power or the autopilot can be turned on, and the system itself will adjust to the desired temperature.
All modern heating systems are equipped with a circulation pump. With the help of which, a continuous circulation of hot water occurs in the pipes , as a result of which the room is heated.
They are available in different configurations and can have 3 speeds : minimum, medium and high.
Pump device
Since the engine stator is energized, it is separated from the rotor using a glass made of stainless steel or carbon material
The main elements that make up the circulation pump are:
- housing made of stainless steel, bronze, cast iron or aluminum;
- rotor shaft and rotor;
- wheel with blades or impeller;
- engine.
Typically, an impeller is a structure of two parallel disks that are connected to each other by means of radially curved blades. One of the disks has a hole for liquid to flow through. The second disk secures the impeller to the motor shaft. The coolant passing through the engine acts as a lubricant and coolant for the rotor shaft where the impeller is fixed.
Since the engine stator is energized, it is separated from the rotor using a glass made of stainless steel or carbon material. The walls of the glass are 0.3 mm thick. The rotor is fixed on ceramic or graphite bearings for sliding.
Open logic
There are also freely programmable types of devices with open logic. They are also often found in circulation-type pumping products. Such devices can be easily adjusted to any environmental conditions and temperature conditions.
But managing them is quite difficult; special qualifications are required. That is why they are not widely used; in circulation-type devices, closed logic is most often found.
You should not save on purchasing a thermostat for your heating system, because this product significantly increases productivity and efficiency.
Why do you need a pump in a heating system?
Circulation pumps for heating private houses are designed to create forced movement of coolant in the water circuit. After installing the equipment, the natural circulation of liquid in the system becomes impossible; the pumps will operate in constant mode. For this reason, high demands are placed on circulation equipment regarding:
- Productivity.
- Noise insulation.
- Reliability.
- Long service life.
A circulation pump is needed for “water floors”, as well as two- and one-pipe heating systems. In large buildings it is used for domestic hot water systems.
As practice shows, if you install the station in any system with natural coolant circulation, the heating efficiency and uniform heating along the entire length of the water circuit increases.
The only disadvantage of this solution is the dependence of the pumping equipment on electricity, but the problem, as a rule, is solved by connecting an uninterruptible power supply.
Installing a pump in the heating system of a private home is justified both when creating a new one and when modifying an existing heating system.
Operating principle of the circulation pump
The operation of circulation pumps may differ slightly depending on the type of design, but the principle of operation remains the same. Manufacturers offer more than hundreds of equipment models, with various performance and control parameters. Based on the characteristics of the pumps, stations can be divided into several groups:
- According to the type of rotor - to enhance the circulation of the coolant, models with a dry and wet rotor can be used. The designs differ in the location of the impeller and moving mechanisms in the housing. Thus, in models with a dry rotor, only the flywheel, which creates pressure, comes into contact with the coolant fluid. “Dry” models have high performance, but have several disadvantages: a high level of noise is created from the operation of the pump, and regular maintenance is required. For domestic use, it is better to use modules with a wet rotor. All moving parts, including bearings, are completely enclosed in a coolant medium that serves as a lubricant for the parts that bear the greatest load. The service life of a “wet” type water pump in a heating system is at least 7 years. There is no need for maintenance.
- By type of control - the traditional model of pumping equipment, most often installed in small domestic premises, has a mechanical regulator with three fixed speeds. Regulating the temperature in the house using a mechanical circulation pump is quite inconvenient. The modules are distinguished by high power consumption. The optimal pump has an electronic control unit. A room thermostat is built into the housing. The automation independently analyzes the temperature in the room, automatically changing the selected mode. Electricity consumption is reduced by 2-3 times.
There are other parameters that distinguish circulation equipment. But to choose a suitable model, it will be enough to know about the nuances listed above.
TeremOK
| « | October 2021 | |||||
| Mon. | Tue | Wed. | Thurs. | Fri. | Sat. | Sun. |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
House in Spain
Not far from Barcelona you can see a stylish house that integrates modern technologies to reduce energy consumption
Laser rangefinder Maka
Laser measuring instruments are increasingly popular and in demand in construction and repair work. Firstly, accuracy increases significantly.
Leak control system
A water leak in an apartment is a rather unpleasant event. And not only for your premises, but also for the neighbors below. Although the opposite happens.
Pipes for water heated floors
Warm floor water systems are very popular among owners of private houses and cottages. This is due to the fact that such heat is dispensed with.
New PVC profile KBE
As has been repeatedly pointed out, modern PVC windows are a complex and reliable design. And what would this “reliability” You did.
Roofing ICOPAL 3D
Everything flows and everything changes... This phrase is quite applicable to roofing materials. Today there is a roof for every taste, color, etc.
VEKA plastic windows
Have you decided to buy plastic windows? The idea is great and now all that remains is to make a choice. And as practice shows, the buyer chooses first.
Which pumps are suitable for installation in residential premises?
Installation of a circulation pump.
The optimal temperature of the heating system of a country house is achieved using built-in thermal valves. If the set temperature parameters of the heating system are exceeded, this may lead to the valve being closed and the hydraulic resistance and pressure increasing.
Using pumps with an electronic control system helps prevent noise, since the devices will automatically monitor all changes in water volumes. The pumps will provide smooth adjustment of pressure drops.
To automate the operation of the pump, use an automatic type unit model. This allows you to protect it from incorrect operation.
The pumps used may differ in their type of application. For example, dry ones do not come into contact with the coolant during operation. Wet pumps pump water when they are submerged. Dry types of pumps are noisy, and the installation of the pump in a heating system is more suitable for enterprises rather than residential premises.
For country houses and dachas, pumps designed to work in water and having special bronze or brass bodies are suitable. The parts used in the housings are stainless, so the system will not be damaged by water. Thus, these structures are provided with protection from moisture, high and low temperatures. Installation of this design is possible on the return and supply pipelines. The entire system will require a certain approach to its maintenance.
In order to increase the degree of pressure applied to the suction section, you can install the pump so that the expansion tank is nearby. The heating pipeline must fall down in the place where the unit needs to be connected. You will need to make sure that the pump can withstand strong pressures of hot water.
Setting up the pump yourself
The final stage of equipping the heating system with a pump is to connect it. This is a fairly simple process. To do this, you will need a separate machine on the dashboard, which will be specially designated for this mechanism. To connect the unit, you need to connect the power cable to the terminal box. It is critical that the connection correctly matches the specified designation. The maximum cable cross-section is 2.5 mm2.
Also, do not forget about grounding the pump. The ideal option would be to have a grounding loop in the living room. If it is not there, a metal rod will come to the rescue, which is driven deep into the ground.
The need for a circulation pump
As mentioned above, there are two types of heating systems: convection, that is, with natural circulation of coolant, usually this type is used in houses with an area not exceeding one hundred square meters, and pressure, where a circulation pump is installed. The convection heating method with a large area of the house will not be able to ensure uniform distribution of coolant throughout all branches of the system, so there is a possibility that some radiators will not work efficiently. It’s just that the coolant will reach them poorly or with large heat losses, but simply cooled.
The pump creates the necessary pressure inside the system, which helps distribute the coolant evenly throughout the entire circuit and drive it at a certain speed, which does not interfere with the transfer of heat through the radiators. Therefore, when approaching the choice of a circulation pump, it is necessary to know exactly the parameters of the entire system, especially its hydraulic components.
Calculation of operating pressure in the circuit
Video
When choosing a circulation pump for a heating system, calculations must also be made based on such an indicator as the pressure inside the pipeline. To do this, you can use the relationship:
P = (R x L + Z) / pxq, where:
P – pressure value;
R – flow resistance for straight sections of the pipeline;
L – total length
Z is the value of flow resistance determined by the fittings, taps and other fittings used in the system;
р – value of coolant density at operating temperature;
q – value of free fall acceleration.
If there is insufficient data for calculation using the given formula, you can use the simplified relationship:
P = R x L x ZF, where
R is the value of flow resistance in a straight pipe section, approximately 100 - 150 pascals per 1 meter, expressed in a form convenient for calculation, it will be 0.01 - 0.015 meters per meter pipe section;
L is the total length of the pipeline; in a two-pipe heating scheme, both forward and return circuits are taken into account;
ZF – magnification factor, depending on the following indicators:
- for a system with ball valves, for which it is unusual to reduce the clearance of the pipeline, and with correctly selected fittings it is taken equal to 1.3;
- when using throttle or temperature control devices, its value will be 1.7.
Video
When choosing a circular pump for a heating system, calculating its characteristics appears to be a necessary procedure.
The practice of using circulation pumps makes it possible to select them without calculating the necessary parameters. Recommended parameters are shown in the table.
Table for empirical pump selection
Table 1.
| Heated area (m2) | Productivity (m3/hour) | Stamps |
| 80 – 240 | From 0.5 to 2.5 | 25 – 40 |
| 100 – 265 | Is the same | 32 – 40 |
| 140 – 270 | From 0.5 to 2.7 | 25 – 60 |
| 165 – 310 | Is the same | 32 – 60 |
Note: in the third column, the first number is the diameter of the pipes, the second is the lift height.
Video
Using the given data, you can select the right device for stable and long-term operation without much hassle.
Main manufacturers
Circular pumps for heating systems are produced by many European manufacturers with fairly high quality and a wide range.
Wilo company. The pumps of this concern, produced in Germany, occupy a fairly large place in the specialized market. They are distinguished by high quality and stable operation. Almost all models of this manufacturer are equipped with automatic and manual controls. Not only the rotor speed is adjusted, but also the release functions, including the amount of pressure in the system.
DAB company. This Italian manufacturer successfully competes with other suppliers to the Russian market, presenting centrifugal pumps for more than 40 years. A special feature of DAB products is the displays used on the control panel, which are very convenient for interacting with the installation and monitoring the work process.
Manufacturer Grundfos. The Danish company under this name has existed for more than 70 years, supplying the market with pumping equipment for various purposes. It should be noted that this manufacturer is clearly and has long been recognized in the specialized market. The fruitfulness and creativity of the company, which launches up to hundreds of new models of its products on the market every year, is impressive.
This manufacturer’s equipment for heating systems is marketed under the UPS label and the product line is intended for both domestic and industrial use. The main feature of circular pumps for heating is their suitability for operation in a very wide temperature range: from -25° to +110°C.
The UPS product line can operate using 3 performance modes.
Gilex company. A domestic manufacturer of circular pumps, successfully competing in the market with European companies.
The units are unpretentious in operation and can ensure active circulation of coolants of various densities in heating networks, which determines a wide selection of liquids, including transformer oil. They operate in 3 power modes, stepless adjustment. It compares favorably with its competitors in price level.
Conclusion
The choice of a circular pump for a heating system and its calculation will allow the consumer to make the optimal purchase for the actual conditions of a particular room.
The options for preliminary assessment of the necessary equipment proposed here allow you to confidently make such a choice. I wish you success!
Installation instructions
So, we will describe the installation stages when circulation pumps are installed on the bypass. This scheme is used most often and is recommended by experts due to the following advantages:
- quick, convenient dismantling;
- convenient temporary shutdown.
For wet options, a horizontal, level position is critical:
There are various modifications of already assembled bypass loops on the market: for welding, for flanges, with segments for shut-off elements.
If it is not advisable to buy a ready-made assembly, for example, when all the parts are in stock or if there are specific features of the location, then the bypass piping is made from scratch. But you will need skills in working with pipes (welding, thread cutting).
A good, recommended location is between the membrane tank and the boiler. Below is a universal option: for open/closed circuits, for connecting using the collector method (several pumps).
Assembly order
Diagram showing the movement of water, please note: shut-off valves are mandatory - when removing the device for repair or maintenance, they are turned off:
They start by assembling a unit (module) with taps: one per inlet/outlet. pump, the third is part of the lower straight pipe. It is necessary to carefully measure the return segment in order to accurately weld the segment with the shut-off fittings.
The bypass section from the central station is assembled. The nuts are only screwed on, tightening is postponed until the final stage. The top is the pump part (in the photo below the GRUNDFOS UPS pump) with two already screwed in taps, a filter, at the ends of the module there are small sections of pipe with threads like squeegees, they serve as material for welding. Below is a shut-off valve for the supply pipe (main).
They try on a bypass loop, mark the welding points on the pipe, use a drill with special drills to make a hole for the diameter of the section being mounted, and weld the joint.
They cut in the entire assembly with the lower shut-off valve on the main pipe, in our case, on the supply from the gas boiler:
The last step is to connect the pump to power.
Connecting the pump to power
So, the system is completely assembled, the pump is selected, installed, and then the device is connected to the power supply. Before the procedure, the entire line is completely de-energized—the machine is turned off on the panel. The device may have a plug for a socket or without it - just wires of a certain length for connecting directly to the home network on the panel.
Procedure: The pump wires are connected, taking into account the polarity, to the line. The terminals are labeled and have standard colors. If the device does not have a cable with a plug for a socket and you decide to use just such a connection, then you can buy it in any store, you will need a three-core cable, usually a cross-section of 2.5 mm² is more than enough.
It is highly desirable to have grounding (three-wire wiring), since proximity to water creates a significant risk of current entering the equipment elements. It is recommended to connect the device via an uninterruptible power supply (UPS); you can also connect a boiler to it.
An excellent solution is to insert a thermostat into the system (see diagram below), it can also be immediately included in the unit, which will automatically switch off when the coolant temperature drops below the set limits.
It is also highly advisable to install the device with a connection to the network through a difavtomat (its analogue of an RCD + AB) or through the boiler automation system, on which all these measures should be taken by default. And also, if there is an automatic protective device on any line with an outlet and the pump is not too powerful, for example, 90 W, that is, it will withstand all the consumers hung on it, then separate individual wiring with RCBOs and RCDs under the pump may not be installed. The device can be connected to such an outlet and not bother.
Connections without grounding are allowed, for example, when the house is old with two-wire wiring, but then the presence of a difavtomat or RCD+AV in the diagram is vital.
As you can see, the main difficulty of installation for a circulation pump is the need for welding, cutting pipes, and threading. The assembly itself is elementary: you need to carefully measure all the distances and screw in the elements. The connections are sealed with tow and sealant.
What to pay attention to during operation:
- it is necessary to periodically clean the filter and check the pressure gauge readings;
- The noise emitted by the device does not always indicate a breakdown; often the cause is air accumulating in the circuit. The problem can be solved simply - by bleeding with special valves;
- Dry pumps may require periodic lubrication.
Wet rotor pumps
In wet modifications, the shaft and impeller are in contact with the pumped resource, and it also serves as lubrication and cooling.
The stator is separated by a special flask that seals parts of the electric motor, otherwise voltage would be transmitted through water to all metal elements of the system.
Components and how they work
- housing that can withstand high pressures is made of cast iron, steel, aluminum. For standard home conditions, this is a small block that is attached directly to the pipe, bypass;
- a shaft (moving segment), also known as a rotor made of steel, ceramics with a bearing unit, a working disk with blades. The latter is fixed motionless, it consists of 2 wheels with holes connected by blades: on one - for moving the resource, on the adjacent one - for securing to the electric motor shaft;
- a stator (fixed unit) on the rotor with an excitation winding (inductor) to stabilize the rotation speed and flow, for which it has small blades at a certain angle. This part prevents flow stalling. This part consists of a core and a frame. In the grooves of the first there is a winding. The stator is also a magnetic circuit and a supporting structure;
- control chip, power terminals. On models without the first element there is a capacitor, and on the contact block there is a speed selector.
When starting, the blade disk rotates, a vacuum is created inside the pipe, the coolant is drawn in and moved by the rotor further along the equipment (from inlet to outlet). Fence and ejection are carried out. Centrifugal force helps move the resource throughout the circuit. The resulting pressure creates the required force on different segments of the pipe line and creates circulation on its rises.
Nuances, pros and cons
Wet circulation pumps, however, like everything else, are usually modular. The devices are selected according to the parameters of the circuit (pressure, required maximum amount of pumped volume). An important plus is that the device is prefabricated, which simplifies its repair; broken parts are replaceable.
Wet central heating systems are installed on the vast majority of home systems, this is the standard, and here’s why:
- the device is almost silent, which is suitable for living, for better comfort;
- compactness, light weight - the device is a small box that does not require special fastening, partitions, or space on the floor. The product simply crashes into the pipe and “hangs” on it;
- there is no need for additional cooling (unlike dry models), this function is performed by the water flowing inside;
- There are fewer spare parts, the ability to replace them, easy repairs, dismantling, minimal maintenance frequency;
- wide range of settings;
- long-term performance if there is a filter and working fluid without fine particles;
- cheaper if the device is for low standard productivity.
Disadvantages for home heating with a wet pump:
- if the water contains fine abrasive particles (lime, iron, etc.), then the impeller and other parts (hydraulics) in contact with the liquid will wear out relatively soon and fail. For such products, a closed system with a purified resource is recommended; a dirt filter is mandatory;
- low efficiency - about 55%;
- the performance range is more limited than dry options. But it is enough to service the average private home, therefore, and also because of the low price, it is often used for housing.
Installation Basics
The inclusion of autonomous heating in the circuit and the presence of central heating there is regulated by SP 60.13330. According to this act, a heating system with forced circulation is considered priority (not with natural circulation, although this is also possible).
The installation process briefly consists of securing the assembled pump unit (with filters, taps) with union nuts to a pre-cut pipe in a certain place.
Peculiarities
- placed so that the position of the shaft is clearly horizontal (not necessary for dry options) - this will eliminate airing, spare parts will not break because of it;
- the filter is a standard mud trap; it is mounted with its branch downwards along the flow of water to reduce resistance and facilitate maintenance.
For older products, the factory can indicate the installation location; once upon a time only the return line was considered such, but modern pumps can be installed anywhere (on the supply side too).
Autonomous heating pump installation diagrams
Let's look at the basic diagrams of how to install a pump and embed it onto a pipe.
They put it on return/feed, there is no difference. You can cut it directly onto the main pipe or make a bypass (outlet) and place it on it. The last method is the best, it makes it possible to more conveniently dismantle/install the device for maintenance; when replacing, it is usually so familiar that it is assumed by default.
There are several options for the installation location; there is also a diagram for several pumps (manifold connection).
Let's consider the traditional option with installation on a bypass.
For modern models, the location - return or supply - is not significant. They choose at their own discretion, as is more convenient for the user.
But, undoubtedly, in all cases the best option is to tap into the bypass in these places.
Some specialists remain adherents of the old traditional rule, according to which the return is the best section for installation. Through this segment, the liquid that has given off heat returns to the boiler. A less warm, cooled resource does not have such an aggressive effect on the device. The described opinion has completely lost its relevance for modern models designed for high temperatures, however, we indicate it for a full disclosure of the topic. It is important to read the instructions, since for older products the manufacturer may recommend a return line.
Dry rotor pumps
The entire internal working unit of dry devices does not come into contact with water and is completely isolated. These products are slightly larger and heavier. There is noise and vibration. Here, more often there is a need for a separate place, a fence, installation on the floor with larger piping and wiring. But the devices can also crash in the standard way, like wet ones - directly into a pipe, bypass on the line.
“Dry” pumps are installed to transport significant masses of coolant along long-distance circuits, for example, for a large number of apartments in a high-rise building, for objects with several floors, entertainment centers, administrative and industrial buildings.
The design features are as follows. Between the electric motor and the hydraulic working segment there are sealing insulating gaskets (2 rings). There are 2 discs with a close fit. One is movable on the shaft, the other is static, firmly fixed inside the housing. A thin film of the pumped resource is created between the wheels, pressing on the elements, increasing the tightness.
The efficiency of dry pumps is 85%, according to this parameter they are the best, but they are used less often for home systems due to the noise and vibration created by the cooling fan.
Dry circulation pumps can be of the following sizes:
- monoblock - motor, all parts of the pump in a single body. Advantages: ease of maintenance and installation. But such devices, like console ones, are more often installed for MKD, on large objects, and these products are usually with a stand-foundation;
- console option. Assembled on a single base, the axes of the elements are on 1 line, but the shaft and pipes are remote from the drive;
- in-line. Compact, placed directly on the pipe. The pipes are on the same line (there are no snails, as in the previous version). There is automatic compensation for seal production. These are the popular options; they are usually used for not particularly demanding standard home heating.
Advantages and disadvantages of dry circulation pumps Advantages of dry circulation pumps:
- productivity, higher power, efficiency 85%;
- more energy efficient;
- does not require horizontal positioning;
- low requirements for cleanliness of the coolant; abrasive particles will not damage the working parts of the mechanism, since they do not come into contact with it. Can be used on all systems - open, closed. The filter does not have to be mounted, although it is desirable;
- Dimensions and weight are slightly greater. For high performance, a typical installation option is on the floor (not directly on the pipe, as with most dry pumps). Accordingly, installation becomes more complicated and costs increase. But such a need does not arise often, since for home systems a compact, not particularly powerful model is sufficient; in most cases, the device is mounted directly on the pipe;
- Large devices require lubrication. For compact sizes, such a procedure may not be required or may be required extremely rarely, but this should be prescribed in the instructions;
- if the cooler breaks down, the device will overheat, with a high probability of failure;
- The cooling impeller is noisy and vibration occurs. A very significant drawback, since extraneous sounds, unnerving users, will nullify all the advantages. Sound insulation will be required, at least a box/fence with it or installation in a remote segment;
- repairs and replacement of spare parts are somewhat more labor-intensive: the design is complicated by the cooling impeller, there are features associated with the insulation of internal parts;
- expensive.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Calculation of the required pump characteristics depending on the parameters of the heating circuit:
Detailed video instructions for assembling a bypass from polypropylene pipes:
For any hydraulic circuit, you can select a pump that helps achieve the required pressure. First of all, you need to pay attention to the pressure and flow characteristics of the device, and then to other technical data: efficiency, noise, reliability and connection method.
Share with readers your experience of using a circulation pump. Tell us what the choice of unit was based on, and whether you are satisfied with the purchase. Please leave comments on the article, ask questions and participate in discussions. The contact form is located below.
Options for sediment selection
Flow and pressure
Circulation models are selected according to parameters traditionally important for pumps of all types - flow (performance, usually measured in liters per minute or cubic meters per hour of the pumped liquid) and pressure (measured in meters). Both flow and pressure are determined during the hydraulic calculation of the heating system, which must be done by a specialist.
A number of circulation pump models support several operating speeds (usually three), and their electronic control systems allow you to change the speed depending on the needs of the heating system.
Among other parameters, we note such as geometric dimensions, placement method, temperature and type of pumped liquid. All this is also determined during system design.
Dimensions
Of the geometric dimensions, the cross-section of the pipes (and, accordingly, the inlet and outlet pipes of the pump) and the distance between the pipes (installation length) are important. Depending on these parameters, a pump with a nominal pipe bore is selected, usually equal to 15, 20, 25 and 32 mm. Also, as a rule, there is a choice of two standard sizes with an installation length of 130 and 180 mm. At the same time, do not forget that a compact pump can always be installed instead of a model with a larger installation length, but installation, on the contrary, may cause difficulties.
Vertical or horizontal installation
Many modern pump models have a universal design and can be installed in any position. But for some models, it is important how the main axis of the pump is located - vertically or horizontally (check the type you need in advance, before purchasing).
Coolant temperature
Approximately half of the models are designed for pumping clean water, usually with a temperature of at least 2°C. If you plan to use a coolant based on ethylene or propylene glycol, choose a model designed for the corresponding liquids, whose minimum temperature can be -10-15 ° C (this is indicated in the equipment description).
Almost all models of circulation pumps are capable of pumping very hot (up to 110 °C) liquid, but problems may arise with cold water: most models are not designed for liquid temperatures below zero.
In addition, other requirements are imposed on the circulation pump. It is also desirable that it be economical and low noise. Economical - because even a small difference in the level of energy consumption (50-70 W) due to the length of the heating season gives savings on average up to 15-20 thousand rubles. per season. And a low noise level is necessary when placing pumping equipment near residential premises.
Based on cost, circulation pumps can be divided into two groups. The first is products from market leaders with a long-standing reputation, such as Grundfos, Wilo or DAB. The second group is Russian or Belarusian equipment, such as Gilex or Kalibr, or products from Chinese brands such as Oasis. The choice between the two groups depends on the needs of the buyer. Leaders' products are preferable when it is necessary to create a reliable and durable system that will work for a long time. Pumps of the second group are suitable for building a basic economical solution.