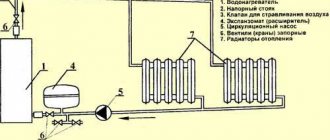
Water as a coolant, despite its availability and excellent thermophysical characteristics, at the same time has a significant drawback. In the event of an unexpected cessation of its circulation in the heating system, the pipes at subzero temperatures are doomed to destruction.
You can, of course, use heating circuits based on solar systems, but this is not possible in all cases.
Therefore, when developing and installing individual heating systems, attention is increasingly paid to the use of alternative coolants based on non-freezing liquids. Propylene glycol for heating systems rightfully comes first on this list.
The use of propylene glycol in heating systems of a private home
Heating with antifreeze or water
After reading this section, you will most likely refuse antifreeze in your heating system.
The main advantage of antifreeze - the safety of the system at subzero temperatures - is completely negated by its disadvantages. Low heat capacity of antifreeze. Increasing the size of radiators by 20-23% The heat capacity of antifreeze is significantly lower than the heat capacity of water. By diluting water with 35% antifreeze, we lose approximately 200 W per 1 kW of thermal energy. This means that the size of pipes, radiators and boiler must be increased by 20%. In terms of a country house of 300 m2, we lose approximately 60 thousand rubles by increasing the size of the system.
The service life of antifreeze is from 5 to 10 years. Over the years, antifreeze oxidizes and safely destroys brass connections. After 5 - 10 years, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol must be drained, disposed of and replaced with a new one. You will not only have to buy new antifreeze, but also pay to dispose of the old one. Unfortunately, in our country there is no service for recycling ethylene glycol in small volumes, so finding someone to hand over this chemical to will be difficult. I won’t consider the idea of dumping antifreeze on my neighbor’s property.
The use of sectional radiators in systems with antifreeze is unacceptable. Rubber sectional gaskets quickly oxidize, and the radiators leak. We use only steel panels. The use of galvanized pipes is also unacceptable. Antifreeze safely washes away the zinc, and the pipe remains bare.
Why is antifreeze useless for a country house? Antifreeze will successfully cope with the task - the heating system will not freeze in winter in your absence, but what to do with the water supply system? Water supply pipes at subzero temperatures will freeze faster and with worse consequences, because... laid not only in the floor, but also in the walls. You will have to remove the tiles, beat the screed and change the pipes in the bathrooms, showers, kitchen, and replace the entire water supply system of the boiler room. Of course, it will not be possible to pump antifreeze into the water supply system, nor will it be possible to lay all the pipes with heating cables.
Conclusion: Antifreezes are suitable either for heating small country houses for temporary residence, or large warehouses, workshops and enterprises. In the heating system of a full-fledged country house, antifreeze is useless.
Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house is needed if: you do not plan to live in the house in winter; the house has 1-2 bathrooms with a tee water supply system (without a collector), which can be drained before the onset of cold weather.
It is impossible to leave a full-fledged country house in winter without heating on duty. In winter, it is necessary to maintain constant standby heating +10-12°C. Heating a full-fledged country house for permanent residence with antifreeze is the same losing option as heating a house with warm floors, which is applicable only in the southern regions of our country.
This way your engineering systems will be truly protected without antifreeze.
If you liked my article and are looking for reliable design specialists, call or email me.
Types of heating systems
Experts distinguish two heating systems.
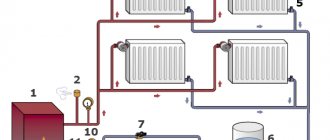
Construction specialists primarily classify heating systems by the type of coolant used. There are water and air heating systems for houses. When using a water system, heat is delivered to the house by water heated in special heating elements, for example, in a boiler room. Water, usually using pumps, is supplied to the radiator system and thus heats the house. The air system uses a network of ventilation equipment through which heated air fills the entire room. Alternative heat sources have also recently become increasingly popular. These include solar panels, biogas heating and much more.
Water heating systems
Basically, water heating systems are powered by gas boilers.
Water systems are also divided into several categories based on the principle of using different heating equipment. There are radiator systems, baseboard systems and warm water floors. Most water heating systems operate from gas boilers. You can find more detailed information about gas boilers here. They are quite environmentally friendly, highly efficient, and the most modern models have maximum automation functions, which makes them safe and easy to install and operate. In addition, gas heating can be used in completely autonomous systems, independent of city communications, which is why they are often used in country and private homes. The disadvantage of a gas boiler is the need to manually control the fuel supply to the heating element.
Air heating systems
When using air systems, the main heat carrier is heated air, which spreads throughout the room, displacing cold masses. The center of such a system is a programmable thermostat, which allows you to set the required temperature and create a unique microclimate necessary for this room. The main advantage of an air heating system is energy savings because there is no intermediate heating element as in a water heating system. Thus, the air temperature is much easier to regulate and adequately respond to weather changes outside the walls of the house. In addition, in warm weather, this system can work as a ventilation system, saturating the room with fresh air.
Operational moments
A ready-made solution of propylene glycol for heating devices has lower thermal conductivity and heat capacity than water. Therefore, when using a substance, it often becomes necessary to add the number of batteries in the room. Heating equipment may also need to be replaced.
To productively use polypropylene-based antifreeze for a heating system, you should consider some operational recommendations:
- due to the high viscosity of this coolant, it is necessary to install a pipeline with a diameter of at least 25 millimeters, and also select a sufficiently powerful circulation pump;
- for metal pipes, antifreeze with additives that prevent the formation of corrosion should be used;
- use an aerometer annually to check the concentration of the main reagent;
- use an expansion tank of at least 10 liters;
- provide free access to all connections of heating equipment in case of leaks;
- replace propylene glycol coolant every five operating seasons;
- use and regularly monitor strainers for heating systems.
- When replacing antifreeze, thoroughly flush the heating equipment.
Replacement of propylene glycol-based coolant must be done every 5 seasons.
If it is necessary to mix this coolant, it must be taken into account that the solution is compatible with liquid based on glycerin, propylene glycol or ethylene glycol. In this case, the type of additive included in the composition is taken into account, since incorrect combination of different additives can cause a decrease in the technical characteristics of antifreeze.
Due to its many advantages, propylene glycol is considered one of the best coolants for heating equipment. But in order to ensure the efficient operation of the heating system for several years in a row, all technical and operational requirements must be observed when using it.
Advantages and disadvantages
To prevent scale formation, propylene glycol is mixed with distilled water.
In water at temperatures above +75°C, carbonates decompose and scale is deposited. Propylene glycol inhibits the corrosion process, ideally if the substance is added to a distilled liquid.
Advantages of using energy carrier with additives:
- protects the heating circuit and devices from rupture in frost, freezing occurs slowly with gradual crystal formation;
- the frozen substance in the pipes acquires a working consistency when the heating unit is started;
- the second most environmentally safe coolant after water, long-term inhalation of vapors, ingestion, contact with skin is not dangerous;
- does not damage materials upon contact with floor and wall finishes;
- promotes rapid heating and slow cooling of the system;
- reduces hydraulic resistance and improves the functioning of the pump in the return branch;
- reduces electricity consumption when pumping energy carriers, due to its low density.
Description of propylene glycol
For a rarely visited country house, it is better to use non-freezing liquid
The substance is actively used in heating circuits due to its non-toxicity and safety. It is a viscous, colorless liquid with a characteristic odor, which is used in many industries.
Liquid properties:
- the solution can withstand temperatures from -40 to +100°C without changing the state; for a pure substance, operating parameters are in the range -60 – +185°C;
- the substance contains up to 5% carboxylates, which protect the inside of the pipe from destruction;
- Anti-corrosion, anti-scale and stabilizing additives are introduced into the composition of glycol for heating.
The density of propylene glycol is less than that of glycerin and ethylene glycol, but higher than that of ethanol. The viscosity of the substance is greater than that of alcohols and ethylene glycol, especially in cold conditions. The substance is produced from propylene oxide by hydration at +160 – +200°C under a pressure of 1.6 MPa.
The reaction takes place in a vacuum, and in the process the following is released:
- propylene glycol – 85%;
- dipropylene glycol – 13%;
- tripropylene glycol – 2%.
Main characteristics
Propylene glycol is a hygroscopic substance that can dissolve in water, acetone, ethanol, chloroform and diethyl alcohol. This colorless liquid containing a carbon atom has a low degree of volatility. It is not capable of causing corrosion and is completely safe to use.
Among the characteristics of propylene glycol are:
- density – 1037 kg/m³, which is almost 4 percent more than that of water;
- a fairly high boiling point - 188 degrees above zero;
- thermal conductivity – 0.218 W/(m*K);
- the beginning of crystallization is at -60 degrees;
- specific capacity value – 2483 J/(kg*K).
What does propylene glycol look like
? The coolant propylene glycol is an aqueous solution that remains in liquid form at temperatures from -40 to 100 degrees. The finished substance, in addition to the main component dissolved in distilled water, includes dyes, as well as no more than 5 percent of anti-corrosion, stabilizing, softening additives.
The density of propylene glycol coolant depends on the concentration of the main component. The higher its percentage, the higher its maximum boiling level. The density indicator also increases accordingly. Based on this, percentage markings are indicated on the coolants produced.
Features of use for heating
The coolant propylene glycol is poured into the system in accordance with the technical specifications. Before using antifreeze, a number of preparatory steps should be carried out:
- drain the liquid from the system, flush all circuits with caustic soda, remove all deposits and rust;
- perform sealing of all connections, including tappings and bends;
- remove and replace all zinc-containing parts.
After this, you can fill the system with propylene glycol solution. In this case, it is recommended to keep the drain valve open at the lowest point. This action will allow you to immediately see when the thermal contours are completely filled. After filling, the system is checked for leaks and a test run of the heating equipment is carried out.
Criterias of choice
The main point that should be taken into account when choosing a coolant for space heating systems is the manufacturer’s recommendation for heating equipment. The instructions for the boiler often indicate the requirements for the liquid that fills the water circuit, and sometimes the brand of antifreeze.
The main factors to consider when choosing a propylene glycol solution for heating systems are:
- Climatic conditions of use. Different brands of products indicate the maximum freezing temperature level. This indicator depends on the concentration of the solution, the percentage of which is also indicated in the name of the coolant.
- Manufacturer. The efficiency of the heating system depends on the quality of antifreeze. You can purchase good products from trusted manufacturers. High-quality products do not contain toxic substances and are completely safe for use.
- Characteristics of additives. Propylene glycol-based products included in ready-made coolants can have anti-corrosion characteristics, while providing protection against metal destruction. Softening components are often added to the composition, which protect rubber elements from deformation. Therefore, when choosing antifreeze, the technical and design features of heating equipment are taken into account.
When choosing a coolant based on propylene glycol, take into account the characteristics of the additives.
Antifreeze with carboxylate-type additives is especially popular. Such a coolant can be used for almost any material included in the design of a thermal device.
Propylene glycol intended for heating systems must meet all technical requirements and comply with the characteristics of the heating equipment used.
Alternative sources of home heating
Alternative sources of heating for the home are economical and safe.
When using alternative or renewable energy sources, such as the sun or earth's energy, the owner of the premises is also independent of external communications. In this case, collectors are used to collect the collected energy or heat pumps to supply it continuously. Such systems are completely safe for nature and save money for owners who do not have to pay for the supply of gas or electricity.
Most often, home owners who want to protect themselves as much as possible from economic crises and the lawlessness of public utilities install autonomous heating. For this system, specialists select the installation methods and format individually, adapting it to the characteristics of the room. Autonomous heating can be electric or gas, if it is possible or necessary to connect to fuel communications. For complete independence from external suppliers, boilers running on solid or liquid fuel are used. In addition, autonomous heating allows you to combine different energy sources, creating the most adaptable and convenient option for most buildings.
Alternative sources of home heating
Alternative sources of heating for the home are economical and safe.
When using alternative or renewable energy sources, such as the sun or earth's energy, the owner of the premises is also independent of external communications. In this case, collectors are used to collect the collected energy or heat pumps to supply it continuously. Such systems are completely safe for nature and save money for owners who do not have to pay for the supply of gas or electricity.
Most often, home owners who want to protect themselves as much as possible from economic crises and the lawlessness of public utilities install autonomous heating. For this system, specialists select the installation methods and format individually, adapting it to the characteristics of the room. Autonomous heating can be electric or gas, if it is possible or necessary to connect to fuel communications. For complete independence from external suppliers, boilers running on solid or liquid fuel are used. In addition, autonomous heating allows you to combine different energy sources, creating the most adaptable and convenient option for most buildings.
Coolant for heating system
Modern coolant has a complex set of constituent chemical elements. Known antifreeze fluids used in heating systems are based on three fundamental components. Accordingly, each liquid is endowed with different properties and characteristics. The main difference in the technical characteristics of the presented brands is determined by the fillers on which the coolant is mixed:
- ethylene glycol; - propylene glycol; - glycerin.
The coolant is produced in the form of a concentrate or is often offered a little more expensive, ready for use, without additional enrichment with water. Manufacturers offer high-quality antifreeze. Thanks to the moderate concentration and proper proportions of polyhydric alcohol, a good coolant does not “corrode” the rubber gaskets of pumping equipment. There is a complete absence of negative impact on polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes.
The Russian market offers antifreeze liquids with a huge variety of brands from various, both domestic and foreign manufacturers. In common parlance, “anti-freeze” is found under the names: “Warm House”, “Dixis”, “Thermagent Eco”, “Thermos Eco”, “TeploDom”, “Antifrogen N” and many others. As a rule, antifreezes have different colors, repeating almost the entire range of the rainbow palette: green, blue, yellow, red and even pink.
Blitz tips
- The choice of coolant must be made during the design process.
- Ethylene glycol mixtures are strictly prohibited for use in double-circuit boilers.
- The use of propylene glycol is true in relatively small heating circuits and only in the absence of leaks.
For normal functioning of the heating system in severe frosts, it is recommended to use a special coolant. On the modern market you can find various substances that prevent the heating system from freezing. But propylene glycol-based coolant is considered safer and more effective. This product has many positive characteristics and its own characteristics of use.
Using glycerin as a coolant
To obtain a glycerin-based coolant, the pure substance is mixed with various impurities that allow it to remain liquid when used in cold conditions. The resulting composition is chemically inert, and no chemical processes occur inside that can have a detrimental effect on the elements of the entire system.
The ability to maintain a liquid state at sub-zero temperatures and absolute safety for humans allows the coolant to be used for heating systems in residential buildings, including floor heating.
The operation of this heating system is based on one principle: there is a heater, heating elements and coolant. In this case, the main characteristics of the coolant will affect the overall heating efficiency.
Advantages of glycerin coolant
Compared to propylene glycol or ethylene glycol compounds, this antifreeze has the following advantages:
Can be used in a wide temperature range from -30 to +105 °C. Even when the substance is completely frozen, it does not expand and does not cause damage to the pipes. After thawing, all its original properties are restored. The coolant is sold ready-made and does not require additional dilution with water.
Glycol formulations must be diluted; Antifreeze does not cause corrosion or other damage to heated floor elements, including galvanized pipes and rubber gaskets; The substance is absolutely safe for human health and the environment, which is very important in case of leaks or damage to the system as a whole; At a relatively high price, the composition has a long service life of up to 8 years. Another type of antifreeze has been used for about 5 years; The coolant can be poured into the pipes after any other type of antifreeze; no flushing is required; Antifreeze is produced only from high-quality raw materials, which are also used in the food and cosmetic industries; Belongs to the class of non-flammable substances.
Disadvantages of glycerin composition
Glycerin-based coolant has its disadvantages, which must be taken into account when designing a heated floor:
- When freezing, the density and viscosity of the glycerin composition increases, which leads to a decrease in its heat capacity. In the heating system project, you will have to use pipes of a larger diameter than when using ordinary water;
- The high viscosity of the composition will require the installation of a more powerful circulation pump in the heating system;
- Glycerin-based antifreeze requires the use of reliable and expensive gaskets and seals during heating installation. Teflon or paronite gaskets are recommended;
- Antifreeze has a tendency to foam, which can cause the heated floor to become airy. Special additives help to partially reduce foaming;
- A glycerin-based composition has a density and mass greater than a glycol-based one. The use of a glycerin composition in a heated floor system will increase the load on the floors and foundation of the building.
Scope of application
Propylene glycol is quite in demand in modern industry. Coolants made on its basis are widely used not only for heating systems, but also as antifreeze for ventilation and air conditioning equipment.
The safety of the substance allows it to be used in residential and public buildings. At the same time, antifreeze can be poured into structures made of various materials, including rubber, aluminum, steel, copper or cast iron. The exception is galvanized coating.
The scope of application of propylene glycol in the industry is quite extensive:
- pharmaceuticals;
- tobacco production;
- production of food products;
- automotive and aviation industry;
- Oil and gas industry;
- cosmetology, perfumery;
- medicine.
Uses of propylene glycol include livestock and agriculture. It is practiced to improve the quality of feed, as well as to extend the shelf life of vegetable crops. In chemical production, a viscous substance is used in the production of polyurethanes, paint solvents, plastics or polymers.
New mineral coolants
We decided to highlight the description of these liquids, since they are made based on the natural mineral - bischofite. The substance is a magnesium salt of hydrochloric acid, the full name is magnesium chloride hexahydrate. The manufacturer declares the following characteristics of the finished antifreeze, designed for a minimum temperature of minus 30 degrees:
- the color of the aqueous solution is light yellow, the density is 1117...1250 kg/m³;
- boiling threshold - 116 °C, freezing point - minus 30 °C;
- specific heat capacity - 0.77 kcal/kg •°С (3.23 kJ/kg•°С);
- thanks to the additives, there is no foaming and no aggressive effect on various seals - silicone, paronite, EPDM and BMS rubber;
- the substance is not toxic;
- In terms of viscosity and fluidity, the drug is very close to glycol chemicals.
Compared to traditional glycol analogues, mineral antifreeze benefits due to its high boiling point, cost and health safety. The negative point is the increased density and low heat capacity, 23% worse than that of water.
The practical use of the coolant has revealed a number of shortcomings, as evidenced by reviews from homeowners:
- The fluidity of the solution is extremely high. There have been cases where antifreeze penetrated through the soldered joint of polypropylene pipes.
- Upon contact with air, the liquid fraction quickly evaporates, leaving a noticeable salt build-up. Similar phenomena are observed in heat exchangers and pipelines where air bubbles have penetrated.
- The substance reacts with bare metal on welds. Stalactites of iron and salt form inside the system, reducing the flow area and clogging the mud traps.
- In case of overheating, antifreeze turns into a liquid of unknown color, as shown in the photo.
Taking into account the experience of users, we do not dare to recommend mineral antifreezes for use in heating systems of private houses.
Perhaps over time, manufacturers will eliminate the above problems and the magnesium chloride solution will be able to compete on equal terms with glycols. Date: September 25, 2022
What happens if you pour water from a well into a heated floor?
Kardinale FORUMHOUSE user
Hi all! Help me solve the problem. I have a heated floor installed. Filled with water from the well. Look what happened after the summer heat. The water bloomed. There's some mucus inside. The system works, but I want to flush it. And most importantly, how to avoid this in the future?
MycraftUser FORUMHOUSE
I advise you:
- Flush the system.
- Remove all ferrous metal components and replace them with copper, stainless steel, etc.
- Fill the closed system with water purified by reverse osmosis.
- Additionally, install a sludge separator.
If you think that rust in a heated floor will lead to nothing, look at the photos taken by Mycraft.
This is what pipes clogged with rust look like.
TP combs.
System elements and branches.
And this is an experiment that Mycraft conducted. Two cans of water. On the left is plain water, on the right is desalted water. Samples of metals commonly used to make heating system components - copper, brass, steel and aluminum - were added to the jars. The water was periodically heated and cooled.
Start of the experiment:
11 months later:
In 2 years.
As they say, comments are unnecessary.
Do not pour water from a well or distilled water into the heated floor, because... The pH value of distilled water decreases after contact with air when filling the system. As a result: the acidity level of distilled water increases and acid corrosion can occur. Pour into warm, specially prepared coolant or demineralized water.