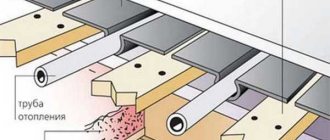
new ceiling, without insulation, etc. fuck? Well, that is, the ceiling, a water-heated floor pipe on top, then screed and laminate - and that’s it.
Has anyone done this? Any impressions?
probably like this: “Ordinary Marketing Bullshit” (OMF) For those who didn’t go to school: IR radiation penetrates a solid body only a few microns. And it is completely absorbed by this thin layer. This means that IR radiation, reflected by the aluminum layer, will move away from it by several microns, heat the concrete, which in turn heats the aluminum. Hence the simple conclusion: with or without the film, the temperature of the concrete-thermal insulator transition will remain exactly the same. But applying an aluminum film, which costs 3 kopecks, allows suckers to sell it for 3 thousand rubles - the profitability of the “business” is 1000%.
PS: Do not confuse the operation of the reflector in air, and even more so in airless space (for example, on spacecraft, where infrared radiation is the only way to cool the device).
warm the floor under beds, cabinets, tables, . useless and meaningless.
TP is generally made for comfort, not for heating. And comfort is a constant temperature. But a constant floor temperature cannot compensate for variable external conditions.
You are making a classic mistake: you have two variables but one regulator - mathematics and logic deny such somersaults.
Therefore, 1. You do TP around the bed (this is only a couple of m2). 2. Place a standard water battery under the window, with a thermal head).
You have two regulators (TP and battery), and you can always set two comfortable parameters - so that your bare heels are comfortable, and so that it is not hot in the bedroom.
It won't work any other way.
PS: An electric TP does not consume as much as the cable power, but approximately 20 W/m2 (this is the difference between +22 in the air and +24 on the floor (my comfort)). So there will be no “ruin”.
and yet what is the task? to be heated? or for comfort?
Personally, I plan to go directly to the floor slabs so that there is a heat accumulator
be heated comfortably. > personally, I plan to use the floor slabs directly, > so that there is a heat accumulator
I planned that too, but now they say you can’t do that.
Of course you need to listen to Brutus)) but.
I think that in the “comfort” mode the stove will be heated - 23 degrees
Let's look at the system from top to bottom
item 1 room air (
23 degrees) item 2 laminate ( . ) item 3 warm floor (24 degrees - on average.) item 4 floor slab ( . ) item 5 air in the base (??
So I think yes! There is heat removal from the laminate (whether due to ventilation flows) but! the slab (item 4) is also insulated from below (item 5 is a poor heat conductor)
thus the proportions 70-30 are somewhat exaggerated
20 watts per meter - that’s per room - 20 square meters = 400 watts - that’s a lot in the mode of “maintaining” the temperature from 20 to 22.
this means that in fact it is necessary to supply less power, that is, the system is even more viable
I won’t say anything about the eerie descent of some terribly heated air somewhere
PS – by the way, I really liked the idea of insulating the ceiling of the plinth)
yes. You will insulate the ceiling, but the heat will spread to the sides - onto the walls of the basement. Moreover, concrete is perhaps the best conductor of heat (from building materials) - the heat loss zone will be approximately 1 m from the edge of the slab. How much area is the room? 20 m2? this is a 4.5x4.5 square. So, subtract 1 m along the perimeter. What remains? a square in the center 2.5x2.5 = 6 m2 - you protected this area from losses, and from the sides 14 m2 heat flows to the walls of the base.
The main task performed by thermal insulation in heated floors
The home heating systems we rely on are designed to provide us with efficient heating. In houses where radiators are installed, heat enters the heated room due to the contact of the surface of the heating devices with the air mass. As a result of heat exchange, up to 60% of the heat goes to heating the internal space as a result of air convection. Water heated floors are much more effective in this regard. By heating the floor surface, heat is distributed evenly inside the room, creating comfortable living conditions.
High efficiency of an in-floor heating system can be achieved through proper installation and placement of all structural elements. Not the least important place in this regard is played by thermal insulation for your heated floor, based on the water principle of operation. An incorrectly laid insulation layer or its absence will lead to your heating system running 50% idle. The heat from the heating circuit should go up, not down, heating the concrete screed or stacked wooden structure.
Note: experts say that a warm water floor without insulation leads to significant heat loss in winter. Up to 50% of thermal energy is spent on heating the ceiling in the basement. The lack of insulation for heated floors on interfloor ceilings causes insufficiently comfortable temperatures in the heated room.
For clarity, the following example can be given:
The previously used polystyrene foam has a density of 20-22 kg/m3, however, in accordance with the technology for laying warm water floors, the density of the insulating material should be at least 35 kg/m3 for interfloor floors and 50 kg/m3 for floor equipment on the first floor. The presence of such restrictions on thermal insulation materials is caused by technological factors that are determined by the very principle of operation of heated floors.
Water floors are a low temperature heating system. The floor in a heated room should not heat up above 30 0 C. Exceeding these parameters will create discomfort inside the room. A negatively high floor heating temperature will affect the design features of the floor covering, and the heating devices will work with increased load. The presence of a thermal insulation layer of the required thickness will eliminate heat losses during the operation of water circuits and create optimal conditions for the spread of heat in the desired direction. A smaller thickness of thermal insulation will lead to the fact that heat will go into the underground. The large thickness of the insulating material will become a serious obstacle to heating the floor and floor covering. In this case, the operation of warm water floors will be fundamentally disrupted.
No damper tape
You may remember from school that when heated, a substance expands, and when cooled, it contracts. It’s the same story with underfloor heating screed; when heated, it expands. To compensate for the expansion of the screed, a damper tape is installed around its perimeter.
The green thing nailed to the wall is called damper tape
You can buy ready-made damper tape. It is sold in many stores. We make it ourselves from centimeter-long polyethylene foam (foamed polyethylene). If we find one for sale. This is the cheapest way.
To compensate for the expansion of the heated floor screed with a damper tape, it is necessary that the maximum area of one fragment of the screed be no more than 40 m².
What is the basis for choosing an insulating material?
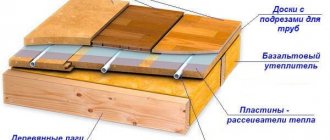
The basis for a heated floor is the so-called “layer cake” - a stacked structure in which each layer performs its own specific functions and tasks. Insulation takes one of the leading places in this pie, so a lot depends on the quality of the insulating material, its composition and structure. Thermal insulation must meet any changes in the operating conditions of the heating communication. The safety of the insulating material is one of the main factors determining its choice.
A large number of water heated floor pipe circuits per manifold group
According to European standards, collectors with up to 12 circuits can be used. I heard that there is SNiP, which states that in Russia it is allowed to make no more than eight circuits per collector, but I did not find it.
If they make a heated floor collector with more than 12 circuits, then there is a very high risk of getting a non-working system. Some of the circuits may not warm up; there may be a “swing” with the system.
It is not worth assembling such large underfloor heating collectors. We made it out of desperation in a commercial property; there was no room for a cabinet. Coolant supply from both sides. The heated floor worked for two seasons without any problems. But this should be done only in extreme cases.
I saw an object where there were 20 circuits on one collector, where the left side of the building was heated for a day or two, the right side was cold. Then the right one heats up, but the left one doesn’t. It is not clear how to regulate or balance this.
It turns out that in fact there is a warm floor, but it doesn’t really work.
Features of the practical use of various insulating materials
Expanded polystyrene
Let's start with the fact that the thermal insulation is laid at the very bottom of the layer cake, directly on the rough covering. Before laying the layer of thermal insulation, waterproofing is laid on the subfloor and only after that they begin laying the thermal insulation layer. Let's look separately at how work is done with the most common and popular materials.
Let's start with polystyrene foam. The material is available in the form of sheets or plates. This form is very convenient for installation work. The thickness of polystyrene foam may vary. The thickness of the sheets varies from 30 to 120 mm. For installation work of all categories, especially in the case of heated floors, a type of polystyrene foam is used - penoplex (extruded polystyrene foam).
Expanded polystyrene has extremely low thermal conductivity and is very convenient and practical during installation. However, this material has a significant drawback, insufficient hardness.
Important! Do not forget that penoplex is a fragile and fragile material, however, to give strength and rigidity to the entire subsequent structure of the water floor, you will need a concrete screed or a stable flooring system.
In order to get rid of this drawback when forming a pie, reinforcement for a concrete screed is used, or additional flooring is made from plywood slabs or gypsum fiber board sheets.
A simpler way out of this situation is to use a cheap analogue - ordinary polystyrene foam.
For polystyrene foam, the optimal thickness of the thermal insulation layer is at least 100 mm. When installing heated floors on ceilings, a foam thickness of 25-30% less will be sufficient.
We use mineral mats
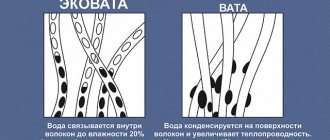
To obtain the necessary rigidity for a layer cake, people most often pay attention to mineral mats. They are based on the well-known mineral wool, but thanks to production technology, the material has a rigid structure. With the help of mineral mats, you can easily fill the existing voids in the subfloor and fill all the cells of the layer cake with a rack layout. Despite the obvious advantages over expanded polystyrene, the material is not resistant to moisture.
Note: a damaged layer of steam and waterproofing can lead to the mats absorbing existing moisture and losing their insulating properties. The water floor can be laid on mineral mats made of basalt or fiberglass.
Other, less commonly used thermal insulation materials include cork. Cork thermal insulation has low thermal conductivity, but weakly resists moisture. Fungal growths often occur in floors with such thermal insulation. For best performance, it is necessary to use waxed cork material. In this case, the price increases, and in terms of its technological characteristics, cork is inferior to foam plastic and expanded polystyrene.
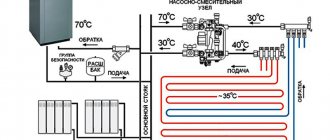
How does a wall system work for cooling?
With heating, everything is clear: all pipes are connected to the collector, heat supply to the collector can be organized from any source.
If the heat generator is high-temperature, it can be a gas, electric or even solid fuel boiler - we install a three-way valve and reduce the temperature of the coolant to 25 - 40°C.
If the heat source is low-temperature, for example, a heat pump, then we connect it directly to the collector.
Cooling is realized using a heat pump. Although I have personally seen a universal wall-mounted system with passive cooling. This house was built on the shore of a lake and the owner simply pumped water through his system.
Thus, it cooled the house, expending energy only to power the circulation pump. Using this principle, it is possible to organize passive cooling using a geothermal circuit. There are actually a lot of options, they all have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Is insulation needed for underfloor heating (specific case)
Dear specialists! Having shoveled through a bunch of threads about heated floors, I still haven’t resolved one question for myself. Whether to put insulation under the screed or not. The diagram of the house is shown in the figure below.
The house is one-story, made of expanded clay concrete, with a pile foundation, more than twenty years old. It doesn't move or move anywhere. All floors are covered with reinforced concrete slabs. In a year, additional external insulation is planned. The underground is made with the possibility of storing vegetables and other natural gifts there. To do this, a square concrete container is dug in the middle. Between the walls of this container and the perimeter of the house there is simply earth. From the ground to the ceilings is about 90 cm, and the height of the container itself is about a meter or more. This winter, the house was heated purely “to support the pants” with three electric heating elements of 1.5 kilowatts each, the windows in some places were without glass, the outside was clogged with film, but even at -38 outside the house remained at +12. But there was a specific disadvantage in the underground. The walls of the basement were covered with a cap of frost, the water in the concrete container froze even in slight frosts. Most likely this was due to poorly closed vents and sagging earth under the walls.
So I have questions. The first is whether there will be enough heating for the house with purely warm floors (although I think it will be enough). And is it necessary to separate the heated floor screed from the reinforced concrete slab? On the one hand, I like the idea of a stove as a heat accumulator and low-temperature emitter (heat it once and then just maintain it), but won’t it be too warm in the underground later? I'd like to hear your opinions.
The name of such a heating and cooling system
To be honest, I myself did not fully understand how to correctly name such a system in a nutshell.
Uponor calls these systems: Uponor Plaster - Universal system for walls and ceilings.
Rehau calls such systems: Rehau Rautherm S - Unified surface heating/cooling system.
If you think that warm walls are a new thing, then you are mistaken. During Soviet times, such systems were made. Recently, an acquaintance from Germany came to visit me; he lives in an apartment with warm walls. The apartment was built by Soviet builders about 40 years ago.
In Soviet plumbing books of the 80s, such a system was called a panel heating system. In our company, the name “warm walls” has stuck. First one client said so, then a second, a third, and it stuck. The name is not entirely correct, since everyone we installed pipes on their walls used for cooling.
By the way, both Uponor and Rehau produce ready-made panels with pipes built into them. True, due to high prices, such panels have never been ordered from us. But we install pipes on walls very often.
Incorrect pipe installation
This error occurs due to inexperience. This includes everything related to the quality of laying pipes for water heated floors. I saw how the pipe is attached to the mesh with binding wire. The pipe may expand and break at the attachment points.
It is better to use nylon ties, but they should not be tightened all the way. I saw how they fastened a pipe to the foam with staples, and then they came off when the screed was poured. This is not because the staples do not hold well, but because they were rarely installed.
Incorrect circulation pump
A selected low-power circulation pump will not be able to circulate coolant in heated floors. Which will lead to partial heating of the heated floor. Some of the floor will heat up, and some will not.
A higher power pump will “eat” electricity. Taking into account the fact that the heated floor circulation pump operates 24 hours a day throughout the heating season, the amount for electricity can run up quite a bit.
Some people don’t pay attention to this, but for others, one extra ruble is two thousand rubles a month. At the same time, electricity will continue to rise in price, which means overpayment will only increase over time.
Do not forget that the more powerful the circulation pump, the more expensive it is.
Incorrectly selected flooring
This is a sore subject for me. We made warm floors, and the customer laid an engineered board on top. First he complains about the lack of power in the heating system, and then about the cracking of the engineered wood.
Warm floors work well with laminate
Most floor coverings can be combined with warm floors. But you need to calculate warm floors for laying this particular floor covering. That is, you need to decide on the floor covering before installing warm floors .
Pouring technology
Having understood the subtleties and nuances, let's look at how to make a concrete floor warm. When carrying out floor installation work, the room temperature should be in the range from 5 to 25 0 C. If the base is in good condition, it should be cleaned and dusted. If necessary, a rough screed is arranged.
Preparation
Damper tape is glued over the prepared base and plastered walls.
This is done without fail in order to:
If you decide to save money, you can lay strips of thermal insulation, for example, foam plastic, around the perimeter, the effect will be the same.
Important! It is necessary to install a thermal barrier not only between the system and the wall, but also between two systems. If the kitchen and corridor have different heating circuits, a damper tape must also be laid at their junction.
After thermal insulation of the joint area, a waterproofing film and heat-reflecting material are laid on the floor.
System installation
Laying a water floor, or any other horizontal heating system with your own hands, is done in strict compliance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. The instructions always come complete with the elements of the system itself. If a cable or pipe passes through an expansion joint, it must be protected with a corrugated hose.
After laying and fixing the system, the heating elements are connected. Before pouring concrete into the system, it is necessary to check the operation of all elements of the system. If the test run was successful, work can continue.
The video in this article will show the installation of a water floor.
Finishing fill
It is not always necessary to fill the system with concrete from above. Sometimes other materials are used for this.
Important! The layer with which the floor heating is poured must have the highest possible thermal conductivity in order to reduce the cost of operating the system.
Combination of heated floors and radiators on one collector group
Radiators and underfloor heating pipe loops have different hydraulic resistance. By installing heating radiators on a heated floor collector, it may turn out that the radiators heat, but the heated floors do not. There is simply no circulation in them.
The coolant circulates through radiators because they have less resistance. You can tighten the radiator taps, thus creating resistance on them and the warm floors will begin to work. But then the power of the radiators will decrease significantly and their power will not be enough.
There is one collector for the warm floor, another for the radiators
Of course, you can calculate and select suitable radiators. But it will be much cheaper to install manifolds for radiators and manifolds for water heated floors.
Lack of insulation on the pipe where the lines are laid
From the collector to the room where the heated floor will be installed, the pipe goes in transit. All transit sections of the pipe must either be insulated or taken into account, while room-by-room temperature control should be abandoned.
In his calculations, Alexander indicates how and where transit pipelines should be laid
Otherwise, it may turn out that at the same temperature of the coolant in the system, one room will be hotter or cooler than the other and this will be difficult to regulate or configure.
Semi-dry screed
The main distinguishing feature of semi-dry screed is the use of a composition with lower humidity, namely, with a significantly smaller amount of water in the solution. The quality of the solution can be easily checked by hand.
A small amount of the mixture is clamped in a fist. Water should not flow from the resulting lump, and it should not crumble. The photo shows the composition of the correct consistency.
Semi-dry screed has some advantages over concrete pouring: