Today we will tell you about bulk insulation, which is available in eight different types. The variety is simply impressive, as they are made from paper, stone, resin, polymers and even clay. Each material has its own strengths and weaknesses, although there are also those that there is nothing to praise for, even if one would like to. All bulk insulation can be installed using two methods: manually or using a compressor. Such materials are good because they fill all the cracks and voids. And negative qualities include shrinkage, which is inherent in all insulation materials from this cohort.
Expanded polystyrene crumbs
Styrofoam crumbs.
The first bulk insulation we will consider is polystyrene foam. If you look closely at a sheet of polystyrene foam, you can see that it consists of many balls. These component parts may not be fastened together, and their density decreases. If you take a sheet of polystyrene foam and loosen it into individual balls, they will take up much more space. Naturally, as the density decreases, the material’s resistance to heat transfer decreases somewhat, so unless absolutely necessary, it is better to use sheets. Also read: “Technological features of insulating facades with foam plastic.”
Bulk insulation for walls made from foam spheres is used only when it is necessary to fill the cavities of already built structures. The crumbs are simply blown out using a special machine, trying to achieve maximum density. The disadvantage of crumbs is that the insulation can shrink. In addition, the material:
- burns;
- emits toxic smoke;
- Rodents feel great in it.
This bulk wall insulation is transported in plastic bags. Can be used to insulate floors, ceilings, and pitched roofs.
How does a chimney for a solid fuel boiler differ from its counterpart for a gas heater with a sealed combustion chamber?
You will find everything about how to choose a chimney for a gas boiler here.
Loose penoizol
Penoizol flakes have a random shape.
In appearance, penoizol looks like foam chips, but if you look more closely, the difference is obvious. Despite the visual similarity, these are two completely different materials. Penoizol is more reminiscent of snow flakes, it does not have an ideal ball shape, this material is softer. Penoizol is used as fill-in insulation for walls and horizontal ceilings. In addition, it is also available in sheets, but is mainly used in liquid form. Unlike polystyrene foam, penoizol:
- does not burn;
- does not smoke;
- allows moisture to pass through, but does not absorb it.
The thermal conductivity characteristics of both materials are almost equal.
Penoizol backfill insulation for walls is made from resin. The quality of the material primarily depends on the quality of the resin used for production.
First, the liquid substance is poured into blocks, about a meter by meter. Then the blocks are cut into sheets, and only then the sheets are crumbled. Installation is carried out using a blowing machine or manually. When working, you need to control the degree of density of the material.
Fly in the ointment, or shortcomings
Of course, they exist, and there are a lot of them, which explains the rather limited use of insulating materials of this type. This is mainly due to vertical insulation. Bulk insulation is quite impractical in this regard.
With the bulk insulation method, strong compaction is required, which requires additional equipment and, accordingly, costs. Otherwise, the material will compact and sag over time. This means that some of the walls will remain without thermal protection, and the house will lose its heat-saving properties.
Pouring granules (or laying cotton wool) requires a certain space for filling or laying. This means that additional formwork will be required - temporary or permanent (another wall at a specified distance from the insulated one). And this will lead to heavier construction of the house, the need to strengthen the foundation and, as a result, to considerable additional expenses and “eating” square centimeters of living space.
You can, of course, add a composition based on cement mortar to the insulation. But here the disadvantages are the same: the need to strengthen the foundation and reduce the usable area of the home. And its main property - flowability - in this case the isolate loses, and accordingly, its sound-insulating and heat-saving properties are significantly reduced.
However, despite all these disadvantages, when insulating a house horizontally, dense “monolithic” insulation is significantly inferior to bulk insulation. Especially if the house has an attic or second floor, that is, when high-quality sound insulation of the second floor floor is needed.
By choosing the right thermal insulation material for your home, you can not only save money, but also build truly high-quality, energy-saving housing. Yes, and nerve-saving too. After all, by protecting residents from street and interior noise, such houses are able to preserve their health for many years not only due to their environmental friendliness, but also a comfortable psychological microclimate.
Foam glass in granules
Fractions of foam glass come in different sizes, up to crushed stone.
It is made from broken glass, which is crushed into smallest fractions, melted and mixed with coal. As a result, carbon dioxide begins to escape from the material, which forms air spheres in the structure of the foam glass. This is a very expensive material; it is used in industrial facilities or in the construction of high-rise buildings. It is used extremely rarely in private construction, since not everyone can afford such a cost. They are used as bulk insulation for ceilings, floors and walls, and in the form of slabs or blocks. Bulk comes in different fractions, based on this, it looks like:
- granules;
- crushed stone
Bulk foam glass insulation has the following characteristics:
- does not absorb water;
- does not burn;
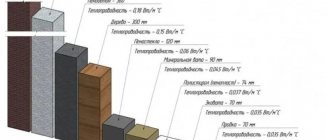
- thermal conductivity 0.04–0.08 W/m*C;
- does not allow steam to pass through;
- high compressive strength 4 MPa;
- bending strength is even more than 0.6 MPa;
- operating temperature range from -250 to +500 degrees.
The peculiarity of using bulk insulation for floors is that foam glass can be part of the cement mortars with which the screed is poured. The same is true when pouring foundations; instead of ordinary crushed stone, you can use foam glass.
Why is it necessary to include filters for gas boilers in the heater piping? Wiring diagram and installation methods.
Interested in installing a safety group for heating: video instructions here.
For ceilings
Just like floors and walls, ceilings require insulation.
The insulation materials discussed above may well be used in this case. A more specific insulation material is penoizol. In appearance it somewhat resembles foam chips. This is where the similarity ends, if you do not take into account the thermal conductivity characteristics.
Penoizol is absolutely not flammable. Has high chemical and biological resistance. Rodents avoid it. It is good for insulating ceilings because it is very light in weight. Its density is from 5 to 75 kg/m³. Due to low thermal conductivity, an insulation layer thickness of 5 cm or more is sufficient. When working, bulk material is used, in sheets and in liquid form.
When considering bulk insulation for ceilings, one cannot ignore such a widely used material as sawdust. Sawdust is used for insulation as the cheapest material. Their use as an independent insulation material is highly undesirable. The fact is that they are susceptible to rotting due to moisture absorption.
They are also excellent breeding grounds for mice. Even if you do not take into account the fact that they are a fire hazardous material, it is easy to conclude that they are unsuitable. “Craftsmen” go to all sorts of tricks in order to somehow reduce these negative factors. To do this, sawdust is mixed with expanded clay, lime, even broken glass and other building materials. Such measures somewhat improve the properties of the insulation, but not much.
As a conclusion, it should be noted that when insulating ceilings, the advantage is on the side of backfill heat-insulating materials.
Expanded clay
Expanded clay is ugly, but time-tested.
Probably the oldest and most well-known fill-in insulation is expanded clay. Made from clay by firing. Depending on the size of the fractions, it comes in the form of:
- gravel;
- crushed stone;
- sand (dropouts).
It should be noted that expanded clay is much cheaper than its competitors, namely perlite and vermiculite, which we will talk about a little later. The density of the material can vary between 250-800 kg/m. cube The degree of thermal conductivity ranges from 0.10 to 0.18 W/m*C.
Expanded clay practically does not absorb moisture; this process occurs very slowly. But, having filled up with water, he is very reluctant to part with it, which cannot but affect his characteristics.
It is used as bulk insulation for walls, floors, ceilings and roofs. Also read “Use of expanded clay for roofing.” It does not enter into any chemical reactions, mold does not grow in it, and mice do not live in it. Since the starting material for manufacturing is clay, expanded clay has all its positive qualities:
- does not harm health;
- does not burn;
- does not contain poisons.
Expanded clay can be mixed with sawdust, but the insulation layer should be slightly larger, since wood has a slightly lower resistance to heat transfer.
Production
Fiber
It is produced in two ways:
- The molten basalt rock is pressed through dies - high-strength and heat-resistant molds that form threads of the required thickness, after which it is inflated with an air flow.
- If there are no specific requirements for fiber thickness, a stream of basalt melt can be inflated by an air flow. This production method is cheaper, but the resulting fiber is usually used only as an inexpensive thermal insulation material.
Workshop producing basalt fiber.
Insulation
Well, how is ready-made basalt fiber insulation made in the form of slabs?
- The feed mechanism, reminiscent of a pendulum, lays the fiber in several layers. Their number depends on the required thickness of the insulation. At the same stage, the fiber is treated with a water-repellent composition.
- The endless web passes through rollers, which compress the shapeless mass to the desired size. At the same time the edges are aligned.
- The web is then treated with a binder inside the oven (usually phenolic resins are sprayed onto it) and then cooled.
- Another roller rolls the hardened web to make it more elastic. The material should not be excessively hard.
- Circular saws cut the insulation into blocks of equal width.
- The printing press applies markings with paint - the manufacturer’s logo and insulation parameters.
- Cross cutting is carried out using high pressure water jets. Unlike saws, this method does not generate dust. Each manufacturer has its own final dimensions; for example, Thermobasalt insulation is sold in slabs measuring 1000x600 millimeters, and insulation slabs with one-sided coating with Rockwool INDUSTRIAL BATTS BLACK fiberglass - 1200x600. Domestic insulation Basalit is produced in slabs one meter long, but with a width of only 500 millimeters.
- Finished slabs are packaged and sent to the finished products warehouse.
Loose thermal insulation ecowool
Ecowool was developed as part of a waste recycling program.
This type of insulation was developed in Europe as part of a recycling program. That is, the main goal is to usefully recycle waste. It is made exclusively from newspapers; no more than 10% cardboard is allowed. To prevent ecowool from burning, microorganisms from growing in it, and mice not gnawing on it, borax and boric acid are added to the detailed newsprint.
It is used as bulk insulation for floors and walls, installation is carried out using dry and wet methods. The density when blown by machine is 65 kg/m in the wall. cube, on floors 45 kg/m. cube, density for manual laying - up to 90 kg/m. cube Thanks to fire retardants, the material does not burn, but smolders successfully.
The service life of ecowool produced in the Omsk and Tomsk regions is 10–12 years. Western manufacturers claim that the material will last 50 years. But they give such forecasts based on the climatic conditions of their region, where temperature differences are smaller and, accordingly, less moisture settles in the insulation (due to the dew point). For Russia, with its cold and humidity, these forecasts are unlikely to come true.
The thermal conductivity of ecowool is 0.037–0.042 W/m*C. It easily absorbs moisture and releases it just as easily.
When wet, it becomes heavier, which leads to shrinkage, which is inevitable. In fact, ecowool has nothing to do with environmental friendliness. It is simply stuffed with chemicals and we do not recommend using it.
Bulk perlite insulation
Perlite is always white.
Perlite is a volcanic ore (acidic glass). For insulation, construction perlite is used, the fraction of which varies from 0.16 to 1.25 mm. After ore is mined, it is crushed and heated to 1 thousand degrees. It is important that the heating is carried out sharply, and the water that is in the structure of the rock begins to evaporate. As a result of this process, perlite swells and reaches a porosity of 70–90%.
Material characteristics:
- thermal conductivity 0.04–0.05 W/m*K;
- does not burn;
- does not absorb moisture;
- allows steam to pass through;
- chemically inert.
The density of insulation in the wall varies from 60 to 100 kg/m. cube Membranes cannot be used during installation, as they quickly become clogged during operation. For installation on pitched roofs, perlite treated with bitumen is used. After a solvent is added to bituminized perlite, it becomes sticky, and after it hardens, it forms a single insulating layer of any shape.
Vermiculite backfill insulation
Vermiculite has become very popular recently.
Loose thermal insulation vermiculite is made from mica - an ore that is mined in quarries. The ore is broken into small fractions, which are subsequently intensively heated to 700 degrees and due to the evaporation of moisture, swelling occurs; naturally, the fractions increase in volume. If you gradually heat the mica fractions, the moisture will slowly evaporate and swelling will not occur.
The service life of the material is unlimited, because there are no adhesive impurities in it, there is simply nothing there to spoil. Material characteristics:
- thermal conductivity 0.048-0.06 W/m*K;
- density 65-150 kg/m. cube;
- does not burn;
- non-toxic;
- allows steam to pass through;
- when moistened by 15%, it does not lose its thermal insulation properties.
Vermiculite transports and distributes liquids well. This means that even with intensive, deliberate moistening of a separate area, perlite will evenly distribute moisture over all its areas, and then completely remove it outside. This property allows you to minimize the consequences of getting the insulation wet. Vermiculite costs almost the same as ecowool (about 4,500 rubles per cubic meter). It can be mixed with sawdust in a 50/50 ratio.
Why insulate a house with basalt filler?
Based on the above listed features and advantages of the material, we can say with confidence that basalt backfill belongs to the category of high-quality insulation materials that maintain their performance characteristics regardless of the type.
The fibrous structure gives the material special elasticity and mechanical strength in use. The thermal insulation properties of basalt backfill remain unchanged over a long period, and the material itself does not shrink.
Wood sawdust
The thermal conductivity of sawdust is 0.07–0.08 W/m*C. Sawdust is rarely used as an independent insulation material, as it is prone to absorbing moisture and further rotting. Therefore, they are mixed with other materials:
- clay;
- expanded clay;
- perlite;
- vermiculite
The ability of these materials to remove moisture prevents sawdust from being blocked even when laid in a thick layer. By the way, you can only use small sawdust, which is obtained when processing wood on modern machines with high speeds.
Having examined all types of bulk insulation, we can conclude that heat insulators made from rocks and clay have proven themselves to be the best. In terms of price/practicality/heat transfer resistance, the best option is penoizol. An outsider in our rating, ecowool is poison in its purest form, nothing less.
Material quality
The material is characterized by the following qualities:
- high heat-saving indicators;
- Cold “bridges” are not formed when using this material;
- the ability to insulate surfaces of any thickness;
- convenience in insulating inaccessible or inaccessible places;
- affordable price;
- ease of storage and transportation;
- compact and reliable packaging;
- vapor permeability and noise insulation.
The use of basalt chips allows you to reach and insulate even hard-to-reach parts of the house, floors, ceilings, attics, etc.
The material is supplied to the market in bags, in a loose and free-flowing state. Compared to other options for existing thermal insulation (slag, sawdust, expanded clay and others), the material surpasses them in technical characteristics.