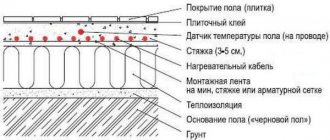
Warm floors are of two types, depending on the heating method.
Selecting and laying the underlay under the heated floor
Mermen
Heating is carried out by a pipeline system, the coolant is hot water.
Water heated floor
They are used in most cases in private homes; when connecting hot water in multi-apartment buildings, big problems arise due to the disagreement of management companies to give permission to connect to common building heating networks for two reasons. Firstly, in this case it is difficult for them to control the specific consumption of thermal energy by each consumer individually. Secondly, boilers may not be able to withstand a significant increase in energy consumption.
Water heated floor diagram
It is not always possible to install a separate heating boiler in city apartments, and such installation, together with the price of the equipment, is quite expensive.
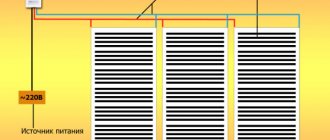
Electrical
Standard electrical diagram for connecting an infrared film heated floor
The temperature rises due to the resistance of the current conductors. From school we know the formula Q (energy released) = I (current strength) × R (conductor resistance) .
Connection diagram for cable heated floors
Depending on the physical characteristics of the conductors, heated floors can be film (infrared) or cable (conducting elements are ordinary flexible cables and improved insulation). Electric floors have their own difficulties; during their installation, it is necessary to take into account the parameters of the existing wiring and special protective fittings.
Infrared heated floor diagram
To effectively heat floors, the power per square meter must be at least 250 kW; in total, larger values are used.
Types of electric heated floors: 1 - Cable. 2 — Cable with reinforcing mesh
Currently, manufacturers produce a wide range of substrates, differing in linear characteristics, materials of manufacture and the ability to perform additional functions.
Power of electric heated floor
Electricity consumption of film heated floors
Warm floor marking
Types of lining materials
Foil polystyrene.
High heat/noise insulation characteristics, water resistance. The heat-reflecting effect is provided by a layer of foil. One of the most expensive substrates. Another foil backing for water heated floors is foamed polyethylene coated with foil. Two-millimeter thick film. Reflective effect, good heat/noise insulation characteristics. Cons: wrinkles easily, not waterproof enough. The price is the lowest.
Single-sided polyethylene: one side is foil-coated, the other is laminated with polyethylene. Thickness is 8 millimeters, waterproofing is better than the previous material, the price is higher.
Foil self-adhesive polyethylene 8 mm thick. All the necessary characteristics are in order, easy to install, and hides minor unevenness of the base well. The price is average.
In addition to foil, reflective Mylar film is used for laminating polyethylene. The thickness of such a substrate is three millimeters, and the price is higher than that of foil polyethylene. The material is valuable when laying electric floors, because... does not conduct current (unlike foil). For installation under a water floor, it has no advantages over foil pads.
Cork lining for a warm water floor. Does not crack, does not rot, and is resistant to fungal infections (unlike most wood materials). High thermal insulation and noise-absorbing characteristics, environmental friendliness. There is no thermal expansion. Not the most expensive material, since in fact it is made not from balsa wood, but from crushed oak bark.
Cork comes with or without a foil layer. In the second case, the foil is purchased separately and placed between two layers of insulation. The material is sold in slabs and rolls.
Extruded polypropylene. All the necessary characteristics are excellent, there is a foil layer. Mechanical strength, heat resistance. Sold in mats up to ten centimeters thick. The price is average.
A separate category of lining materials is a substrate for a water-heated floor with bosses. On most substrates, pipes are laid according to markings, and reinforcing mesh is used for fastening. The surface of the mats with bosses consists entirely of raised projections, between which pipes are laid.
The bosses not only mark the laying line, they also fix the pipes, preventing them from moving to the sides. Additional fixation - with clips and staples (not required for all mat models).
The mats () are made of polystyrene foam: a material with low thermal conductivity, waterproof, and a good sound insulator. If there is no foil layer, installation of reflective metal plates is necessary.
Another advantage of such mats is that they are equipped with locks for connecting to each other, which greatly simplifies the installation procedure. Minus - they are expensive compared to other materials.
Ideal combinations
There are many options for combining substrates with insulation when installing water floor heating systems. The choice of their thickness depends on the permissible reduction in the height of the room, its location (thicker products are used on the first floors) and the available funds.
Let's look at the most popular combinations.
Expanded polystyrene + metallized film
Expanded polystyrene is considered the main one, and the metallized substrate is an additional layer of thermal insulation that prevents heat loss through the ceilings.
When installing such floors, an ordinary polyethylene film is initially laid on the base (as waterproofing), then a damper tape is attached along the contour and polystyrene foam is laid out. The thickness of the insulation is assumed to be greater than the planned screed (the strength allows you to secure the reinforcing mesh and pipe fasteners). A backing is placed on it (with the foil layer facing up), and the connections are sealed with tape. Then the reinforcing mesh is laid down. The red lines on the substrate serve as a guide for marking for pipe fasteners. The pipe is laid, connected to the system and checked for leaks. If everything is in order, proceed to pouring the screed, which covers the pipes by at least 4.5 cm.
Note! For water heated floors with cement-sand screeds, the use of an aluminum foil layer is prohibited; in this combination, a reaction begins that destroys the substrate (this does not happen in a gypsum screed)
Mats with bosses + extruded polystyrene foam
The combination is the most convenient for installation, because the purpose of the mats is to install floors with a water coolant. Let's take a closer look at the installation mechanism:
- Before laying the insulation, waterproof the base with a bitumen primer or polyethylene film, which is rolled out onto the wall.
- Expanded polystyrene is laid out on a waterproofed base or glued.
- Thermal insulation is carried out over the entire floor area; construction tape is applied to the joints.
- A damper tape is secured along the perimeter with self-tapping screws, together with plastic film.
- Before laying the mats, the work surface is thoroughly cleaned.
- The carpet is made from mats over a layer of polystyrene foam; it is not necessary to glue them; they snap into place with light pressure and form a continuous layer without gaps. If necessary, the mats are cut with a stationery knife according to the factory markings on them.
- Pipes are laid between the bosses starting from the wall to the center (step 40 cm). When the middle of the room is reached, the pipe is rolled out in the opposite direction between those already laid, resulting in a step of 20 cm.
- Next, the system is connected to the boiler and tested for leaks.
- A screed is installed that does not require reinforcement.
- The protruding film and damper tape are cut off after the solution has hardened.
Important! Warm floors with water heating are incompatible with finishing parquet and wood flooring due to the possibility of drying out. Summing up, it should be noted that it is better to put both a substrate and insulation on the safe side than to waste money and get ineffective, energy-intensive, not very warm floors
To summarize, it should be noted that it is better to be on the safe side by installing both a substrate and insulation than to waste money and get ineffective, energy-intensive, not very warm floors.
Briefly about the use of heated floors and its varieties
Distribution comb for heated floors - purpose, types, installation
The most common class is water heated floors. They can be mounted directly inside concrete screeds and are reliable and durable. Insulation under warm flooring of this class can be made from a wide range of materials. There is also a choice of options for constructing the surface for laying.
Water heated floors have an impressive list of advantages:
- There are heating boilers for sale on the mass market using different types of fuel, in which the connection of a heated floor is provided for by the design;
- solutions proven over the years are used for installation;
- the proposed pipe installation options provide trouble-free operation times of 10-15 years;
- the base for a heated floor can be constructed using different methods;
- heat transfer is controlled and uniform over the entire installation area.
The only disadvantage of water-type heated floors is the installation restrictions in apartments. They are prohibited from being connected to centralized heating systems, since it becomes impossible to track the total heat consumption, and also, if the systems are installed on a mass scale, the heating stations may not be able to withstand the load.
A universal, but relatively expensive to operate, floor heating system is electric. It is based on the use of film heaters or cables laid under thin finishing coatings. The advantages of electric heated floors include simplicity and the possibility of installation inside the apartment. However, it is worth especially noting that the base for laying film heaters must be prepared very carefully.
The underlay for electric-type underfloor heating is selected taking into account additional criteria. Electrical conductivity and the ability to retain moisture play a big role; both factors can lead to both short circuits and the occurrence of parasitic leakage currents, which increase the cost of paying for consumed energy.
conclusions
- Installation of warm water floors must begin with an assessment of the situation and measurements. It is necessary to decide whether the heated floor will be the main or additional type of heating of the room.
- The choice of the best underfloor heating must be approached responsibly and based on the characteristics of the room, taking into account not only the area of the room and the expected temperature, but also the humidity and height of the ceilings.
- It is much safer to use those materials that are specifically designed for warm water floors. This approach will not only save time, but will increase service life and save up to 20% on energy spent on heating the room.
Choosing material
Mats for warm water floors
When choosing such a material, you must follow certain criteria
There are several important points that you should also pay attention to, for example, the thickness and quality of the installed substrate.
The material must have the following properties:
- high level of resistance to mechanical and temperature deformation;
- corresponding indicator of thermal insulation and waterproofing materials;
- the material used must be classified as environmentally friendly and at the same time safe;
- use should be convenient and simple. This will save your own time and effort during installation work;
- the material must have heat-reflecting properties;
- must have excellent soundproofing characteristics;
- the material must be able to withstand any, even the most drastic, temperature changes.
A foil surface material can be used on the floor. For installation of a warm water floor, it is the most optimal and a high-quality substrate is made.
The most popular types of substrates are:
- Tuplex products. This thickness is no more than 2.5 mm, while they are characterized by the presence of excellent heat-reflecting characteristics and waterproofing properties.
- High performance characteristics.
- Foil self-adhesive fabric. The thickness is about 7.5 mm. Use on difficult surfaces. It has a high heat transfer rate and waterproofing properties. It is worth considering the presence of soundproofing properties.
- PPS foil. It can be sold in different thicknesses, and the higher the indicator, the better thermal insulation qualities the material has. Has reflective ability.
- PE one-sided laminated. The undeniable advantages include a very small thickness (less than a centimeter), with high thermal insulation and waterproof characteristics.
- Foamed PE. With a very insignificant thickness, only 2 mm, it has truly excellent characteristics, including waterproofing and thermal insulation.
Nuances of work
All of the above features of screed installation are basic. However, there are additional subtleties that should also be remembered before starting finishing work and operation.
First of all, you need to check the condition of the pipes immediately before pouring. Very often, immediately after putting the floor into operation, pipes begin to leak, become covered with corrosion or rust. Reliable prevention of heat loss is ensured by laying a heat-reflecting layer.
First of all, you need to check the condition of the pipes immediately before pouring
You should carefully select the materials used when installing heated floors. The main material of this type is cement. Most brands of this product begin to cake after a certain period of time and lose their quality characteristics. Professionals recommend purchasing cement on the eve of its use so that it does not remain inactive for too long and does not lose its properties.
Further care of the finished screed does not cause any difficulties. The main thing is to ensure normal humidity for a week after pouring. This is necessary because the cement becomes strongest 25 days after the mortar is prepared.
To maintain various chemical processes that have a beneficial effect on the condition of the coating, you need to use ordinary water. The material should completely harden, but not dry completely. Due to the natural drying of the screed, the material will not have time to harden at all, its performance properties will not meet the requirements. Thus, the screed can dry only after it has reached the required strength. Otherwise, the frozen mortar may crack.
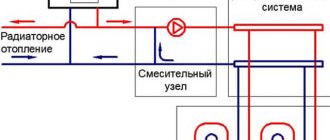
Connection diagram for a warm water floor
Substrate requirements
How to install a mixing unit for a heated floor with your own hands
It is worth approaching the selection of a suitable underlay for a heated floor in terms of service life and the cost of its installation.
Each system has its own requirements, among which it is customary to highlight:
- Thermal insulation. The lower the thermal conductivity of the material, the more suitable the underfloor heating is considered. As a rule, better thermal insulation properties are achieved due to a greater thickness of the substrate. However, this does not work in all rooms. Because it is not always possible to further raise the floor level. In this case, you have to put in thinner options. On the positive side, samples made of foamed polymers with a heat-reflecting coating showed themselves.
- Resistance to loads. It was previously noted that a warm floor consists of several layers. The substrate, as the lowest one, bears the weight of the rest of the structure, as well as the load when walking. Constant pressure leads to compression over time. This is more typical for porous materials. In deformed areas of the lining, thermal conductivity increases and, accordingly, the efficiency of the entire system decreases. In this case, materials with a higher density are preferable.
- Waterproofing. This criterion is important for a water floor system. Leakage is equally harmful to both concrete and wooden foundations. And the neighbors below will not be happy with such a gift. Detecting leaks in pipes with waterproofing is more difficult, but possible. In this case, the indicator is a drop in water pressure. For a classic electric floor system, waterproofing is not so important, since the cables and heating mats have their own. But infrared film floors absolutely cannot tolerate moisture, so complete insulation is necessary both from below and from above.
- Manufacturability. This characteristic means ease of installation of the substrate. Let's compare a few examples:
- Foamed polystyrene is very easy to install. It is thin, flexible, easy to cut with scissors, and sold in compact rolls. It is a pleasure to work with it, if you forget about the big disadvantage - deformation under load.
- Extruded polystyrene foam in rolls is a strip of rectangular segments connected by foil film. It is more difficult to cut due to its thickness, and the seams need to be sealed. All the inconveniences are covered by a big plus - it is an excellent insulation. And the high density of the material prolongs its performance. (Fig. 2)
- Extruded polystyrene foam in sheets is easier to lay, but more seams will have to be sealed.
In fact, all three options are made of the same material, but the form of delivery determines their manufacturability.
- Environmental friendliness. Each of the synthetic linings releases toxic substances to varying degrees when heated. Naturally, the less evaporation, the better, especially for residential premises.
- Resistance to biological influences is completely absent in substrates made from natural materials. Antibacterial impregnation helps save the situation a little. However, it is not recommended to use it as insulation.
- Sound insulation is generally a big plus (for apartment buildings), but it does not matter for the functionality of the heated floor.
- Resistance to high temperatures - allows you to mount heating elements directly on the film. There are samples on the market that can withstand up to plus 90 degrees Celsius.
- Additional qualities. The products of some manufacturers come with markings or bosses (bulges), which help to quickly and evenly install heating elements (pipes, wires).
A few words about ultraviolet resistance.
The presence of this criterion in the list of characteristics of the underfloor heating substrate is nothing more than a marketing ploy, since it will in no way be exposed to direct ultraviolet radiation.
What does saving on insulation lead to?
For example, let's take a room with an area of 50 square meters.
Usually they use polystyrene foam with bosses, the cost is 1 sq. meter on average 600 rubles, thickness - 2 cm. In most cases, this thickness is not enough for insulation, with the exception of the southern regions. Additional insulation up to 4 cm will cost another 150 rubles per square meter. The total amount will be 7,500 rubles.
Saving this amount is what we are talking about when choosing insulation. The owner of the house strives to cut costs and often chooses the cheapest option - underlayment for heated floors, instead of the insulation itself. Ultimately, the thrifty home owner heats the outdoors and spends even more money to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
We have two rooms in front of us:
- the first with normal, high-quality insulation of the required thickness;
- the second - with a substrate for a warm floor under insulation and a “thrifty” owner.
| Characteristic | House No. 1 | House No. 2 |
| Floor area | 50 | 50 |
| Pipe temperature | 40 | 40 |
| Pipe diameter | 16 | 16 |
| Insulation | 60 | 20 |
| Heat flow upward | 73,76 | 65,81 |
| Heat flow down | 18,88 | 58,72 |
| Maximum floor temperature | 26,82 | 26,18 |
In the first house, with 4 cm of insulation, the heat flow into the room exceeds the heat flow down three times. All the heat that the owner of the house pays for is used to heat the room, not the street! In the house of a “thrifty” owner, the heat flow upward (to the room that needs to be heated) is almost equal to the heat flow down (to the street, to nowhere). Forty watts per square meter go down the drain.
- On 1 square meter with underfloor heating we lose 40 W, on 50 square meters - 2000 W.
- 1 cubic meter of natural gas provides 10 kW of thermal power and costs 4.5 rubles (the price depends on the region, from 4 to 8 rubles).
- 10 00 W/2000 W = 5 hours – this is how much 1 cubic meter of natural gas is enough for heat loss.
- The boiler operates on average 12 hours a day. 12/5=2.4 cubic meters of gas are spent per day on heating the street.
- 2.4 (cubic meters) x 4.5 (rubles) x 30 (days) x 7 (months of the heating period) = 2,268 rubles per year.
They paid 7,500 rubles for the insulation / 2,268 rubles = 3.3 years - the payback period for the insulation. When using underfloor heating, heat losses will increase! These materials are not insulation!
When using insulation materials with insufficient thickness for complete thermal insulation or when using foil insulation, isoline (they are also a substrate for a heated floor), the owner of the house loses a lot of heat in the lower direction. This is either unreasonable savings or a serious misconception of the homeowner.
Heat losses in this case are comparable to the heat flow entering the room. The use of high-quality insulation of the required thickness pays off in an average of 3-3.5 years of operation of a heated floor, when using natural gas as an energy source. Natural gas is the cheapest source of energy. If we talk about other sources, then insulation can pay for itself in 1 heating period (i.e. in 7 months).
What type of substrate should be used for the water system?
The main condition for a heated floor system is to ensure an increased degree of heat transfer. In this case, heat will not be wasted. Provided that the floor is based on pipes, the underlay in the event of an accident will perform an additional waterproofing function.
Sometimes you can use a special molded foam cover that is very easy to secure the pipeline into. The same coating acts as a substrate
Typically, a typical base for the substrate is foil, which helps to reflect heat, which should not go to heating the ceilings of the neighbors below. If the foil is sufficiently thick, it can be in its pure form or on a polymer base (glued in a thin layer). In principle, the heat insulator has a low degree of waterproofing. This protection must be ensured by laying a separate layer of insulating material.
The substrate does not need special fastening, since it is laid on the insulation. When installing a water heated floor, a reinforcing screed is used, which presses down the substrate
The main difference when comparing identical underlayment models is the cost and different service life. And the modern market offer does not yet offer a wide range.
The value of thermal insulation substrate
Insulating material is an intermediate layer between the subfloor and the water pipeline with the coolant.
The main purpose of the substrate is to preserve and redirect heat flows upward, that is, to the living area of the room. In addition to the task of preserving heat, the intermediate layer performs a number of equally significant functions:
- Waterproofing. In emergency situations, a waterproof substrate will retain water, protect the lower layers of the underground “pie” and prevent water from leaking to the basement floor. In addition, it will prevent the flow of moisture vapor from the screed to the finishing floor covering.
- Thermal insulation. The layer acts as a kind of barrier between elements with different temperatures. Otherwise, contact with a cold floor will contribute to condensation and a decrease in the characteristic qualities of the insulation.
- Uniform heat distribution. The substrate minimizes the likelihood of obvious temperature changes - there are no excessively warm or cold zones. This feature reduces the negative thermal impact on the final flooring, appliances and furniture.
- Sound barrier. Most underlay materials absorb noise from walking on the floor and improve the overall sound insulation of the room.
The substrate softens shock loads on the base, distributing point pressure - this helps maintain the integrity of the screed.
The insulating layer, due to the low thermal conductivity of the material, gives a heat-reflecting effect - the main flow of heat energy rushes upward. In the absence of a substrate, the efficiency of the heating circuit decreases sharply, and energy bills increase ( )
When installing a water floor, the substrate is usually laid on top of the insulation to maximize heat retention - a “thermos effect” is realized, reducing heat loss.
The lining with beads makes installation easier - you can use different options for placing the heating circuit, choosing the optimal locations for connecting the system and installing control sensors
Types and characteristics of the substrate
So, when buying thermal insulating flooring, you first of all need to navigate its variety of types:
- Lavsan is a film-based coating (foamed polyethylene) with a metallized reflective top layer. Characterized by resistance to aggressive environments. A lavsan underlay for a heated film floor fits perfectly.
The photo shows the laid lavsan.
Note! This type of insulation is characterized by a certain power density. Therefore, the choice must be made taking into account the finishing coating
So, when installed under tiles, the power of lavsan is 220 W per m²; under laminate/parquet – 150W per m²; under carpet/linoleum – 220W per m². If you lay a film with a higher UV value than specified, the floor covering may deteriorate due to overheating.
- Expanded polystyrene is a cellular insulation material. It has a high temperature threshold: from -180° to +180°, and is wrinkle-resistant. It is an excellent sound insulator and has increased resistance to bacteriological influences. Has a foil or polypropylene coating. It is considered an excellent option for underlayment for water heated floors.
Expanded polystyrene boards.
A distinctive feature of this heat insulator is that it is produced in slabs with ready-made markings (50 to 50), which greatly simplifies the subsequent process of installing the floor. Slabs with different thicknesses are available for sale: from 20 to 50 mm.
- Technical cork, cork backing. It is environmentally friendly and therefore hypoallergenic. Its composition is compressed cork oak bark + astringent substance – suberin. Not eaten by rodents. As a rule, cork is used as a substrate for laminate flooring.
Despite this composition, the insulation is not flammable and shows excellent resistance to mechanical stress. It is optimal for arranging a water floor.
Cork backing in sheets.
- Polypropylene (penofol). Combined insulation, consists of foamed polyethylene. One side of it is covered with foil. Thanks to this structure, polypropylene has high heat retention properties. It is somewhat inferior to its cork counterpart in terms of its qualities. This foil backing for underfloor heating is practical and durable.
Polypropylene insulation.
Note! The substrate should not contain aluminum, since it is an excellent conductor of electricity. Therefore, if the contacts are defective, a short circuit is possible.
Functions of insulating flooring
If you are wondering whether an underlay is needed for an infrared heated floor, then you should pay attention to the following functions of the flooring:
- The main task is to reduce heat loss. The substrate directs IR rays into the room, preventing them from spreading to the lower floors or basement of the building. Due to this reflection, heat is not wasted, and the efficiency of the system corresponds to 95-100%. The use of such insulation can reduce heat loss by an average of 20-30%.
- As mentioned above, the underlay acts as a waterproofing layer, protecting the flooring from steam and moisture.
- It is capable of leveling out minor surface imperfections, which is very important when using film-type floors.
- High-quality insulation, for example, Valtec underfloor heating, can significantly reduce the amount of noise. It is made of foamed polystyrene and has a foil side.
Film floor installation.
Note! Fiberboard slabs can be used as a bedding for coverings that require a solid base (support for a tile covering, for example).
How to choose a quality product
The main criterion for choosing this material is not the price, but the technical characteristics, which should be based on two criteria:
- Finish coating. For example, if you plan to lay laminate flooring, then you should choose a soft underlay, as it perfectly levels the base. For linoleum, it is recommended to choose solid thermal insulation, since this coating is a soft material, and therefore, together with soft insulation, it can easily be pressed through by furniture legs.
- Levelness of the floor. If you are dealing with a coating characterized by significant level differences, then you should choose soft thermal insulation, since it is more flexible. If the unevenness is small, then it is better to choose a more rigid flooring.
Reproduction of articles, as well as their individual parts, is prohibited. We want to reserve the right to exclusive placement of this material on our website home-engineering.net. Here we share the knowledge and experience gained by our team over the years of work in the field of design and installation of engineering systems.
→Home →To the list of articles
Introduction Chapter 1. Is a film needed between underfloor heating pipes and insulation? Chapter 2. Should the film over the layer of the main insulation of a heated floor be something special? Chapter 3. What kind of heat savings do sellers of multifoil, foil penofol, isolon, etc. promise? does the system have a heated floor and what does the consumer actually get? Chapter 4. How are things going with the capitalists? Chapter 5. Aren't they ashamed?
Introduction to top
When installing water heated floors, in the vast majority of cases we are faced with the so-called. “heavy” or concrete installation system for underfloor heating: when underfloor heating pipes laid on top of a heat-insulating layer are covered with a layer of screed based on a cement binder - concrete, traditional or semi-dry mortar. Very often, to install such a system, the customer chooses at his own discretion or is interested in the need to purchase and install such a system element as a special foil or multifoil, which sellers usually offer to mount on top of the main layer of thermal insulation directly under the heated floor pipes. To save your time on constant explanations, whether it is necessary or not, we wrote this article in which we will try to answer the following questions:
- Do you need a film between underfloor heating pipes and insulation?
- Should this film be special: have a reflective layer, special markings, magical bubbles of mountain air, spell inscriptions, etc. and so on.?
- Does special foil, foil, multifoil, penofol, etc. allow you to save heat? in a heated floor system with concrete screed and what is the economic efficiency of using special reflective films?
- How are things going on this issue abroad?
Chapter 1. Is film needed between underfloor heating pipes and insulation? up
Let's first consider the classic layout of materials in a concrete heated floor system. Here, each material has its place and purpose.
Classic pie of water heated floor with concrete floor screed. It is proposed to use ordinary polyethylene film between the insulation and underfloor heating pipes, primarily to prevent concrete from leaking into the cracks between the insulation slabs.
A clear understanding of what a person (customer) gets for his money from this or that material allows him to understand whether he really needs it or not. Otherwise, a direct path opens to superstitions, shamans, amulets and amulets. Does it need a shiny “reflective” surface, special markings, air bubbles, or is regular film from the store enough? Or maybe you can easily do without unnecessary details?
What, theoretically, can a substrate under heated floor pipes provide:
- Protection against leakage of cement laitance into the cracks between the slabs of the main floor insulation.
- Markings for easy pipe laying.
- Waterproofing.
- It's just beautiful ;).
- Improving thermal insulation, saving on building heating.
- Better heat distribution in the screed.
Here we have placed the factors in descending order of importance and will comment on each of them below: 1. Protection against leakage of cement laitance into the cracks between the slabs of the main floor insulation.
It was this factor that was fundamental in the development of underfloor heating several decades ago. And it is relevant only when filling heated floor pipes with liquid concrete/mortar (photo on the left). When installing a semi-dry machine floor screed (which is very common today), there is simply no cement laitance, and therefore film is not necessary (photo on the right). Yes, as some say, it “can’t hurt,” but the most ordinary recycled plastic film from a hardware store “for a ruble per bag” will do the job. As they say, low-tech in action.
2. Marking for easy pipe laying.
The marking cells (usually in increments of 5 cm and 10 cm) on special films for heated floors look impressive. They come in black, blue and even red! Marking can help a beginner in laying a pipe, but it is not necessary for a person who knows how to do this work and does it all the time, believe me. Marking can be useful when photographing pipes before pouring the screed, so that later you can more accurately determine the position of the pipe from the photograph, although for accuracy it is still better to use a tape measure with divisions in the frame.
3. Waterproofing.
A dubious purpose, because extruded polystyrene foam, used for floor insulation, due to its closed-cell structure, has low water absorption and is itself a kind of waterproofing. In addition, a more suitable place for laying waterproofing is between the subfloor and the insulation slabs.
4. It's just beautiful.
Yes, indeed, some people like the look of a shiny film under floor heating pipes. True art connoisseurs say that true beauty is when blue pipes are combined with red markings on golden foil or vice versa! It’s a pity that all this beauty is not visible after laying the floor screed….
5. Improving thermal insulation, saving on heating of the building.
Manufacturers claim an increase in efficiency, heat flow from the heated floor pipes upwards and a reduction in heat losses downwards when using reflective foil under the heated floor pipes without indicating the magnitude of such “improvement”.
Many (especially sellers) claim that the use of reflective films can significantly reduce the irretrievable loss of thermal energy downward due to the reflection of infrared (IR or thermal) radiation from the heated floor heating slab back into the room. They say that in this case the efficiency of heating increases significantly, thermal comfort improves, finances are significantly saved, chakras are opened, etc. and so on. To prevent the foil from being eaten by the alkaline environment of concrete, it is carefully covered with layers of film and even figures are given about the reflection of 97% of IR waves... They just forget to mention that there is no IR radiation in concrete, because it is optically opaque. More advanced sellers sell multifoil with a special air gap between the concrete and the foil, so that there is still something to reflect. But this also works very poorly, see below.
6. Better heat distribution in the screed.
It is claimed that the aluminum layer in multifoil and special films for underfloor heating allows for more even distribution of heat from underfloor heating pipes across the screed. After all, aluminum has excellent thermal conductivity! They “forget” to indicate the exact values of this “improvement”, they do not say that in most cases a metallized polymer film is used instead of aluminum foil, and they do not indicate the thickness of the aluminum layer (usually only about 10 microns). They also do not pay attention to an annoying nuisance: how can a layer of thin aluminum, separated from a heated floor pipe and concrete screed by a layer of air in a multifoil structure, effectively distribute heat?
In multifoil, if there is a layer of aluminum, it is very thin and separated from the screed and underfloor heating pipes by an air layer. Much more important in equalizing the temperature of a heated floor screed is the thermal conductivity and thickness of the floor screed itself and the type of finishing floor covering. This is described in detail in our article: Thermal conductivity of semi-dry machine screed when installing a water-heated floor.
Chapter 2. Should the film over the layer of the main insulation of a heated floor be something special? up
So, the film laid on top of floor insulation slabs does not have to have any special structure or design. If there is a need to prevent the leakage of liquid concrete or liquid mortar into the cracks between the floor insulation, then it will be sufficient to use a conventional construction film with a thickness of 100..200 microns. When installing a semi-dry floor screed, the need to use film is doubtful. Marking on the film for a heated floor can be useful, but it is also far from necessary, and when using the fastening of heated floor pipes on the MAK reinforcing mesh (Classic UPONOR system), it is clearly unnecessary.
And by the way, saying “folia” instead of “foil” is the same as saying “eliminate obfuscation” instead of “speak more simply.”
Chapter 3. What kind of heat savings do sellers of multifoil, foil penofol, isolon, etc. promise? does the system have a heated floor and what does the consumer actually get? up
In the vast majority of technical descriptions, advertising brochures or articles on the websites of sellers of films for underfloor heating, there is no explicit technical information about the thermal resistance R[m²⋅°С/W] of the multifoil, which quantitatively characterizes the benefit directly to the buyer of the product being sold. material. Not how cool, warm and wonderful it is, but how good it is for thermal insulation and heat distribution, how many banknotes it will save the customer. The width of the roll is there, the thickness of the material is there, even the name of the layers of materials is there, but the characteristics of the thermal insulation properties are not, or they are given in an implicit form and in passing. Yes, if this characteristic was truly outstanding, do you think that marketers would not put it in first place?
Let's look at a few examples of such materials with the original description of the manufacturer, with characteristics and cost, and evaluate the economic feasibility of their use for installing heated floors:
Multifoil VALTEC VT.HS.FP Multifoil thickness - 3mm, roll width - 1.2m, length - 25m. Price of VALTEC multifoil: 0.9$/m².
Quote:
“The combined roll material VALTEC is made from foamed polyethylene, which is an effective heat and sound insulating material, low flammable, moisture resistant, resistant to building mixtures, and environmentally friendly. A 3-mm polyethylene foam layer is covered with a metallized film, which helps reduce heat loss, uniform heat distribution, and plays the role of waterproofing. The main use of the product is underfloor heating. The cellular markings applied to the multifoil make it easier to lay out the heating pipe. The underlay is used for underfloor heating in insulated rooms (the small thickness of the material is an advantage that saves internal space) or as additional thermal insulation.”
It is not surprising that somewhere, but not on the product page, you can still find information about the thermal insulating properties of the material:
“The basis of VALTEC thermal insulation products is foamed polyethylene. This is a material with a so-called closed cellular structure. It is characterized by low thermal conductivity (0.035..0.045 W/m⋅°C) and vapor permeability (water vapor diffusion resistance coefficient μ - more than 3000), high sound absorption capacity and belongs to the G1 flammability group (low flammability).“
There is a bit of intentional manipulation or unintentional error here: it is not the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material λ [W/m⋅°C], but the thermal conductivity of a product made of this material 1 meter thick U [W/m²⋅°C] that is given.
It would be more correct to say that Valtec multifoil 3 mm thick has a thermal conductivity of about 13.5 W/m²⋅°С (the same as that of conventional polystyrene foam for floor insulation of the same thickness), which gives a heat transfer resistance of R=0.075 m²⋅°С/ Tue.
Only 0.075 m²⋅°С/W!
Despite the fact that the recommended values of the heat transfer resistance of the insulation layer under the heated floor should be in the range from 0.75 to 2.5 m²⋅°C/W (and this is the thickness of the polystyrene foam layer from 30 to 100 mm)! In this case, an additional 3mm of extruded polystyrene foam with the same insulation effect as multifoil costs the customer a maximum of 0.3 $/m², and Valtec multifoil will cost 0.9 $/m². “This is a C grade...” Anna Ivanovna told us after an unsuccessful essay in the Russian language.
Multifoil Polyairpack Multifoil thickness - 4mm, roll width - 1.2m, roll length - 25m. Price of polyairpack Multifoil: 2.0 $/m².
Quote:
“MULTIFOIL® is a modern high-tech multilayer material consisting of a three-layer air bubble film laminated on one side with polished aluminum foil coated (PET), which protects the reflective layer from exposure to aggressive environments (alkali). A marking grid is applied to the inner surface of the material for easy installation of heating elements. The marking step is 5x5cm. The fundamental difference between the MULTIFOIL® material and the thermal insulation materials currently available on the market for use in underfloor heating systems is the provision of an air gap between the heating elements in the floor screed and the reflective layer. As a result, this ensures higher efficiency in reflecting heat back towards the room and more uniform heating of the floor, which entails a reduction in the cost of operating this system. Multifoil is an environmentally friendly material, harmless to the health of people and animals. The MULTIFOIL® material is not inferior in quality to European analogues. Heat from the heating element (water pipe or electrical cable) is transferred to the concrete screed and then spreads upward due to the thermal conductivity of the concrete. At the same time, the downward spread of heat (heat loss) is hampered by two factors: - low thermal conductivity of the air, which is located in the bubbles of the MULTIFOIL® material (Multifol); - the ability of aluminum foil to reflect up to 97% of IR (infrared) rays emanating from the heated surface of the concrete screed. The foil, located at the bottom of the MULTIFOIL® material and with its polished (reflective) surface facing the air bubbles, creates the necessary thermal insulation gap between the concrete screed and the surface of the foil. Due to too small air bubbles in the MULTIFOIL® material, the convection phenomenon does not occur. Thanks to the use of aluminum foil, heat distribution on the surface of the heated floor occurs more evenly. Thus, the use of MULTIFOIL® material maximizes the amount of heat transferred upward and minimizes the amount of heat loss downward.“
Nice, but some questions remain:
- What is the thermal resistance of MULTIFOIL multifoil?
- How thick is the layer of polished aluminum in a multifoil structure to evaluate its thermal conductivity and heat equalization effectiveness?
- How can foil, separated from the screed by a layer of heat-insulating air (see foil design) effectively distribute heat?
We did not find an answer to the first two questions on the website and did not hesitate to ask the manufacturer. Here's what the manufacturer said upon request:
- Thermal resistance R1sl = 0.1 m²⋅°С/W, effective thermal conductivity λ0 = 0.042 W/m⋅°С.
- PET - 12 microns; P/E - 20 microns; PET - 12 microns; aluminum - 7 microns; P/E - 20 microns.
Everything fits: the thermal resistance is the same as that of 4 mm polystyrene foam, and aluminum is as much as 7 microns.
In this case, an additional 4 mm of extruded polystyrene foam with the same insulation effect as that of MULTIFOIL multifoil costs the customer a maximum of $0.4/m², and MULTIFOIL multifoil will cost $2.0/m². “This is an A!”, as our chemistry teacher at the university, Viktor Solomonovich, said.
When assessing how much thermal power a 7-micron thick aluminum film can remove from underfloor heating pipes, we got a value of about 1.5 W/m² with a typical underfloor heating power of about 50 W/m²! And this is with direct contact of aluminum with underfloor heating pipes, which multifoil does not have...
Heat distribution in a thin plate when heat is supplied along one of its sides.
Uponor MULTI multifoil article 1000017 Multifoil thickness - 4mm, roll width - 1m, roll length - 60m. Uponor MULTI multifoil price: $6.0/m².
Quote from Uponor catalogue:
“Multi-layer soundproofing polymer material with reflective foil for waterproofing and improved thermal insulation. It has a marking grid on the surface with a pitch of 50×50 mm. Permissible load 15 kN/m² (1500 kg/m²).“
Quote from the Uponor underfloor heating installation manual:
“A feature of underfloor heating systems is the undulation of temperature on the floor surface. The heat-reflective properties of multifoil make the floor temperature more uniform, reduce warm-up time, allowing the floor surface to respond more quickly to changing conditions. Multifoil can also be used in combination with additional thermal insulation supplied locally to the customer. It is waterproof, which prevents the penetration of cement laitance and moisture into the underlying thermal insulation material. The coordinate grid applied on it with a pitch of 50x50 mm facilitates the layout of pipes when laying underfloor heating loops. Advantages of using multifoil:
- Ready to install, supplied in rolls.
- Installs quickly and easily.
- Can be laid on standard thermal insulation.
- Can be installed with Uponor MLC pipes and Uponor PE-Xa pipes.
- The applied coordinate grid will help when laying out the loops.
- Suitable for any type of pipe laying: coil, double coil, spiral.
- Can be installed by one person.
- Increases the amount of heat radiated upward.”
“Ready to install, supplied in rolls...” - this is a scientific breakthrough! The last point: “increases the amount of heat radiated upward.” They forgot to write in the penultimate paragraph that multifoil can be used to make Halloween costumes (see below, what does Halloween have to do with it).
Why does the buyer need information about the thermal insulation characteristics of the material? It's such a small thing... But if we search, we find that the thermal conductivity coefficient of Uponor Multi multifoil λ=0.045 W/(m⋅°C) is the same as that of any other effective insulation.
In this case, an additional 4 mm of extruded polystyrene foam with the same insulation effect as Uponor Multi multifoil costs the customer a maximum of 0.4 $/m², and Uponor multifoil will cost 6.5 $/m²! “Total for the morning - 6 pounds. Not bad.” - Andrei Mironov’s hero said in one film. Those. for the same money it would be possible to increase the thickness of the floor insulation made of extruded polystyrene foam by 65 mm!
Illustration of the manufacturer's intended heat equalization process from the use of Uponor Multifoil. There are no numerical values or even mention of this effect in the list of product benefits.
Chapter 4. How are things going with the capitalists? up
Developed countries, despite the work of our media, are far ahead of us in the use of reflective coatings in building structures. In many countries, manufacturers of controversial materials have been forced by regulatory pressure to retract unsubstantiated claims about their materials, and in some cases have paid hefty fines for false advertising.
Those interested in queries in a search engine like “foil insulation controversy” can get acquainted with foreign experience.
Here the author proposes to use such a wonderful and high-tech nanomaterial as multifoil, only for Halloween costumes. We miraculously discover the incredible properties of such films, and naturally, more serious applications are found for them. Checkmate, Elon Musk!
It is necessary to take into account the difference in the value of heat transfer resistance R (for them) and RSI (for us). Heat transfer resistance in imperial units R [ft²⋅°F⋅h/BTU] is about 5.6 times greater than our RSI [m²⋅°C/W].
Interesting full-scale experiments comparing the thermal insulation properties of multifoil, traditional thermal insulation and... SB newspapers: Belarus Today The Washington Post. Spoiler: multifoil (even with 14 internal layers of aluminum) is not as cost effective as conventional thermal insulation and is quite comparable to thermal insulation with several layers of newspaper.
Results of an experiment comparing the thermal insulation properties of various materials.
Chapter 5. Can a reasonable person, taking into account the experience of past centuries, have even the slightest hope for a bright future for humanity? Aren't they ashamed? up
It won't take long to read chapter five. It consists of just one word and a period: “No.”
If you need to design and install engineering systems for your home in Minsk and the Minsk region; you want to get advice and install a heating system, water supply, sewerage, ventilation, built-in vacuum cleaner, and perform electrical work; make the necessary calculations and select equipment; or you encounter difficulties in implementing your ideas - we will be happy to help you.
Underlay for infrared heated floors
For the high-quality functioning of infrared underfloor heating, two recommendations must be followed:
- strict adherence to installation technology;
- installation of heat-reflecting material with foil facing up.
When laying a reflective layer under a heated floor, it is recommended to follow the following advice from professional craftsmen:
- Magnesite boards and particle boards. Before installing such material, an aluminum film is laid on the base, and a substrate is laid on top. For these purposes, foil layers can be used.
- Metallized polymer-based materials are mounted with the smooth side up. As a result of this installation, a thin and effective heat-reflecting coating is formed.
- The layer is laid over the entire floor surface on which the heating system will be installed. The material is laid overlapping, firmly gluing the joints with special tape. Such measures will create sufficient indicators of hydro- and thermal insulation. The adhesive tape for the backing must be metallized. Ordinary materials may not withstand heat and melt.
By following these simple rules, you can easily install and select a high-quality substrate yourself. Be sure to consider the composition of the material and its compatibility with your heating system.
There are reflectors that can greatly facilitate the process of installing electrical cables. These are the so-called layers with bosses. The design of such material is a carpet dotted with dense rows of protruding cylinders. These projections are called bosses. It is very convenient to lay the underfloor heating cable between them. This installation does not require additional fasteners or adhesives - the bosses firmly hold the cable on the surface of the interlayer, preventing them from moving to the side.
Installation Rules
Installation of the underlay under a warm water floor is carried out on a flat surface
In this case, the material from which the substrate is made is important. All work on the installation of the substrate can be represented in the form of a certain algorithm of actions:
- The surface of the subfloor is prepared. It eliminates differences and all irregularities. It is recommended to use a self-leveling mortar mixture for this;
- the floor level is checked, a diagram for laying water pipes is drawn up;
- the substrate is laid. At the same time, its reflective layer remains on the surface. The substrate is laid out in an even layer over the entire surface on which it is planned to install the thermal water floor system. Docking areas must be additionally insulated with mounting materials - tape or adhesive tape;
- if the lining is assembled from several elements, then they are laid tightly, the joining seams are taped with tape with a metallized base. This will improve the steam and waterproofing properties of the floor.
The substrate under the water heated floor is laid in an even layer over the entire surface
. Having completed all of the above measures, you are allowed to begin installing the heating system itself. Experienced specialists recommend laying pipes exclusively on reflective coatings.
If we consider the general requirements, then the substrate for a warm water floor must fully comply with the thermal capabilities of the system and represent an additional factor in their improvement.
After studying all the characteristics of water floor underlays, you can make the right choice to keep your home warm.
Which is the best underlay for laminate? Corporate approach
Tuplex branded underlay may be the ideal solution to the issue of choosing underlay for laminate flooring. It has a thickness of 3 mm, is made in the form of two layers of film, the internal space between which is filled with granulated polystyrene. It removes moisture well, protects against the formation of fungus, and is convenient to use, but its price encourages you to choose similar materials from other manufacturers.
Also easy to use, the backing for polystyrene laminate is produced in the form of small sheets measuring 60x120 cm and is in no way inferior in quality to its cork counterparts. Moreover, polystyrene better smoothes out unevenness of the screed, can even be laid on top of wooden floors, has a high noise absorption coefficient, promotes thermal insulation, but... is short-lived compared to cork. Over time, it loses its elasticity and after 6-10 years it becomes useless in terms of supporting the laminate. In addition, polystyrene is very dangerous when burned; it emits abundantly caustic and poisonous smoke.
Polystyrene laminate backing photo
There are cases when laminate is laid on top, where, in principle, there cannot be any moisture, however, a lining is needed. The underfloor heating for laminate flooring must conduct heat, so cork and polystyrene will be ineffective. There is a special underlay for arbiton heated floors; its perforated (small hole) sheet allows heat to pass through freely, while also performing its main function - supporting the laminate.
It is also possible to use a polyethylene backing without foil; in extreme cases, you can simply lay corrugated cardboard; on a warm floor, where there is no moisture at all, this method also works. Since laminate itself conducts heat very poorly, it is necessary to use samples specially made for heated floors.
As you can see, the choice of underlays for popular flooring is wide, so it is difficult to say which underlay is best for laminate; it is better to listen to what laminate manufacturers say and choose the type of underlay that they recommend.
Rules for laying foil backing
Foil underfloor heating can be in rolls, mats or slabs. When laying, this coating must be joined both in length and width. In order for the connections to have the same properties, the fragments are glued together with special metallized (foil) tape. You must glue carefully, avoiding gaps, try to make the fit as precise as possible, without gaps.
When laying thin rolled foil material in a screed, the strips may overlap one another. The size of this “overlap” is at least 10 cm. This joint is glued twice on one side and on the other. We make cross connections according to the same rules.
It is recommended to use foil tape for connection.
When laying mats or slabs, they are joined close to one another, then glued with the same shiny tape. Some manufacturers make a lock along the edges of the slabs, which reduces the possibility of heat leakage through the joints. Despite this, we also glue the locking joints with tape. This makes it much more reliable.
Adviсe
One of the most modern trends in solving the issue of thermal insulation at home has been the installation of a “warm floor” system. Nowadays, manufacturers have brought to the market three main options for underfloor heating - water, infrared and cable. The water method is used for large areas. This technique involves circulating hot water through pipes built into the floor. Such a system has a number of limitations:
- it cannot be used in multi-storey buildings, as it creates additional pressure on the floors;
- in the event of a breakthrough, there is still a risk of “flooding” the neighbors below, which will lead to large expenses for troubleshooting;
- high cost of materials, as well as installation work.
The infrared floor is a polymer film, which is divided into identical squares, each of which contains special plates responsible for high-quality heating.
It is better to install such a system under laminate or linoleum. If you use it under tiles, it bonds quite quickly with the adhesive solution.
Cable is an electric floor that can function year-round. In order to reduce energy costs, special thermostats are built into the design. The structure itself is assembled from two- or three-core cables or electrical mats.
This method is optimal for tiles, as it helps them heat up quickly and retain heat.
The “floating floor” technology is very popular; Isover coating is used for it.
Laying technology: a set of basic rules
Installing the substrate is not difficult; you can do the work yourself. The main thing is to follow simple and clear rules.
The order of installation depends on the form of the lining: roll insulation, individual modules or puzzle slabs, fixed together with a locking connection
General requirements for installation of the substrate:
- Accurate calculation. It is necessary to determine in advance the amount of material taking into account the standard sizes of the lining. It is optimal if the insulation is placed with a minimum number of joints.
- Preparing the subfloor. The base must be level. You shouldn’t rely too much on the ability of dense material to mask unevenness - any product will take the shape of the base over time.
- Waterproofing. Substrates made from natural components (cork, chipboard, OSB) require preliminary installation of a water barrier. It is enough to lay thick polyethylene.
- Laying. Rolled, sheet material is rolled out without stretching; overlap onto the walls is required. The slabs are placed close to vertical surfaces, protected by 10 cm of damper tape.
- Docking. Rolled insulation sheets are overlapped and secured together with construction tape. Plates and mats are grouped end to end.
When installing a heated floor under a laminate, it is necessary to take into account the direction of the panels - they are placed mutually perpendicular to the roll backing.
What kind of substrate to lay under a warm electric floor
So, you can install a “floating floor” system.
The floor must be reliably hydro- and vapor-insulated; for this, the joints of the panels must be glued with aluminum tape.
After installing the heating elements, you can begin laying the reinforcing mesh, only then can you begin arranging the screed. After the filling has been completed, the edges of the insulation should be carefully trimmed. Afterwards, the floor will have to warm up for quite some time, then it can be put into operation.
Insulation of surfaces with penofol provides hydro-, heat- and noise insulation, reducing the level of impact noise by 20 dB, which guarantees uniform heating due to the reflective properties of penofol.
Before insulating a floor using penofol, you should familiarize yourself with the installation features of one or another type of insulation of this class, since incorrect installation technology can cause ineffective thermal insulation.
Advantages and disadvantages
As mentioned above, a substrate with a foil surface is an excellent material for saving energy. In addition, foil has a number of other advantages, but there are also disadvantages.
| pros | Minuses |
| Does not affect the height of the floor, since the foil material is only 2-10 mm thick. | High cost is the main disadvantage. |
| It is not difficult to install, so even an inexperienced person can handle the job. | It is not recommended to use a mineral substrate with a metallized layer for heated floors, since toxic substances are released during the heating process. |
| It has soundproofing and waterproofing properties. | Using such a substrate in rooms with high humidity significantly reduces its service life. A foil-coated product is recommended. |
| Withstands heating up to +90 degrees and more. | Dissolves upon direct contact with cement. |
| Most products with foil are equipped with markings, which simplifies the process of laying heating elements. | |
| There are models with a sticky layer, this makes installation easier. | |
| Reduces heat loss and promotes its uniform distribution. |
It should be noted that the foil product is strong and durable if installed and used correctly.
Choosing the type of installation of water systems for flooring laminated boards
It is most rational to install such a warm floor in a private cottage. Water heated floor under laminate –
This is a structure made of pipes laid under a covering of laminated panels. Hot water moving through the system heats the concrete screed and the finishing surface of the floor.
Warm water constantly circulates through the metal-plastic pipes of this system, heating the finishing floor covering
It would not be out of place to add that modern floor heating systems are made from innovative materials. Metal-plastic and polyethylene structures are reliably protected from leaks and serve no worse than traditional copper pipes, and their cost is much lower.
Installation of a water heating system under a laminated coating has certain nuances, since the lamellas do not conduct heat well enough. You should also know that not all methods of laying this thermal system are suitable for such a floor surface. Thus, when installing water heating pipes in a flat manner, the floor heating effect will tend to zero. Therefore, the best option would be to lay the heating system in a layer of cement screed.
Professionals say that it is best to install warm water floors under laminate using the concrete method.
Thus, the layer of solution will protect the pipes from mechanical damage. In addition, the screed will warm up completely, which will allow heat to be transferred evenly.
To install the heating structure correctly, you need to take into account some details. Work begins by dividing the floor surface into segments and determining the location of the heating elements. Next, the plane is leveled, a layer of thermal insulation is laid, and reinforcement for the concrete screed is secured. Afterwards the mounting rail is attached and the underfloor heating pipes are laid. They are fixed with wire to the cells of the already laid metal base. The reinforcement mesh acts as a marking for the installation of a floor heating system.
Pipes can be laid in any of two known ways - parallel or in a spiral, depending on the previously drawn up project.
To lay laminate flooring over a heated floor, experts advise filling the heating system with cement mortar
The next step is to fill the installed system with concrete to form a screed. After final polymerization of the solution, a test run of the system should be carried out. It is necessary to check the pressure in the pipes and adjust the temperature. If the design works effectively, it can be considered ready for use.
Laying pipes and heating system
Heated floor pipelines are:
- copper;
- metal-plastic.
The first option is more difficult to implement, but also more reliable and efficient. But metal-plastic is often chosen due to its low cost.
On insulation with a reflective film, the pipes are fixed with fastening wire, staples or special tape. These fastenings should be located at a distance of 0.5–1 meter from each other.
Most often, pipes are attached to a reinforcing mesh. But if, instead of reinforcement, fiber is chosen for the screed, or if a flooring made of wood boards is provided instead of the latter, then staples will have to be used to fix them in the insulation. However, screwing or driving in fasteners up to and through the waterproofing when installing a water underfloor heating system is unacceptable.
Options for laying water floor pipes
The waterproofing underlay must remain undamaged and continuous during all manipulations. If it is damaged and a heated floor is made on a leaky layer of water insulation, then if there are leaks in the system, the rooms on the floor below will have to be repaired immediately. Plus, you shouldn’t forget about constructing a screed made from liquid concrete mortar. Without waterproofing from below, it itself or moisture from it may well seep through the ceiling.
After laying the pipes and connecting them to the collector, it is necessary to carry out hydraulic tests by supplying water to the system for a day at a pressure of 5–6 bar. The pipeline must not be closed until the leak check has been completed.
Step-by-step instruction
Stability of characteristics
Groups of porous materials, such as polyethylene foam and expanded polystyrene, have an unpleasant feature. Over time, under the influence of static stress (burden from lying pipes and the load when walking on the floor) they are compressed. The thickness of the substrate decreases, the process may proceed unevenly, differing in different areas of the room. This can cause unpleasant consequences.
You need to select a substrate material based on the service life and physical characteristics declared by the manufacturer. Temporary changes in geometry are taken into account, as well as production technology. For example, expanded polystyrene foam has an open structure and sticks together over time. At the same time, extruded has completely closed cells, is elastic, retains its geometry and properties for decades.