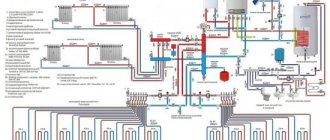
When operating heating systems with natural coolant circulation, owners of apartments and private houses are often faced with the problem of insufficient heating of radiators installed in remote rooms.
It all depends on the length of the heating circuit. If its length is more than 30 meters, the level of water pressure becomes insufficient to maintain the required temperature at its most distant points.
To achieve stable operation of the equipment, devices are used that ensure rhythmic circulation of the coolant. Preliminary calculation of a pump for a heating system makes it possible to determine the parameters necessary to select the most optimal model.
Why are calculations needed?
Most modern autonomous heating systems, used to maintain a certain temperature in residential premises, are equipped with centrifugal pumps that ensure uninterrupted circulation of liquid in the heating circuit.
By increasing the pressure in the system, it is possible to reduce the temperature of the water at the outlet of the heating boiler, thereby reducing the daily consumption of gas consumed by it.
The correct choice of the circulation pump model allows you to significantly increase the level of equipment efficiency during the heating season and ensure a comfortable temperature in rooms of any size.
What you need to know to calculate power
To understand the algorithm for calculating a circular pump, it is necessary to start from some parameter, the accuracy of which cannot be doubted. To do this, you need to open the technical passport of the room in which you plan to install an autonomous heating system and find out its area. For example, let’s take a separate building (private house) with an area of 300 m².
The next step is to determine the quantities needed for the calculation.
You need to know three main parameters:
- Qn —heat source power (kW);
- Qpu is the performance of the circulation pump, an indicator of the volumetric supply of coolant for the type of room we have chosen (m³/hour);
- Hpu is the pressure power required to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the system (m).
Calculation of heat source power (AOGV)
For each room, depending on its area or volume, there are certain technical standards for the power of the heating source.
To calculate this parameter we use the following formula:
Qn = Sn × Qsp ÷ 1000
| Designation | Parameter | Units |
| Qn | heat source power | kW |
| Sn | heated area | m² |
| Qsp | specific heat demand of the room | W/m² |
We know the area of the heated room (300 m²), and the second indicator depends on the type of structure: if it is an apartment building, then its value is 70 W/m², in our case (a separate building), it will be 100 W/m².
Let's plug these values into the formula and see what we get:
300 × 100 ÷ 1000 = 30 kW.
So, the power of the heating unit for our room was 30 kW. There is another method for determining this value.
The volume of the heated room and the power of the heating unit can be found in the following table.
| Thermal power | Room volume new house (m³) | Room volume old house (m³) |
| 5 kW | 70 – 150 | 60 – 110 |
| 10 kW | 150 – 300 | 130 – 220 |
| 20 kW | 320 – 600 | 240 – 440 |
| 30 kW | 650 – 1000 | 460 – 650 |
| 40 kW | 1050 – 1300 | 650 – 890 |
| 50 kW | 1350 – 1600 | 900 – 1100 |
| 60 kW | 1650 – 2000 | 1150 – 1350 |
Let me remind you that the volume of a room is equal to the product of its area and height.
(V = S × h), where:
- V is the volume of the room;
- S - heated area;
- h is the height of the rooms.
In our case, with a ceiling height of 2.5 m, it will be:
300 × 2.5 = 750 m³
We look for this indicator in the second column of the table and get the same 30 kW.
Calculation of pump performance
Correct calculation of pump power allows you to provide the heating system with the required amount of coolant at any point. Having determined the technical characteristics of the heating boiler, we can calculate the performance of the circulation equipment sufficient for our premises.
Let's use the following formula:
Qpu = Qn ÷ kτ × Δt
| Designation | Parameter | Units |
| Qpu | pump performance | m³/hour |
| Qn | heat source power (AOGV) | kW |
| kτ | liquid heat capacity coefficient | — |
| Δt | temperature difference at the system inlet and outlet | ⁰С |
If water is used as a coolant, its specific heat capacity is 1.164. If a different liquid is used, then the value of this parameter must be looked up in the corresponding tables.
With a functioning heating system, the value of the temperature difference (Δt) can be calculated by the method of elementary subtraction of indicators taken from measuring instruments installed at the input and output of the system (Δt = t1 – t2, where t1 is the temperature at the inlet of the heating circuit, and t2 is the temperature at the outlet from him).
Otherwise, you will have to use standard indicators. The temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the system (Δt) ranges from 10-20 ⁰С.
Let's take the average value - 15 ⁰С and substitute the results obtained into the formula:
Qpu = 30 ÷ 1.163 × 15 = 1.72 m³/hour
Now one of the technical characteristics of the circulation pump is known.
Calculation of the required power (height) of pressure
The power of the heating boiler and the performance of the pump are known; the next step is to determine the coolant pressure sufficient to overcome the internal hydraulic resistance of the pipes and elements of the heating system.
To do this, the heat losses on the longest section of the circuit are taken into account - from the heat source to the distant radiator. To deliver heat to any point, the pressure power of the supplied liquid must be higher than the total hydraulic resistance of all heating devices.
The heating pump pressure is calculated using the following formula:
Hpu = R × L × ZF ÷ 10000
| Designation | Parameter | Units |
| Hpu | Power (height) of pressure | m |
| R | Losses in supply and return pipes | Pa/m |
| L | Heating circuit length | m |
| ZF | hydraulic coefficient resistance of shaped and shut-off valves of the system | — |
Depending on the diameter of the pipes, the value of the parameter R is in the range of 50–150 Pa/m (the minimum value is applicable for water supply systems with a pipe diameter of 2 inches and above; for modern plastic and metal pipes the losses are 150 Pa/m). For our premises it is necessary to use the maximum value.
If the exact length of the circuit (L) is difficult to determine, this parameter is calculated based on the dimensions of the heated room. The length, width and height of the house are added and then doubled. With a total area of 300 m², we can assume that the length of the house is 30 m, the width is 10 m, and the height is 2.5 m. In this case, L = (30 + 10 + 2.5) × 2, that is, 85 meters.
The simplest option for determining the ZF value is as follows: if there is no thermostatic valve in the system, it is equal to 1.3, and if it is present, it is 2.2.
To calculate, take the maximum value of this coefficient and substitute all the obtained values into the formula:
150 × 85 × 2.2 ÷ 10000 = 2.8 m.
The proposed calculation method is not the only one. To more accurately determine the pressure indicators of the pump, there are formulas that take into account not the loss coefficient, but the real values of these indicators.
Hydraulic resistance
This term expresses the total pressure loss in the system. The heating circuit consists of individual elements, each of which has its own value for this characteristic.
These include:
- valves;
- valves;
- filters;
- measuring and control instruments;
- radiators;
- convectors, etc.
To accurately determine losses in the system, the values specified in the technical documentation for each component of the heating circuit are usually used.
If this is not possible, you can find this information in the following table:
| System element | Pressure loss | Units |
| Boiler | 1000 – 5000 | Pa |
| Compact boiler | 5000 – 15000 | Pa |
| Heat exchanger | 10000 – 20000 | Pa |
| Heat meter | 15000 – 20000 | Pa |
| Water heater | 2000 – 10000 | Pa |
| Heat pump | 10000 – 20000 | Pa |
| Radiator | 500 | Pa |
| Convector | 2000 – 20000 | Pa |
| Radiator valve | 10000 | Pa |
| Control valve | 10000 – 20000 | Pa |
| Check valve | 5000 – 10000 | Pa |
| Filter (clean) | 15000 – 20000 | Pa |
| Thermostatic valve | 5000 – 10000 | Pa |
| Mixer | 2000 — 4000 | Pa |
In this case, to calculate the head height it is convenient to use a slightly different formula.
H = 1.3 × (R1L1 + R2L2 + Z1 + Z2 + .... + Zn) ÷ 10000, where:
- R1, R2 – losses in the supply and return pipes (Pa/m);
- L1, L2 – length of supply and return pipeline lines (m);
- Z1, Z2 ... Zn – pressure loss on individual elements of the system (Pa).
The number in the denominator of the formula (10000) is the conversion factor from Pascals to meters.
Choosing a pump
Once all the necessary parameters for purchasing a circulation pump have been determined, you can begin to select a specific model. The technical characteristics of devices of this type are reflected in the graphs of the relationship between device performance and pressure height, attached to their passport. This data can be easily found on the Internet.
Depending on the number of velocities in the coordinate system, one, two or three graphs are constructed indicating the point of the optimal relationship between these quantities. We plot the pump performance value on the X axis, and the height of its pressure on the Y axis. The intersection point of these parameters should be as close as possible to the point indicated on the graph - their complete combination would be ideal.
The most common models have a three-speed operating mode. If you choose one of them, then the selection of characteristics must be carried out according to the schedule corresponding to the second speed, that is, the average. In other cases, the parameters are combined using any of them.
Prices for different models of pumps for the heating system
heating pump
Features of forced circulation
A circulation pump installed in the system creates a slight pressure inside. In this case, the coolant moves at a low speed, evenly distributing heat across all radiators.
Is it really impossible for the natural circulation of the coolant to distribute thermal energy evenly?
Maybe, but due to the fact that private country houses under construction are becoming larger in size, and accordingly, the layout of pipe lines is becoming more and more complex, it is increasingly difficult for the coolant to overcome the configurations of the pipe circuits. And in such houses you simply cannot do without a circulation pump.
Advantages
Under the action of the pump, the coolant passes faster through the entire circuit of the heating system, returning to the heating boiler. However, its temperature will not be low. This means that it will be easier to heat a coolant that is not very cool. Less fuel consumption costs.
For the natural circulation of the coolant, a large volume is required so that the bulk of it can maintain the required temperature. Accordingly, for normal operation of the heating system in a private house, you will need pipes with a large diameter, radiators with wide cavities, and shut-off valves to match the pipes.
For the system in which the pump is installed, there is no need to hold a large volume of coolant. Therefore, you can safely use pipes and valves with a smaller diameter. And this means a reduction in prices for all products and savings on materials.
Flaws
In principle, such heating has only one drawback - it is energy dependent. The device runs on electric current. Firstly, these are, albeit small, costs. Secondly, when the power supply is turned off, the pumping unit stops working.
Of course, the craftsmen, taking this situation into account, install a bypass through which the heating begins to work on the principle of natural circulation of hot water. And this is a decrease in operating efficiency, plus a decrease in efficiency.
How to calculate a pump if the boiler power is known
Situations often arise when a boiler is purchased in advance or a pump is added to an already functioning heating system. In this case, the power of the heating unit is known, and all other elements of the circuit are selected depending on the value of this indicator.
To calculate the performance of the circulation pump at a given power of the heating source, use the following formula.
Q = N ÷ (t2 - t1), where:
- Q – pump capacity (m³/hour);
- N – power of the heating device (W);
- t2 – coolant temperature at the system inlet (⁰С);
- t1 – liquid temperature at the outlet of the circuit (⁰С).
If it is not possible to accurately determine the specified supply and return parameters, use the average temperature difference - 15 ⁰C.
Basic Design Rules
Heated floor design
- The length of each 16 mm loop should not exceed 100 m (or 120 for pipes with a diameter of 20 mm). The shorter the length of the pipes, the more economical the system will be, since a weaker circular pump will be required.
- The optimal option for 16 mm pipes is considered to be a length of 65 m, or approximately 10 m2. The pump flow rate to operate in such a room (10 m2) must be at least 2 liters per minute.
- It is necessary to design the circuits in such a way that they have a uniform length and do not differ from each other by more than 10-20%, taking into account the supply to the collector.
- The optimal distance between pipes is 150 mm.
- The surface temperature should not exceed 30 degrees. In most cases this is enough. Keep in mind that the coolant temperature may be 10-20 degrees higher.
- The most optimal way to lay pipes is “snail”. This option distributes heat evenly over the surface and does not create large hydraulic losses due to smooth turns.
- Since it is colder on the floor next to the outer walls, the laying step there is 1.5 times smaller, but not less than 10 centimeters.
- Fastening the pipes is best done according to the markings. You can’t do without it especially if there are obstacles that need to be avoided or oblique corners.
An example of an ideal heated floor
Warm floor design
- The base has height differences of less than 3 cm;
- Insulation with a thickness of 3 centimeters is used, thereby increasing the efficiency of the system; it does not heat the floor in the downward direction. It is best to use polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam with a density higher than 35 kg/m3.
- The concrete screed has a thickness of 4-10 cm.
- Reinforcing mesh is used to reinforce the screed and distribute heat evenly.
- Pipes made of polyethylene or metal-plastic are used. There is not much difference between them, except in ease of installation: metal-plastic will be easy to install, since it simply bends.
- The larger the diameter of the pipes, the lower the flow resistance and heat transfer will be, and therefore the higher the efficiency. Therefore, pipes with a diameter of 16 and 20 mm are usually used.
- A concrete screed with fine crushed stone is used as a protective and heat-distributing layer on top of the pipes.
Number of pump speeds
By its design, a circulation pump is an electric motor mechanically connected to the shaft of an impeller, the blades of which push the heated liquid out of the working chamber into the heating circuit line.
Depending on the degree of contact with the coolant, pumps are divided into devices with a dry and wet rotor. In the former, only the lower part of the impeller is immersed in water, while in the latter, the entire flow passes through itself.
Models with a dry rotor have a higher coefficient of performance (efficiency), but create a number of inconveniences due to noise during operation. Their analogues with a wet rotor are more comfortable to use, but have lower performance.
Modern circulation pumps can be operated in two or three speed modes, maintaining different pressures in the heating system. Using this option makes it possible to quickly warm up the room at maximum speed, and then select the optimal operating mode and reduce the energy consumption of the device by up to 50%.
Speed switching is carried out using a special lever mounted on the pump body. Some models have an automatic control system that changes the engine speed in accordance with the air temperature in the heated room.
Additional functions and capabilities of pumping units
What else will help you choose a circulation pump for heating? How to choose by additional features? Please note what additional functions may be available to simplify the operation of pumping units:
Automatic operating mode. Devices with this function have an automatic system that starts the device depending on the specified parameters. For example, you can set the pump to start by time. So some people set the start for the morning before waking up so that the house warms up faster. However, the start of the automation must be coordinated with the operation of the heating boiler. In general, the automatic mode relieves the owner from constant contact with the device. Among the automatic ones, we would like to recommend the Grundfod ALPHA2 L 25-40 130, which has excellent build quality and good performance characteristics. There are six varieties of this pump with different pressures and for different pipeline cross-sections.
Availability of display. The display shows the current water temperature, total system resistance, pressure and performance at a certain minute. Also, some models display messages about errors and problems in the pipeline. However, devices with displays are somewhat more expensive than their “simple” counterparts. If you want to always monitor the status of your heating system, then a model with a display is for you. Among the high-quality ones with a display and control panel, we would like to recommend Leberg Eco Line Star, which has the possibility of both horizontal and vertical installation.
Twin design
If you are thinking about how to choose a circulation pump when the water has a lot of impurities, then you should pay attention to models with a paired design. There are two impellers at once, which are connected in parallel.
If suddenly the first fails due to damage from solid particles, the second continues to work. Models with a paired design are necessary for an uninterrupted supply of water (and, accordingly, heat). They are worth buying if, for example, your heating system is routed through an incubator or barn with “livestock”, and its abrupt shutdown will affect the death of the animals. For home use, such pumps are quite expensive, so it is better to take a closer look at their cheaper counterparts. If you suddenly need a twin-type circulation pump, then take the DAB D 56/250.40 T - it is relatively inexpensive and at the same time high-quality.
Useful tips
When choosing a pump for a heating system, preference should be given to designs with a “wet” rotor, since they operate very quietly and withstand higher loads than hydraulic devices of other modifications.
In addition, pay attention to the material of the case - opt for products made of stainless steel, bronze or brass. Preference should also be given to models with bearings and shafts made of ceramics. The service life of such equipment exceeds 20 years.
When installing the device into the system, it is necessary to ensure that the impeller shaft is positioned horizontally, that is, parallel to the pipe. If a suspicious noise appears during operation of the pump, this does not indicate a malfunction or a manufacturing defect. Try bleeding the air remaining in the system after starting.