In the Russian Federation, for the most part, the heating systems of multi-storey buildings are centralized, that is, they operate from a combined heat and power plant or a central boiler house. But the water circuits themselves are mounted differently, that is, they can be made either single-pipe or double-pipe.
For passive users, this does not matter, but in the case of a major renovation of the apartment with your own hands, you will have to learn to understand these nuances.
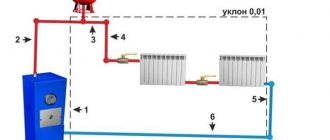
Two-pipe and one-pipe radiator connection system
Single-circuit heating pipework
The principle of its operation is to ensure the movement of working fluid through one pipe. What does it mean? Heated water or antifreeze is squeezed out through a common riser to the upper level of the heating system, and radiators are connected in series in the coolant return pipe to the boiler. Obviously, the upper floors or the very first radiators in the scheme will heat up faster and stronger, so a single-pipe heating system is used only in one-story or low-rise (2-3 floors) houses, where the difference in supply and return temperatures is not so noticeable. In a one-story house, all radiators will heat up to almost the same temperature.
Advantages, features and differences of a single-pipe heating system:
- Maintaining hydrodynamic equilibrium in the system;
- Simple project, quick installation;
- Low financial and labor costs due to the installation of only one highway without sensors and other monitoring and automatic control devices;
- Organization of the movement of the working fluid according to the principle of natural circulation (gravity circuit), which does not require the insertion of a circulation pump and the connection of electricity. This is what primarily distinguishes single-pipe wiring from two-pipe wiring.
But a single-pipe heating system also has disadvantages, and significant ones:
- Complex calculations due to the need to maintain hydraulic stability and high hydraulic resistance;
- Complete dependence of all devices and components of the system due to their sequential inclusion;
- For one riser, the most optimal would be to connect no more than 5-7 radiators;
- It is impossible to regulate the temperature in each individual radiator;
- High heat losses.
For owners of one-story country houses, the question of which is better - a single-pipe or two-pipe heating system and which is better to choose is not worth it - if the house is one-story, then single-pipe heating is the best option both in terms of installation, and in terms of labor costs, and in terms of savings energy carriers.
How can you improve a single-circuit wiring diagram?
If you don’t know what is better to choose - a single-pipe or two-pipe heating system - then stop at the intermediate option, the scheme of which is called Leningradka. This scheme adds a bypass - a pipe jumper for each radiator, allowing it to be bypassed completely or partially. A shut-off valve is inserted into the bypass, which can be used to regulate the full or partial supply of heat, bypassing the battery.
In addition, a temperature sensor can be connected to the bypass, and temperature control will improve. Also, with a bypass, you can repair or replace components without stopping the entire heating. The jumper can be easily installed into an existing system.
A single-pipe heating system for a private house is assembled using a horizontal and vertical scheme. If the main riser is a vertical riser, then all outlets and radiators are connected to it from top to bottom. The horizontal riser works on the principle of connecting radiators in series. In both the first and second pipeline layout options, air pockets will appear, and this can also be attributed to the disadvantages of a single-pipe heating system.
Single-circuit system assembly technology
- First, the boiler is installed, after which pipes are installed in the rooms;
- If Leningrad is assembled, then tees are installed at the connection points of the batteries and bypasses;
- In a scheme with natural circulation, a pipe slope of 2-4 degrees per linear meter is maintained;
- A pump is inserted into the liquid return pipe and connected to the network;
- At the highest point of the piping, the expansion tank is attached and connected;
- Radiators are connected, Mayevsky taps are installed on them so that the air can be vented;
- Single-pipe heating is pressurized and put into operation.
Malfunctions
What problems in the operation of the water supply system can the apartment owner eliminate on his own? Here are some of the most typical situations.
Valves leaking
Description: leakage along the stem of screw valves.
A typical leak location is shown by an arrow.
- Reason: partial wear of the oil seal or wear of the rubber O-ring.
- Solution: open the valve knob all the way. In this case, the thread on the rod will tighten the seal from below, and the leak will stop.
Crane noise
Description: when you open a hot or (less often) cold water tap, you hear a loud noise and feel the vibration of the mixer. Alternatively, your neighbors faucet could be the source of the noise.
A noisy neighbor's faucet can become a source of a lot of negative emotions.
Cause: a deformed and crushed gasket on the screw valve in the half-open position causes a continuous series of water hammers. Its valve closes the seat in the mixer body at intervals of a fraction of a second. In hot water, the pressure is usually noticeably higher, so the effect is more pronounced.
Solution:
- Shut off the water to the apartment;
- Turn out the problematic valve housing;
- Replace the gasket with a new one;
- Use scissors to remove the chamfer from the new gasket. The removed chamfer will prevent the valve from beating in a turbulent stream of water in the future.
Replacing the gasket on the screw valve
The photo shows a ceramic crane box
Cold heated towel rail
- Description: The heated towel rail in your bathroom has cooled down and is not heating up.
- Reason: if the water supply scheme of a residential apartment building uses continuous circulation of hot water, the air remaining in the jumper between the risers after water is discharged (for example, for inspection and repair of shut-off valves) is to blame.
- Solution: go up to the top floor and ask your neighbors to bleed the air from the jumper between the DHW risers and heated towel rails.
If for some reason this cannot be done, the problem can be solved from the basement:
- Shut off the DHW riser passing through your apartment, to which your connections are connected;
- Go up to the apartment and open the hot water taps all the way;
- After all the air has come out of the riser through them, close the taps and open the tap on the riser.
If a vent is installed on the riser, it can be diverted directly from the basement
Immediately after the end of the heating season, the difference between the lines of the route may be zero
Does a single-pipe forced circulation heating system save energy?
In the two-pipe heating option, heat energy is directly saved. When rooms overheat, thermostats reduce the flow of coolant through heating devices, and at the same time its flow through the risers decreases, i.e. the excess volume does not circulate through the pipes.
In a single-pipe heating system with thermostats, when the rooms overheat (when their valves close), the overall forced circulation of liquid does not decrease - it simply does not enter the batteries, and, accordingly, does not cool down in them. Heat energy is not saved here, but it is not wasted either, remaining in a stable volume of heated coolant. But its temperature in the “return” increases, which leads to an increase in losses in pipelines. However, in heating stations of apartment buildings, the DHW heat exchanger (if available) is powered from the return line, in which the water cools before returning to the boiler room.
Traditional approach or full automation
If we consider heating options for an apartment building with several floors, a single-pipe system will ultimately create more problems. In the future, we can expect uneven heating and additional costs to increase the efficiency of the heating structure.
If you still choose a single-pipe system, then the most difficult part of it will be a carefully calculated professional project.
There are many supporters of this option; they are inspired by the low cost of work and old houses in which such a system has been successfully operating for many decades.
A more flexible option is a combination of two-pipe and one-pipe systems. It will allow you to save money and take advantage of the advantages of both systems.
Main types
Despite the fact that the design features of a single-pipe system are not particularly complex, a number of its types can be noted. In private houses, it is possible to use two main types of systems:
- Sequential (unregulated). Its peculiarity is that the coolant enters each of the structural elements in order. This option is simple and inexpensive. But the possibility of adjusting the coolant is completely absent here, which is why the radiators furthest from the boiler have the lowest temperature. Such sequential type systems are used mainly for heating small rooms.
- Adjustable. In this case, the elements are connected in parallel. Here you can adjust the coolant. This occurs due to the presence of shut-off valves in the system. This option can heat a room with a considerable area.
There is also a variety of single-pipe heating systems, depending on the method of coolant circulation:
- Natural ensures the movement of coolant in the system due to gravitational forces. It is used only in small rooms where the main line is small. In order to increase efficiency, a special collector is immediately installed after the boiler unit, which works to accelerate the coolant. This device is a tall, even pipe in which the coolant develops speed and passes through a full closed circle much faster, which helps reduce heat losses. To install such an amplifier you will need fairly high ceilings (more than 2 m). This system is very popular because it is completely independent of the power supply.
- Forced, which moves the coolant due to the installed special pump. Compared to the first type, it is more productive. Such a system is installed if there are several heating circuits. Often several circulation pumps are installed in them.
- The combined one is carried out on the same principle as a heating system with natural circulation of coolant, but a special pump is also installed in the bypass area, which increases the performance of the structure. This heating option is installed in case of frequent power outages.
Open tank
An open expansion tank is a partially or completely open tank connected to the circuit in its highest section, immediately after the boiler. To prevent the liquid from overflowing over the edges of the vessel, there is a special pipe closer to the top: it serves to drain excess water into the sewer or onto the street. When organizing heating of one-story buildings, a compensating tank is usually installed in the attic. To avoid freezing of water in winter, the walls of the tank are additionally insulated.
Such heating systems are called open. Most often we are talking about non-volatile or combined heating. In this case, the coolant comes into direct contact with the air: this leads to its natural evaporation and enrichment with oxygen.
Open circuits have the following disadvantages:
- Accurate observance of slopes (if gravity systems are used). This will allow the air leaking into the pipes to escape through the container into the atmosphere.
- The need for constant monitoring of the water level in the tank. From time to time, the volume of coolant must be replenished, since part of it evaporates through the open top.
- The use of non-freezing liquids that emit toxic substances during evaporation is prohibited.
- Oxygen saturation of the circulating fluid provokes corrosion processes inside metal steel heating radiators.
Strengths of open systems:
- You may not need to regularly check the pressure level in the pipeline.
- Small leaks in the circuit will not prevent it from properly heating your home. The main thing is that there is enough liquid in the pipes.
- To replenish coolant losses, it is allowed to use a simple bucket. This is done by simply adding water to the expansion tank to the required level.
Installation of Leningradka in a private house
After making calculations, developing a diagram and purchasing all the necessary materials, you can begin assembling the structural elements.
Sequence of main works:
- The tank is installed;
- The polypropylene pipeline is laid along the perimeter of the building, starting from the boiler and closing the entire circuit on it;
- After laying the main line at a short distance from the source of heating the coolant, a technological insert for the vertical pipe is made;
- An expansion tank is attached to the top of this section;
- Lastly, the lines are connected to the radiators: to the pipes from below - a lower horizontal connection, and the inlet and outlet pipes cut into the battery at different heights - a diagonal one.
Despite the apparent simplicity of the Leningrad heating system for private houses, it is dangerous to do it yourself without special knowledge. Consultation with professionals is necessary at all stages of preparation and installation.
Connecting the battery to the main pipeline
The level of heat transfer from radiators is affected by the way they are connected to the main line:
- Diagonal (cross) . This option demonstrates the greatest efficiency. Makes it possible to heat radiators as much as possible over the area, practically eliminating heat losses. In this case, the supply pipe is connected to the upper radiator pipe, and the return pipe is connected to the lower pipe (it is located on the opposite side of the device). Diagonal connection is mandatory for multi-section radiators.
- Lateral (one-sided) . Provides uniform heating of all sections of the battery. In this scheme, the supply and discharge pipelines are located in the same direction. The side connection is most popular when organizing heating with top wiring.
- Nizhny . Least efficient connection method. Despite this, it is often used when the main pipe is hidden under the floor. The inlet and outlet pipes are connected to the lower outlets on different sides of the battery.
New single-pipe heating systems for apartment buildings
Russian new buildings are equipped with single-pipe radiator units with thermostatic valves (thermostats). They look as shown in the photo below.
Radiator assembly with thermostat.
Such heating systems are 30–40% cheaper than their two-pipe counterparts and have high hydraulic stability. But do they provide a level of operating comfort for two-pipe circuits, determined by the following components:
- automatic mode for stabilizing the set temperature in each room;
- overall energy savings in the heating system;
- possibility of hidden pipe laying;
- apartment heat metering.
Let's evaluate the single-pipe heating option according to these criteria.
Disadvantages of a one-pipe system
- increased vulnerability to defrosting of the entire system. Freezing of the system in at least one place makes the circuit inoperable.
- as it moves away from the boiler, it requires an increased size of heating devices. Due to the fact that not only hot water (directly from the boiler), but also cooled water (from heating devices) enters the pipe main, increasingly cooled water comes to the inlet of each subsequent radiator. But heat loss remains the same. To compensate for them, more sections are required. This factor directly negates and even detracts from the initial apparent gain in the cost of the material.
A two-pipe heating system is a system in which two pipes are used to supply and remove coolant.
Fireproof water supply.
In accordance with the requirements of SNiP RK 4.01-41-2006 “Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings”, fire hydrants are provided in the building. The water consumption for internal fire extinguishing is one jet with a water flow rate of q=2.6 l/s. The fire-fighting water supply ring network is made of steel water and gas pipes in accordance with GOST 3262-75*. Fire hydrants are installed at a height of h=1.35m above the floor of the inter-apartment hall and are placed in cabinets that have a hole for ventilation, adapted for their sealing and visual inspection without opening. Each fire hydrant has a “Start” button. PC cabinets are equipped with levers designed to open fire hydrants. To reduce excess pressure, fire hydrants located on the 1st and 2nd floors are provided with the installation of diaphragms with a central hole ∅16mm. The fire cabinets provide space for 2 fire extinguishers with a capacity of 10 liters.
Advantages of a one-pipe system
- To supply coolant, one pipe is used instead of two. This is a direct saving of your money on the cost of pipes, fittings and installation work.
- virtually does not require any adjustment of individual branches and risers.
- has a smaller coolant volume. In the case of using antifreeze, this is again a direct saving of your money.
- increased hydraulic stability of this system.
- if it is necessary to drain the system, this process speeds up and does not lead to an excessive volume of water in the drain hole, because has a smaller coolant volume.
- installation time is shorter than in a two-pipe system.
- if there is a ready-made (calculated) project with as-built diagrams and specified diameters, it does not require highly qualified installers.
Closed tank
A closed expansion tank is a durable, sealed container separated inside by a flexible membrane. One part is inflated with air, and the second is connected to the pipeline. When the coolant heats up, its volume increases. As a result, the membrane bends towards the air section, which acts as a damper. Cooling the water leads to a decrease in hydraulic pressure. Thanks to compressed air, the system comes into equilibrium, squeezing excess water back into the main line.
Systems equipped with an expansion tank with a membrane are called closed. We are talking about sealed closed hydraulic circuits. The compensating tank can be installed on any part of the system. A popular installation location is the return pipe near the boiler: this increases the ease of maintenance of the tank.
In closed heating systems there is usually a slight excess pressure, so they are necessarily equipped with a safety group. The unit includes an air vent, a pressure gauge and a safety valve for discharging the coolant in emergency mode. These devices are installed on the supply pipeline, which allows shutdowns for repairs and maintenance. On elevated pipelines, the safety group is usually located at the highest point.
Local automatic temperature stabilization
Single-pipe adjustable radiator unit with a straight-through (a) or three-way (b) thermostatic valve on the top supply.
An adjustable radiator unit for vertical single-pipe heating can be made with a straight-through (Fig. a) or three-way (Fig. b) thermostatic valve (thermostat). The piping unit branches the coolant into two flows: through the device and through the bypass. The diameters of the thermostat valve plunger and the opening for the passage of liquid are made to the maximum. The thermostat does not clog when the coolant is contaminated and ensures its free flow (when fully open). Unauthorized replacement of the radiator, accompanied by removal of the thermostat, does not lead to imbalance of the entire heating system, as in the two-pipe version.
If the room air temperature exceeds the set one, the valve will close (go to minimum mode), directing the liquid through the bypass past the radiator. Closing (minimum opening) the valves of all thermostats of a given riser increases the proportion of coolant passing through the bypasses from 80% to 90%, while simultaneously reducing the flow through the radiators, i.e. without changing the total flow rate.
The difference between one-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
When installing heating, they focus on two ways to install the circuit:
- single-circuit;
- double-circuit.
The difference between these methods is the specificity of connecting the heat exchanger to the main wire. Single-circuit ones are a ring closed system. Radiators are installed in the pipeline, and the line extends from the boiler and closes on it.
The double-circuit method consists of two lines installed in parallel. The coolant moves along the upper level to the radiators and heats the room. At the bottom, the waste liquid is returned to the boiler for further heating. Using this method, it is possible to ensure uniform heating of the batteries in the room. Energy costs for heating one element are reduced.
The final stage of work
At the last stage, the radiators are connected, and their internal diameter and volume of sections are calculated taking into account the type of supply and cooling rate of the coolant. Since central heating is a complex system of interconnected components, it is quite difficult to replace radiators or repair jumpers in a particular apartment, because dismantling any element can cause interruptions in the heating supply of the entire house.
Therefore, apartment owners who use central heating for heating are not recommended to independently carry out any manipulations with radiators and the piping system, since the slightest intervention can turn into a serious problem.
In general, a well-designed, efficient heating scheme for a residential apartment building allows one to achieve good performance in matters of heat supply and heating.