An old house in the village, which is a hundred years old or even more, is sometimes better not to try to improve it. Yes, it looks rather flimsy, in winter it seems that it will be cold, only a huge stove can save it. There is no talk at all about heated floors in a wooden house - it seems that in cold weather you will only be walking around in warm slippers.
We may not be a great connoisseur of nuances, but we will never deny ourselves the pleasure of learning something new and applying the experience gained in business. Note that it is not always achieved through active actions - sometimes it makes sense to just see how everything works.
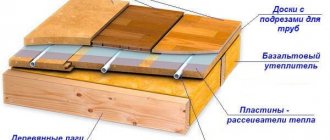
WARM FLOOR IN A WOODEN HOUSE
They decided to test the old wooden house as is. His appearance is so-so, of course, but the walls are smooth, the roof is intact - what else is needed? The windows were insulated the old fashioned way: they put a layer of cotton wool inside the frame, sealed the cracks with paper tape, and left it at that. Gas should still be carried out only in the spring. We relied on a stove, air heaters and a couple of Chinese electric sheets.
We thought that in the cold weather we would be frozen to the floor, how could the stove heat the corners? However, the fears were premature. In fact, we didn’t use heaters, and the sheets only came in handy a couple of times - we were waiting for the stove to warm up. We can’t say that it’s really hot, but it’s quite comfortable. And, most importantly, the floor is not cold at all. No matter what anyone says, our ancestors knew a lot about it. Even if empirically, we found solutions. To do this, it is important to understand how this very wooden house works. Old village houses were placed on stones, without a foundation. Zavalinka, which is often mentioned in fairy tales, covers the walls from the outside, so the underground rarely freezes.
History of wooden floors. Installation recommendations, errors and secrets.
Wooden floor. History and secrets. How to make a wooden floor correctly.
History of wooden floors.
Installation recommendations, errors and secrets. Flooring is an integral part of any home. The very concept of “floor, floors” appeared in ancient times. It is likely that at one time in the mists of time there were no floors. In the Stone Age, the main elements of a dwelling were walls and roofing. Ancient hunters and gatherers built huts from scrap materials (branches, leaves, grass, animal bones, skins, stones, snow, etc.) on a natural foundation, that is, right on the ground or even on snow, like among the northern peoples.
The word gender comes (or is related) from the concept of "half". In Russian and many other languages, the root of such a word is often found. Gender (male and female), floorboard, half, shelf, log, block, plate, plane, field, clearing. And similar words: raft, carpenter, unite, density. Literally, the word "pol" means "plank flooring made of split logs" See etymological dictionaries
.
History of wooden floors.
Installation recommendations, errors and secrets. Such a wooden floor in a residential building, in countries with a cool climate, turned out to be preferable to earthen or stone. Initially, floorboards were often laid directly on the ground or, at best, on stones or logs (joists). To prevent the logs and floorboards from rotting, they were burned and tarred. The plates were adjusted in height, the edges were hemmed, and they were tightly fitted to each other (pulled together). The plates (floorboards) were connected to each other using a tenon (dowel). I had to make such floors, and I will tell you that this is not a quick and difficult job. The cohesive floors were then leveled with a planer (or jointer), first with a rounded blade for rough finishing.
History of wooden floors. Installation recommendations, errors and secrets. History of wooden floors. Installation recommendations, errors and secrets.
Still, it’s worth mentioning a little about earthen floors, although they are distantly related to the word “floor.”
Mud floors are made in this order.
They cut off the plant layer, level the soil surface, compact it, and add crushed stone or gravel for strength. Prepare a thick clay dough with straw chaff, lay it on the ground in a layer of 6-7 cm, compact it, level it and smooth it. After drying, seal the cracks. The top of such a floor can be covered with lime-clay mortar and rubbed down. “How to build a rural house” Shepeleva A.M.
1984 These floors were cold and there was a lot of dust from them. The floors had to be watered and fresh clay poured into the holes. It was possible to walk on such floors only in shoes.
In the second half of the 20th century in the USSR, earthen floors in individual houses were almost universally replaced by wooden plank floors. An unedged board could be ordered from the forestry enterprise at a sawmill or bought at a construction site from a watchman “for a bottle.” Then the board was cut using a homemade “circular saw”, planed and nailed to the joists.
The lucky ones could purchase a tongue and groove floorboard processed on a four-sided machine. The tongue-and-groove board could be laid on the reverse side first. And when the boards dried, they were turned over with the front side and nailed together. This way the gaps between the boards were very small. Then these cracks could be filled with small sawdust and glue.
In the old days, rural residents did not insulate wooden floors. An acceptable floor temperature was achieved by insulating earth around the perimeter of the house. Such a mound of earth was called “Zavalinka”.
History of wooden floors. Installation recommendations, errors and secrets.
Zavalinka
( synonym prizba - in a hut , Ukrainian prizba, Belarusian prizba) is an embankment structure along the outer walls at the base along the perimeter of a wooden house (bath), serves to protect the building from freezing in winter. The rubble can simply be an earthen mound along the walls. In a more advanced version, it is made of boards, planks whitened with lime for beauty ) or poles installed at a distance of 30-50 cm from the walls of the house; Sawdust , straw , firewood , slag , peat , and earth ( turf are poured into the formed space .
The height of the pile is up to the second crown (row of logs). A wooden flooring on top of the pile protects the backfill from moisture penetration and turns the pile into a long and wide bench (bench), on which it is convenient for household members to rest. In the old days, a hut or a log house could be built on any soil and even without
a foundation . Oak logs, large stones or stumps were placed at the corners, on which the frame stood. In the summer, the wind blew under the hut, drying the boards of the so-called “black” floor from below. By winter, the house was covered with earth or a pile of turf was made. In the spring, the rubble, or embankment, was excavated in some places to create ventilation. Improper arrangement of the heap could lead to skewing [1] of the house and (or) rotting of the lower crowns [2] . A modern log house should not be embanked or equipped with heaps. Instead, it is placed on a columnar or strip foundation and a fence and blind area .
Nowadays, a zavalinka is often simply called a bench (bench) standing against the wall of a house.
Material from Wikipedia - the free encyclopedia.
History of wooden floors. Installation recommendations, errors and secrets.
The underground floor was ventilated with air from the room in winter, heating the soil and flooring. Air circulated between the floorboards through cracks or through special holes in the floor "Products". In the summer, vents opened into the street in the ruins. The tradition of closing fruit trees for the winter and opening them in the spring has survived to this day.
In a more modern version, this option is called “Cold floor with warm underground.”
History of wooden floors. Installation recommendations, errors and secrets.
Attempts to insulate the floor (ceiling) led to rapid mold damage and rotting of the floor.
Not enough attention was paid to underground ventilation. Reliable vapor barrier materials were not available. Roofing felt*, glassine, roofing felt, and later polyethylene film produced for greenhouses were used as vapor barriers. And the very structure of the layers of the floor insulation cake was incomprehensible to many builders.
History of wooden floors. Installation recommendations, errors and secrets.
* Roofing felt (from the French tôle - sheet iron, sheet material) is a roofing and waterproofing material obtained by impregnating roofing cardboard with coal or shale tar products.
Available in rolls. Compared to roofing materials impregnated with bitumen (such as glassine and roofing felt), roofing felt is less durable and is mainly used for roofing temporary structures. The biostability and water resistance of roofing felt determine its use for hydro- and vapor barrier of building structures. Currently rarely used. Sometimes roofing felt is called glassine and roofing felt. Wiki correct.
If there were enough air vents, then in severe frosts the underground would freeze. Products may have frozen. The ground froze and the forces of frost heaving lifted the support columns under the floor beams and the shallow foundation.
What common mistakes did builders make when insulating floors above a cold subfloor?
1. They did not pay enough attention to the ventilation of the underground space.
2. The vapor barrier was installed incorrectly.
Any of the two mistakes led to rotting of the floor within 5-10 years. In my practice of repairing floors, there have been cases when the ceiling rotted into dust within one year, where the owners had not even lived yet.
1 . • The subfloor under insulated floors must be ventilated throughout the year. Vents (vents) must not be closed either in summer or winter.
• The total area of vents must be at least 1/400 of the area of the house.
• Vents should be located approximately evenly along the entire perimeter of the base and no further than 50 cm from the internal corners.
• The height of the vents must be no less than the height of the snow cover.
• Vents in internal partitions must have no smaller area than the external ones located opposite.
• If the soil under the house is damp, the soil must be covered with a vapor barrier material (waterproofing material, vapor barrier film or the like).
2 • The ceiling must be protected from the ingress of steam from the heated room by high-quality vapor barrier.
• On the subfloor side of the ceiling, you cannot use vapor-limiting materials laid “solidly” (blocking the exit of steam from the ceiling).
• There should be no layers in the floor pie that are trapped between layers of vapor barrier without a ventilated gap. Of course, except for layers of materials that are not capable of accumulating moisture and which cannot be affected by mold fungi.
• Wooden floor elements must be treated with a high-quality antiseptic.
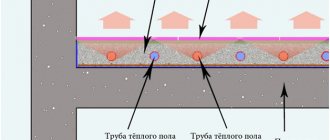
Warm floor in a wooden house
In the summer, the underground is ventilated through vents, and in the winter they are closed. This way, a special microclimate is maintained in the underground. What does the underground have to do with it, you rightly ask? And the connection is as direct as it gets. The floorboards are thick and tightly fitted, so a flea won’t get through, but we noticed what looked like a cat hole near the stove vent. The same one was found on the opposite wall. At first we thought they were made for cats; so they can go down to the basement right from home and hunt for mice. But still this is a secondary function. We realized this when we started actively heating the stove. The fact is that the vent in the stove is made almost at floor level, and next to it is the same vent.
When we heat the stove, it literally sucks in cool air from the underground (this is also better for the hood, because the temperature difference is greater). At the same time, the cat hole on the other side allows warm air from the hut into the underground. Because of this, it is always dry there and the temperature is above zero. And on the street - hello please! - minus 30! That's where the warm floor comes from, guys! They finished heating the stove, covered the holes, the house is warm, the underground is dry and cool, Barsik is happy, because the entire basement is at his disposal, and we are comfortable and cozy! By the way, our neighbors, who bought a similar house nearby, sealed all these holes, disrupted the circulation and their floor was cold and damp below. But for wooden supports this is no good. From the editor
Live and learn! Of course, we can’t do without gas; modern solutions are more economical, but we won’t clean the stove either. This is such a beauty, the food there is especially delicious. Write in the comments what you think about this and do you have a large oven at home? How do you keep the floor warm? Warm floors in a wooden house are a real challenge; you can’t get much faster here. But our people can find a solution even without studying at prestigious universities. Our breed is such that it can figure out everything with its own mind.
Insulation with other materials
In earlier times, wood was usually used for construction. construction of the house had to be ensured:
- multi-layer attic floor;
- installation of double window frames.
Cotton wool was used to insulate the windows. The most common method of thermal insulation was the use of hay or straw. The material was folded
To protect the house from the outside, woodpiles were made. There was a double calculation here. Logs were needed to heat the stove; in addition, they acted as an insulating barrier to allow cold air to pass through. Turf was also often used.
Specifics of bathhouse ceiling thermal insulation
Having finally decided on the choice of how to insulate the ceiling in the bathhouse, you can proceed directly to insulation. But first you still need to figure out how to properly insulate the ceiling in a bathhouse. The specificity of bath rooms is such that for high-quality thermal insulation, in addition to the insulation itself, it is necessary to equip two more layers: vapor barrier and waterproofing. These two layers are necessary to protect the thermal insulator from getting wet, thereby maintaining its thermal insulation characteristics and protecting it from mold.
The vapor barrier is always laid on top of the insulation on the side of the bathhouse, and the waterproofing on the roof side. If the bathhouse is built without an attic, then for reliable thermal protection, waterproofing is first installed, and an insulating layer is laid underneath, protected from below by a vapor barrier. If there is an attic in the bathhouse, the arrangement of general insulation is done in the reverse order: first the vapor barrier, then the insulation and on top of it - waterproofing.
Methods
The easiest way
to insulate with clay begins with covering the ceiling with boards. Their minimum thickness should be 4 cm, but it is better if it is 6 cm. Before carrying out work, the boards must be thoroughly dried. In no case should you paint or varnish boards, because many paints and varnishes are simply not adapted to high temperatures and, under its influence, can begin to release toxic resins and polyesters into the space.
In general , it is better not to use chemicals in the bathhouse.
, unless you intend to constantly inhale its destructive fumes.
After completing the sheathing, you must carefully and carefully cover the gaps between the boards with clay and wait for it to dry completely.
The next stage begins with preparing a mixture of sand and clay, which should be quite thick. All boards laid on the ceiling are covered with this mixture. The thickness of the layer should be at least 5-7 cm. Next, you should wait until the layer is completely dry, and this can take quite a lot of time. A thick layer of sand is laid on the dried clay.
Then the ceiling is impregnated first with liquid steam and then with dry steam. The clay, accordingly, first gets wet, and then finally dries and acquires the ability to retain the heat of your bath for many years.
To ensure that the insulated ceiling retains its heat-insulating properties for as long as possible
, there must be ventilation in the attic. The simplest and at the same time reliable way to create ventilation is two windows opposite each other.
Another way
consists of insulation with several layers of clay with intermediate layers of sawdust or expanded clay. In order to prepare the clay, it is slightly moistened and thoroughly mixed with straw until smooth. The straw is pre-chopped. The final consistency should be similar to soft plasticine or mortar, which is used in laying brick walls.
The clay layer will again be 5-8 cm. After application, it must be carefully smoothed. Seal the perimeter of the ceiling requires special care. The clay will dry in 20-30 days, provided that the outside temperature is above zero. After drying, cracks may appear. This is normal. You can apply another thinner clay layer to the cracks, and cover it with sawdust, expanded clay or wood chips on top.
Insulating foundations prolongs their life for a long time, since it reduces the impact of negative temperatures, and waterproof insulation also acts as waterproofing. It so happens that in some houses the floors are warm all winter without any heating, in others they are cold, despite a fair layer of thermal insulation underneath. Practice shows that insulating foundations helps solve this issue. The temperature in the underground is much higher than outside, and the floors cool more slowly.
Rose of Wind
During the construction of the house, the wind rose was certainly taken into account. All windows were located on the south or southeast side of the house. There were no doorways or windows that faced north. In addition, the stove was located next to the coldest wall or in the center of the house. In this case, it coped with heating the entire room. In Rus', they approached home insulation in the most careful manner, and at any time of the year the homes were truly warm.
The bathhouse is not only a place for washing. This is a place where you can simultaneously enjoy water treatments and heat, activate the immune system, metabolic processes, and cause an accelerated cleansing of the body from waste and toxins.
Insulation is made using a variety of materials. Insulating a bathhouse ceiling with clay
- an old and inexpensive option.
This technology has been used for hundreds of years, and therefore it has been worked out to the smallest detail, which allows you to carry out insulation yourself without special training or construction skills.
Insulating the attic with an effective “old-fashioned” method in bookmarks 3
If we paraphrase the classic saying, then we can safely say: warmth is not where it is often heated, but where it is well insulated! Every experienced owner will say that this is the first thing. Otherwise, a lot of wood will be wasted, but there will be little use. The topic of this article was attic insulation .
© Depositphotos
We probably need to make a reservation. We will rather talk about the method of insulation. Our grandfathers used it, and, as they say, there is something to compare it with. All based on the example of one house.
Option for an attic
Until step No. 5, you do everything according to the technology described above, only instead of mineral wool, stock up on foam plastic, and don’t skimp on its thickness, choose sheets from 4 cm or even thicker. You will also need polyurethane foam, reinforcing mesh and screed materials.
Bought it, cleaned it, repaired the cracks? Then continue like this. Lay the polystyrene foam, filling the gaps formed between the sheets with polyurethane foam. Install the reinforcing mesh and pour in a screed about 5 cm thick. This condition is mandatory, otherwise the foam will sag over time, and everything will have to be redone. The finishing coat is at your discretion.
Selection of insulation materials
Again, using the experience of our ancestors, you can not buy materials, but find them on your site or ask your neighbors for something they don’t need. Or don’t save money and buy something from the know-how category. Let's talk about this in more detail.
Natural raw materials
Such insulation materials include:
- sawdust;
- shavings;
- land;
- sand;
- dry grass;
- tow;
- reed;
- moss;
- other gifts of nature with a small specific gravity.
The main advantages of such raw materials are their low cost and naturalness.
The main disadvantage is their fragility, they are prone to rotting, so you will have to replace such flooring every couple of years. Meanwhile, you already know how to insulate a ceiling with sawdust in a private house, based on the successful experiments of previous generations, so the work will be quick if you want, right?!
Modern materials
Raw materials know-how includes:
- mineral wool;
- ecowool;
- expanded clay;
- fiberglass;
- penoizol;
- Styrofoam.
Such insulation materials last a long time, protect against cold and noise, do not burn, do not rot, weigh little, are easy to use and safe for health. There is one minus - you will have to pay for them, although at the price you are free to choose the option that suits your pocket, because the choice is wide. Nowadays, manufacturers even produce “sandwiches”, where you don’t have to lay layer by layer, you just need to unwrap the finished “sandwich”.
This is important to know! The main principle of laying insulation is as follows: each subsequent layer along the course “from the home” should be characterized by a higher vapor permeability than the previous one.
Are we facing mass extinction?
A mass extinction is a colossal event that is accompanied by easily recognizable phenomena and events. Experts believe that one of these markers of an impending disaster in the distant past was a sharp increase in the number of microorganisms in lakes and rivers.
For example, after the Permian extinction event 252 million years ago, there was a dramatic surge in bacterial and algal blooms that lasted hundreds of thousands of years. The devastating effects of rapid climate change and mass deforestation have left the Sydney Basin, one of Earth's oldest freshwater ecosystems, in a "toxic soup" of phytoplankton and other organisms, according to geologists.
Why is this so important? Recently, massive fires due to the abnormally hot summer destroyed large tracts of forest in Australia. Ash blown by the wind into the ocean contains a lot of iron and organic particles. As a result, it acted as a catalyst that accelerated the proliferation of phytoplankton - now a significant part of the ocean has become toxic due to the abundance of “blooming” microbes.
An unpleasant coincidence, isn't it? Alas, it is far from the only one. Geologist Tracy Frank from the University of Connecticut Fr.
Algae and bacteria are common elements in freshwater environments, but their uncontrolled proliferation literally sucks the oxygen out of the water, creating “dead water” zones where larger creatures cannot survive. Global warming, deforestation and nutrient leaching from soil into water are three factors that contribute to this detrimental phenomenon.
Volcanic eruptions first caused an accelerated and sustained increase in greenhouse gas emissions. This, in turn, triggered an increase in global temperatures on the planet and its sudden deforestation due to forest fires and drought.
As the trees disappeared, the soil structure began to deteriorate and nutrients were released into freshwater ecosystems. For more than three million years, the Earth's forests have struggled to recover. Instead, the Sydney Basin was dotted with low-lying ecosystems that were “regularly inundated by stagnant fresh and brackish water bodies that supported thriving populations of algae and bacteria,” the authors write.
In turn, these persistent “dead zones” prevented the restoration of important carbon sinks such as peatlands and slowed climate and ecosystem recovery.
Findings from other studies around the world also suggest that microbial blooms are common after warming-induced mass extinctions. The exception seems to be the impact of an overly large asteroid, which caused the extinction of the dinosaurs 66 million years ago.
The episode released enormous amounts of dust and sulfate aerosols into the atmosphere, but compared with the volcanic activity, the meteorite caused only a moderate rather than sustained increase in carbon dioxide concentrations and temperatures. Thus, the outbreak of microbial blooms was short-lived.
Alas, all these apocalyptic omens are not very different from the picture of our days. For example, researchers report harmful microalgae in freshwater environments at 20-32 °C. This range corresponds to estimated continental summer surface air temperatures for the region during the Early Triassic. And this is precisely the range predicted for summer surface air temperatures at mid-latitudes by 2100.
What awaits us? Only time will tell. But one thing is already clear today: if the efforts of the entire planet do not take urgent and extraordinary measures to reduce the level of pollution on the planet, then we will not have to wait a century to see the harmful consequences of man’s neglect of the Earth.
Source
Secrets of insulation: the experience of older generations
Our ancestors also knew that the best insulation is air, naturally, “properly packaged.” Therefore, in the old days, they acted wisely by erecting a gable roof on buildings and leaving the attic cold. This roof format allows it to accumulate a certain amount of snow, which becomes insulation. With the correct implementation of this idea, you will be able to achieve zero temperature in the attic when the temperature outside is as low as -25 degrees.
What's the trick? This is where one of nature's best insulators comes into play - trapped air in the attic. By the way, it can be controlled depending on the time of year by closing or opening the windows installed in the gables. Naturally, to be on the safe side, the attic floor was covered with bulk insulation materials, for example, sawdust, sand, and earth. With this technology, inside the hut even in the most severe frosts it was at least +20 degrees. Well, now you know how to insulate a wooden ceiling in a private house without any costs, however, you will have to think about it even before the start of construction, adding the construction of a gable roof to the work plan. But let's look at modern insulation techniques.
This is important to know! If you suddenly decide, adhering to the technology described above, to improve it and insulate the roof slopes, then you will bitterly regret it. The snow will not stay on the roof, but will begin to melt and flow off, turning into huge icicles. In addition, it will be difficult for you to reach the roof covering if repairs are necessary.
Choice of insulation
The first thing you need to do is decide how best to insulate the bathhouse ceiling. You should never take the word of manufacturers who claim that their insulation is the best. When choosing a heat insulator for a bath top, pay attention to the following characteristics:
- moisture absorption coefficient (the lower, the better);
- thermal conductivity coefficient (the lower, the better);
- resistance to temperature changes;
- environmental cleanliness;
- resistance against damage by rodents;
- resistance against fungus and mold;
- compatibility with ceiling material and finishing materials;
- ease of installation.
There is no ideal material for insulating a bathhouse ceiling, but there are a number of materials that meet most of the listed requirements. A good choice would be mineral wool - an insulation that meets most of the listed requirements. The main disadvantage of this material is the sudden loss of thermal insulation properties when wet. And mice can easily make their moves in it. But with high-quality waterproofing, insulating the bathhouse ceiling with mineral wool is considered one of the best options.
Ecowool
Ecowool is a heat-insulating material produced on the basis of cellulose. With all its positive qualities: low thermal conductivity, environmental friendliness, resistance against rodents, fungus and mold, it has a high (up to 20%) water absorption coefficient. For a constantly used bathhouse, this is a very large indicator, but if you heat it once a week, or even two, then you can use ecowool to insulate the ceiling space in the bathhouse.
Izover
Isover is a relatively new insulation material that also has a mineral base. In fact, this is an improved version of glass wool, which has retained its good thermal insulation properties and is devoid of its disadvantages. To insulate the ceiling of a bathhouse, it is better to take an isover equipped with a foil coating for better heat reflection.
The debate about whether it is possible to insulate the ceiling of a bathhouse with foam plastic has been going on for a long time. On the one hand, polystyrene foam has excellent thermal insulation qualities, but on the other hand, over time it begins to disintegrate and release toxic substances.
Expanded clay
Expanded clay is an old, proven material that has been successfully used for insulating bathhouses for a long time. Expanded clay granules made from clay are a good heat insulator and successfully withstand almost all the problems encountered when thermally insulating a bathhouse ceiling. The only “but” is that expanded clay easily absorbs moisture - up to 25% of its mass. If expanded clay is a fairly light material when dry, when wet it becomes heavier and puts pressure on the ceiling. If we are insulating the ceiling of a permanently built bathhouse, then we can use expanded clay, but it is not suitable for insulating light buildings without equipped ceilings.
The same situation applies to available materials: a mixture of clay with sawdust or straw. In the old days, this insulation for bathhouse ceilings was practiced in village bathhouses almost everywhere, but today it is almost never used - there are many problems with it. But, if you need a budget option for thermal insulation, you won’t find it cheaper.