To heat your home efficiently, you should buy high-quality elements. Before this, make the correct calculation of their power.
When calculating, heat loss from housing should be taken into account.
Calculations are made taking into account:
- room area;
- the height of its ceiling;
- number of windows,
- length of the room;
- climate features in the region.
You can calculate the performance of devices on your own. To do this, you need to know how many kW are in 1 section of an aluminum radiator or a cast iron, steel, bimetallic analogue.
Heat transfer property
The power of steel heating radiators, as well as all other types of heaters, is based on the principle of their operation:
- The coolant, entering the battery, circulates through the reservoir (for steel panel models these are channels), while when it is hot it is directed upward, while when it cools it goes downward. In an autonomous or centralized heating system, the boiler heats the medium.
- During the time that hot water comes into contact with the radiator, it gives off its heat to it, heating its walls. This point is very important, since the length of its path depends on the size of the heater, and the longer it is, the hotter the radiator.
- The heated walls of the structure give up their temperature to the air, which spreads throughout the room under the influence of heat flows.
- To increase the level of heat transfer, the heating device is equipped with heat exchangers, as can be seen from steel radiators of types 11, 22 and 33.
The presence of heat exchangers significantly increases the power of steel radiators, working on two heating principles: radiator, which uses the heat of the walls of the device, and convector, which creates the movement of heated air.
As a rule, the manufacturer indicates power indicators in the data sheet, so you can use it as a guide, but it’s even better to make your own calculations taking into account the area of the room, air temperature and the amount of heat loss.
The consequences of an incorrectly selected heater are:
- The so-called overheating, when the room is so hot that you have to keep the window open. This creates a microclimate harmful to the body, forcing you to pay more for energy costs or install thermostats to reduce the load on the system.
- If the power of panel steel heating radiators is below the required level, then the room is cold even at their maximum load.
- Strong pressure drops in a heating system equipped with weak batteries will lead to an accident, since they will not withstand such “stress”.
All of these problems can be avoided if you know what exactly affects the heat transfer of heating batteries and how to increase their efficiency.
Recommendations for choosing a bimetallic radiator
It only makes sense to install a bimetallic radiator in a city apartment. If you have a private house and your own heating boiler, it is better to buy an aluminum battery.
When choosing a bimetallic radiator with the desired heat dissipation, it is recommended to take into account the following characteristics:
- Operating pressure. It usually does not exceed 15 atmospheres. The radiator must withstand such a load;
- Power. It is necessary to calculate the number of sections using the above method;
- Dimensions. The width of the radiator is determined by the number of sections, and the height is determined by the center distance. For standard window sills with a height of 80 cm, the 500th model is suitable, but if it does not fit, you need to take the 350th modification;
- Thickness of steel tabs. Make sure it is not too small. An indirect indicator of the thickness of the tabs is the weight of the device;
- Price. Typically, bimetallic radiators cost at least 15-20% more than aluminum ones.
If you do everything correctly and choose a suitable radiator, there will be no shortage of heat in your home even in severe frosts.
Negative reviews
Before choosing an aluminum radiator, you should read consumer opinions, which are not always positive. For example, some buyers note that water leaks are sometimes noted at intersectional joints. The heat distribution in such batteries is uneven. It focuses on the ribbed surface.
Buyers also do not like the fact that the convection return is very small. Such a battery may not last long - up to 15 years. But some manufacturers have corrected this shortcoming by increasing the warranty to 25 years. Buyers quite often refuse aluminum radiators for another reason that they are chemically reactive, so corrosion is a serious enemy for these devices. But manufacturers introduce anti-corrosion treatment into the production process, covering the surface with a layer of oxide film.
How many kW in one section of a cast iron radiator
The heat output of a cast iron radiator depends on the volume of water, wall thickness, presence of fins, height and width of the section. There are several standard models of cast iron batteries, the declared heat transfer of one section of which is:
- MS-140 – 175 W;
- MS 140-500 – 195 W;
- MS 140-300 – 120 W;
- MS 110-500 – 150 W;
- MS 100-500 – 135 W;
- MS 90-500 – 140 W.
In the classification, the first number indicates the width of the vertical cast iron channel, the second - its height.
Standard 6-section cast iron radiator MS-140-500.
Modern cast iron batteries differ from standard MS brand products. They may have other sizes and designs; there are models with air cutoffs. Manufacturers claim the performance of one section ranges from 150 to 220 W.
If thermal power indicators are given for a temperature difference ΔT of 60-70 degrees, they differ from the real ones.
For batteries with a water temperature of 55-60 °C, the actual performance will be 75-85%, for batteries with a water temperature of 65-70 °C - about 85-90% of that specified in the manufacturer’s specifications.
Radiators 500 mm - standard batteries
Standard aluminum and bimetallic models with a center distance of 500 mm are suitable for most rooms. They can have from 1 to 14 sectional elements. The more there are, the more powerful the thermal device.
Power also depends on the brand, and the difference is significant. Let's compare the parameters of one 500 mm section of different brands.
| Brand | Country of origin | Power, W |
| HEATING APPLIANCE | Russia | 191 |
| Faral | Italy | 212 |
| Mirado | Spain | 196 |
| Global | Italy | 187 |
| Nova Florida | Italy | 178,5–182 |
| Fondital | Italy | 178–182 |
| Alltermo | China | 177 |
| Tenrad | Germany | 161 |
| Solar | Croatia | 114 |
What affects heat transfer?
When choosing a heater model, you need a table of the power of steel radiators, which should be provided to consumers by the manufacturer or sales consultant.
You should also take into account several nuances that are inherent in them:
- Before purchasing new heating batteries, you should ask what the temperature of the coolant in the system is. The hotter it is, the higher the radiator will be heated, which means the heat transfer will be greater. Having found out the exact temperature, you need to compare it with the indicators of the selected model, which are indicated in the data sheet. They must match for safe and efficient operation.
- The size of the radiator matters. The larger it is, the longer the carrier stays in it, and this makes its walls hotter.
- The thermal conductivity of the material is also important. In this case, we are talking about sheet steel no more than 1.5 mm thick, which indicates the ability to heat up quickly.
Such nuances determine the power of panel radiators, so when calculating it, all their parameters should be taken into account.
Conclusion
Having found out how many kW there are in 1 section of a steel radiator or an analogue made of another metal, you can calculate the heat transfer of the purchased product. This will allow you to install an efficient heating system in your home.
The video in this article continues to clearly inform you on the topic.
In order for the heating of your home to be effective, you need to purchase high-quality elements. Before this, make a correct calculation of their power.
Calculations are made taking into account:
- room area;
- the height of its ceiling;
- number of windows,
- length of the room;
- highlights of the climate in the region.
It is possible to calculate the performance of devices on your own. To do this, you need to know how many kW are in 1 section of an aluminum radiator or a cast iron, steel, or bimetallic analogue.
Thermal power
The photo shows the approximate heat transfer of cast iron.
In the room, heating devices are placed against the outer wall under the window opening. As a result, the heat emitted by the device is distributed optimally. The cold air coming from the windows is blocked by the heated air flowing upward from the radiator.
Cast iron batteries
Cast iron analogues have the following advantages:
- have a long service life;
- have a high level of strength;
- they are resistant to corrosion;
- Excellent for use in utility systems operating on low-quality coolant.
- Now manufacturers produce cast iron batteries (their price is higher than conventional analogues), which have an improved appearance thanks to the use of new technologies for casting their housings.
Disadvantages of products: large mass and thermal inertia.
The lower table states how many kW is in a cast iron radiator, based on its model.
| Radiator model | Thermal power of one section in Watts |
| MS-140/M-2 | 160 |
| MS-140/M-300 | 117 |
| MS-90 | 130 |
| T-90/M | 127 |
Note! To heat a room with an area of 15 m², the power, that is, kW of a cast iron radiator, must be at least 1.5. In other words, the battery should consist of 10-12 sections.
Aluminum radiators
This is how the heat transfer of aluminum products changes.
Aluminum products have greater thermal power than cast iron counterparts. When asked how many kW is in one section of an aluminum radiator, experts answer that it reaches 0.185-0.2 kW. As a result, for the standard level of heating of a fifteen-meter room, 9-10 sections of aluminum sections will be sufficient.
The advantages of such devices:
- a light weight;
- aesthetic design;
- high level of heat transfer;
- You can control the temperature yourself using thermostatic valves.
But aluminum products do not have the same strength as their cast iron counterparts, for example a 2 kW oil radiator. Therefore, they are sensitive to surges in operating pressure in the system, water hammer, and excessively high temperature of the coolant.
Note! When water has a high pH (acidity) level, aluminum releases a lot of hydrogen. This negatively affects our health. Based on this, it is advisable to use such devices in a heating system in which the coolant is neutrally acidic.
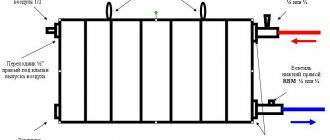
Bimetallic products
The structure of a bimetallic product.
Before you find out how many kW are in 1 section of a bimetallic radiator, you should take into account that such batteries have similar operational parameters to their aluminum counterparts. However, they do not have any inherent disadvantages.
This circumstance was determined by the design of the devices.
- They consist of copper or steel pipes through which coolant flows.
- The tubes are hidden in an aluminum plate housing. As a result, the water circulating inside does not interact with the aluminum of the case.
- Based on this, the acidic and mechanical characteristics of the coolant do not in any way affect the operation and condition of the device.
It is steel pipes that provide the bimetallic product with excellent technical characteristics.
Thanks to the steel pipes, the device has high strength. Increased heat transfer is ensured by external aluminum fins. When trying to find out how many kW is in a steel radiator, keep in mind that bimetal has the highest heat transfer - about 0.2 kW per fin.
What you need to know about radiator power?
The heat transfer of a radiator depends on the temperature of the coolant and the air in the room. The greater this difference, the better it transfers thermal energy.
An illustrative example:
If the room is 0 degrees, the battery will cool faster than if the room was +24. Accordingly, it gives off more heat. It turns out that at 0 degrees the power of the heating device is greater.
Manufacturers often claim inflated technical specifications. They show power for a temperature difference of 65-70 °C. But in reality the temperature difference is 35-50 degrees.
Therefore, if you see in the instructions the thermal power of a section of 200 W at ΔT = 70, in reality it is 150-160 W (ΔT indicates the temperature difference).
Knowing the real power value, you can calculate the required number of sections in an online calculator.
Compliance with State Standards
For all heating systems and their elements there is a single register of State Standards, which they must comply with. Everything is taken into account:
- Quality and safety of production.
- Compliance with temperature conditions and pressure in pipes.
- What should be indicated in the data sheet of the finished product.
- Standards according to technical characteristics and permissible deviations from the norm.
If you want to buy bimetallic radiators, GOST will tell you what parameters they should have, and they must correspond to the indicators in the documentation for each product. If they do not match, it is better not to purchase such products.
How many kW in one section of an aluminum radiator
The thermal power of an aluminum radiator section depends on the volume of water contained in it. Standard volumes are 0.35 and 0.5 l.
Aluminum batteries give off heat 50-60% by radiation and 40-50% by convection. The air cutter enhances convection by 20-25%, which increases heat transfer.
At an air temperature of 20-24 °C and water temperature in the circuit of 65-70 °C, the thermal power of one aluminum section is:
- Volume 0.35 l., without cut-off – 0.1-0.12 kilowatts;
- Volume 0.35 l., with cut-off – 0.12-0.13 kilowatts;
- Volume 0.5 l., without cut-off – 0.155-0.170 kilowatts;
- Volume 0.5 l., with cut-off – 0.170-0.200 kilowatts.
It is difficult to name the exact amount of heat transfer - it depends on the design features, the diameter of the pipes, and the thickness of the fins. Performance is affected by the type of battery connection, water pumping speed, and contamination of internal surfaces.
Aluminum radiator without air cutoffs.
Correction factors
Despite the same values in the data sheet, the actual heat transfer of radiators may differ depending on operating conditions. Considering that the above formulas are accurate only for houses with average insulation rates and for areas with a temperate climate, under other conditions it is necessary to introduce amendments to the calculations.
Correction factors when calculating the number of heating radiator sections
To do this, the value obtained during the calculations is additionally multiplied by a coefficient:
- corner and northern rooms - 1.3;
- regions with extreme frosts (Far North) - 1.6;
- screen or box - add another 25%, niche - 7%;
- for each window in the room, the total heat transfer for the room increases by 100 W, for each door - 200 W;
- cottage - 1.5;
Important! The last coefficient when calculating bimetallic radiators is used extremely rarely, because such heating devices are almost never installed in private homes due to their high cost.
Bimetallic radiators