SNiP 2.04.05-86 in Appendix No. 10 gives instructions on the use of steam and water heating systems in industry and everyday life. Steam is used in production, water is used in housing. The steam heats heating appliances to temperatures above 100°C, which is dangerous for residents. This document does not apply to private households. The physics of steam heating processes consists of using dry steam, which, when condensed, releases a lot of heat. During the condensation process, 1 kg of steam releases 2300 kJ of thermal energy. Water cooled to 50°C gives 120 kJ.
Strengths and weaknesses of single pipe systems
The popularity of single-pipe heating in private construction is explained by the fairly low cost of the structure and the ability to independently carry out installation work.
This makes it possible to save on hiring specialists. Among other advantages of single-pipe systems, the following should be highlighted:
- High level of hydraulic stability. If you turn off some of the circuits, this will not affect the heat transfer of the remaining elements of the system. The same applies to replacing batteries or increasing the number of their sections.
- Low pipe consumption for organizing a main line.
- Slight inertia. To heat up the system, an order of magnitude less coolant is required than in schemes with two pipes.
- External aesthetics. Installation of a single-pipe system usually does not affect the beauty of the interior of the room, especially when using hidden laying of the main pipe.
- Thanks to the use of innovative shut-off valves (automatic and manual thermostats), it is possible to fine-tune the operating modes of the heating circuit and its constituent devices.
- Simplicity and reliability of the design, which makes it possible to install a single-pipe heating system on your own. The same applies to heating maintenance during operation.
By organizing the connection of control and monitoring devices for the heating system, it is possible to achieve its functioning in automatic mode. Integration into the Smart Home system is also allowed: as a result, it becomes possible to program optimal heating modes, taking into account the time of day, season, etc.
The main disadvantage of a single-pipe heating scheme is the presence of an imbalance between the heating of the radiators, depending on their distance from the boiler. This is explained by the gradual cooling of the coolant as it circulates through the pipes. As a result, the batteries closest along the coolant path turn out to be hotter than those located further away. In such cases, it is better to use cast iron devices, which are characterized by slow cooling.
Heating system without a pump - how to make water circulate without a pump
The operating principle of heating with natural circulation (click to enlarge)
The operating principle of a heating system without a pump is based on the movement of fluid under hydrostatic pressure. In other words, a liquid in a heated state has a lower density than a cooled one, so the top rises, thus facilitating the circulation of the coolant in the system.
As a rule, heating with natural circulation is installed in country cottages and country houses. This is due to the fact that in such residential premises there are very often interruptions in electricity, or even no electricity at all, as a result of which it is impossible to install heating with forced circulation.
A distinctive feature of this heating system is that it is very convenient to use, and you can install it yourself.
Diameters of heating pipes and features of their selection
When starting to solve such a problem as calculating the diameter of heating system pipes, you should take into account that there are several concepts united by the general term “pipe diameter”. Each pipe can be characterized by the following parameters:
The internal diameter is the main characteristic of a pipe, indicating its throughput capacity. The external diameter is an equally important characteristic that must be taken into account when designing a heating system. Nominal diameter (nominal diameter) is a certain rounded value that is indicated during marking. We should also not forget that pipes made from different materials have a number in their markings corresponding to one or another of its diameters:
We should also not forget that pipes made from different materials have a number in their markings corresponding to one or another of its diameters:
- Steel and cast iron pipes are marked by the size of their internal diameter. Pipes made of copper or plastic are marked by the size of the outer diameter.
That is why, when calculating the cross-section of a heating pipe, it is imperative to take into account the material of the pipes. Especially if you plan to create a system that is a combination of different pipes.
One of the features that influences the choice of size of any pipes is the unit of measurement adopted to estimate the size of their diameter, and therefore their marking. The basic unit indicating pipe size is a whole number or fraction of an inch. To convert inches to our usual measurement system, remember that 1 inch = 25.4 mm.
Structure and types of systems with a natural type of circulation
Typically, a heating circuit without a pump includes a list of required components:
- heating device - a boiler or stove that can be heated with the type of fuel available in a particular region;
- expansion tank, which allows you to relieve excess pressure or add water to the heating circuit;
- pipes that form the circuit along which water will move in the system;
- batteries that allow you to heat the room more efficiently by increasing the area of the heat-transferring surface.
The diameter of heating pipes with natural circulation will be slightly larger than if a circulation pump is used.
Based on what kind of coolant will be used, heating systems with natural circulation can be water or steam.
Here are the distinctive features of each type of heating.
Closed tank
A closed expansion tank is a durable, sealed container separated inside by a flexible membrane. One part is inflated with air, and the second is connected to the pipeline. When the coolant heats up, its volume increases. As a result, the membrane bends towards the air section, which acts as a damper. Cooling the water leads to a decrease in hydraulic pressure. Thanks to compressed air, the system comes into equilibrium, squeezing excess water back into the main line.
Systems equipped with an expansion tank with a membrane are called closed. We are talking about sealed closed hydraulic circuits. The compensating tank can be installed on any part of the system. A popular installation location is the return pipe near the boiler: this increases the ease of maintenance of the tank.
In closed heating systems there is usually a slight excess pressure, so they are necessarily equipped with a safety group. The unit includes an air vent, a pressure gauge and a safety valve for discharging the coolant in emergency mode. These devices are installed on the supply pipeline, which allows shutdowns for repairs and maintenance. On elevated pipelines, the safety group is usually located at the highest point.
The principle of operation of a gravity heating system
The principle of heating operation looks simple: water moves through a pipeline, driven by hydrostatic pressure, which appears as a result of different masses of heated and cooled water. This design is also called gravity or gravity. Circulation is the movement of cooled and heavier liquid in the batteries under the pressure of its own mass down to the heating element, and the displacement of light heated water into the supply pipe. The system operates when the natural circulation boiler is located below the radiators.
In open-type circuits, it communicates directly with the external environment, and excess air escapes into the atmosphere. The volume of water that increased due to heating is eliminated, and the constant pressure is normalized.
Natural circulation is also possible in a closed heating system if it is equipped with an expansion tank with a membrane. Sometimes open-type structures are converted into closed ones. Closed circuits are more stable in operation, the coolant in them does not evaporate, but they are also independent of electricity. What affects circulation pressure
The circulation of water in the boiler depends on the difference in density of the hot and cold liquid and on the magnitude of the height difference between the boiler and the lowest radiator. These parameters are calculated before the installation of the heating circuit begins. Natural circulation occurs because The return temperature in the heating system is low. The coolant manages to cool down, moving through the radiators, becomes heavier and with its mass pushes the heated liquid out of the boiler, forcing it to move through the pipes.
Water circulation diagram in the boiler
The height of the battery level above the boiler increases the pressure, helping the water more easily overcome the resistance of the pipes. The higher the radiators are located in relation to the boiler, the greater the height of the cooled return column and the greater the pressure with which it pushes the heated water upward when it reaches the boiler.
Density also regulates pressure: the more the water warms up, the less its density becomes in comparison with the return. As a result, it is pushed out with more force and the pressure increases. For this reason, gravity heating structures are considered self-regulating, because if you change the heating temperature of the water, the pressure on the coolant will also change, and therefore its flow will change.
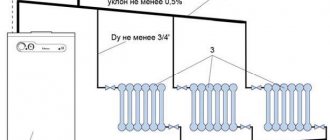
Slopes of pipes of water heating systems
The slopes of the horizontal lines, 2¸5 mm per 1 meter of pipeline, serve to ensure the removal of air from the highest points of the system and emptying of the heating system.
If the supply and return lines are laid together, then for ease of fastening during installation, it is rational to lay them with a slope of 0.002¸0.003 in one direction towards the heating unit.
The supply and return lines to heating devices, with their length up to 500 mm, are laid horizontally; with a slope of 0.005 and 0.01 along the entire length of the line - for a length of more than 500 mm, in the direction of the coolant movement.
Thermal insulation of pipes
When laying in unheated rooms and in places where freezing of the coolant is possible, to reduce heat loss, supply and return lines and sections of risers at the points of connection to the lines are covered with thermal insulation. Thermal insulation can be wrapped, assembled or cast, applied to pipes in the factory. The outside insulation of pipelines is covered with a protective layer: asbestos or aluminum sheet, or synthetic fireproof film. Currently, new thermal insulation materials are being used.
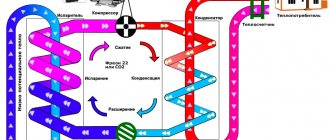
Steam heating
Heating with membrane tank
Sometimes steam heating is associated with water heating structures for a room. And there is actually no mistake here, but there is one nuance: steam is water heated to boiling.
Thus, the principle of operation of a steam heating system is that the water in the boiler is heated to form steam, and then this coolant flows through pipes into the heating elements .
The heating system with coolant in the form of steam consists of the following structural elements:
- a heat generator, presented in the form of a boiler, which heats water and accumulates steam;
- an outlet valve that controls the flow of steam into the system;
- main pipes;
- heating radiators.
It is important to know: when installing a steam heating structure, the use of plastic pipes is strictly prohibited.
As for the classification of steam heating, it is absolutely similar to water heating systems.
Types of heating systems
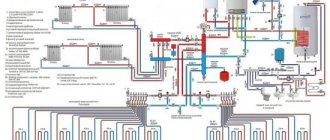
The main elements of any heating network are: a heat-generating device, a main pipeline, heat-dissipating, compensation devices and a device that ensures coolant circulation. Heating pipelines can have different configurations and degrees of technical equipment.
Heating systems are classified according to three parameters:
- number of pipe circuits of the main pipeline,
- type of compensation device,
- type of circulation.
One- and two-pipe systems
The heating system can be:
- single-pipe or sequential,
- two-pipe or parallel.
In the first case, the coolant moves along one pipe circuit, alternately passes through all the heat-releasing devices, arriving at each increasingly cooler. The part of the main pipe after the last heat exchanger is called the return pipe or return pipe and serves to drain the cold working medium back to the heat generator.
In a two-pipe system, the energy carrier circulates through two parallel circuits: supply and return. The first circuit supplies hot coolant to each heat-releasing device, and the second circuit collects the cooled working medium from the heat exchangers and takes it to the heating device.
Types of circulation in heating systems
Heating of the premises occurs only if the coolant moves along the circuit. Circulation can be either natural or forced.
In systems with natural circulation, the energy carrier heated by a heating device is accelerated to give it an impulse sufficient to pass through the entire thermal circuit. To do this, immediately after the heat generator, an accelerating manifold is installed - a vertical section of pipe, when descending from which the working medium picks up speed under the influence of gravity.
Types of compensation devices
Depending on the method of compensating for pressure differences of the working medium in the circuit, there are two types of heating systems: open and closed.
In an open system, the pressure is controlled by a compensation tank, partially or completely open. When the pressure in the heating network increases, the excess working medium enters the tank, and when it decreases, it goes back into the pipeline.
How a heating system works without a pump - options and methods of installation
In order to be able to live in a built country house at any time of the year, it needs high-quality heating. Among the wide variety of heating devices, it is sometimes difficult to decide what exactly is needed in a given situation. One of the simplest options that you can arrange yourself is a heating system without a pump, that is, with a natural type of coolant circulation. It is this type of heating that we will talk about later in the material.
Factors affecting heating pipes in the ground
A heating pipe buried in the soil is subject to the same influences as an external pipeline, plus factors caused by deepening:
- internal pressure of the coolant, causing circumferential and elongated tensile stresses in the pipe section;
- temperature of the coolant is a factor, in addition to thermal influence, also causing pipeline stress;
- soil temperature - in winter, taking this into account is very important;
- soil deformations - the pipe is affected by any of its displacements (settlement, shear, etc.);
- pre-bending stress of the pipeline - the ditch profile often follows the local terrain;
- vertical load - the influence of the weight of the ditch backfill layer;
- the resistive action of the soil on the walls and bottom of the pipeline - resistance to vertical load;
- vibration loads - from passing vehicles, excavation work in the neighborhood, etc.;
- moisture – precipitation and groundwater;
- the influence of chemical substances - compounds in the soil and heat carrier;
- biological factor - bacteria, decomposition.
Likewise, laying a pipeline in the soil should be carried out taking into account all the factors listed above and solving the problem of how to make heating pipes in the ground warmer.
Calculation of heating pipes: diameter, heat transfer, slope and other characteristics
One of the main stages of planning a heating system in a house or apartment is the calculation of heating pipes. At this stage of project development, the type of pipes, as well as their diameter, are determined. The duration and quality of its operation will depend on the correct selection of all the starting materials for creating the heating system.
Correctly selected and installed heating pipes will ensure minimal heat loss and uninterrupted operation of the system
Features of polypropylene pipes
To install the pipeline, high-quality and reliable material is required. This could be, for example, stainless or galvanized steel. Over time, polypropylene replaced these types from the construction industry. The main reason was the combination of useful properties at a reasonable price.
Polypropylene is suitable for hot and cold water supply and heating. The material is durable and does not require maintenance, so you can safely wall up water pipes into the wall.
The main thing is that their use does not exceed the temperature limit of 95 ° C, when the material loses its resistance to pressure and deforms. In residential water pipes and heating systems, such pipelines operate at lower operating temperatures, so no problems should arise.
The disadvantage of the material is thermal expansion, which can directly affect the integrity of the wall into which the pipes are walled. The expansion coefficient of polypropylene is quite high. The linear increase can be up to 10 mm per meter of pipe at a temperature of 70 °C; accordingly, the diameter of the pipe also increases slightly.
The higher the temperature, the more the expansion coefficient of the pipe increases. Therefore, the laying of heating networks, their correct installation, and the selection of types of pipes that suit the conditions deserve special attention.
Heating pipe is sloped, can it be leveled: recommendations, installation
SNiP 2.04.05-86 in Appendix No. 10 gives instructions on the use of steam and water heating systems in industry and everyday life. Steam is used in production, water is used in housing. The steam heats heating appliances to temperatures above 100°C, which is dangerous for residents.
This document does not apply to private households. The physics of steam heating processes consists of using dry steam, which, when condensed, releases a lot of heat. During the condensation process, 1 kg of steam releases 2300 kJ of thermal energy.
Water cooled to 50°C gives 120 kJ.
Steam heating
The slope of the pipes allows you to organize a heating system without electricity
The difference in energy output explains the advantages of steam heating:
- reduced number of radiators;
- quick system warm-up;
- lack of “defrosting” effect during breaks in work;
- noticeably lower heating costs during installation and operation.
The second and third points are important for dachas and country houses - buildings in which residents are visiting.
Plastic pipes are:
- metal-plastic;
- polypropylene;
- made of cross-linked polyethylene.
Their common advantages include ease of installation, low weight, and reasonable price.
Recommendations for installation and assembly
After installation, you need to check the joints by crimping for leaks.
When starting installation, you should, in accordance with the existing heating system design, determine the location of the boiler, radiators, pumps, expansion tank, etc. Next, using a level, marks are applied to the walls indicating what slope the heating system should have in all its sections. When installing heating pipelines with forced circulation, slopes may not be required.
Testing the system after installation
After installation is completed, the quality of the work performed is visually checked. The purpose of the test is to identify leak locations. As a rule, the hydrostatic method is used. The system is filled with water and pressure is applied 25-50% higher than the working one. Stand for 1 hour.
The total length of the test section should not exceed 100 m. Another method is a compressed air test. Before filling the heating system with coolant, compressed air is supplied to the system with a pressure 1-1.5 atm higher than the working one, and the pressure drop is monitored for 30 minutes. If there is no fall, the system is sealed.
Otherwise, look for the leak. Determine the leak by washing.
How to organize a connection
The next step in the process is choosing the connection type. The following methods are most effective:
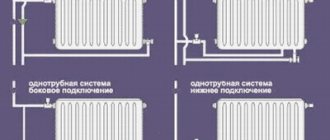
- Lateral one-sided - the inlet is connected to the upper branch pipe, and the outlet is on the same side of the battery, but to the lower branch pipe. The option provides excellent heat dissipation, but is suitable for batteries consisting of 12 sections.
- Bottom - both directions are connected to the lower pipes of the heating device from different sides. The method is ideal for hidden pipe laying.
- Diagonal - the inlet is carried out through the upper pipe, and the outlet is carried out on the other side through the lower pipe. The method is used to connect devices with more than 12 sections.
Connection to polypropylene pipes
To properly install radiators with propylene heating pipes, you will need to acquire a special soldering iron. The connection is implemented using two technologies:
- In the case where the radiator valve is propylene, the connection is made by soldering directly to the liner. Next, you should unscrew the American metal end cap from the tap and screw it into the radiator sleeve. For tightness, FUM tape or linen winding is used. As a result, reassemble the “American” and tighten the union nut with a wrench.
- If the radiator valve is made of metal, then a split-type combined coupling with internal thread is used to connect to the plastic liner. It is similar in principle to the “American” one, but the union nut is adapted for soldering. Through the connecting fitting, the plastic part of the coupling is soldered to the underwater pipe. After this, the coupling must be disassembled, and the metal part with the winding must be screwed onto the valve. Assemble the coupling and tighten the union nut.
Connecting the battery to the metal connection
Many homeowners who want to know how to properly install a heating radiator are worried that when working with metal pipes, they may need a welding machine and related skills in its use. We hasten to reassure you - nothing like that is needed here, everything is done using threaded connections. To do this, a thread is cut on the newly cut section of the eyeliner using a die. The process technology looks like this:
- Cut the supply pipes using a grinder so that the cut line is clearly perpendicular to the center line of the pipe.
- Clean the end of the pipe from corrosion or paint and make a chamfer with a file.
- Apply lubricant to the clamp cutters and pipe section.
- Place the head on the chamfer and center it.
- Using a gas wrench, turn the head clockwise.
- For a high-quality connection, you should get a threaded section equal to the long part of the drive.
As a result, you need to screw a locknut and a coupling onto the finished thread, and aligning the axes of the ball valve and the connection, move the coupling from the connection to the valve body. The process uses rewinding or FUM tape. Next, you should screw the winder onto the thread near the coupling and move the locknut. After final fixation of the stopcock or temperature regulator, it is connected to the radiator liner through the “American” connection.
Symptoms and diagnosis
If a characteristic hum appears in the pipes, it is possible:
- a large amount of sediment has accumulated on the pipe walls, which has led to a narrowing of the lumen;
- there is a water leak from the system;
- The system contains devices with too small a diameter.
To determine the cause of the noise more accurately, you should inspect all elements of the heating system and find the location of the leak.
If the pipes look undamaged, no steam or streams of flowing water are visible, you need to pay attention to the connecting elements and shut-off valves, perhaps the leak is occurring here
Sometimes it is difficult to determine the location of the leak, since it is hidden by a layer of insulation. To accurately diagnose the problem, you should call a professional plumber.
If there are no leaks, but the pipes are humming, you need to find the source of the sound. Most likely, this is where the pipe clearance has become too small due to accumulated mineral deposits or debris that has entered the system. Eliminate the problem by flushing the heating system. This is described in detail in the video:
Usually, a good plumber can identify parts of the system that are not properly sized, causing the pipes to hum. This item may need to be replaced or modified. Of course, such work should be carried out as best as possible, in full accordance with technology, so that new reasons for unpleasant noise in pipes do not appear.
Clicking sounds and the characteristic sound of bubbling water can be caused by air trapped in the system. To fix the problem, it is enough to bleed excess air from the radiators, for example, using a Mayevsky tap. Clicking sounds may also indicate the presence of foreign objects or debris in the pipes. In this case, you should clean the system.
If air gets into the heating system, it can cause clicking and bubbling sounds. To bleed air from the system, use the Mayevsky valve
Intermittent crackling, knocking and clicking noises may appear if:
- there are small foreign particles in the pipes;
- system parts are worn out;
- the ventilation valve has broken;
- unstable operation of the system caused expansion of the metal.
To stop the crackling in heating pipes, sometimes it is enough to drain some of the water and debris. In other cases, you will need the help of a professional plumber to repair or replace damaged elements.
Sometimes the cause of noise in the heating system is a heating pipe overgrown with deposits and particles of rust. This pipe should be flushed or replaced.
The breakage of the ventilation valve is often caused by its incorrect installation, for example, when the valve is installed in the wrong direction. Such an error can lead to significant damage to the entire heating system.
The reason for the tapping may also be the condition of the brackets on which the pipes and heating radiators are mounted. A loose bracket moves under the influence of metal expansion and contraction processes, which causes knocking. To stop this unpleasant phenomenon, it is enough to strengthen the old brackets or replace them with new ones. Sometimes special gaskets are installed between the pipe and the bracket.
How and what to seal pipe joints with
Types of seals, sealing methods
To prevent leakage of the pipeline working fluid, it is necessary to properly seal the pipe twists.
When threading steel pipes, the following are used as seals:
- gasket This method of sealing a threaded connection requires relatively thick end pipe cuts. The presence of smooth pipe ends can never ensure tightness. When using a rubber or plastic gasket, this problem is successfully solved. This option is ideal in case of articulation using a union nut;
- winding The materials can be linen strands, polymer threads, FUM tapes in combination with hardening sealants, paints, pastes.
When installing plastic risers, a sealing method is used based on the deformation properties of the material. The essence of this method is that a plastic pipe with an external thread is screwed into a riser with an internal thread. During deformation, plastic contributes to excellent filling of the intermediate space, eliminating the appearance of gaps.
When it comes to pipeline structures with high pressure, cylindrical threaded pipe connections are not entirely appropriate here. In such cases, a conical type connection is used. The principle of connection is that when screwing in, the pipes are tightly pressed until the gap completely disappears.
Materials for sealing joints
To make the joint impenetrable, the following are used as seals:
- flax (tow);
- asbestos;
- FUM tape;
- natural drying oil;
- whitewash;
- minium;
- graphite lubricant, etc.
A reliable sealant when twisting steel pipes onto threads is strands of flax impregnated with red lead or white lead. This connection is easy to install and reliable in terms of sealing. The seal has been used for a very long time and does not lose its popularity today, despite the emergence of artificial analogues.
For those who have little experience in installing fittings and pipes, we suggest that under no circumstances use flax without paint.
At first, the joint will not allow moisture to pass through. But several months will pass, the flax fibers will get wet and begin to decompose. Therefore, the quality of all connections will deteriorate, and in another month or two, water will leak at the junction.
Many people use FUM tape, which is in no way inferior to old traditional materials - tow with paint.
Sometimes there is no tightness at the junction of the risers. To eliminate this defect, you need to replace the sealing material, and clean the threaded area from dirt and sealant residues. After this, rewind the linen thread, FUM tape or other sealant, and assemble the structure.
Pastes and sealants of chemical origin are used as additional sealants, which will help strengthen this section of the pipeline.
Installation of pipelines with a slope in the heating system
So, the pipes have been purchased, the project has been developed and everything has been carefully thought out, now you can proceed directly to installation. To work you will need the following tools:
- adjustable wrench;
- “universal” gas wrench of good quality;
- special wrench for metal-plastic pipes;
- special stepped wrench for detachable connections.
Step-by-step instructions for installing heating pipelines:
Heating pipe installation diagram.
- The pipes must be installed so that they are inclined towards the section of the system that is located below. A valve or drain valve must be installed at this location.
- Then the pipeline must be delimited into sections. Each such area should be easily covered if necessary. This condition must be met in order to make the operation of the system as convenient as possible, as well as to avoid emergency situations.
- If the pipes are made of polypropylene, then during installation it is necessary to strictly monitor the reliability of fastening. For this purpose, there is a special holder system, which is mounted additionally and warns of the appearance of sagging in the pipeline.
- If the installation involves dividing the riser into sections, then it is possible to build a fixed support for this purpose. It is attached at the branch point under and above the tee located there. This will prevent the pipeline from settling.
- Pipeline compensation, which is necessary between fixed supports, can be performed using various methods: change the pipeline route; install a U-shaped compensator; install the compensator in the form of a loop.
- Welding is performed strictly according to the instructions that come with all materials and equipment.
- If there is a need to cut pipes, then for this you need to take only a sharpened tool. These can be special cutting scissors or a pipe cutter.
- If you install a hot pipeline from polypropylene pipes yourself, then all transitions must be made with a pressed-in brass insert, which has internal and external threads.
After installation work has been completed, you should definitely check the heating system for possible deficiencies and errors in order to detect and eliminate them.
Features of gravity flow systems
Due to the fact that turbulent flows are formed, it is not possible to carry out accurate calculations of the systems, therefore, when designing them, average values are taken, for this:
• raise the acceleration point as much as possible;
• use wide supply pipes;
Then, from the beginning of the first divergence to each subsequent one, a pipe of a smaller diameter is connected at a step equal to it, which involves inertial flows.
There are also other features of installing gravity systems. Thus, pipes should be laid at an angle of 1-5%, which is affected by the length of the pipeline. If the system has a sufficient difference in heights and temperatures, horizontal wiring can be used
It is important to ensure that there are no areas with a negative angle, since they cannot be reached by moving the coolant due to the formation of air pockets in them
Thus, the operating principle can be based on the open type or be of the membrane (closed) type. If you make a horizontal installation, it is recommended to install Mayevsky taps on each radiator. since with their help it is easier to eliminate air locks in the system.
Watch the video in which a specialist talks about the conditions for using a gravity-fed, pumpless, gravity heating system:
In what cases can you do without a pump?
The movement of coolant inside the heating circuit occurs under the influence of the laws of physics. This means that when heated, the liquid rises, and as it cools, it falls again, thereby heating the room.
Most of all, a heating system without a circulation pump is in demand precisely in country houses and dachas, since in suburban conditions the power supply is not always stable or absent altogether. In this regard, heating equipment with a forced circulation type is impractical.
It is noteworthy that it is quite possible to install heating with natural coolant circulation yourself. In addition, such a system is very convenient to use.
Installing heating radiators correctly: markings
For the correct location of radiators, it is necessary to carry out markings, following all the recommendations set out in the instructions for installing such heating devices. The bottom line is this:
1) first you just need to attach the radiator to the wall, maintaining its horizontal position and the required distances from the floor and window sill;
2) after this, mark its outline with a simple pencil on the wall;
3) then set the battery aside and draw two horizontal lines that will serve as axes for the location of the upper and lower rows of brackets;
5) at the end you should hammer the dowels into them and tighten the brackets.
If the markings are done correctly, the battery will fit on all brackets without any difficulty. Separately, it is worth noting that for heating devices longer than 1 meter, a larger number of fasteners may be required.
Now you can start connecting the battery to the heating system.
How to install heating correctly
In order for a finished heating system with a natural circulation type to function correctly and efficiently, it is important to adhere to certain rules when installing it.
In general, the installation diagram looks like this:
- Heating radiators must be installed under the windows, preferably at the same level and maintaining the required indentations.
- Next, install the heat generator, that is, the selected boiler.
- Install the expansion tank.
- The pipes are laid out and the previously fixed elements are joined into a single system.
- The heating circuit is filled with water and a preliminary check for the tightness of the connections is performed.
- The final stage is to start the heating boiler. If everything works correctly, then the house will be warm.
Please pay attention to some nuances:
- The boiler should be located at the lowest point of the system.
- The pipes must be installed with a slope towards the return flow.
- There should be as few turns in the pipeline as possible.
- To increase heating efficiency, pipes with a larger diameter are required.
We hope this article will be useful to you, and you will be able to independently install a heating system without a circulation pump in your country house.
Source
Installation recommendations
When arranging a single-pipe heating system, despite its simplicity, it is necessary to carry out all stages of work carefully and competently, taking into account all the nuances and design features.
To ensure everything is done correctly, you should use the following recommendations:
Conclusion
As a result, we can say that a single-pipe heating system, with all its advantages, is completely unsuitable for large and multi-story buildings. In addition, despite its simplicity and low cost, such a system causes many problems and requires a careful approach when arranging.
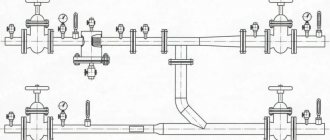
Testing of the piping system after installation
To start checking the system, you need to acquire a device for deaerating pipes without installing water meters. The process of testing the system is carried out in the following order:
- Fill the pipeline. This should be done from the lowest place in the entire system.
- The area selected for testing should not be more than 100 m.
- Slowly increase the pressure and bring it to the maximum level.
- The check lasts no more than an hour. This time is enough to identify possible leaks.
The installation is complete, and now the pipeline together should form a single heating system.
Other ways to solve the problem
In addition to the use of cast iron batteries, the introduction of a circulation pump into the single-circuit system helps to optimize the situation. After this, the temperature in the heating circuits becomes more uniform, but too long pipelines still lead to its noticeable cooling.
To smooth out this unpleasant phenomenon, two methods are proposed:
- As you move away from the boiler, it is recommended to increase the number of sections on the radiators. In this way, an increase in their heat-releasing area is achieved: thermal energy begins to spread in greater quantities in the rooms, contributing to their uniform heating.
- Before carrying out single-pipe heating, it is necessary to consider the most rational placement of radiators in the rooms. It is better to place devices with the highest power in children's rooms, bedrooms and rooms on the cold north side. Further, the highway leads to the living room and kitchen. At the end of the circuit there are non-residential and utility rooms.
Thanks to these measures, some compensation for the shortcomings of the single-pipe system is achieved. This especially applies to low-rise buildings with an area of up to 150 m². In such cases, single-pipe heating is the most economical option.
What should be considered during design and installation?
To ensure that the water inside the batteries and pipes does not stagnate, but circulates freely, pipes must be installed with a noticeable slope.
In the project, it is necessary to take into account that each linear meter should deviate from the plane by 1 to 2 degrees. Such a design trick will not be very noticeable, but it ensures the necessary gravity flow of the coolant. Another important detail is the boiler power. Its intense heat will cause the water to move quickly, which will increase the temperature in the radiators and pipes. Before selecting and purchasing equipment, you should make calculations and evaluate the future thermal efficiency of its operation.
The performance of a gravity heating system in a house can be worsened by the location of the pipes. Their frequent bends and turns at right angles significantly reduce the natural pressure of water, slow down its flow, and the temperature in the house drops significantly.
One-pipe and two-pipe gravity systems
Diagram of a one-pipe system.
A gravity-flow heating network can be installed in a single-pipe or two-pipe design.
Single-pipe heating involves a sequential installation scheme of pipes and batteries. During its operation, water will flow through them sequentially. There are two ways to install the equipment:
- the coolant flow passes directly through the batteries;
- The movement of water through the system is carried out through the main pipe, to which radiators are attached using additional branches.
More uniform heating of the air is achieved with the second method.
A two-pipe heating scheme with natural circulation involves the arrangement of separate lines for water flow - the main and return supply. The coolant from the boiler (hot) sequentially enters the heating radiators, and after cooling, it returns cold to the boiler through the return pipes.
If you install a gravity heating system in a two-story house in a two-pipe design, in order to uniformly heat the rooms and maintain the required temperature in them, you will need to install an additional unit - a circulation pump. Such equipment will increase the water pressure inside the pipes and maintain optimal heat transfer from the heating system.
Rules for the selection and installation of pipes
The choice between steel or polypropylene pipes for any circulation is made according to the criterion of the possibility of their use for hot water, as well as from the standpoint of price, ease of installation and service life.
The supply riser is mounted from a metal pipe, since water of the highest temperature passes through it, and in the case of stove heating or a malfunction of the heat exchanger, steam can pass through.
With natural circulation, it is necessary to use a pipe diameter slightly larger than when using a circulation pump. Typically, for heating rooms up to 200 square meters. m, the diameter of the acceleration manifold and the pipe at the return inlet to the heat exchanger is 2 inches.
This is caused by a lower water velocity compared to the forced circulation option, which leads to the following problems:
- reduction in the volume of transferred heat per unit time from the source to the heated room;
- the appearance of blockages or air pockets that a small pressure cannot cope with.
When using natural circulation with a bottom supply circuit, special attention must be paid to the problem of removing air from the system. It cannot be completely removed from the coolant through the expansion tank, because
Boiling water first enters the devices through a line located lower than themselves.
With forced circulation, the water pressure drives air to an air collector installed at the highest point of the system - a device with automatic, manual or semi-automatic control. With the help of Mayevsky taps, heat transfer is mainly adjusted.
In gravitational heating networks with a supply located below the devices, Mayevsky taps are used directly for bleeding air.
All modern heating radiators have devices for releasing air, therefore, to prevent the formation of plugs in the circuit, you can make a slope, driving air to the radiator
Air can also be removed using air vents installed on each riser or on an overhead line laid parallel to the system mains. Due to the impressive number of air exhaust devices, gravity circuits with bottom wiring are used extremely rarely.
With low pressure, a small air lock can completely stop the heating system. Thus, according to SNiP 41-01-2003, it is not allowed to lay heating system pipelines without a slope at a water speed of less than 0.25 m/s.
With natural circulation such speeds are unattainable. Therefore, in addition to increasing the diameter of the pipes, it is necessary to maintain constant slopes to remove air from the heating system. The slope is designed at the rate of 2-3 mm per 1 meter; in apartment networks, the slope reaches 5 mm per linear meter of the horizontal line.
The supply slope is made in the direction of water movement so that the air moves to the expansion tank or air bleed system located at the top point of the circuit. Although it is possible to make a counter-slope, in this case it is necessary to additionally install a valve for air removal.
The slope of the return line is usually made in the direction of movement of the chilled water. Then the lowest point of the circuit will coincide with the entrance of the return pipe to the heat generator.
The most common combination of supply and return pipe slope directions for removing air pockets from a natural circulation water circuit
When installing a heated floor of a small area in a circuit with natural circulation, it is necessary to prevent air from entering the narrow and horizontal pipes of this heating system. It is necessary to install an air removal device in front of the heated floor.
Basic installation rules
Connecting a heating element to a one-pipe system.
In order to carry out high-quality installation of heating with natural circulation of coolant, it is necessary to perform the following important steps:
- Heating radiators should be placed preferably under windows and at the same level.
- Install a heating boiler.
- Secure the expansion tank.
- Connect the installed elements using pipes.
- Introduce coolant into the heating system and check all components for leaks.
- Start the boiler and start enjoying the comfortable warmth of your home.
Important tips for installers:
- The boiler should be positioned as low as possible.
- Pipes must be installed with a slope towards the return line.
- It is advisable to avoid a large number of turns in the system.
- Use large diameter pipes.
You may be interested in an article on how to install a heat pump in a private home.
You can read about how to choose a circulation pump here.
We hope that we have revealed all the nuances of a heating system without a pump, which will help when equipping the heating of your home.
How to install a heating system without a pump, see the explanation of the gravity system diagram in the following video:
Calculation of the power of a circulation pump for a heating system: necessary parameters and calculation procedure, detailed video Advantages and features of installing a water-to-water heat pump for heating a private house Selecting a pump for heating a private house: types of pumps and selection criteria Uninterruptible power supply for a heating pump: operating principle and selection criteria
Connecting metal heating pipes without welding
The fastest connection method without welding is a compression fitting. However, we will consider other methods: threaded connections and installation of a repair and mounting clip. The latter is used both for joining and eliminating leaks caused by metal cracking.
Thread
It is possible to create a threaded connection only if there is free access to the pipe, i.e. at the initial installation stage. In other cases, thread cutting will be quite problematic or impossible. The procedure itself is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Clean the pipe from paint and rust. If there are metal deposits after previously performed welding, they should be cut off. The surface to be joined must be clean and smooth.
- Using a file, chamfer the end where the cut was made.
- Take a die of a suitable size and screw the handles into it. Lubricate the cutters with grease or lard.
Place the tool on the pipe, making sure that it is positioned strictly perpendicular. Make a half turn of the die clockwise, then a quarter turn counterclockwise. Then repeat the movement until the thread is cut.
Now let's figure out how to cut into a heating pipe without welding. To do this you will need to use a coupling with a nut. It can have three branches to create wiring. When creating a thread, remember that on one pipe it should be 2 times longer. Securing the coupling:
- A nut is screwed onto the longer thread, then a coupling.
- A nut is screwed onto the second pipe.
- The parts are matched together, after which the coupling is twisted off the long thread and partially screwed onto the short one. The element should be approximately in the middle of the cut.
- All that remains is to screw the nuts on both sides, having previously wound a sealing material (fum tape, tow) onto the threads.
Such a connection is considered quite strong and can last for more than one year.
Compression fittings for steel pipes
This type of connection allows heating without welding pipes and cutting threads. At the same time, experts note the high reliability of compression fittings, the leader in production of which is Gebo. This often results in confusion of concepts - many name these connecting devices after a popular manufacturer (a striking analogy is the Xerox brand, which has become a household name for document copying work).
Among the advantages of this connection method are the speed of operation and the absence of the need to use special tools. All you need are two balloon wrenches to hold and tighten the fitting.
The working method is as follows:
- Place the fitting parts onto the pipe in the following sequence: nut, clamping ring, clamping ring, sealing ring.
Put on the coupling, make sure that all elements are positioned correctly and without distortions. Tighten the nut. One turn of thread should remain visible. If after supplying the coolant a small leak appears, the nut can be tightened. Carry out the same actions for the second side of the fitting.
You can learn more about compression fittings by watching the video:
Repair and installation clip
When operating old systems or exceeding pressure, the question often arises of how to seal a heating pipe without welding. For these purposes, a repair and installation clip is used. It can be made in the form of a coupling or tee. The outer part of the part is metal with clamping bolts, inside there is a rubber gasket.
The element is often used for emergency repair of leaks, but can also be used as a permanent option for connecting water supply pipes. Instructions for use:
- Clean the pipe contact areas from paint and other deposits that may affect future tightness.
- Apply a rubber seal to the joint. Make sure that its cut does not hit the junction of the upper and lower parts of the holder.
- Coat the cut with sealant and, if possible, allow some time to dry.
- Install the frame parts and secure with bolts.
These are all options for creating a strong connection between metal pipes without using a welding machine. Now we will describe several methods when working with metal-plastic parts.
Angle of inclination of heating pipes with natural circulation
The use of this type of heating, such as a heating system with natural circulation, is most common for country houses and cottages. Its advantages are availability, cost-effectiveness, ease of installation and operation.
Creating a heating system with natural circulation does not require the use of pumps or additional equipment or power sources, since hydrostatic pressure arises spontaneously during the movement of the coolant.
Heating scheme with natural circulation
Many consider the disadvantage that the use of this system is permissible only in fairly small buildings. In particular, the radius of the system (horizontal arrangement) should not exceed 30 meters. In addition, not everyone prefers to use heating without a pump, since the network turn-on speed is also quite low.
Advantages of a natural circulation system
The first and one of the main advantages of the system can be called its efficiency. In fact, its installation, as well as further maintenance, require relatively small financial costs.
The heating scheme with natural circulation does not require additional equipment in the form of circulation pumps. This means you will not feel the vibration and noise of their operation.
Plus, not having to install such a pump means you won't have to spend extra money on the electricity needed to run it.
Schematic diagram of heating with natural circulation
Another significant advantage of this system is that the coolant circulates continuously.
This is due to the fact that the temperature and density of the coolant constantly changes. Moreover, thanks to this cyclicity, there is an even distribution of heat by all heating elements included in the heating of the house with natural circulation.
The popularity of the system is also due to the fact that its design, installation and further maintenance do not require special skills.
That is, in order to create a high-quality heating system, you do not need to involve additional specialists - everything can be done yourself.
Likewise, the owner of the building will be able to deal with minor breakdowns independently in the future.
However, with proper planning and high-quality execution, the heating of a private house without a pump can operate without requiring major repairs for at least 30-35 years.
How does this system work?
The movement of the coolant (water) through the pipes is due to the fact that as the temperature increases and decreases, the mass and density of the liquid changes.
A decrease in the mass and density of water occurs when it is heated in the boiler. At this time, the pipes contain colder water that has already given up its heat and has greater mass and density.
In this case, under the influence of gravitational forces, cold water in the radiator is replaced by hot water.
In order to understand exactly how a gravitational heating system functions, you just need to remember your physics course. The water heated in the boiler, being lighter, freely rises through the pipes of the central riser.
At this moment, heavy cold water descends into the heating boiler. Hot water, having reached the top point, is evenly distributed over the radiators.
In them, cold water sinks to the bottom of the battery, and then leaves it completely, because it is simply “replaced” by hot water.
When hot coolant enters the radiator, the process of heat transfer occurs. That is, the radiator materials gradually heat up, transferring heat directly into the room. Next, the cooled coolant is again replaced by hot water. This process is continuous. The liquid circulates as long as it is heated - that is, while the boiler is operating.
The principle of constructing a heating system with natural circulation
The gravity heating system of a private house consists of the following elements:
- boiler. It is he who heats the coolant. There are a large number of types of boilers that operate on different types of fuel.
- pipeline. It can be either single or double (for reverse current).
- heating elements - radiators.
- expansion tank.
When designing and installing a scheme such as a gravity heating system, it is extremely important to adhere to the mandatory requirement - the pipe through which the coolant moves must certainly have a slope.
It must be at least 0.005 m per linear meter of pipe and be directed towards the heating tank. That is, if the radiator and boiler are located on the same floor, then the level of the pipe entry into the radiator should be slightly higher. The need for a slope is explained by several factors:
- through a pipe that has a slope, cold water moves much faster to the heating tank.
- the presence of a slope is extremely important so that air bubbles that appear during the heating process of the coolant rise more efficiently into a special expansion tank, and from there they are removed into the atmosphere.
Required slope of gravity heating system
The presence of an expansion tank in a system such as a gravity heating system made of polypropylene has a beneficial effect on creating additional pressure in the system, which makes the coolant move at a slightly higher speed.
It should be noted that the speed of movement of the coolant in the pipe directly depends on several factors. First of all, this is the difference in such quantities as density, mass, volume of coolant in hot and cold states.
In addition, the speed of movement of the coolant is also affected by the level of location of the heating elements (radiators) relative to the heating boiler. However, the gravitational pressure that occurs during the movement of the coolant is consumed to some extent at the moment when the liquid overcomes the resistance of the pipeline.
Additional obstacles, which also consume a significant amount of gravitational pressure, are additional radiators, branches, and turns present in the system.
For more efficient heating (and to achieve maximum coolant movement speed), heating with natural circulation should be designed so that there are fewer such obstacles.
If such “complexity” of the system is caused by necessity, the solution to the complexity that has arisen is to use pipes of larger diameter.
Two-pipe heating system with natural coolant circulation
A more complex gravitational heating scheme, which provides for the presence of two heating system circuits at once. One by one, hot water moves from the boiler to the radiators.
And the second circuit is intended for the outflow of cooled coolant from the radiators to the heating boiler.
This gravity heating system requires more careful planning and the use of an increased amount of materials (pipes).
Two-pipe heating system with natural coolant circulation
The principle of installing a two-pipe system, which involves heating by gravity, is a rather labor-intensive process that can be divided into several stages:
- installation of the main riser. The heating pipe (through which hot water moves) rises from the boiler to the expansion tank. It should be noted that the best place to connect the riser to the tank is the lower third of its total height.
- at a level of approximately a third of the height of the room (should be measured from the floor level), the heating pipe is connected to the wiring. It is from this that the pipes will be laid to the heating devices - radiators.
- To timely remove excess liquid in the system, an overflow pipe must also be cut into the tank. By using it, excess liquid will be directed into the sewer.
- pipes for discharging already used (that is, cooled) water should be cut into the lower part of the radiator. Through these pipes the water returns to the heating boiler. They are laid parallel to the hot coolant supply pipes.
When planning natural heating at home, you should consider some features. First of all, the main riser pipe must be insulated - otherwise there is a possibility of significant heat loss.
How to choose a pump
Before proceeding with the selection of equipment and the heating installation itself, it is necessary to calculate its characteristics. Important parameters:
- Performance;
- Hydraulic resistance (pressure);
- Device size;
- Temperature regime.
In addition, you should consider the electrical connection point to power the pump. In case of power outages, it is advisable to have an alternative energy source, such as a generator.
Advice! There is no point in choosing a pump that is too powerful and has one speed. It will operate by consuming excessive amounts of electricity. It is more logical to purchase a device with several speeds.
Characteristics of heating pipes: heat transfer and slope
Thermal conductivity of pipes and heating radiators
Having installed an autonomous heating system in their home, everyone decides for themselves what the temperature of the water flowing through these pipes will be. It all depends on the wishes of the household, external climatic conditions and the type of heating radiators installed in the house. Since there is no standard or limitation on such a parameter as coolant temperature, the determining value here should be the heat transfer of heating pipes.
The lower the thermal conductivity of the pipes, the less heat loss will occur before the coolant is directly delivered to the radiator. Let's consider which pipes have less heat transfer:
- Here, polypropylene pipes seem to be the best option, since their thermal conductivity coefficient is the lowest among other types of pipes used in heating systems.
- Metal-plastic and reinforced polymer pipes have somewhat higher thermal conductivity, although they are also a good option for installing a heating pipeline.
- And finally, steel pipes, laid in the vast majority of houses built in the last century, give off heat the fastest.
Heating pipes of various diameters in low-temperature areas of the environment are recommended to be thermally insulated with special materials
As for radiators, here, on the contrary, products made from materials with the highest heat transfer are welcome. The rating of increasing quality of radiators relative to their heat transfer will look like this:
- Radiators made of cast iron have the lowest heat transfer coefficient among modern heating devices.
- They are followed by bimetallic radiators.
- Aluminum batteries have the highest coefficient of heat transfer from the carrier to the surrounding space, so they are recommended to be used to increase the efficiency of the system.
In addition, there is a parameter that will help determine the number of radiator sections. This is their thermal power, which must be indicated in the product passport. Usually it corresponds to the value specified on the basis that the water flowing through the heating pipes will have a temperature of 75°C. To maintain comfort and save energy in the house, this value can be varied, changing in one direction or another.
Also, for the normal operation of the in-house heating system, it is important to know what the pressure is in the pipes heating the house. The standard indicator is 1.5-2 atm. An increase in pressure above the specified values may result in the wall thickness of the heating pipe being insufficient. In this case, depressurization and equipment failure will inevitably occur. To avoid such trouble, you should use pressure gauges to monitor the pressure in the system.
Organization of the slope of heating pipes
The correct direction of slope of heating pipes during natural circulation
When creating an autonomous water heating system at home, we must not forget that it should be installed with a slight slope, which helps its proper functioning. This is especially true for a system of natural coolant circulation through pipes. Rules for choosing the slope of heating pipes:
- A correctly selected slope of heating pipes will ensure unhindered circulation of coolant throughout the system. The slope towards the water flow should be 10 mm per 1 m of pipe, both in the direction from the heating boiler to the heating radiators, and when exiting the system.
- In systems that use forced circulation of coolant using a pump, a slope is not necessary. Typically, in such systems, pipes are laid horizontally or with a minimum slope towards the drain shut-off valves of 2–3 mm. This helps drain water from pipes for repair work or to prevent pipe rupture when the system is not used for a long time during the cold season.
- A horizontal outlet for connecting to the battery from vertical pipeline systems longer than 0.5 m is arranged with a slope of 10 mm in the direction of water movement. If this branch has a shorter length, it is not necessary to arrange a slope.
Design features
There are two types of forced circulation heating systems - closed and open.
An open system does not require a pump, but forced circulation is installed in it. To do this, calculate the slope of the pipeline and install an expansion tank. The boiler used for heating is solid fuel or gas. This type of heating is considered the most economical in terms of installation costs.
The system is called “open” due to constant contact with the environment through the expansion tank. Therefore, corrosion of metal components is possible.
For an open look, it is necessary to use pipes with a large diameter. When developing a project, it is necessary to take into account in advance the method of masking them, as well as calculate the effective slope of the pipes.
A closed system is the most productive for any home (apartment, cottage, country house). To install it yourself you will need the following components:
The coolant is heated in the boiler, its excess enters the expansion tank, and the liquid flow is pumped by the pump. A valve is also installed to relieve pressure. The expansion tank for a closed system must be sealed. Disadvantage of the closed type: the mandatory presence of an uninterruptible power supply for the pump.
When arranging heating with your own hands, you should first decide on the type of circuit.
Single-pipe
In such a system there is no incoming and return coolant pipeline.
The flow moves from the boiler, fills the radiator, leaves it and moves on to the next one. The liquid is then returned to the boiler. This seemingly logical and simple scheme has a significant drawback: as it moves, the coolant cools down, especially if the system does not have a pump and it is very problematic to use a slope as forced circulation. However, making one-pipe wiring with your own hands is quite simple.
Experts recommend taking into account such nuances as rapid cooling of the liquid and cold “return” in a single-pipe scheme. The boiler must be protected from condensation.
Two-pipe
The wiring diagram in this type of system is more complex, but more efficient.
The coolant enters the pipe, then into the radiator. The cooled liquid then goes into a parallel return pipeline. Thus, the supply and return flow go through two branches, which guarantees the same temperature in the subsequent radiator. The advantage of a two-pipe system is a constant temperature in each element, as well as the ability to turn off any radiator. For example, a single-pipe scheme does not involve selective shutdown - when one element is blocked, the entire heating system is blocked. The disadvantage is the branched pipeline system, which must be installed with your own hands, having specialized knowledge.
Principle of operation
During natural movement in the heating system, the heated liquid from the boiler under the influence of temperature itself creates pressure and rises up through the pipes, enters the radiators, and when cooled, returns to the heating device.
Accordingly, radiators close to the boiler will be warmed up well, while those further away will be the opposite. In order to maintain a more or less stable temperature in different rooms, it is necessary to increase the number of sections on the heating radiators and increase the diameter of the pipes, as well as calculate the slope of the pipeline so that the coolant moves along the line according to the laws of physics. A forced circulation pump promotes rapid fluid movement without increasing pressure or losing temperature. There are several more advantages:
- There is no need to use pipes with a large diameter for installation;
- There is no temperature difference - no rapid wear of system elements;
- Ability to regulate temperature in individual rooms;
- There is no need to calculate the slope for unimpeded movement of the coolant.
The disadvantage of the pump is its noise during operation. You need to choose good low-noise models.