Due to its ease of installation, low cost and sufficient efficiency, the open heating system continues to be in demand. Once you understand the principle of operation, equipment and installation rules, you will be able to organize the heat supply to your home yourself.
We will tell you how to create a workable open-type heating circuit. We will show you how to build a system, strictly following technological requirements and standards when selecting and connecting elements. Taking into account our recommendations, you will build a trouble-free, efficient circuit.
We offer independent craftsmen to familiarize themselves with practice-tested assembly options. The information presented for consideration is supplemented with useful diagrams, photo collections, and video instructions.
How to choose a heating pump
Special low-noise centrifugal-type circulation pumps with straight blades are best suited for installation.
They do not create excessively high pressure, but push the coolant, accelerating its movement (working pressure of an individual heating system with forced circulation is 1-1.5 atm, maximum - 2 atm). Some pump models have a built-in electric drive. Such devices can be installed directly into the pipe; they are also called “wet”, and there are devices of the “dry” type. They differ only in the installation rules. When installing any type of circulation pump, it is desirable to install it with a bypass and two ball valves, which allow you to remove the pump for repair/replacement without stopping the system.
It is better to connect the pump with a bypass - to be able to repair/replace it without destroying the system
Installing a circulation pump allows you to regulate the speed of movement of the coolant through the pipes. The more actively the coolant moves, the more heat it carries, which means the room heats up faster. After the set temperature is reached (either the degree of heating of the coolant or air in the room is monitored depending on the capabilities of the boiler and/or settings), the task changes - it is necessary to maintain the set temperature and the flow rate decreases.
For a heating system with forced circulation, it is not enough to decide on the type of pump
It is important to calculate its performance. To do this, first of all, you need to know the heat loss of the rooms/buildings that will be heated
They are determined based on losses in the coldest week. In Russia they are standardized and installed by public utilities. They recommend using the following values:
- for one- and two-story houses, losses at the lowest seasonal temperature -25 o C are 173 W/m 2. at -30 o C losses are 177 W/m 2;
- multi-storey buildings lose from 97W/m2 to 101W/m2.
Based on certain heat losses (denoted by Q), you can find the pump power using the formula:
c – specific heat capacity of the coolant (1.16 for water or another value from the accompanying documents for antifreeze);
Dt – temperature difference between supply and return. This parameter depends on the type of system and is: 20 o C for conventional systems, 10 o C for low-temperature systems and 5 o C for heated floor systems.
The resulting value must be converted into productivity, for which it must be divided by the density of the coolant at operating temperature.
In principle, when choosing pump power for forced circulation of heating, you can be guided by average standards:
- with systems heating an area of up to 250 m 2. use units with a capacity of 3.5 m 3 / h and a generated pressure of 0.4 atm;
- for an area from 250 m 2 to 350 m 2, a power of 4-4.5 m 3 / h and a pressure of 0.6 atm is required;
- in heating systems of areas from 350 m2 to 800 m2, pumps with a capacity of 11 m 3 / h and a pressure of 0.8 atm are installed.
But you need to take into account that the worse the house is insulated, the greater the power of the equipment (boiler and pump) may be required, and vice versa - in a well-insulated house, half of the indicated values may be required. These data are average. The same can be said regarding the pressure created by the pump: the narrower the pipes and the rougher their internal surface (the higher the hydraulic resistance of the system), the higher the pressure should be. A full calculation is a complex and tedious process, which takes into account many parameters:
Boiler power depends on the area of the heated room and heat loss
- resistance of pipes and fittings (read about how to choose the diameter of heating pipes here);
- pipeline length and coolant density;
- number, area and type of windows and doors;
- the material from which the walls are made, their insulation;
- thickness of walls and insulation;
- presence/absence of a basement, basement, attic, as well as the degree of their insulation;
- type of roof, composition of the roofing pie, etc.
In general, thermal engineering calculations are one of the most complex in the field. So if you want to know exactly how much power you need for the pump in the system, order a calculation from a specialist. If not, select based on average data, adjusting them in one direction or another depending on your situation. You just need to take into account that if the coolant flow rate is not high enough, the system makes a lot of noise. Therefore, in this case, it is better to take a more powerful device - the energy consumption is low, and the system will be more efficient.
Arrangement of gravity type heating
It is better to entrust the development of a gravity system project to heating specialists. The document specifies the type of heating, method of connecting radiators and circulation of coolant, recommended equipment parameters, number of radiators and pipeline footage.
Heat supply system calculation
It is necessary to determine the hydraulic characteristics of the system, which will subsequently help to correctly select the optimal pipeline diameter.
In a natural heating system, it is recommended to install the boiler in the basement or basement. This allows you to increase the length of the transit riser
To calculate the value of the circulation pressure ( Рc ), you must have the following data:
- Distance from the center of the heating boiler to the center of the radiator ( h ). The greater the distance between these devices, the more stable the circulation.
- Pressure of cooled ( Po ) and heated ( Pr ) water.
The circulation pressure depends only on the temperature difference of the coolant. Exact indicators can be found in the tabular data.
The greater the difference in coolant temperatures, the higher the pressure in the line. Therefore, it is important to take care of the “incoming” temperature of the liquid
The cross-sectional width of the pipeline is influenced by the type of material. The diameter of the steel pipe must be at least 50 mm. After branching, the cross-section of the highway narrows by one size. The return, on the contrary, is assembled with subsequent expansion.
Particular attention is paid to the volume of the expansion tank. The size of the reservoir should not be less than 5% of the total volume of coolant in the system. Failure to comply will result in water draining from the system or pipe rupture.
Selection of main components
For an open system, it is better to choose a boiler that runs on solid fuel or fuel oil. Installation of electric boilers and gas equipment is prohibited. Air jams sometimes form in the line - this can lead to an emergency.
The heater power is determined based on the calculation - 1 kW of heat energy per 10 sq.m of house. Depending on the quality of the room insulation, 10-30% is added to the obtained value.
The boiler is located in a separate room equipped with forced air circulation. The equipment is installed on fire-resistant material or concrete floor
The expansion tank for a gravity-type heating system must be made of steel. It is highly undesirable to use polymeric materials. For heating a small one-story house, a tank of 8-15 liters is suitable.
Image gallery
Photo from
Simple open tank design
The principle of homemade devices
Space for expansion tank
Optimal location for feed input
To construct the pipeline, pipes made of the following materials are used:
- Steel . They are characterized by high thermal conductivity and resistance to high pressure. The disadvantage is the complexity of installation and the need to use welding equipment.
- Polypropylene . Main advantages: resistance to temperature fluctuations, strength, tightness and ease of installation. Service life – 25 years.
- Metal-plastic . The material does not corrode and prevents clogging of the circuit. Disadvantages of the highway: limited service life (up to 15 years) and high cost.
- Copper . Pipes with maximum heat transfer and resistance to high temperatures - up to +500°C. The main disadvantage is the high cost of the material.
Radiators made of high-strength metals are installed in the open heat supply circuit.
The most common are steel models. They have an optimal balance of key parameters: appearance, price and thermal power.
Due to their thin walls, light weight and high degree of heat transfer, steel radiators are compared to convectors. The equipment quickly warms up rooms due to accelerated air movement
Open system installation steps
The entire process of organizing a gravity heating system can be divided into several stages:
- Boiler installation . The equipment is fixed on the floor surface or hung on the wall. The choice of method depends on the dimensions of the boiler.
- Pipeline layout according to the selected scheme and developed project. It is important to observe the recommended slope angle of the pipe circuit.
- Installation of heating radiators and connecting them to the system.
- Installation of the expansion tank and its insulation.
- Connecting all elements , checking the tightness of joints and starting the system.
After the boiler, on the supply pipe, it is advisable to install a temperature sensor to monitor the efficiency of the heating system.
Installation of the heating system must be carried out in the warm season. Construction of the highway and commissioning will take about one week
Options for single-pipe heating of a private house
Below is a simple diagram with bottom connection of radiators.
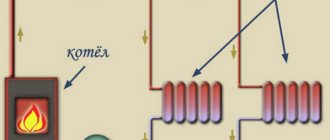
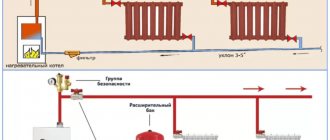
Typical single-pipe heating system of a private house.
The system is of the open type - its expansion tank 3 is connected to the atmosphere. Overflow pipe 2 serves to release air and drain water during the initial filling of the circuit. Shown above is a single-pipe heating system with forced circulation, which is provided by circulation pump 4 installed on the “return” in front of the boiler. This is due to the fact that the temperature of the liquid in the “return” is lower than in the “supply”, and operating the pump at a lower temperature of the pumped coolant simply increases its service life.
There is a supply of network water through filter 12 and make-up valve 11 (the system is also initially filled through them). Drain water (for repairs and at the end of the heating season) through valve 5 and sewer drain 10 with valve 11 closed.
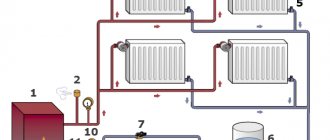
The bottom connection of radiators 7 was used, i.e. Only their lower collectors are connected to the pipes, and the outlets of the upper ones are plugged. Devices are installed in the bypasses (indicated in the diagram by the letter “a”) to regulate the flow (needle valves), but a simpler circuit without them is also possible. It is shown below and is called “Leningradskaya”.
Scheme of the “Leningrad” single-pipe heating system with forced circulation.
In it, the closing sections 14 are bypasses in their pure form without shut-off or control valves with a diameter less than the main pipeline. At the same time, part of the flow through the batteries increases, but it also cools faster, since more cooled water is mixed into the general flow as it flows. In private homes, this is done in order to reduce its overall consumption (and, accordingly, the electricity consumption of pump 4 for forced circulation), as well as to increase the heat transfer of the batteries, although they warm up very unevenly.
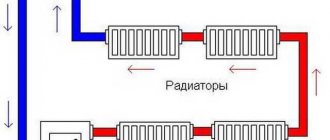
It is possible to connect heating devices diagonally, as shown in the diagram below.
Single-pipe system with diagonal connection of radiators.
Here, the uneven heating of the batteries in the chain remains (and even becomes higher), but the heat transfer of each of them increases by several percent due to the intensive flow of water around them with the simultaneous presence of forced and natural circulation. After all, its temperature at the entrance to the upper collector is several degrees higher than at the exit from the lower one, due to cooling in the device itself. Therefore, conditions arise for the natural circulation of water through the batteries (as in corresponding systems without pumps). The pressure in bypass 14 will not allow this flow to close, but it will rise up to valves 13 quite intensively.
How to implement alternative heating for a private home
Two-pipe heating system for a private house - classification, types and practical design skills
Single-pipe and two-pipe heating distribution in a private house
Open or closed system. What's better?
Closed and open types of heating differ in parameters and functionality, as well as other characteristics. In each specific case, the scheme is chosen strictly individually. The open version of the system is more suitable for organizing heating in small buildings, including country houses or private households. Given the simplicity of the circuit, such a system has a high level of reliability and does not require the constant use of expensive electricity.
The design of a closed-type heating system is characterized by the complexity of installation, as well as operational features, including the need to provide electrical power. However, this option becomes the most optimal for organizing year-round and most reliable heating in multi-storey buildings or large country cottages with a high-power dedicated power supply line.
It is important to see the following: open heating systems are not capable of competently regulating the temperature in rooms due to their limitations. With closed pump systems, all this can be achieved.
Basic heating schemes
Heating systems, where forced circulation of coolant is provided, can be organized according to a variety of schemes. The most common ones are discussed below. You should start with single-pipe water heating schemes:
Figure 2: Single-pipe horizontal system with end sections.
Flow (Fig. 1). For small houses, a single-pipe horizontal flow-through water heating system is perfect. It provides the following operating scheme: the coolant enters the main riser, and is then distributed among all horizontal risers and begins to flow sequentially through the batteries, cooling, it immediately returns through the return line. With closing sections (Fig. 2). There is another horizontal single-pipe system, which provides for the creation of sections that are subsequently closed. During its organization, a valve designed to remove air must be installed on each radiator. To regulate the temperature of the heating elements, shut-off valves are provided, which are installed at the beginning of the heating system with forced circulation on each floor of a country house. Single-pipe (Fig. 3). A water heating system that provides forced circulation can be vertical. In this case, the coolant immediately reaches the top floor of the house, then it flows through the risers into the installed radiators, then the liquid goes into the heating elements located on the previous floor, and so on until it drops to the very bottom. Such a water heating system can be organized both according to a flow-through circuit, and according to one where there are closing sections
It is important to take into account that it has one significant drawback: heating of the batteries in the house on the floors occurs unevenly.
Figure 3: Single-pipe vertical heating system.
There are also two-pipe water heating systems, where forced circulation of the coolant is provided (Fig. 4). They can be organized according to 3 schemes:
- Dead end. Here, each subsequent element of the heating system in the direction of movement of the coolant is located at the farthest distance from the heating element. This scheme leads to an increase in the circulation circuit, which makes it difficult to control the operation of the heating equipment. However, this system provides for a short pipeline length, which allows minimizing the costs associated with organizing heating for the home.
- Along the way. There is equality of circulation circuits here. This factor makes it easier to regulate the operation of the heating system, where forced circulation is provided. However, here the length of the pipeline increases significantly compared to a dead-end circuit, which leads to additional costs when installing heating.
- Collector. This provides for connecting each heating element individually to the heating system. Thanks to this, the coolant enters the radiators at the same temperature. However, this also implies a large consumption of pipes when installing the system.
Figure 4: Two-pipe horizontal system.
In addition, there is another scheme for the vertical organization of forced heating (Fig. 5). It implies the presence of a lower wiring. Here, the coolant enters the boiler using a pump, then it enters the pipeline and is distributed throughout the entire system, and then passes into the heating elements, giving up its heat, the liquid returns through the return pipeline through the pump and expansion tank to the heating element. A vertical heating system can also be organized with overhead wiring (Fig. 6). This means the location of the main pipelines above the heating elements (in the attic or under the ceiling of the upper floor). The water, which circulates using a pump, enters the boiler, then is distributed through the risers to the heating elements; the liquid, having given up its heat, goes into the return line, which is located in the basement or under the floor of the lower floor.
Operating principle
In a water heating system, liquid is a means of transporting thermal energy to devices that transmit heat to the air. These devices can be radiators or the pipeline circuit itself inside the floor or along the walls (in the latter case, large cross-section pipes are used: 8-10 cm).
Thanks to this, the heat from the boiler (which is the only source of heat) is sufficient even to supply heat to several rooms located at a distance from the heat generator. In addition, by changing the number of radiators, you can evenly heat rooms of different sizes. This is the advantage of water heating over installing a conventional stove, which can only heat the rooms adjacent to it.
Due to physical laws, the movement of liquid along the circuit can be carried out by gravity: the density of the heated coolant is lower than that of the cooled one. In addition to the principle of thermodynamics, operation is ensured by installing pipes at a certain slope. You can also use a circulation pump to increase efficiency. Many people mistakenly believe that a pump is an attribute only of a closed system: in open circuits, forced circulation of coolant is also permissible.
An open heat supply system is characterized primarily by an open-type expansion tank. It is a container without a lid for excess coolant formed as a result of thermal expansion of water. The reservoir allows you to automatically stabilize the pressure in the system. And to ensure that the liquid does not spill out according to the principle of communicating vessels, the expansion tank is mounted at the highest point of the circuit. The reservoir simultaneously performs the function of an air valve: through it, air from the system escapes into the atmosphere (during its filling and operation).
Detailed diagram of the operation of an open heating system
Heating of the house is provided according to the following principle
:
- supply - the coolant is heated in the boiler and moves to the radiators;
- return - the liquid that has cooled in the expansion tank and radiators tends to “go” to the lowest point and, due to the inclination of the pipes, enters the boiler.
Installing a circulation pump makes the process more intense, but the principle of operation does not change.
Forced circulation system elements
Forced circulation is a process that requires the installation of not only a pump, but also other required elements.
- These include:
expansion tank to compensate for the volume of coolant when temperature changes; safety group, including pressure gauge, thermometer, safety valve; radiators connected according to one of the wiring diagrams; Mayevsky taps or air separator; check valve; system fill and drain taps; coarse filter.
In addition, when using a solid fuel boiler as a heater. without the automatic fuel loading function, it is recommended to include a heat accumulator in the system - a storage tank of the required volume. This will equalize the temperature of the coolant and avoid its daily fluctuations.
How to turn an open system into a closed system
An open expansion tank promotes natural evaporation of the coolant and its saturation with oxygen from the air masses. To get rid of these problems and extend the life of the system, it is enough to perform a simple conversion of an open heating circuit into a closed one. In this case, the principle of circulation can be preserved, and the water will move due to its physical properties, but the best option would be to purchase and install a circulation pump.
The main stages of modernization are as follows:
- dismantling and replacing an open expansion tank;
- setting up a security group;
- installation of the expansion machine.
The standard safety group is represented by a pressure gauge, safety fittings, and an automatic air vent. After the alteration, it becomes possible to increase the length of the line and change the connection diagram, increase heat transfer and regulate the heating level of radiator batteries in an individual mode.
Selecting an expansion tank for closed heating
The coolant in heating systems of private houses is usually ordinary water. When heated, water tends to expand, thereby increasing the pressure in the system. If the pressure in a sealed system exceeds a critical point, a pipeline rupture may occur. How to make a closed heating system that will not damage pipes?
To solve this problem, expansion tanks were created that eliminate excess fluid, thereby preventing pressure build-up.
The expansion tank consists of two parts: a metal body and an elastic diaphragm, which is located inside and divides the body into two halves. The “back” part of the tank is filled with air or gas, and the expanded liquid enters the lower part. As the temperature rises, the water continues to increase in volume, affecting the membrane, which begins to shrink.
Membranes in tanks can be of two types:
- Fixed
. Such a membrane is fixed around the perimeter of the expander and ensures stable operation, but if it is damaged, the entire tank will need to be replaced. - Replaceable
. Membranes of this type are usually produced in the form of bulk rubber products that are filled with water. Replaceable membranes are installed on the tank flange, and if they rupture, you can replace them yourself.
Conclusion
The heating system is an important element of the house, and its calculation must be carried out in accordance with all rules. The question of which is better: a closed heating system with your own hands or one built by professionals remains open, but it is not the most important.
It is very important to choose the right system elements that will ensure maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness, are reliable and of high quality. A closed heating system, the diagram of which is shown in the photo, can be an excellent choice to ensure that all requirements are met
If everything was done correctly, the closed heating system will heat the building for many years, creating a cozy and comfortable environment.
Is it possible to make open systems from polypropylene?
A gravity-flow heating system made of polypropylene pipes is one of the affordable and easy-to-install options. Reinforced polypropylene pipes have an operating temperature within 70°C and peak performance at 95°C. An analogue of steel and cast iron structures is distinguished by its ability to withstand pressures of 20 Bar and above, and also has high thermal insulation, anti-corrosion resistance and hygiene. If the installation rules are followed, the system can last 50 years.
As you understand, PPR pipes can be used to make open heating systems, but from an aesthetic point of view, steel pipes will look better in the house. They can always be restored to a civilized appearance, while polypropylene pipes will become less presentable over the years.
Nuances of calculating the installation of a heating system with forced circulation
The proper installation of the heating circuit determines how long and trouble-free the heating in the house will operate. Since the liquid in a closed system is not in contact with the environment, it cannot evaporate. When heated, the coolant expands, thereby increasing the pressure inside the system. Since a closed heating system with forced circulation does not imply the possibility of water leaving the circuit, an expansion tank is needed that will absorb the excess volume.
The tank is connected to the return pipeline, just like the circulation pump, because It is in this area that the heating of the coolant is minimal. Since hot liquid shortens the life of the pump, it is better to install it in a place where the water temperature is minimal.
Due to the fact that the pipes in a system with a pump have a smaller cross-sectional diameter, the volume of coolant circulating through them is less than the volume of liquid required to heat a similar house without a pump. This factor has a positive effect on the operating conditions of the expansion tank; in a system with a pump, the tank does not fail longer. A heating system with forced circulation does not cause as many inconveniences as natural circulation.
Also, modern models of heating boilers often have mechanisms for regulating water temperature depending on the time of day, which work automatically. This nuance allows you to make the operation of the circuit more economical.
A modern heating boiler has great capabilities and various adjustments, which makes it easier to operate.
In order to increase the heating surface, a finned heating pipe can be installed in the circuit. The well-known heating radiators made of cast iron are a type of finned tubes. Such designs, by increasing the surface of the heater, provide more uniform and high-quality heating of the room. It is better to install finned pipes in non-residential premises, because... Due to their complex shape, they easily accumulate dust.
Unlike a gravity circuit, where there is no circulation in the heating system, a design with a pump requires a careful approach. One of the primary problems that needs to be resolved when designing is whether it will be a single-pipe forced circulation heating system or a two-pipe one. The first option is more economical and easier to install, but a two-pipe forced circulation heating system is more productive.
The heating circuit of a three-story house with gravity circulation can easily be converted into a circuit with forced water circulation. To do this, attach a water pump and an expansion tank to it. Thus, they modernize the heating circuit and maintain a comfortable temperature in the home, regardless of the weather outside the window. Selecting a circulation pump
When buying a circulation pump, take into account its reliability, the amount of electricity consumed and its clear operating principle. Forced heating depends on the power of the unit and the pressure it is capable of creating. When assessing these characteristics, they are based on the size of the room for which the pump is purchased. So, for a private house with an area of 250 sq.m. you will need a pump with a pressure of 0.4 atmospheres and a capacity of 3.5 cubic meters. m/hour. If the house is spacious and its area exceeds 500 square meters. m, then the required pump power is 11 cubic meters. m/hour, and the pressure is 0.8 atmospheres. When purchasing a pump for a specific room, it is advisable to carry out an individual calculation that takes into account individual characteristics: length of the circuit, number of heating radiators, pipeline diameter, pipe material, type of fuel.
WATCH THE VIDEO
Heating with forced circulation reduces heat transfer when air pockets form inside the pipeline. The movement of coolant along the circuit becomes difficult. Air congestion occurs near radiators, in vertical sections of the circuit. To avoid this problem, a Mayevsky tap and automatic air vents are installed on each radiator. This is an effective way to prevent system disruptions caused by air getting into the pipes. The forced circulation heating system is always at its best.
Requirements for arrangement and operation
When installing heat supply to a home, it is important to take into account a number of features of an open heating system:
- To ensure normal circulation, the boiler is installed at the lowest point in the line, and the expansion tank at the highest point.
- The optimal place to place the expansion tank is the attic. During the cold season, the container and supply riser within the unheated attic must be insulated.
- The laying of the main line is carried out with a minimum number of turns, connecting and fitting parts.
- In a gravity heating system, water circulates slowly (0.1-0.3 m/s), so heating should occur gradually. Do not allow it to boil - this accelerates the wear of radiators and pipes.
- If the heating system is not used in winter, the liquid must be drained - this measure will keep the pipes, radiators and boiler intact.
- The coolant level in the expansion tank must be monitored and periodically replenished. Otherwise, air pockets will appear in the line, reducing the efficiency of the radiators.
- Water is the optimal coolant. Antifreeze is toxic and is not recommended for use in systems that have free contact with the atmosphere. Its use is advisable if it is not possible to drain the coolant during an unheated period.
Particular attention is paid to calculating the cross-section and slope of the pipeline. Design standards are regulated by SNiP number 2.04.01-85.
In circuits with gravitational movement of the coolant, the cross-sectional size of the pipe is larger than in pumping circuits, but the total length of the pipeline is almost two times less. The slope of the horizontal sections of the system, equal to 2 - 3 mm per linear meter, is suitable only when installing heat supply with natural movement of the coolant.
Failure to comply with the slope when installing systems with natural movement of coolant leads to airing of the pipes and insufficient heating of radiators distant from the boiler. As a result, thermal efficiency decreases
Where to put
It is recommended to install a circulation pump after the boiler, before the first branch, but on the supply or return pipeline it doesn’t matter. Modern units are made from materials that can withstand temperatures up to 100-115°C. There are few heating systems that work with a hotter coolant, so considerations of a more “comfortable” temperature are untenable, but if you feel safer, put it in the return line.
Can be installed in the return or direct pipeline after/before the boiler up to the first branch
There is no difference in hydraulics - the boiler, and the rest of the system; it makes absolutely no difference whether there is a pump in the supply or return branch. What matters is the correct installation, in terms of strapping, and the correct orientation of the rotor in space
Nothing else matters
There is one important point regarding the installation location. If the heating system has two separate branches - on the right and left wings of the house or on the first and second floor - it makes sense to install a separate unit on each, and not one common one - directly after the boiler. Moreover, the same rule remains on these branches: immediately after the boiler, before the first branch in this heating circuit. This will make it possible to set the required thermal conditions in each part of the house independently of the other, and also in two-story houses to save on heating. How? Due to the fact that the second floor is usually much warmer than the first floor and much less heat is required there. If there are two pumps in the branch that goes up, the speed of movement of the coolant is set much lower, and this allows you to burn less fuel, without compromising the comfort of living.
There are two types of heating systems - forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump; systems with natural circulation work, but in this mode they have lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is installed into it. This gives high heating efficiency and reliability. It is clear that the installation of a circulation pump in these systems is different.
All heating systems with heated floors are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
Forced circulation
Since a forced circulation heating system without a pump is inoperative, it is installed directly into the gap in the supply or return pipe (of your choice).
Most problems with the circulation pump arise due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They can jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a mesh dirt filter must be placed in front of the unit.
Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
It is also advisable to install ball valves on both sides. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps and remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
Natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not working. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed the entire time the pumping is running. In this mode, the system operates as forced.
Installation diagram of a circulation pump in a system with natural circulation
When the electricity goes out or the unit fails, the valve on the jumper is opened, the valve leading to the pump is closed, and the system operates as a gravity system.
Installation features
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require rework: it is necessary to rotate the rotor so that it is directed horizontally. The second point is the direction of flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating which direction the coolant should flow. This is how you turn the unit so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, just when selecting a model, make sure that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (pressure created) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.
Advantages and disadvantages
The pros and cons of a two-pipe system should be considered taking into account the operational properties and technical characteristics.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Same coolant temperature in all radiators | Increased pipe consumption - 2 branches need to be led to the radiator, inlet and outlet |
| Adjusting the heat output of each battery | Large diameter riser pipes and supply pipes to the first radiators in the circuit |
| Low hydraulic resistance | |
| Operation of the entire system in case of failure of one or more radiators | |
| Use in high-rise buildings | |
| Flexibility of hose options – in the floor, in the walls, along the walls, under the ceiling and behind a false ceiling |
The table shows common to all two-pipe networks. However, each wiring option may have negative qualities that limit its use, which we will consider later.
How a single-pipe heating system works: we explain it in diagrams
Types of circulation pumps
A pump with a “wet” rotor is made of stainless steel, cast iron, bronze or aluminum. Inside there is a ceramic or steel motor
To understand how this device works, you need to know the differences between the two types of circulation pumping equipment. Although the fundamental design of a heating system based on a heat pump does not change, the two types of such units differ in their operating features:
- A pump with a “wet” rotor is made of stainless steel, cast iron, bronze or aluminum. Inside there is a ceramic or steel motor. The technopolymer impeller is mounted on the rotor shaft. When the impeller blades rotate, the water in the system is set in motion. This water simultaneously functions as an engine cooler and a lubricant for the working elements of the device. Since the “wet” device circuit does not provide for the use of a fan, the operation of the unit is almost silent. Such equipment only works in a horizontal position, otherwise the device will simply overheat and fail. The main advantages of a wet pump are that it does not require maintenance and also has excellent maintainability. However, the efficiency of the device is only 45%, which is a minor drawback. But for domestic use this unit is perfect.
- A pump with a “dry” rotor differs from its counterpart in that its motor does not come into contact with the liquid. As a result, the unit has less durability. If the device operates “dry,” then the risk of overheating and failure is low, but there is a risk of leakage due to abrasion of the seal. Since the efficiency of a dry circulation pump is 70%, it is advisable to use it to solve utility and industrial problems. To cool the engine, the device circuit provides for the use of a fan, which causes an increase in the noise level during operation, which is a disadvantage of this type of pump. Since in this unit water does not serve as a lubricant for working elements, during operation of the unit it is necessary to periodically carry out technical inspection and lubricate parts.
In turn, “dry” circulation units are divided into several types according to the type of installation and connection to the engine:
- Console. In these devices, the engine and housing have their own place. They are separated and firmly fixed on it. The drive and working shafts of such a pump are connected by a coupling. To install this type of device, you will need to build a foundation, and maintaining this unit is quite expensive.
- Monoblock pumps can be used for three years. The body and engine are located separately, but are combined by a monoblock. The wheel in such a device is installed on the rotor shaft.
- Vertical. The service life of these devices reaches up to five years. These are sealed advanced units with a seal on the end side made of two polished rings. For the manufacture of seals, graphite, ceramics, stainless steel, and aluminum are used. When the device is running, these rings rotate relative to each other.
There are also more powerful devices on sale that have two rotors. This dual circuit allows you to increase the performance of the device at maximum load. If one of the rotors fails, the second can take over its functions. This allows not only to enhance the operation of the unit, but also to save energy, because with a decrease in heat requirements, only one rotor works.
What type of wiring to choose
The choice of construction scheme depends on the expected operating conditions:
- In buildings above 2 floors, heating is installed with main risers in a vertical pattern.
- In areas with frequent or prolonged power outages, preference is given to gravity systems with non-volatile boilers.
- For large objects, systems with forced circulation are installed, built using a horizontal type of wiring. The most suitable scheme in is the Tichelman loop.
- For independent execution, inexperienced users choose a dead-end wiring with several arms.
- When pouring pipes into the floor, it is advisable to choose a radial scheme with collectors on each floor - in the event of an emergency pipe rupture, you can turn off 1 radiator, postponing costly repairs with opening the floors.
- Small country houses, bathhouses and utility rooms are equipped according to a dead-end scheme.
Each specific case must be considered individually, taking into account the advantages and disadvantages of the types and types of heating systems.
One and two-pipe heating systems
Many heating schemes have been developed and installed. But they are all modifications or combinations of two system options that can be defined as basic options.
Basic or basic schemes can be considered:
Single-pipe heating circuit
A simple one-pipe system is popular. how does it work? Simple, extremely simple. Hot coolant flows from the boiler through one pipe and, after passing through a sequential chain of batteries, returns to the boiler. This principle is actually used by the heating scheme of a one-story house with forced circulation, and installing a bypass on the pump turns it into a “gravity” system.
- uneven heating of radiators;
- To replace the battery you need to turn off the system.
The disadvantages of the above-described scheme are practically eliminated in the modernized single-pipe heating scheme, which is known as the “Leningradka”, after the place of its invention in St. Petersburg.
In St. Petersburg, “Leningradka” is used even in multi-storey buildings. Ball valves at the battery inlet/outlet will allow you to replace or repair batteries without turning off the heating. The batteries cut into the supply pipe in parallel. When organizing a heating circuit for a two-story house with forced circulation, a vertical wiring diagram is installed.
The pipeline rises to the second floor, water enters the batteries located horizontally in series. Then, from the last radiator, the pipeline goes down and is connected to a horizontal line of radiators, and then the coolant that has cooled down and given off its energy enters the boiler. The disadvantage of such a system is considered to be uneven heating of the radiators. This drawback is especially noticeable if gravity flow is used, but if a circulation pump is installed, the difference in temperature is almost unnoticeable.
Two-pipe heating circuit
The most optimal are considered to be heating system designs with forced circulation in the circuit. Such systems are effective for one-story cottages, houses and dachas and can easily provide heat for a two-story house with a large area. To implement this scheme, two pipes are installed - a supply pipeline and a return line. The batteries are connected in parallel, they are equipped with shut-off valves and devices for removing air. This scheme ensures uniform heating of the batteries, but the pipe consumption for installation is much higher. Additional costs are offset by efficient heating operation.
Vertical two-pipe scheme
A vertical closed heating system with forced circulation is implemented in two versions - with lower (horizontal) or upper wiring. Horizontal wiring is organized as follows. The “supply” pipe rises to the top floor, and all the batteries that are connected to the “return” are connected to it. The disadvantage is the presence of two pipes in the room.
Using a pump in an open system
Installing pumping equipment ensures uniform heat distribution across all radiators, minimizing problems with insufficient pipe diameters and non-compliance with slopes. The addition of a pump is especially in demand in conditions of excessive length of pipelines. It is advisable to install the circulation pump between the water heating boiler and the expansion tank.
Advantages and disadvantages
The open heating system has not yet lost its relevance, and recently it has even experienced a rebirth, and there are reasons for this. Many homeowners are concerned about the energy independence of their communications, and the open tank scheme allows this to be achieved. She has other advantages:
- Filling an open heating system and bleeding air is easier than in a closed one. There is no need to monitor the maximum pressure, and when filling, the air leaves the pipelines very quickly through the open expansion tank. All that remains is to ventilate the radiators;
- it’s easier to refill: again, pressure control is not required, and water can be added to the container even with a bucket;
- the operation of the system does not depend on the presence of leaks: here the operating pressure is very low, so as long as there is water in the heating network, it will function properly.
As usual, there were some drawbacks, due to which such systems began to be gradually replaced by closed-type circuits with a membrane expansion tank. Due to the direct contact of the coolant with atmospheric air, two processes occur in the container at once: natural evaporation of hot water and its saturation with oxygen. This leads to the following requirements:
- you need to monitor the water level in the tank and replenish it on time;
- Do not fill the heating network with antifreeze, which releases harmful substances when evaporated.
Oxygen saturation of the coolant leads to a decrease in the service life of steel parts of the boiler. For the above reasons, the open system has not been used in apartment buildings for a long time, although in the 60-70s of the Soviet era such practice took place in low-rise residential buildings. It is also undesirable to operate it with high-temperature heat sources when the coolant is close to the boiling point. The fact is that with increased pressure in a closed network, this threshold increases, and there is nowhere for water to evaporate. In an open system, the amount of water will quickly decrease, freeing up the entire volume of the expansion tank for air.
Pipe location
Depending on the layout of the room, dimensions, different methods of arranging batteries and pipes are chosen.
One or two pipes – what to choose
Thermal systems involve preheating the liquid in the boiler, moving it, entering the heating radiators, and returning it through the return line to the boiler. The system can be using one or two highways.
In a single-pipe system, the liquid moves along one circuit with a large diameter, the heating radiators are located on the same line.
Advantages:
- Little material is required during installation.
- Easy installation.
- There are not many pipes in the room.
The batteries warm up unevenly; due to the remote location of the boiler, the heat transfer rates are lower.
For a private home
In the second case, a closed ring effect is formed, where heating devices are connected to a pipe for supplying and discharging (return) water.
Advantages:
- Heating radiators warm up evenly.
- Each battery has its own temperature - convenient if the rooms are different in size.
- Reliability.
Disadvantages: difficult installation, high cost.
Water supply methods
The direction of hot water supply depends on the location of the main line - from below or from above. In a one- or two-story house, the first option is chosen; the heated coolant rises through the central riser, circuits, and is supplied to the radiators.
Bottom distribution: the supply pipe is located near the return.
Battery connection methods
The location of the riser determines the type of wiring - vertical or horizontal.
When connected vertically, the batteries are connected to the central riser on each floor. Airing of the system is avoided. A multi-storey building receives efficient heating.
During horizontal wiring, batteries on one floor are connected to a common line.
Types of open heating schemes
In an open heating system, the coolant moves in two different ways. The first option is natural or gravitational circulation, the second is forced or artificial stimulation from a pump. The choice of scheme depends on the number of floors and area of the building, as well as on the expected thermal conditions.
Natural circulation in heating
The gravitational system does not have any mechanism to ensure the movement of the coolant. The process is carried out solely by the expansion of hot water. For the operation of the circuit, an accelerating riser is provided, the height of which is at least 3.5 m.
If you neglect to install a vertical transit riser, then there is a high probability that the coolant coming from the boiler will not develop a sufficient speed
The natural circulation heating system is optimal for buildings with an area of up to 60 square meters. m. The maximum length of the circuit capable of providing heat is considered to be a 30 m mainline. An important factor is the height of the building and the number of storeys of the house, which allows the installation of an accelerating riser. The natural circulation scheme is not suitable for low-temperature applications. Insufficient expansion of the coolant will not create the proper pressure in the system.
Possibilities of the gravity circuit:
- Connection to heated floors . A circulation pump is mounted on the water circuit leading to the floor. The rest of the system operates as usual. If the power goes out, the house will continue to be heated.
- Working with a boiler . The heating device is mounted at the top of the system - slightly below the expansion tank.
To ensure uninterrupted operation, a pump can be installed on the boiler. Then the heat supply and hot water production scheme automatically becomes a forced option. Additionally, a check valve is installed to prevent recirculation of the coolant.
Forced system with pump
In order to increase the speed of the coolant and reduce the time for heating the room, a pump is built in. The movement of water flow increases to 0.3-0.7 m/s. The intensity of heat transfer increases, and the branches of the main heat up evenly.
Pumping circuits are constructed of both open and closed types. In open circuits, the expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the system. The presence of the pump allows you to increase the pipeline between the heating boiler and the batteries, both in height and in length (+)
Important points in organizing a compulsory system:
- The circuit with a built-in pump is volatile. To ensure that the heating of the room does not stop during a power outage, the pumping equipment is placed on the bypass.
- The pump is installed in front of the boiler inlet on the return pipe. The distance to the boiler is 1.5 m.
- When installing the pump, the direction of water movement is taken into account.
Two shut-off valves and a bypass elbow with a circulation pump are mounted on the return line. If there is current in the network, the taps close - the coolant moves through the pump. If there is no voltage, then the valves must be opened - the system will switch to natural circulation.
A check valve must be installed on the supply pipeline. The element is placed immediately after the boiler and prevents recirculation of the coolant during pump operation
Open Network Package
To assemble an open circuit, you will need the following elements:
- heating equipment;
- pipelines;
- atmospheric expansion tank;
- heating appliances;
- pumping equipment will only be needed for open-type water heating with a pump;
- drain valve;
- tap for filling the network with coolant.
Boiler
Open circuits can work with the following types of boilers:
Closed heating system and its filling
- It is advisable to use gas heating equipment in regions where there are gas mains. Gas boilers are the most economical, but they are installed after obtaining permission from the gas service.
- Solid fuel units operate on wood, coal, pellets or briquettes. There are long-burning boilers on sale that are economical, efficient, and do not require frequent loading of fuel.
- Electric heaters are not used as often because energy resources are quite expensive.
- Combined type units can operate on two different types of fuel, which makes the equipment non-volatile.
Important! Electrode boilers are not used in open networks, because they are only suitable for coolant with a constant chemical composition. This cannot be achieved in a leaky circuit.
Circulation pump
If we compare natural and forced circulation, the latter is much better because it increases the efficiency of the heating system. Despite the energy consumption of the pump, there is a saving in the energy carrier used by the boiler.
Pumping equipment is selected according to the diameter of the pipes at the insertion point, liquid pressure and productivity. When choosing a pump, pay attention to its technical characteristics.
Expansion tank
You can make an expansion tank yourself or buy it. The stainless steel tank is equipped with an opening lid to control the coolant level. A pipe is installed in the upper part of the container to drain excess liquid.
The expansion tank can be installed at the following network points:
- on a remote riser;
- at the highest point of the system;
- on the return pipeline;
- together with pumping equipment that is installed on the supply pipes.
Important! The capacity of the compensation tank should be 10% greater than the total volume of the heating network.
Heating radiators
Open heating can work with the following types of heating devices:
- Cast iron batteries are ideal for open systems because they have great inertia, which ensures energy savings.
- Steel radiators with anti-corrosion coating are lightweight and inexpensive, but it is better to avoid using them. The device cools down quickly, which will lead to frequent operation of the heater and excessive energy consumption.
- When choosing aluminum appliances, give preference to units with anti-corrosion coating. They are valued for their durability, good heat dissipation, light weight and attractiveness.
- The most expensive bimetallic devices. They combine the advantages of steel and aluminum appliances, but are completely devoid of their disadvantages. But they are better used in centralized networks with high pressure.
Pipes
For natural coolant flow, large diameter pipes will be needed.
Pipelines made of the following materials can be used:
Automation and thermostats for controlling the heating circulation pump
- steel pipes are almost never used due to the complexity of installation and heavy weight;
- copper pipelines are the highest quality and most durable, but they are very expensive;
- metal-plastic pipes themselves are not bad, but they are connected to fittings that often leak;
- it is better to choose elements made of cross-linked polyethylene with oxidation protection and reinforcement;
- There is another inexpensive and practical option - polypropylene pipelines with fiberglass reinforcement.
Important! For coolant flow by gravity, the slope of horizontal pipelines should be 1/100-3/100. In other words, by 1 m.p. pipeline, the height difference is 10-30 mm.