Are you looking for how to make a heated floor correctly? Do you want to get into the process rather than rely on installers? Are you choosing insulation for underfloor heating? An overview of underfloor heating insulation is offered; it will tell you which energy-efficient insulation to choose and why it is beneficial. Let's analyze doubts about choice and give two types of cost-saving calculations to make the right decision.
Types of heated floors
Warm floor is used:
- for heating a cottage or house without radiators, it is also possible to combine it with radiators;
- for heating floor coverings made of ceramic tiles or other materials and providing a comfortable feeling for human feet.
Warm floors, based on this, happen:
- water;
- electric.
Now we will talk about water underfloor heating systems and their component - insulation for water heated floors. Let us also consider with calculations the effect of insulation on heat loss.
Why insulate?
A floor heating system will release a large amount of heat into the concrete the floor is made from. In this regard, additional fuel costs are inevitable, and there will be no savings . Thermal insulation is placed under the electric heated floor in order to avoid unnecessary fuel consumption.
Along with decreasing natural heat losses, sound insulation also increases. The floor covering also prevents moisture from entering from the basement or ground.
Why do you need insulation for underfloor heating?
The insulation is used during installation and ensures maximum heat transfer of the heated floor. Thermal insulation must meet the following characteristics:
- Create maximum heat flow upward.
- Ensure that there is no heat loss down to the floor slabs.
- Do not collapse over time.
Let's imagine the structural composition of a heated floor pie. It consists of:
- Concrete base of floor slabs.
- Waterproofing.
- Side damper tape.
- Insulation for underfloor heating.
- Distribution of pipes with coolant.
- Screeds with plasticizer.
- Floor finishing coating.
The minimum thickness of the screed is about 50 mm.
Which substrate is better to choose and why?
There are a large number of products on the modern market that are used as reflective underfloor heating.
When choosing a substrate for a film floor, you should not be guided only by savings; you need to build on the technical features, characteristics of the room and the material. Let's look at the most effective and safe types.
Substrate thermal insulation and heat-resistant tape STEM Energy
Extruded polystyrene foam
The structure of extruded polystyrene foam is evenly spaced closed cells. The material has a low density and a high degree of moisture resistance.
It does not bend, so it is often used as a backing for laminate flooring. In addition, it has great strength and good thermal insulation properties.
The product is produced in rolls and sheets. The IR film spreads directly onto this substrate.
Lavsan
The substrate is made of foamed polyethylene with a lavsan metallized layer - the product is resistant to aggressive chemicals and microorganisms.
Lavsan flooring is laid under the film, thereby minimizing energy loss, increasing the efficiency of the floor, and ultimately leading to cost savings.
This type of reflective substrate is most suitable for infrared floors. It has a certain power density. Therefore, when choosing a lavsan bedding, the floor covering that is planned to be laid on a heated floor is taken into account.
Cork
Cork is a natural material made from crushed and compressed tree bark. The product is environmentally friendly and safe for health. It's not cheap, but it will last a long time. Available in rolls or sheets.
In addition, cork is resistant to deformation (it can take its original shape), has good heat and sound insulation, and is easy to install. The main disadvantage of cork bedding is its sensitivity to moisture. But this drawback is important to take into account when arranging water floors, and for infrared systems, cork is quite a suitable material.
Self-adhesive backing
The self-adhesive backing is equipped with a heat-reflecting foil layer on one side, and an adhesive layer on the other, with which the product is attached to the concrete base. The material is ideal for use on uneven and non-standard surfaces.
The advantages of these linings are high sound and waterproofing, and ease of installation, due to the ability of the product to be self-adhesive (no additional fixation is required).
Izolon, Penofol
These types of insulation consist of polyethylene foam. Their advantages are that they simultaneously act as both a reflector and a heat insulator.
These substrates are durable, have excellent noise insulation properties, are durable and practical. Recommended for laying film flooring in a “pie” with a laminate or parquet board finish.
Fiberboard
Fiberboard - boards made of cellulose fibers and various additives. It has increased rigidity and reliability, so it is ideal for laying under a film with a topcoat made of ceramic tiles or laminate.
Magnesite slabs
Magnesite boards are moisture resistant, have good sound insulation, are durable, and have a high density. The product is environmentally friendly, as it is made from natural raw materials.
This type is recommended for installation in the “pie” of an infrared floor, as it has sufficient density, despite good flexibility. Therefore, it perfectly levels any surface.
For your information! It is not recommended to lay a lining with an aluminum foil layer under the infrared floor, because this coating is a conductor of electricity. It is better to use a reflective metallized layer.
Types of underfloor heating insulation
Main types of insulation:
- Expanded polystyrene 2 cm plate with bosses without coating.
- 2 cm polystyrene foam board with coated bosses.
- Expanded polystyrene 2-10 cm smooth plate with a quarter.
A foil underlay for underfloor heating with markings 3-5mm thick is used during installation, but it is not insulation.
It is worth using a slab with coated bosses rather than uncoated ones. Cheaper coated slabs require additional anchor plates to secure the pipes between the bosses.
Smooth polystyrene foam is interesting for its price and is used not only for heated floors, but also for insulating foundations, basements, and building facades. It is precisely on such smooth slabs and a quarter that you can lay a foil backing with markings and mount the pipe using fasteners.
Is an underlay for an infrared floor necessary or not?
Infrared heated floors are a film with a carbon plate inside. When heated, infrared radiation is released, which spreads in different directions. To direct the flow of warm air in the right direction, and not heat the ceiling of the neighbors below, a layer of heat-reflecting material is required under the film.
Main functions of underfloor heating:
- level the surface - extruded polystyrene foam is ideal for this; it is equipped with side locks, which allows you to make the plane level;
- prevent heat loss - infrared rays are directed straight upward, which leads to energy savings;
- make the process of laying the floor covering easier - it is recommended to select the base for the film based on the floor product.
Doubts about choosing insulation
To remove all doubts about choosing insulation for a heated floor, let’s consider the financial side of the issue. To do this, we will calculate the warm floor of a room of 50 sq.m. All installers recommend a 2 cm slab with a coating and bosses costing 600 rubles per square. The total cost of such insulation is about 30,000 rubles. If you add another 4 cm of smooth slabs and a quarter, it will cost 150 rubles per square meter and in total it will be 7,500 rubles. This amount of “savings” is what we are talking about. This is only plus 25% to the cost, but let’s calculate what the final result will be. Let's make calculations in the program for heated floors in two rooms:
- Room 1 is the correct option for choosing thermal insulation.
- Room 2 - standard insulation option.
Room 2
Let's start with him. We set the standard type of ceiling under unheated basements, pipe pitch 20 cm, room temperature +20 °C, layers above the pipes and layers under the pipes with 2 cm of insulation. Coolant temperature +40 °C. After calculation, the program produces standard standard data, except for the downward heat flow, which is 58 W/sq.m., which is comparable to the upward flow. We can conclude that with this option, the lower floor slab is heated.
Room 1
We set all the same data, only in the layers under the pipes we provide additional thermal insulation of the floor with 35-density polystyrene foam, 40 mm thick. After calculation, the program produces a result with an increased heat flux upward and reduced by three times to 18 W/sq.m. flow down. And this will give real savings in money.
In a design room of 50 square meters we lose 2 kW! If we translate this into money for gas heating at average Russian prices for blue fuel, we get 2,268 rubles. in year. The simple payback period for additional costs for more efficient insulation is 3.3 years.
URSA brand products
The company produces a wide range of different types of insulation materials designed specifically for thermal insulation of electric and water heated floors. Extruded polystyrene foam in rigid boards URSA XPS N-III-L is one of them. The slabs can be installed both on a concrete base and on the backfill or directly on the ground. Although the properties of the slabs allow the use of the last two options, the manufacturer still recommends starting with arranging a screed to level the base. In this case, the risk of slab deformation or destruction is eliminated.
To seal the joints, special protrusions are provided along the side edges, resembling steps. During installation, they engage and the plane becomes monolithic. The slabs are excellent for insulating large areas in one layer. Cold air and dampness do not penetrate through the joints.
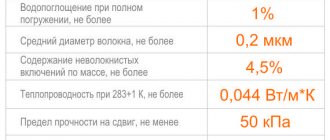
Technical characteristics of the plates:
- compressive strength - 0.25 MPa = 25 t/m²;
- thermal conductivity - 0.032 W/mK;
- flammability group - G3;
- temperature range of use - -50...+75 oC.
Slabs are produced in a standard size of 1180x600x50 mm. One package, which includes 8 slabs, covers an area of 5.6 m2.
URSA GEO P-60 is also used for thermal insulation of heating systems. This is a semi-rigid fiberglass material based on fiberglass. With small thickness and weight, it provides not only reliable thermal insulation, but also noise protection. With a thickness of no more than 25 mm, noise absorption exceeds 35 dB.
In the production of insulation, the patented Water Guard technology is used, which reduces the level of moisture absorption to almost zero. In case of accidental contact with liquid water, or storage and transportation of the material in humid conditions, it absorbs very little moisture and steam. After being placed in normal conditions, URSA GEO quickly dries and returns to its condition.
- dimensions - 1250Х600Х20-25 mm;
- thermal conductivity - 0.032 W/mK;
- flammability group - NG;
- water absorption - no more than 1 kg/m3.
The insulation is part of the brand’s group of absolutely environmentally friendly materials produced in the GEO series.
URSA mats are available in roll form and are designed for installation on a solid base. They contain only natural ingredients that do not cause allergies and do not emit fumes when heated. During installation, certain safety regulations regarding working with fiberglass materials must be observed. Workers must wear gloves and respirators to protect themselves from tiny glass particles.
Also, TERRA URSA series slabs are used for floor insulation and sound insulation. The material is quite hard, non-flammable, and moisture resistant. URSA TERRA Floating floor is suitable for heating systems, the technical properties of which allow it to be used under a screed. The material is chemically resistant and does not react with cement, gypsum, tile adhesive and other building substances. The slabs are quite rigid and are produced in the standard format for URSA materials - 1250X600 in thicknesses of 25 and 50 mm. This allows them to be used both in small rooms and in spacious rooms.
Another convenient modern material is Ursa PureOne 34 PN. These are mineral slabs with an excellent thermal conductivity coefficient (0.034 W/(m*K)), optimal for underfloor heating systems. The material is distinguished by a wide temperature range of application - -60 ... +220 ° C. Such properties allow the use of slabs for thermal insulation under:
- water pipes;
- heating cables and mats;
- emitting films.
All URSA brand materials are universal. They belong to the best heat and sound insulators, are very easy to install and are practically not subject to external influences of a mechanical and chemical nature. When laying fiberglass materials, it is recommended to fill the screed, and only then lay the heating elements.
The choice of floor insulation should be made taking into account the expected loads on the coating, requirements for the heating temperature of the elements, and environmental safety. Also, the price of the material and installation costs play an important role among the selection criteria. In terms of price/quality/durability ratio, Ursa brand products are best suited for private and industrial construction.
All materials are developed for domestic construction technologies. At the same time, they interact well with imported building mixtures and underfloor heating components, without causing the risk of incompatibility. But among the company’s entire assortment, it’s easy to get confused and buy the wrong product. To guarantee success, it is best to consult with professional builders or official dealers of the brand.
Bibliography:
- E. Pisarev “Warm floor, water or electric” Robur, 2012, 47 pp., ill., (13.1 mb pdf);
- L. V. Leshchinskaya, A. L. Malyshev “Heating - water, electric, stove” Literary Boulevard, 2010, 336 pp., (44.1 mb. pdf);
- Nizovtsev M.I., Sakharov I.A. DETERMINATION OF THERMAL AND DESIGN PARAMETERS OF WATER HEATED FLOOR. Institute of Thermophysics SB RAS, Novosibirsk;
- . Bearzi V. Warm floors. Theory and practice // ABOK.- 2005. No. 7.- P. 70-82;
- SNiP II-3-79. "Construction heating engineering".
- GOST 13732-2-2008. “Ergonomics of the thermal environment. Methods for assessing human reaction upon contact with surfaces. Part 2. Contact with a moderate temperature surface."
Why you shouldn't save on floor insulation
In the calculations, we used the minimum cost of natural gas for the consumer. If we consider more expensive energy sources, diesel fuel or electricity, the simple payback period decreases significantly and can be one heating season.
What other advantages do energy-efficient insulation have:
- They allow for excellent thermal insulation of the floor of a house or cottage, which leads to the overall energy efficiency of the house and brings its characteristics closer to passive houses.
- Raises the energy efficiency class of the house, which increases the value of the property.
- Makes it possible to install dispatch and control systems, including underfloor heating.
Main conclusions:
- When using thin insulation, heat is lost in the lower direction. Heat losses are comparable to the heat flow upward into the room.
- Insulation of the required design thickness pays for itself in an average of 3 years of operation of a heated floor when using natural gas as an energy source.
Thermal insulation requirements
Why is thermal insulation (also called insulation) needed when installing heated electric floors? During the operation of such a floor, heat losses occur, which are associated with heating of the cable/mat/film and the floor. Laying a special material called thermal insulation will help to avoid heat loss. It will be the basis on which the components of the heated floor are mounted.
In the retail chain, materials with thermal insulation properties are presented in a large assortment; buying them is not difficult. They are made from different components in the form of rolls, panels, films and membranes. Not all materials are suitable for creating electric heated floors. The requirements for thermal insulation material for electric heated floors are as follows:
- must have a low thermal conductivity coefficient;
- have resistance to elevated temperatures;
- easy to install and not deform during operation;
- should level out minor unevenness in the base;
- must withstand heavy loads;
- have soundproofing properties;
- withstand aggressive environments;
- have a high degree of strength;
- do not absorb moisture;
- be electrically safe;
- be made from environmentally friendly materials (should not release toxic substances into the environment);
- have a long service life.
Types of thermal insulation
What is the thickness of penoplex for insulating a loggia? insulation technology
This material is foamed polystyrene in slabs, which is created by extrusion. It is ideal if you need to carry out high-quality and proper insulation of the loggia with penoplex foam, which involves doing all the steps yourself. In this case, its excellent insulating characteristics and comparative simplicity of installation operations will be useful.
What you will need to purchase for do-it-yourself thermal insulation of a loggia
Here is a list of consumables that will be needed for the work:
- Polystyrene in Penoplex boards. The main insulation layer will be created from it.
- Drywall forms an outer, smooth surface. It is also permissible to use gypsum fiber or glass magnesite analogues. Any sheet options should be selected to ensure good moisture resistance.
- Ready-made dry construction mixture for leveling the floor.
- Vapor barrier film with a foil layer.
- Construction foam. It is recommended to purchase only a product that does not contain toluene.
- Guides (slats) and fastening (screws) elements.
Do-it-yourself technology for insulating a loggia with penoplex
In each specific case, the set of techniques will be different. You will have to take into account certain decorative options and structural features. But the following algorithm can be used as an example, with necessary modifications:
- All outer layers of the floor and walls are removed.
- Window blocks are being installed. All joints are sealed with construction foam.
- Using dowels and plastic disc-shaped attachments, penoplex is attached to the walls and ceiling. Large joints are filled with construction foam. The gaps between the plates are sealed with high-quality tape.
- A vapor barrier film is attached to them with the foil side facing the inside of the room. For this operation, it is necessary to use a polyurethane-based adhesive that is not capable of damaging the penoplex. The joints between these elements are closed with metallized tape.
- A screed for a loggia can be created from a dry mixture with a thickness of 4-5 cm. It is necessary to leave a technological gap of 0.8-1 cm between it and the walls. This is necessary to prevent cracks from appearing when temperature fluctuates.
- Wooden beams are installed on the vapor barrier film and attached to the main part of the wall. They are “sewn up” with drywall.
As it is not difficult to see, all of the above operations can be done by anyone with their own hands. To eliminate possible mistakes due to lack of previous experience, the following recommendations should be used:
- Various heating and lighting devices and communications equipment can be installed on the loggia. The corresponding utility networks are installed before finishing work is carried out.
- There is no need to create a vapor barrier layer between the penoplex and the main wall. This solution will stimulate the accumulation of condensation in the corresponding hidden area.
- If wooden slats or other sheathing elements are hidden in the thickness of the insulating layer, this will impair its effectiveness.
- For such frames there is no need to use metal guides. Such options will create favorable conditions for the penetration of cold into the premises.
How to calculate the thickness of penoplex slabs
You can do a variety of jobs with your own hands. You can also independently calculate the thickness of the foam insulation layer. To make the calculations more specific, we will make the following assumptions:
- Building location: Moscow. According to current standards for this city, the thermal resistance coefficient of walls in a residential building must be at least 3.14 square meters. on gr. Celsius/W
- Main wall: two bricks. Its heat transfer resistance will be 0.99 sq. m. on gr. Celsius/W
Thus, for these climatic conditions it is necessary to improve the existing insulation indicators by the following amount: 3.14-0.99 = 2.15 sq. m. on gr. Celsius/W With a thermal conductivity coefficient of penoplex of 0.028, the following final thickness of the slab will be required: (2.15*0.028)*100=6.02 cm.
If it is inconvenient to make calculations with your own hands, or there is not enough initial data, then you can use special programs, “calculators”. They are posted on specialized websites of penoplex sellers.
Purpose
The underlay is placed between the concrete surface in the room and the heating system. The main purpose of the material is to prevent the loss of heat that comes from the heating elements of the heated floor. Otherwise, the heat will be wasted without showing any effect. This way, only the ceiling on the floor below will warm up. If the substrate is chosen correctly, then heating of the subfloor will not only be uniform, but also twice as fast.
Another purpose of this material in a heated floor system is as a barrier. It does not let in cold, moisture, or steam from the lower floors. This is especially true for the first floors above basements. Since the substrate has excellent soundproofing qualities, in apartment buildings you will not have to listen to screams and noise from neighbors. Other materials can be used for the substrate:
- Cork.
- Fiberboard.
- Foamed polymer.
- Penofol.
- Foil material.
- Extruded polystyrene foam.
But even this cannot be called an exceptional option. Technologies do not stand still and materials are constantly being improved, which can be chosen as a substrate for electric heated floors. The choice of a specific material will depend on the levelness of the base, where the installation is carried out, as well as on the type of floor covering in the finishing.
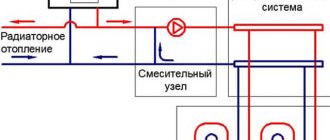
Arrangement of edge zones
In cases where underfloor heating cannot completely compensate for the heat loss of the room, you can try to compensate for the lack of thermal energy by installing edge zones. Edge zones are areas of heated floors with an increased temperature of the floor surface, which are usually installed along external walls to a width of no more than 1 m.
- The specific heat flux in the edge zones can be increased in several ways:
- reduce the pipe pitch ( Table 4
;
Fig. 5 A
); - use a separate loop with an increased coolant temperature ( Fig. 5 B
); - use a separate loop with an increased pipe diameter ( Table 5
); - use a separate loop with an increased coolant temperature, reduced pitch and increased pipe diameter.
Table 4. Effect of pipe pitch on the change in specific heat flux (relative to a pitch of 15 cm)
| Pipe pitch, cm | 7,5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Change in specific heat flow, all other things being equal, % | +13 | +8 | 0 | –8 | –15 | –22 |
Table 5. Influence of pipe diameter on the change in specific heat flow (relative to the outer diameter of 16 mm)
| Pipe outer diameter, mm | 12 | 16 | 20 | 25 |
| Change in specific heat flow, all other things being equal, % | 9 | 0 | +10 | +25 |
The use of separate loops with increased coolant temperature makes sense when there are several rooms with edge zones. In this case, the pipelines of the edge zones can be served by a separate pumping and mixing unit.
In any case, the temperature of the floor surface in the edge zones should not exceed 31 ° C, as well as the temperature for which the finishing floor covering is designed.
Rice. 5. Options for installing edge zones of heated floors
Mixture for pouring screed
Filling a floor or screeding is a procedure that requires great care and precision. You can avoid cracking of the floor during drying and during the operation of the system by carefully observing the temperature regime and strictly following the instructions for preparing solutions.
For pouring, use ready-made self-leveling mixtures for heated floors or self-mixed ones on a concrete base.
In the first case, the mixtures are made on the basis of gypsum and require dilution with water to the consistency of sour cream. The drying time for the floor in this case is from 3 to 5 days. During this period, it is recommended to minimize air humidity.
It is better to refrain from using these solutions for floor screeding in rooms that are constantly exposed to water (bathroom, cellar).
Homemade mixtures are made based on cement. Recommended brand - M300 and above. The composition of the mixture is as follows:
- Cement - 1 part.
- Fine-grained sand - 4 parts.
- Water. Add water until the mixture reaches the consistency of dough. When adding water, constant stirring is necessary.
- Plasticizer. It facilitates screeding and is applied in concentrations recommended by the manufacturer, ranging from 1 to 10% of the volume. The criterion for the correct consistency of the mixture is the ability to form lumps from it that do not crumble or spread. If the plasticity of the composition is not sufficient, the ball cracks, which means there is not enough liquid in the mixture. If the mixture is too liquid, sand and cement must be added.
Before pouring, the perimeter of the room is covered with damper tape, which serves for sound insulation and prevents cracking of the floor when heated.
Pipes and cables are secured with rigid clamps.
The screed is produced at air temperatures from 5° to 30° (a number of professional mixtures allow installation at lower temperatures, they have a special marking).
The maximum area for one-time filling is 30 sq. m. Large spaces are best divided into sections. In places where the surface is divided into sections, protective corrugated hoses are put on the pipes.
The shelf life of the prepared solution is 1 hour, after which it cannot be used.
Filling one area is carried out quickly and in one step.
Immediately after the procedure, the mixture should be pierced in several places with an awl or a thin knitting needle to ensure the release of air bubbles. For the same purposes and additional leveling, use a needle roller or a stiff brush. The needle should be longer than the thickness of the solution layer.
Drying of homemade mixtures occurs within 20-30 days and has a number of features:
- Sudden changes in room temperature and exposure to direct sunlight are unacceptable. This is fraught with uneven drying and subsequent deformation.
It is better to cover the floor surface with plastic wrap and periodically (every few days) moisten it with liquid.
After drying, it is recommended to turn on the heating system for several hours at a moderate heat supply.
Recommended air humidity is 60-85%.
Before laying tiles, linoleum, parquet or wood flooring, the heating must be turned off.
When using materials prone to cracking and swelling, air humidity must be reduced to 65%.
The tiles are laid on tile adhesive, carpet, linoleum and laminate directly on the screed.
Self-installation of a heated water floor is possible only if you have enough time and careful and strict adherence to all instructions and rules.
We invite you to watch a video detailing the installation of water heated floors:
Installation work on laying mats
Before you begin laying the mats, the base is equipped with film-type waterproofing. Next, a damper tape is passed along each wall and mats begin to be laid. The plates are connected using special locks. If the slabs are light in weight and thick, then they are glued and connected using staples - harpoons.
Attention! The stripes marking the edges are designed to mark the end of the heated zone and facilitate installation work. When laying mats, you cannot use metal fasteners, because this will damage the hydro- and thermal insulation.
The correct choice of heat-insulating material will increase the functionality of heated floors, so saving on the quality of insulation is not recommended
When laying mats, you cannot use metal fasteners, because this will damage the hydro- and thermal insulation. The correct choice of heat-insulating material will increase the functionality of heated floors, so saving on the quality of insulation is not recommended.