Correct calculation of thermal insulation will increase the comfort of your home and reduce heating costs. During construction you cannot do without insulation, whose thickness determined by the climatic conditions of the region and the materials used. For insulation, foam plastic, penoplex, mineral wool or ecowool, as well as plaster and other finishing materials are used.
Basic rules for insulating house walls:
There can never be too much insulation. In a house with a wall area of 250-300 sq. m, with year-round living, external insulation made of basalt wool will pay for itself in 5 years +-1 year. When using the house as a weekend dacha, the payback period for external insulation of the walls of the house will shift to the life expectancy of the owner.
However, for such wall materials as aerated concrete, external insulation of the walls of a house theoretically allows you to extend the service life of the material itself and will allow you to save on the thickness of aerated concrete during construction: a cube of insulation costs a third less than aerated concrete and at the same time has greater resistance to heat transfer. It is economically feasible for a country house to make thinner aerated concrete walls and insulate them from the outside. This will be cheaper than building walls from thicker aerated concrete.
Insulating the walls of a house without insulating the base of the house, the foundation and the adjacent soil means losing another 10 to 16% of the heat from the room. In addition, insulating the soil around the foundation of a house (or under the foundation) helps reduce soil movement as a result of frost heaving.
When choosing insulation for walls, you need to pay attention to its heat-shielding properties (thermal conductivity), and not to its density. Most often, there is an inverse relationship between thermal insulation properties and the density of wall insulation (the denser the colder). The resistance of the insulation layers of the walls of the house to slipping is also important.
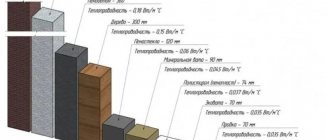
Rating of insulation in terms of thermal conductivity in a dry state. (In reality, you need to take the operating conditions of the insulation in humidity group B - the indicators are different)
Wall insulation Thermal conductivity in a dry state (according to manufacturers' advertising data) (W/m°C) Insulation density (kg/m3) EPPS Penoplex 0.02835-45 Phenolic foam FL 0.0330 Polyethylene foam 0.03220-40 Isover glass wool 0.03320 Isotec mineral wool boards 0.0345 0Glass wool Ursa Urea polystyrene foam (Penoizol) Foam plastic PSB-S0.035 Mineral wool Rockwool 0.03634 Polyurethane foam 0.0440 Ecowool 0.041 Mineral wool Parock 0.04530 Foam glass 0.085200
It is better to install thermal insulation on the outside of the house. Inside the house there should be heated massive heat-intensive wall material.
If the paths for removing steam from the insulation are disrupted (the use of non-vapor-permeable materials, membranes and the absence of ventilation gaps), the thermal insulation properties of the insulation are reduced.
Thermal insulation materials (insulation) must fit tightly to the wall and frame (installation by surprise), as well as to each other. A loose fit of the insulation contributes to the appearance of “air pockets” and “cold bridges” through which heat escapes.
Mineral wool materials have high vapor permeability. The steam passing through the mineral wool insulation condenses in its thickness.
Therefore, in a frame structure, the insulation must be protected from the inside on the “warm” side of the house by a vapor barrier. When insulating externally, you cannot protect the vapor barrier from the inside: the moisture will remain in the wall. Favorable conditions must be created outside the insulation towards the “street” for the free release of steam (drying of the outer surface of the wall and the insulation).
If plaster is used over insulation, it must be vapor permeable. If a curtain façade is used, there should be an air gap of 3-4 cm between it and the insulation for ventilation. If insulation is used for external insulation of the wall of a house, then a vapor barrier cannot be installed between it and the wall - this will lead to dampness of the wall.
What is better to insulate the walls of a house: glass wool (Isover, Ursa) or mineral wool (Rockwool, Paroc)?
Definitely - mineral wool insulation: it has less slipping of layers, less hygroscopicity and greater heat resistance in case of fire. With glass wool insulation, everything is exactly the opposite, only the price is lower. In addition, glass wool generates much more dust when installed in walls.
About the use of polystyrene foam for external insulation of house walls.
My personal opinion: if it is possible to avoid using polystyrene foam, then this should be done. Only ordinary (non-extruded) foam of grades 15-25 (density up to 16-17 kg per cubic meter) has vapor permeability. At the same time, such polystyrene foam has little mechanical strength and is perfectly eaten by mice and rats.
There are special façade types of polystyrene foam that maintain vapor permeability and have a compacted outer layer. Accordingly, the price of such material is in no way lower than mineral wool slabs, which makes its use meaningless. The most common mistake is insulating an aerated concrete house with extruded polystyrene foam with almost zero vapor permeability.
Instead of insulation, this “folk technology” leads to dampening of aerated concrete and a sharp decrease in its thermal insulation properties. Accordingly, mold and other delights appear from moisture. There are special perforated extruded polystyrene foams (Baumit) with high vapor permeability for external wall insulation, but the price and inaccessibility make their use pointless for country house construction.
It is possible and necessary to use ordinary non-preforated extruded polystyrene foam where there is no vapor transfer through the wall and there is a lot of external moisture: on plinths, grillages, underground floors, concrete floors. In this case, extruded polystyrene foam also serves as an additional barrier to moisture. In the event of a fire, polystyrene foam without fire retardants turns into a chemical weapon.
The presence of fire retardants in polystyrene foam can only be checked experimentally: by setting fire to samples of the material. You should not trust manufacturers and sellers of polystyrene foam - the price of “trust” will be too high. In our tests, the best results (it ignited poorly and did not support combustion without a fire source) were obtained from the American XPS Roof mate from Dow Chemicals.
Rating of insulation materials by flammability group (in reality, it is necessary to evaluate the fire hazard group, which is also determined by ignition, flame spread, toxicity and smoke).
Insulation of house walls Flammability group Foam glass NG Mineral wool Rockwool Mineral wool Parock NG Glass wool Ursa, Isover NG-G1 (melts at 500 C) The NG group includes only wool with a density of up to 40 kg/m3 Polystyrene concrete G1 Phenolic foam FL Polyethylene foam Foam Izol G2 Polyurethane EPP foam PSB foam -SG3-G4
Polyurethane foam. If your house is made of wood and you want to quickly get rid of it, order “dousing” the village walls and ceilings with polyurethane foam. The complete absence of ventilation and vapor transfer through polyurethane foam will do its dirty work in 5-7 years. Polyurethane foam is only suitable for vapor-tight concrete structures away from fire (it burns like gasoline) and sunlight (UV rays destroy polyurethane foam in a few months).
But at a price with spraying of 10-15 tr. per cube, a country house builder can easily forget about this type of insulation.
Foam glass. A good thermal insulation material, practically devoid of disadvantages, except for inaccessibility, high price, low thermal insulation ability and the need to widen the foundation for foam glass blocks.
Among the most environmentally friendly materials for wall insulation is high-quality ecowool. But its quality is determined solely by the conscience of manufacturers who add environmentally friendly or non-environmental fire retardants. You need to know that over time, the “non-flammability” properties of ecowool disappear.
Its flammability is actually G1-G2. There are also exotic natural and flammable wall insulation materials made from sheep wool, recycled cotton, hay, etc.
Comparison of average retail prices for various types of wall insulation:
Material price per cubic meter Mineral wool board 1500-2500 rubles Glass wool board 1000-1300 rubles Ecowool 1000-2500 rubles Polyurethane foam (with application) 10000-15000 rubles Foam glass 6000-13000 rubles Expanded polystyrene 2000-3000 rubles Extruded polystyrene foam 30 00-4000 rubles
The need to use WDVS thermal insulation systems is caused by high economic efficiency. Following European countries, the Russian Federation has adopted new standards for thermal resistance of enclosing and load-bearing structures, aimed at reducing operating costs and energy saving. With the release of SNiP II-3-79*, SNiP 02/23/2003 “Thermal protection of buildings”, the previous thermal resistance standards have become outdated. The new standards provide for a sharp increase in the required heat transfer resistance of enclosing structures.
Now previously used approaches in construction do not comply with new regulatory documents, it is necessary to change the principles of design and construction, introduce modern technologies. As calculations have shown, single-layer structures do not economically meet the accepted new standards of building heating engineering. For example, in the case of using the high load-bearing capacity of reinforced concrete or brickwork, in order for the same material to withstand thermal resistance standards, the thickness of the walls must be increased to 6 and 2.3 meters, respectively, which is contrary to common sense. If you use materials with the best indicators of thermal resistance, then their load-bearing capacity is very limited, for example, like aerated concrete and expanded clay concrete, and expanded polystyrene and mineral wool, effective insulation materials, are not structural materials at all.
At the moment, there is no absolute building material that would have a high load-bearing capacity in combination with a high coefficient of thermal resistance. In order to meet all construction and energy saving standards, it is necessary to construct the building according to the principle of multilayer structures, where one part will perform the load-bearing function, the second - the thermal protection of the building . In this case, the thickness of the walls remains reasonable, and the normalized thermal resistance of the walls is observed. In terms of their thermal performance, WDVS systems are the most optimal of all facade systems on the market. Table of the required insulation thickness to meet the requirements of current standards for thermal resistance in some cities of the Russian Federation: Table, where: 1 - geographical point 2 - average temperature of the heating period 3 - duration heating period in days 4 – degree-days of the heating period Dd, °C * day 5 – normalized value of heat transfer resistance Rreq, m2*°C/W of walls 6 – required insulation thickness Calculation conditions for the table: 1.
The calculation is based on the requirements of SNiP 02/23/2003 2. Group of buildings 1 is taken as an example of the calculation - Residential, medical and preventive institutions and children's institutions, schools, boarding schools, hotels and hostels. 3.
In the table, the load-bearing wall is taken to be 510 mm thick brickwork made of ordinary clay bricks on cement-sand mortar l = 0.76 W/(m * °C) 4. The thermal conductivity coefficient is taken for zones A. 5.
Estimated indoor air temperature + 21 °C “living room in the cold season” (GOST 30494-96) 6. Rreq is calculated using the formula Rreq=aDd+b for a given geographical location 7. Calculation: Formula for calculating the total heat transfer resistance of multi-layer fencing: R0= Rв + Rв.
p + Rn. k + Ro. k + Rн Rв – heat transfer resistance at the inner surface of the structure Rн – heat transfer resistance at the outer surface of the structure Rв.
n – thermal conductivity resistance of the air layer (20 mm) Rн. k – thermal conductivity resistance of the supporting structure Ro. k – thermal conductivity resistance of the enclosing structure R = d/ld – thickness of homogeneous material in m, l – coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material, W/(m * °C) R0 = 0.115 + 0.02/7.3 + 0.51/0, 76 + dу/l + 0.043 = 0.832 + dу/l dу – thermal insulation thickness R0 = Rreq Formula for calculating the thickness of insulation for given conditions: dу = l * ( Rreq – 0.832)
a) – the average thickness of the air gap between the wall and the thermal insulation is taken to be 20 mmb) – the thermal conductivity coefficient of polystyrene foam PSB-S-25F l = 0.039 W/(m * °C) (based on the test report) c) – the thermal conductivity coefficient of facade mineral wool l = 0.041 W/(m * °C) (based on test report)
* The table shows the average values for the required thickness of these two types of insulation.
Approximate calculation of the thickness of walls made of a homogeneous material to meet the requirements of SNiP 23-02-2003 “Thermal protection of buildings”.
* for comparative analysis, data from the climatic zone of Moscow and the Moscow region are used. Conditions for performing calculations for the table:
1. Standardized value of heat transfer resistance Rreq = 3.14 2.
Thickness of homogeneous material d= Rreq * lThus, the table shows that in order to build a building from a homogeneous material that meets modern requirements for thermal resistance, for example, from traditional brickwork, even from perforated brick, the thickness of the walls must be at least 1 , 53 meters. To clearly show what thickness of material is needed to meet the requirements for the thermal resistance of walls made of a homogeneous material, a calculation was performed taking into account the design features of the use of materials, the following results were obtained: This table shows the calculated data on the thermal conductivity of materials. According to the table for clarity, it turns out the following diagram:Author: Gennady EmelyanovTweet PrintE-mailWall insulation with mineral wool for wall insulation is always done after the construction of buildings is completed. The finishing of the house begins with insulation. Without installing insulation, any house can be considered unfinished, because it will not withstand external loads well. Moreover, in really cold areas it is necessary to carry out an accurate calculation of the insulation based on which, it is necessary to determine which of all the presented materials that modern developers produce will be better suited in total. Laying mineral wool for wall insulation This is exactly what we will do in this article.
Styrofoam
Usually this word refers to foamed polystyrene and extruded polystyrene (penoplex). In terms of chemical composition and thermal insulation properties, these materials are practically the same, however, penoplex has much greater bending strength and resistance to crumbling than traditional polystyrene foam. For this reason, recently most consumers are abandoning foamed polystyrene (foam) in favor of extruded polystyrene (penoplex).
Styrofoam
The advantage of this type of thermal insulation is its low price, ease of installation and moisture resistance. The disadvantages include the flammability of this material, and when polystyrene burns, a large amount of toxic substances is released.
Polystyrene slabs are produced in thicknesses from 5 mm to 50 mm; a special chamfer is made on the edges of the slabs so that during installation, gaps and, consequently, “cold paths” do not appear at the joints.
Expanded polystyrene
If a layer thickness of more than 50 mm is required, then two or even three layers of polystyrene are laid, with each new layer being laid offset relative to the previous one so that the joints of the slabs of the upper row fall on the centers of the slabs of the lower one.
Screed diagram with foam plastic
When insulating a floor located directly above the ground, the foam layer must be at least 300 mm for a house with a wooden floor, and 200 mm for a house with self-leveling concrete floors. You should lay at least 4 layers of the thickest foam panels, offset from each other.
If there is a cold basement under the floor, then the foam layer can be reduced by 50mm.
To insulate floors between floors of a private house, 150 mm of foam is sufficient for wooden floors and 100 mm for concrete floors.
If you are insulating floors in an apartment building, then for all floors except the first it is enough to lay one layer of foam plastic 50 mm thick. On the ground floor the thickness can be increased to 80-100 mm.
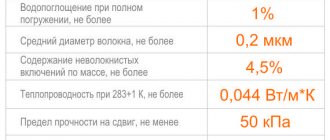
| Index | Polyspen | Polyspen Standard | Polyspen 45 | Control method |
| Density, kg/m3 | 30-38 | 30-38 | 38,1-45 | 5.6 each |
| Bending strength, MPa, not less | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 5.8 each |
| Water absorption in 24 hours, % by volume, no more | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 5.9 each |
| Thermal conductivity at 25+-5 degrees Celsius, W/m * °C, no more | 0,028 | 0,028 | 0,030 | at 5.10 |
| Toxicity, Hcl 50, g/m3 | T2 moderately hazardous | T2 moderately hazardous | T2 moderately hazardous | at 5.11 |
| Flammability group | G-3 normal-flammable | G-4 highly flammable | G-4 highly flammable | at 5.12 |
| Flammability group | B-2 moderately flammable | B-3 flammable | B-3 flammable | at 5.13 |
| Smoke coefficient | High smoke generating ability | High smoke generating ability | High smoke generating ability | at 5.14 |
| Compressive strength at 10% linear deformation, MPa, not less | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,3 | 5.7 each |
Calculated thicknesses of Penoplex thermal insulation
1General information
So, walls, as we noted above, are insulated almost everywhere. This is a real necessity, especially for those whose home is located in climate zones with harsh winters.
It is the walls that are the load-bearing and enclosing structures of the house. Unlike floors or roofs, external walls are in contact with the outside world over their entire area.
And if the temperature outside is very low, then the surface of the walls will quickly cool down. Calculations show that even the strongest brick walls cannot be completely protected from freezing unless insulation is used.
Or rather, this can be done as in the case of insulating a hangar using polyurethane foam. You just need to build walls 1 meter thick, and even with a decent layer of plaster. But as you yourself understand, this option is not the cheapest, and it is better not to use it.
Insulation materials, due to their thermal conductivity, density and other similar characteristics, cope with the assigned tasks much better.
Calculations show that insulation thickness within 10 cm is more than sufficient to protect houses in the average climate zone. If you live in a very cold climate, then the clean layer of insulation will have to be calculated separately.
Then it is possible that at the end you will have to install slabs whose thickness will be up to 15 cm. But this, again, depends on the insulation, as well as on what its density is, what characteristics are better, etc.
But you must admit, it’s still better and cheaper than if you were going to build meter-long brick walls.
How to calculate the thickness of roof and attic insulation
The formulas for calculating resistance for roofs use the same, but the minimum thermal resistance in this case is slightly higher. Unheated attics are covered with bulk insulation. There are no restrictions on thickness here, so it is recommended to increase it by 1.5 times relative to the calculated one. In attic rooms, materials with low thermal conductivity are used for roof insulation.
2Types of modern insulation
Fortunately, at the moment the market provides us with the opportunity to choose from a huge number of materials for insulation. Insulation materials are now available in large quantities.
There are so many of them that you can really get confused. And determining what kind of insulation for external walls should be in your case is a priority task. Only after this can we begin to calculate the specific parameters of the insulation layer.
Extruded polystyrene foam for wall insulation
To calculate the thickness of insulation for external or internal walls, you need to use separate indicators that relate to your home, climate zone, etc. After the calculation, you will determine the thickness of the insulation, its density and other desired parameters.
But you can calculate all the properties of insulation only after you fully understand what kind of thermal insulation materials there are, how they differ, etc.
There are a large variety of insulation materials, but we will now highlight only the most popular ones and then analyze their properties.
So, most often for thermal insulation of walls they use:
- Mineral wool; Expanded polystyrene; Extruded polystyrene foam; Polyurethane, as for polyurethane insulation; Penoizol.
These thermal insulation materials for walls are almost ideal, and therefore are most popular among experienced builders.
Characteristics of various materials
The value of the standardized heat transfer resistance of an external wall depends on the region of the Russian Federation in which the building is located.
The required layer of thermal insulation material is determined based on the following conditions:
- the external enclosing structure of the building is solid ceramic brick of plastic pressing with a thickness of 380 mm;
- interior finishing – plaster with cement-lime composition 20 mm thick;
- external finishing – a layer of polymer-cement plaster, layer thickness 0.8 cm;
- the coefficient of thermal homogeneity of the structure is 0.9;
- thermal conductivity coefficient of insulation - λA=0.040; λB=0.042.
2.1 Mineral wool
Mineral wool is perhaps the most famous insulation material in general. Using mineral wool, you can insulate walls in all possible conditions.
This is an environmentally friendly material, which is extremely important. After all, if the insulation is environmentally friendly, then this is the most preferable option that can be found in any situation.
The health of the person living in an insulated house depends on whether the material is environmentally friendly. Therefore, the calculation of insulation always takes into account whether it is environmentally suitable for interaction with people.
Everyone also notes that mineral wool has a whole bunch of useful characteristics.
This is a non-flammable insulation like polyurethane foam insulation.
The fire only chars the cotton wool, but only a little. But its heat transfer is extremely low. So low that you can put your hand on the other side of the fired slab and you will not feel the difference.
As you yourself understand, a non-flammable heat insulator is preferable when you are going to finish the walls of a house. After all, non-combustible material will prevent a fire from spreading if one occurs. And this is very important.
Roll of mineral wool with foil reflector
It is very convenient to attach cotton wool to walls. Its installation is carried out according to the simplest procedure. Especially if we are considering the installation of slabs that can be installed by one person with a minimum of tools.
Paint and additional finishing materials are not applied to such insulation. It is worth understanding that special primer and plaster solutions must be selected for mineral wool.
But the modern market provides a large number of such goods, so there should be no problems with them. Mineral wool does not absorb water, although this only applies to branded samples. Not eaten by rodents, and very durable.
It is sold in:
- Rolls; Plates as wall insulation with mineral slabs.
The dimensions of insulation in rolls differ from the same insulation in slabs. This is completely natural. In rolls, the dimensions of the material are 1200 mm wide, 5-8 meters long.
In slabs, the dimensions are much more modest. Here the most popular slabs may be those with dimensions of 1200×1000 mm. The thickness of the rolls is approximately 3-6 cm, and the thickness of the slabs is 5-10 centimeters.
Its density is also at a high level.
The main disadvantage of cotton wool is that it is expensive. If you are going to buy the cheapest insulation, then it will definitely not suit you.
Calculation example
Let's calculate how much mineral wool is needed for a gable symmetrical roof with seven rafter intervals 60 cm wide and a slope length of 5 m. at the same time, the dimensions of the slab are 1.17x61x25cm.
First, we determine the number of slabs in one row: 5/1.17 = 4.27 pcs.
We multiply the result by the number of steps (7): 4.27x7 = 29.89 slabs will be needed for one slope and 59.78 for the entire roof. It is better to round the resulting result up, that is, 30 and 60 pieces, respectively.
Mineral wool Source haikudeck.com
2.2 Expanded polystyrene
Polystyrene foam also has the finest characteristics imaginable. It is also a very cheap material. It is its low cost combined with good qualities that gives a good effect.
It is almost ideal for walls, because it is very easy to attach foam boards. Their installation is carried out according to the simplest procedure. Also, foam plastic does not react at all to water and is low in weight (for a non-load-bearing wall this is also an important indicator).
The structure of ordinary polystyrene foam
Its working thickness will be greater than that of mineral wool, but calculations show that the difference there is not so large as to be seriously taken into account.
But polystyrene foam also has disadvantages. If you are looking for a non-flammable material, it will definitely not be polystyrene foam. Its density is also not the highest.
Rodents also like to eat polystyrene foam. And everyone probably knows what problems they cause.
But paint can be applied to foam plastic, although only a special one, and only in unique cases. The dimensions of polystyrene foam are very easy to determine, since it is sold in slabs.
What influences the choice of the thickness of the insulating layer
Another circumstance that influences the determination of insulation consumption is the type of house and its purpose. For a small summer building that is not intended to be lived in in winter, a minimum layer will be sufficient. For a permanent mansion planned for permanent residence, you will have to take this issue seriously and carry out a special thermal engineering calculation. You will also have to determine the dew point and its location in the wall of the building.
The design of seasonal buildings is the simplest, you don’t need to dwell on it further, but it’s better to analyze the structure of the wall of a frame house for winter temperatures in detail.
In such a panel, not only the internal part is insulated, but also the racks themselves, in order to prevent the formation of cold bridges and the penetration of low temperatures into the room.
For this purpose, an additional frame is built on top of the main one, designed to protect the load-bearing elements from contact with the external environment. In this case, the layer-by-layer enumeration of all components looks like this (from inside to outside):
- Interior decoration;
- Vapor barrier;
- Frame (stand);
- Main insulation;
- Wind protection;
- Exterior finishing elements.
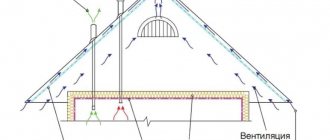
Between the finishing outer layer and the windproof film, free space must be provided for air movement and ventilation; this is where, if calculated correctly, the dew point should be located. And this can be achieved by selecting the thickness of the wall (the main insulation).
2.3Extruded polystyrene foam or penoplex
It is a type of foam plastic that has undergone an extrusion process.
Its density is much higher than that of standard foam. This allows you to mount foam boards in places where the density of foam would not allow it (on the floor, attic, etc.).
Also, high density affects the overall strength of the material.
It is very difficult for a person to break a foam board for walls, the thickness of which reaches 5 cm. In almost all respects, penoplex is better than polystyrene foam. But it also costs more.
Installation of penoplex, as well as liquid insulation for walls, is also simplified, since the slabs can be fastened to large dowels, without fear of their destruction. No paint or additional finishing mixtures are applied to penoplex.
The dimensions of penoplex in slabs are almost identical to those of expanded polystyrene for walls, only its required thickness, as a rule, is almost half as much.
This is possible due to the fact that high density affects the thermal conductivity of the material, further reducing it.
Why is it necessary to insulate buildings made of aerated concrete?
It may seem that the only reason for insulating a house is to save money on heating, but upon closer examination there were more, namely:
- reduction of heat loss through the walls of the building. Insulation allows you to increase the thermal resistance of walls and, accordingly, reduce heating costs;
- sealing cold bridges (window and door lintels, reinforcing belt, thick masonry joints). Through them, not only does heat constantly and quickly escape from the house, but “wet zones” are formed, which cause the appearance of mold and mildew.
- increasing the service life of the building. External insulation of a building made of gas blocks, with a thickness of 100 mm, allows you to move the dew point from the wall into the thermal insulation. That is, freezing of moisture in aerated concrete is excluded and, therefore, it will last much longer.
The thickness of wall structures has a direct impact on the heat retention in the house. The greater the width of the aerated concrete blocks, the warmer the building will be even in the most extreme cold. However, this is not always applicable in practice, since the required amount of building materials and, accordingly, construction costs increase significantly.
The main parameters of wall structures made of aerated concrete blocks are laid down at the stage of developing a house project. The optimal thickness of the masonry is selected in accordance with the climatic conditions of a particular region, SNiP standards and other criteria that affect the thermal conductivity of wall structures. Aerated concrete belongs to cellular concrete and, in comparison with other wall materials, has a low level of thermal conductivity, which guarantees the preservation of heat in the building in winter and the creation of an optimal microclimate in summer.
2.4 Penoizol
Penoizol is a foam liquid insulation. It is also called liquid foam, although this name cannot be called completely correct.
Insulation of walls using penoizol
In terms of characteristics, penoizol is almost identical to polystyrene foam, only its thermal conductivity is lower. And it is worth noting that penoizol is a completely non-flammable material. No paint or primer is applied to it, and even penoizol plaster must be unique.
Separately, we note the interesting process by which penoizol is installed. As you understand, you don’t need to fasten anything when working with it. Installation is carried out using special equipment, which workers use to apply foam to the walls.
After installation is completed, the foam will take in air, expand and fill all the openings around it. This is quite convenient, because you don’t have to worry about the presence of a frame, to determine the dimensions of which you still need to carry out a careful calculation.
Video description
Should you trust online calculators, watch the video:
The calculator helps estimate the cost of work Source www.strojmag.ua
Using the calculator, you can calculate the number of bricks for masonry, the cost of finishing, the dependence of insulation consumption on the width of the material, and many other parameters.
It is important to remember that the calculator does not provide exact numbers that can be used when designing or purchasing materials. It only helps to understand the principle of calculations and determine how much the same work will cost using different materials or projects. Full construction calculations can only be performed by qualified specialists.
2.5Which option is better?
The best option is determined only after an accurate calculation of all its characteristics has been carried out. It is also important to evaluate what procedure is used to install the insulation, and whether it suits you.
In short, it is best, of course, to take mineral wool.
It has the most useful properties. If you are confused by the price, turn to polystyrene foam. Penoplex is better than mineral wool in terms of thermal conductivity and waterproofing, so it is well suited for insulating facades.
Well, penoizol is almost universal, although its special structure looks most appropriate when insulating the frames of internal walls of non-residential buildings.
Thermal insulation method
The effectiveness of insulation depends on the characteristics of the insulation and the method of insulation. There are several different methods that have their own advantages:
- Monolithic structure, can be made of wood or aerated concrete.
- A multilayer structure in which the insulation occupies an intermediate position between the outer and inner parts of the wall; in this case, at the construction stage, ring masonry is performed with simultaneous insulation.
- External insulation using a wet (plaster system) or dry (ventilated facade) method.
- Internal insulation, which is performed when it is impossible to insulate the wall from the outside for some reason.
To insulate already constructed and operating buildings, external insulation is used as the most effective way to reduce heat loss.