Insulating a dacha is an activity that should not be postponed, but completed before the weather gets colder. You should know that the insulation procedure itself concerns many elements of the building, moreover, it can last several weeks. But something else is more important - to choose the materials and execution technology wisely, since this determines how effective the result will be. It is worth adding that with the help of the simple techniques described in the article, you can save a little on thermal insulation.
- 1 External insulation of the cottage 1.1 Stage one. Material selection
- 1.2 Stage two. Warming procedure
- 2.1 Video - Thermal insulation of a country house
So, how to insulate a country house? Let’s immediately say that insulation can be of two types:
- external;
- internal.
Let's look at the features of each of them.
Insulation of the dacha
The design of a country house is usually intended to be used during the warm season. The main task is protection from precipitation, wind and dust.
During the cold season, it becomes impossible to live in a country house; it is not able to sufficiently provide a comfortable temperature. You have to constantly heat the stove or boiler, keep electric heaters on, which creates increased consumption of energy, fuel and, accordingly, money.
Let's look at how to insulate a country house for winter living and solve the problem with your own hands.
Why insulate?
Insulating a country house for year-round use automatically turns it into a full-fledged home. The fashion for country houses has been around for quite some time, and insulating a dacha makes it possible to acquire such a home relatively inexpensively and easily. The possibility of year-round living outside the city limits, in the fresh air, is attractive to most owners of country houses.
In addition to considerations of economy, insulating a country house with your own hands has another, more important reason. When people live permanently, the house develops its own atmosphere, saturated with water vapor. They appear due to cooking, using the bathroom, toilet. But the main amount of steam appears due to people's breathing. The steam that comes out of your mouth in the cold is also released when you breathe in warm rooms, it’s just not visible. In the internal atmosphere of a house, steam is under a certain pressure, which is called partial pressure. Normally, this moisture is gradually pressed through the walls and removed outside, evaporating from the outer surface of the walls.
If the structure of the house is not designed for living in winter, the surfaces of the walls are not able to retain heat. They are constantly cold, which causes steam to condense on them. The walls get wet, become saturated with water, freeze on the outside and begin to collapse. Metal elements begin to rust and fail.
Insulating the dacha for winter living will help to avoid this, which consists of installing a heat insulator on the surface of the external walls, ceilings, floor and (if required) roof.
Dew point problem
From this picture you can easily understand the principle of this term.
The dew point is the point at which moisture that comes from the air begins to condense. This situation inevitably leads to the destruction of walls (brick walls suffer the most) and insulating material. Thermal insulation from the inside helps the dew point move closer to the room. However, the situation can be improved if you take a set of measures:
Purchase insulators with very low vapor permeability and moisture absorption. As a result, the moisture that accumulates inside the room will practically not enter the walls.
- When laying the insulator with your own hands, avoid joints. Even the slightest cracks will contribute to the formation of condensation.
- Install a vapor barrier layer with one-way conductivity. You can use a special membrane film.
- Arrange the layers of thermal insulation in order of increasing degree of vapor permeability. That is, those materials for which this indicator is minimal should be located indoors.
Materials for thermal insulation
To insulate the outside of a country house with your own hands, various materials can be used:
- hard (slab). These include polystyrene foam, penoplex, basalt mineral wool, etc.
- roll . In most cases, these are various types of mineral wool, of which there are several dozen.
- sprayed _ Polyurethane foam, ecowool
- bulk . Expanded clay, vermiculite, sawdust, polystyrene foam granules, etc.
The main indicator characterizing a heat insulator is vapor permeability . Exist:
- permeable materials - mineral wool, all loose types, ecowool, etc.
- impermeable types - polystyrene foam, penoplex, polyurethane foam, penofol and other synthetic types of insulators
In addition, important indicators for heat insulators are:
- heat permeability The lower it is, the better the material is able to retain thermal energy.
- ability to burn . Most heat insulators either do not burn at all or are subject to appropriate procedures during manufacture. At the same time, the possibility of combustion may remain. For example, polystyrene foam does not support combustion , since its granules are filled with carbon dioxide. At the same time, a puddle of molten polystyrene burns quite well
- the ability to hold its shape and not change its linear dimensions over time. If the insulator changes size or shape after several years of operation, so-called problems occur. cold bridges that contribute to wet walls and corrosion of metal parts
- high temperature resistance
- resistance to moisture , hygroscopicity. In this regard, mineral wool, which requires the installation of protective films, lags noticeably behind.
- biologically neutral . The insulator must not rot, support the growth of mold or mildew, or support insects or rodents.
The most common are mineral wool and polystyrene foam. This is due to high performance, relatively low cost and availability. Recently, materials made from polyethylene foam have been actively developed, which are absolutely resistant to moisture and biological manifestations.
The choice is usually determined by price and the user’s general ideas about a particular material, its qualities and properties. For those wishing to insulate a country house for winter living, price is of considerable importance , which often predetermines the choice of material to the detriment of the quality of work. When deciding how and with what material to insulate a country house, you need to take into account the specifics of the operation of a particular insulator and have an idea of the physical processes occurring in the structures of the house.
Brief overview of other methods
They also use other technologies, among which there are both outdated, but cheaper, and modern, requiring considerable investments.
Installation of polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam
With the advent of EPS, it became impractical to use conventional non-pressed polystyrene foam (PSB), since it has deteriorated characteristics.
Namely:
- burns and melts, releasing hazardous substances;
- has fragility, due to which pieces break under mechanical pressure;
- not protected from rodents.
In terms of parameters, it is inferior to extruded polystyrene foam, and this can be seen in the table of physical and technical properties of expanded polystyrene boards:
For example, the compressive strength of EPPS is 0.25-0.50 MPa, and that of PSB is only from 0.05 to 0.1 MPa (at 10% linear deformation), water absorption for EPPS is 0.2% of the volume, and PSB has as much as 2.0
However, light and thick slabs are still used when it is necessary to quickly and inexpensively insulate a room. We recommend using this material for cladding garages and utility rooms, that is, non-residential premises.
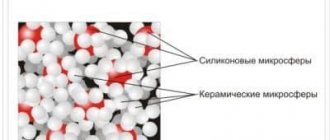
Spraying liquid ceramic insulation
Schematic representation of the composition of the liquid-ceramic mixture: vacuum microspheres of various diameters and a latex binder mixture enriched with antifungal and anti-corrosion additives
Advantages of liquid ceramic spraying:
- moisture resistance;
- mechanical stability;
- elasticity;
- ease of application;
- environmental friendliness;
- minimal load on structures.
The main advantage is the thinness of the applied layer while maintaining important thermal insulation characteristics.
In terms of efficiency, a 1-mm layer of LCD is equal to a 50 mm thick basalt wool slab and can increase the temperature in the room by 3-4 degrees. Builders love the sprayer for its ease and high speed of application.
After applying the liquid-ceramic mixture, additional hydro- and vapor barrier is not needed. A thin layer can withstand temperatures from -60 °C to +250 °C, and, subject to application technology, lasts up to 30 years.
How best to insulate
There are two ways:
- insulation of a country house from the inside
- insulation of a country house from the outside
External insulation is considered the most effective and preferable option. It consists of installing a heat insulator on the outside of the walls and has many advantages:
- The inner surface of the walls is kept intact , which allows you to finish it in any way, install hanging furniture or household appliances
- all conditions are maintained for the unhindered release of water vapor , the durability and safety of wall materials and structures is ensured
- walls are included in the thermal contour of the building, which contributes to more efficient operation
The disadvantages of external insulation include:
- work cannot be carried out in frost , rain or darkness
- not all types of insulation are suitable for outdoor installation
Insulation from the inside involves installing heat insulators on the inside. The room becomes as if enclosed in a cocoon of insulating material installed on all external walls. The disadvantages of this method are:
- the escape of steam through the walls becomes more difficult or even
- the surface of the walls is covered with insulation, requiring the installation of protective sheathing or another layer
- installation of hanging objects on the walls is excluded
- the volume of rooms is reduced
- external walls are excluded from the thermal contour , remaining only mechanical fences
The advantages include:
- ability to carry out work at any time or in any weather
- there is free access to any surfaces
The main difference between these methods is the steam output mode. With external insulation, it passes through the wall, enters the insulation, from where it is removed outside. It is necessary to use a vapor-permeable insulator, the most successful option of which is mineral wool. With internal insulation, steam escape becomes almost impossible. If an impermeable insulator is used, cutoff occurs. If mineral wool is installed, then the steam passing through it ends up in front of the wall. Its permeability is lower than that of the insulator, so steam accumulates in the thickness of the insulation, the material becomes wet and loses its working qualities.
Vapor permeability rule
There is a rule according to which the vapor permeability of materials should increase in the direction from inside to outside. According to him, installing an impermeable insulator on the outside will “lock” the vapors inside the wall, causing it to become wet and begin to deteriorate.
At the same time, installing permeable material on the inside will create conditions for vapor absorption by the insulator, but will prevent passage through the wall. Guided by this rule, you can avoid common mistakes when choosing and installing heat insulators.
When choosing an installation method, you should definitely prefer the outdoor option. However, sometimes you have to choose internal insulation if there is no possibility or access to the surface of the walls. For example, you cannot disturb the architecture of the house, or the walls are located too close to the neighboring building, etc. When choosing internal insulation , you should immediately take care of creating a high-quality ventilation system . The removal of internal air will remove steam, which will eliminate the problem of excessive air humidity.
Penoizol
Liquid carbamide foam plastic (penoizol) is convenient because it can be poured directly at a construction site. It perfectly fills all irregularities and voids without expanding in volume. However, it is possible to obtain a high-quality coating without cracks only at temperatures up to +5°C.
Working in the cold with it is strictly prohibited.
Carbamide foam is also produced in the form of slabs or crumbs, called thermal wool, blown into hollow frames. The absence of seams is the most important advantage of the material. It is used to insulate walls, attics, roof spaces or as a layer in brick walls.
Thermal insulation with foam insulation
In terms of service life, it exceeds conventional foam plastic or extruded polystyrene foam - the service life can be up to 80 years. Builders often complain about its low strength, but this is due to the use of penoizol of insufficient density. The improved material is not inferior in strength to flexible and dense polystyrene foam.
The porous structure of carbamide foam allows for good vapor removal. However, due to its ability to absorb liquid, it requires moisture protection. Not only film followed by finishing with durable panels, but also cement-sand plaster can serve as waterproofing.
Insulation technology
Installation methods for different materials have their own characteristics, but the general procedure remains the same. In addition to vapor permeability, it is necessary to take into account the material of the walls and ceilings in order to select the most suitable thermal insulator. In addition, insulating the walls of a country house will not completely solve the problem.
It will also be necessary to insulate the floor in the dacha from below or above, as well as insulate the ceiling and, if necessary, the roof. Typically, an insulator is installed on the roof in order to make the attic a full-fledged living space.
All work is carried out after appropriate preparation, which consists of removing hanging elements, brackets and other foreign parts from the surfaces. Contaminants are cleaned, crumbling or peeling areas are completely removed. The old coating or layer of paint is removed, if possible.
Gaps or cracks are sealed with putty or solid plaster. After this, the surface is covered with a double layer of deep penetration primer, after which you can proceed to the direct installation of the insulation.
Insulation of floors on the ground
Do-it-yourself floor insulation in a country house is done in accordance with the material or design of the floor slab. Country houses are usually built with floors laid at a low height above ground level or, as they say, on the ground. The proximity to the soil creates high humidity at the lower level of the house; the floor surface is constantly cold, which contributes to moisture condensation.
When insulating the floor in a dacha with your own hands on the ground, you must sequentially perform the following steps:
- remove boardwalk and joists
- level the base soil, compact it
- pour a layer of sand about 20 cm (thickness depends on the level of the floor, existing or desired)
- pour a layer of crushed stone, compact it well, add 305 cm of sand and also compact it tightly
- lay geotextiles and a layer of vapor barrier film on top of it
- lay a layer of insulation. Optimally - extruded polystyrene foam (penoplex), but also a good option is insulating the floor in the country house with expanded clay. It is poured in a layer of 20 cm
- pour a layer of screed 5 cm thick or more, depending on the desired floor level
After the screed has dried, either the floor covering is laid or a heated floor is installed.
Ceiling above the basement and attic
Insulation of the floor in a country house located above an unheated basement is best done from below, from the subfloor side.
A layer of vapor-permeable insulation (mineral wool) is installed on the surface of the prepared floor slab. Since the insulator will need to be protected from moisture , you will first need to install lathing with a thickness of bars no less than the thickness of the heat insulator. The sheathing pitch (the distance between adjacent planks) corresponds to the width of the insulation.
The gaps are tightly filled with insulator , all cracks are filled with polyurethane foam. Then a layer of vapor-waterproofing membrane is installed with the exit down (to the basement), after which you can begin installing the sheathing.
It is optimal to insulate the ceiling of a country house from the outside, from the attic.
The best way is to install high sheathing, fill the resulting cells with expanded clay , and lay plank flooring that allows you to move freely around the attic. It's inexpensive and fast. Alternatively, you can lay a layer of mineral wool.
The use of polystyrene foam or penoplex is allowed only if the attic is residential and heated. Otherwise, the ceiling will get wet and rot.
Wall insulation
There are two ways to insulate the walls at your dacha yourself - from the inside or the outside. We have already examined the advantages and disadvantages of these methods; now we will determine the procedure.
Preparation
Work on insulating the facade of a dacha from the outside begins with preparation - cleaning the walls of all foreign elements, removing cladding or old coating, crumbling or peeling areas. Detected cracks or potholes must be puttied or plastered; the surface is primed with a double layer of primer (deep penetration primer).
Lathing
After this, you need to install the sheathing. First, the outermost vertical strips are installed, aligned vertically and by distance from the wall surface. Then control cords are stretched between them, along which the remaining strips are installed in increments equal to the size of the insulation.
Installation of insulation
Slabs or cut pieces of insulation (mineral wool) are inserted between the sheathing strips. A layer of vapor-waterproofing membrane is installed on top of the insulator with moisture escaping to the outside (you must carefully monitor which side the film is unfolded).
Then horizontal strips for the lining are installed or siding is installed.
Internal option
Insulating a country house from the inside with your own hands is somewhat easier. Heat insulating boards (foam plastic or penoplex) are glued onto the prepared surface of the external wall . As an adhesive composition, you can use a mixture for laying ceramic tiles. The insulator is glued and additionally fixed with special dowels with a wide plastic washer.
After installing the insulation, a reinforcing mesh is attached to its surface with brackets and a layer of plaster is applied.
Mansard roof
If you need to create a full-fledged living space from the attic, you need to insulate the roof. The only available option is to insulate the attic roof from the inside. To do this, you need to install a heat insulator on the lathing layer that supports the roof covering.
A sheathing is installed, between the slats of which heat insulation mats are inserted. It is recommended to use impermeable types of material. All cracks are filled with polyurethane foam. After installing the insulator, sheathing made of clapboard, OSB, chipboard or plywood is installed on the ribs of the sheathing. The choice depends on the type of interior decoration of the attic, since sheet materials allow for more finishing options than lining.
Range of thermal insulators
The range of heat-insulating materials sold on the market today is quite wide.
Let's consider only the main ones:
Foam plastic (cellular plastic)
Inexpensive material made from foamed plastic (mainly polystyrene). The excellent thermal insulation properties of polystyrene foam are explained by the presence of multiple individual granule cells, separated by partitions and filled with gas. An 8 cm thick slab is equivalent in thermal protection to 25 cm of wood or a 1.5 m brick wall.
Polystyrene foam is lightweight, easy to cut, and easy to install. Plates made from it are quite elastic and, unlike rolled materials, do not sag over time.
External foam insulation
The density and strength of polystyrene foam depend on the technology of its processing and the type of raw materials. For façade cladding, it is better to use high-density material - it crumbles less when cutting and has a longer service life.
Despite the fact that the foam itself does not rot, colonies of microorganisms can easily attach to its rough surface and can spread to other structural elements.
Due to its tendency to ignite, as well as the ability to be destroyed under the influence of sunlight, this insulation must be covered with a layer of plaster or used in ventilated facades.
Extruded polystyrene foam
Despite the fact that expanded polystyrene, like polystyrene foam, is made on the basis of polystyrene, its technical characteristics differ significantly. If foam foaming occurs under the influence of steam, then in polystyrene bulk granules are obtained by introducing a foaming reagent and then pressing it through an extruder. As a result, the material acquires a more uniform structure and strength.
All of its air granules are closed and have the same size, which is why polystyrene foam is less fragile than polystyrene foam.
Foundation insulation with polystyrene foam
The service life of this material is up to 40 years. It has minimal water absorption (up to 0.4%) and lower thermal conductivity - on average it is 0.029-0.034 W/(m K). The thermal insulation properties of polystyrene foam are very high - even a thin sheet is enough to create a reliable barrier to the cold.
But still, polystyrene foam is not able to “breathe”; it is better not to use it for wall decoration, otherwise they will get wet. The main purpose of expanded polystyrene is thermal insulation of plinths and foundation blind areas. A special high-strength, high-density material is used in construction as auxiliary or even load-bearing structures.
Entrance door
Entrance doors
To retain heat, a double door was made, the frame was turned from 40mm boards with a hand plane, one door leaf was used from the original, for the second an old balcony door reduced with a saw and chisel was used. The voids in the doors are filled with insulation, and the doors themselves are lined with fiberboard on both sides. In summer, if necessary, one or both doors can be removed.
Window selection
I can safely say that a wooden window with double frames, glazing and fittings ordered from local craftsmen was half the price of metal-plastic. Now (2011) everything is the other way around. When renovating the adjacent attic room, two metal-plastic windows of a larger (2.5 times) area cost (2008) 4800 rubles. After dismantling the old window, oversized building materials were loaded through the resulting opening - fiberboard sheets for interior cladding. The support post was tied to the fence post, and the crossbar was nailed to the ceiling crossbars. After laying the material, the window, painted brown with stain, was installed.
Old window
Storing oversized items
Lift
New window
New window
Let's summarize the comparison
Both materials are characterized by high thermal insulation characteristics.
Therefore, they are most often used to insulate walls in apartments. Their common advantage is that there are no problems with the installation of these insulation materials. Even a person who is far from thermal insulation work can cope with this task on his own. However, there are certain nuances when using them. Laying foam can be done using a frameless method. An adhesive composition is used to secure the insulation to the wall. When thermal insulation is carried out using mineral wool, the creation of a frame is a prerequisite. On the wall, vertically installed slats will act as fastening elements. In terms of installation costs, the use of polystyrene foam is beneficial. In terms of cost, this particular material is also beneficial. Its price is three times lower than mineral wool. However, when deciding to opt for polystyrene foam, you must keep the following in mind. If rodents appear in your home, they will use foam sheets to build their house. They can destroy insulation sheets, which will lead to increased heat loss.
When thinking about which thermal insulation material to choose, you should first consult with a specialist who, taking into account the room, will recommend you a suitable insulation.
Video description
How to lay carpet.
Non-contact fastening of the carpet to the wall is carried out using special slats. You will also need double-sided tape for installation. The entire fastening process is performed according to the following algorithm:
- first of all, the slats are prepared, and then the carpet fabric is cut with the required parameters;
- holes are drilled in the slats, along which markings are subsequently made on the walls; this is needed for installing dowels;
- the prepared slats are wrapped in a piece of finishing material and secured using a mounting stapler;
- Next, they clean the wall in the place where the finishing material will be attached, after which they glue double-sided tape so that a mesh of medium-sized cross-section is obtained;
- then the carpet is attached through the gripper slats and fixed to the top of the wall using dowels;
- then apply a slight tension to the canvas and press it against a mesh of double-sided tape over the entire area.
Preparing carpet for attaching to the wall using special slats Source kantiere.ru
Room paneling
Naturally, I wanted to make lining, but the financial situation was not strong and I had to go for the budget option - fiberboard cladding. And what pushed me to the budget option was the lack of finishing nails for the lining in stores, and using self-tapping screws for the lining... Sheets of fiberboard were cut out locally scissors and fastened with conical screws, the seams on the ceiling and walls were covered with overlays.
Fibreboard covering
Partition paneling
Closet
How to insulate a garden house for the winter
The most practical materials for thermal insulation of a summer house are basalt materials, expanded polystyrene or foam plex boards. Expanded polystyrene should be used for self-insulation of foundations and blind areas.
Penoplex boards are a dense and durable material that is not afraid of high humidity, however, these materials can emit harmful substances.
Insulation of a garden house for winter living
When using mineral wool, high-quality vapor barrier is required on the side of the warm room.
When laying, mineral insulation materials should be placed tightly into the frame. It is believed that mineral wool is not eaten by rodents and is environmentally safe for humans. In order for the thermal insulation layer to be optimal, you should first calculate the thickness of the wall insulation using a thermal calculator.