A properly designed heating system is a combination of elements that provide a comfortable temperature in residential, commercial, and industrial premises. Mandatory components of the heating system include: boiler, radiators, pipes. But the system also includes control components - fittings for heating systems, without which automatic operation of the complex is impossible. Therefore, its installation is an important aspect of the construction of a heating system.
Before arranging a heating system, it is necessary to understand the role played by a certain type of fittings. The general purpose is to adjust the amount of coolant and distribute it along the circuits of the system, reducing/increasing the volume of coolant in certain cases.
Ball Valves
Ball valves are one of the most common types of shut-off valves. They are most often used to disconnect individual elements of the system - radiator, convector, pump, boiler, section of pipeline. The coolant mass flow rate can be adjusted using ball valves, but the accuracy of the adjustment is very conditional.
The crane design includes the following components:
- Housing with connecting threads;
- Stock;
- Rod handle (flywheel);
- Ball with hole;
- Rod seal;
- Ball seal.
The ball has a hole corresponding in diameter to the connected pipeline and is attached to the rod. The ball element is located inside the housing, its outer surface is sealed with fluoroplastic. A flywheel is installed on the rod - a long handle or “butterfly”. Under the force of the flywheel, the ball rotates 900 - in a position parallel to the flow, the valve is open, in a perpendicular position, it is closed. Intermediate positions allow for “rough” adjustment of the amount of passing water flow.
Ball valves come in two types:
- Threaded;
- Threaded with drive.
Ball valves with 3 types of thread
Threaded valves are divided into 3 subtypes - with two external threads, two internal threads, with internal and external threads. The choice of the type of threaded connection depends on the specific conditions, location of the device, and ease of installation.
Threaded ball valves with a drive known as “American” have an important advantage - a collapsible connection. Most often, taps of this type are installed at points where it is necessary to disconnect equipment from the pipeline system without freeing the network from the coolant.
Ball valves with American drive
The simplest example is a heating radiator. The threaded part of the hose is screwed into the passage plug of the heating device, and the pipeline system adapter is screwed into the mating part of the valve.
When removing the radiator, the taps are closed and the squeegee nut is unscrewed. Thus, the radiator is disconnected from the pipelines and can be removed for replacement, repair, or flushing. In this case, there is no need to stop the operation of the entire heating system or drain the water. This method is not applicable in only one case - if there is no possibility of coolant movement besides the radiator, in a single-pipe piping scheme without a bypass jumper.
Ball valves are made from brass, silumin, and stainless steel. The ball is usually made of brass or stainless steel. The conditional working pressure and the nominal diameter of the product are applied to the product body. The taps are available in 2 versions - straight and angular.
Heating shut-off valves
Shut-off valves
Heating valves for regulating the volume of fluid flow in pipes are one of the main elements of any heating system. It is installed at those points in the pipeline where it is necessary to partially or completely limit the flow of water.
Almost every manufacturer provides a catalog of heating fittings. It is necessary for the correct choice of a particular model. The main parameters are:
- Diameter of inlet and outlet pipes. Required for connection to the main line. It is important that when the tap or valve is fully open, it does not limit the speed of movement and volume of coolant;
- Degree of regulation. The accuracy of decreasing or increasing water pressure depends on this. Ball valves are used to quickly cover the flow, and with the help of wedge valves you can smoothly regulate the flow of coolant in the pipes;
- Possibility of installing an automatic regulator for the degree of opening of heating fittings.
Often, taps and valves are used to complete a heating system. In addition to correct installation and selection of a specific model based on performance characteristics, it is necessary to know the structure of these elements of the heating system.
Heating taps
Heating taps
The use of taps as fittings for heating radiators or creating shut-off points for pipelines is due to their relatively simple design and the ability to choose from several model options. Depending on the method of regulating the flow of water, the following types of taps are distinguished.
- Ball . Inside the structure there is a ball with a through hole. As the handle is turned, the bore diameter increases or decreases. This shut-off valve for heating radiators is characterized by the ability to quickly close - to do this, just turn the lever 90 degrees. However, with the help of such a tap it is difficult to make smooth adjustments;
- Stock . A rod with a rubber or ceramic gasket is used as a locking mechanism. To fully close and open, you need to make several full turns of the handle. Such shut-off valves for heating are used to precisely regulate the volume of coolant flow.
Installation and selection of taps should be carried out only in agreement with the operational parameters of the system.
Gaskets for installation should be carefully selected. In systems with antifreeze, it is recommended to install paronite ones, since they are least susceptible to deformation.
Heating valves
Structurally, they are similar to the rod valves described above. The main difference is that their sizes are much larger. The shape of the internal channels has also been changed - the wave structure provides protection from significant pressure drops. This ensures the integrity of the rod and complete sealing of the fittings for heating systems when closed. Similar mechanisms are installed in central heating pipelines where the pipe diameter exceeds 100 mm.
Shut-off and control valves
Heating control valves
Shut-off valves, also known as control valves (manual), are also designed to shut off services. Compared to ball valves, they have higher adjustment accuracy.
According to their design, the valves consist of a rod located inside the housing. The rod changes its height position by rotating through the thread using a flywheel. A poppet valve with a seal made of fluoroplastic, paronite, and so on is attached to the lower part of the rod.
Moving in a direction perpendicular to the flow direction, the valve closes the flow area of the valve when the stem is lowered, and opens when raised, thus changing the amount of coolant flow.
Valves are made from brass, bronze, steel of various grades. Fittings of this type are connected to pipelines using threads, flanges, and welded by electric welding (rarely and only steel products). The product body is marked with nominal diameters and pressures, an arrow indicating the direction of movement of the coolant.
Purpose and scope of application
The fittings are divided into the following types according to their area of use:
- Industrial (industrial pipeline) - used in various industries without any special requirements from users.
- Special (tailored) - designed for operation in conditions with specific characteristics of the transported and environment.
- For hazardous facilities - used at facilities where reagents that are harmful and dangerous to human health (flammable, explosive, flammable, toxic and other substances) are used, as well as equipment operated under pressure from 0.07 MPa or at temperature parameters working fluid over 115 °C.
- Sanitary (sanitary, plumbing) - shut-off valves for water supply, mounted on sanitary equipment. The average consumer most often encounters ball valves installed under sinks and toilets in front of flexible hoses, when connecting washing machines and dishwashers to the water supply.
- Ship (ship, marine) - placed on pipe communications and equipment of ships.
- Vacuum - operating at pressures below atmospheric.
- Control (monitoring) - regulating the supply of medium to control, measuring equipment and devices.
- Cryogenic - operating in an environment with a temperature from 0 to 120 °K.
- Shut-off (quick-acting) - quick-acting in accordance with the production process.
- The inlet is of the reverse type, mounted at the end of the pipeline before the electric pump.
- Antisurge - responsible for reducing the difference in the flow rate of the working fluid of compressors.
Rice. 5 Plumbing fittings in public utilities
- Pressure-reducing (throttle) - performing the functions of reducing pressure in networks by increasing hydraulic resistance.
- Drain (bleed, blow-off, drain) - performs the functions of discharging large volumes of liquids from tanks and pipeline systems in a short time.
- Sampling and bleed - used when taking samples and determining the presence of a medium, discharging it from various types of tanks and boiler equipment.
- Wellhead, oil-and-gas field - designed for operation in the pipes of oil production wells, their piping and beyond the boundaries of pipelines.
- Oil and gas production or fountain (Christmas tree) - installed at the mouth of well pipes during oil and gas production.
- Fountain (wellhead) tree (christmas tree) is an auxiliary variety when installing wellhead devices, designed to ensure the normal functioning of the latter.
- With heating (with heating, jacketed) - has an electric cable built into the body or is covered with a heat-protective casing on top. A heat carrier, for example, steam or heated air, is supplied into the space between the housing and the casing.
- Energy (energy, power) - refers to special varieties for functioning at energy industry facilities.
Rice. 6 Flanges and weld ends
Needle tap
A needle valve differs from a shut-off and control valve in the design of the actuator. It is made in the form of a cone, which is why it is called needle-shaped. When the position of the cone changes (raising or lowering the rod), the flow area of the device changes and, accordingly, the amount of coolant passing through.
The advantage of needle valves is the uniformity and density of the actuating element - the cone. When operating control valves, there are often cases of valve lining tearing off - this does not happen with plug valves. But on the other hand, the valve cover can be replaced, but the cone, if damaged (corrosion, wear), cannot be repaired. Needle valves, like ball and control valves, are produced in two versions - angular and straight.
Types of fittings on pipelines
The term “valve type” refers to its functions, the main ones being:
- constipation,
- regulation,
- prevention,
- obstacle to reverse movement,
- stream separation.
Shut-off valves (on-off, shut-off, stop) are technical devices that perform the function of hermetically shutting off the flow of the transported working fluid.
In addition to the main locking type, in the technical industry there are the following types of combined or multifunctional (combined, multifunction), combining different functions of fittings:
Shut-off and control (on-off and control) - in addition to completely blocking the flow, shut-off control valves for heating, water supply and other needs are capable of changing the volume of a moving medium by partially blocking the channel passage.
Stop and check - in addition to blocking the channel passage, it prevents the passage of the medium in the opposite direction.
Non-return shut-off (stop non-return) - in addition to preventing flow movement in the opposite direction, it implements the function of forced closing or limiting the movement of the shutter element.
Rice. 3 Sectional design of shut-off valves
Gate valve
Heating system valve
Valves are designed mainly to completely shut off pipelines; due to the characteristics of the device, flow adjustment is practically not carried out. The actuator element in the valve is a flat oval or wedge-shaped element, which, when the stem is lowered along the thread, blocks the flow of water. The element can be single or double.
The valves are made from carbon steel, cast iron, and stainless steel. The devices are connected via flange connections. Valves usually have large diameters and are most often used on main heating pipelines. The nominal pressure and temperature values are marked on the device body.
Conditions for the production of fittings
The material used to manufacture pipeline fittings is determined by its future area of application. If the system (or section of the system) will operate at pressures up to 1.6 MPa, ductile cast iron is used; if more - steel. For small cross-section pipelines, high-quality copper alloys are used, which prevent corrosion of elements and sticking of fittings to the pipes.
It should be noted that the production of reinforcing elements is a complex and high-tech matter, and therefore must be carried out using special industrial equipment.
To produce products you need:
- bake;
- special purpose press;
- diagnostic machine;
- table on which assembly is carried out;
- lathe;
- drilling machine;
- conveyor;
- air compressor for painting products;
- auxiliary tools and devices.
Balancing valve
Balancing valves are similar in design to control valves, but have more precise settings and are equipped with additional elements for air release and measuring the flow rate of the working medium.
The stem of balancing valves often has an angular inclined position, the movement thread has a small pitch - this ensures accurate adjustment. The task of the balancing valve is to mutually balance the coolant flow rates in individual sections of the heating system. Some valve models are equipped with flow meters - they are indispensable if the heating project was developed using special software products.
The program calculates the recommended coolant flow rate for each individual branch or circuit of a water heated floor. If these values are available, the flow meters of the balancing valves are set to the appropriate value, and there is no need to carry out long and difficult experimental balancing of the heating system.
The manufacturing material is usually brass, and the body is marked with appropriate markings - temperature, pressure, direction of flow.
Selection of radiator valves
The selection of valves should be made taking into account the following parameters:
- type of locking device;
- technical characteristics of the crane;
- individual characteristics of the heating system.
Types of valves
Three main types of valves are used for installation in a heating system:
- ball;
- conical;
- thermostatic.
Ball valves are installed to autonomously shut off the heat supply and, due to their characteristics, cannot be used to limit the flow of water into the system.
Shut-off ball valves are divided into the following types according to installation method:
threaded (the taps are equipped with threads on both sides for connection to pipes). They are mainly produced in small diameters and are intended for installation in an individual residential heating system;
Threaded shut-off valve
flanged (the device is attached using flanges). Used in most cases on external lines of heating systems;
Valve for heating system, secured with flanges
welded (installed using a welding machine). Due to the complexity of installation, they are practically not used in individual systems.
Welding faucet
A cone valve, unlike a ball valve, allows you to regulate the temperature of the incoming liquid. The control valve can be of two types:
straight. The device is installed on a flat area of the heating system;
Crane for installation on level ground
angular. The device is installed at the bend in the supply pipeline.
Tap for installation on pipe bends
The main disadvantage of cone valves is manual control, which does not allow setting a certain temperature in the living room.
To maintain the temperature of the liquid in the heating system, a thermostatic valve is installed, which may have:
- manual control. A certain indicator is set on the temperature scale built into the valve;
- semi-automatic control. Temperature setting is done on the push-button display;
- automatic control. The valve maintains the set temperature without human intervention.
Valve device with adjustable temperature
Which radiator valve to choose? You need to rely on the capabilities of the device:
- complete (shut-off valve) or partial (cone or thermostatic valve) restriction of the incoming liquid;
- setting the temperature.
Standard requirements for valves
Any radiator valve must meet the following requirements, which are standard for urban heating systems:
- valves on heating radiators must withstand an internal fluid temperature of at least 200ºС;
- the operating pressure of the valve installed on the radiator must be in the range of 16 - 40 atm;
- the valve must be made of materials resistant to corrosion and mechanical stress. High-quality taps are made of steel, bronze or brass.
All valves intended for heating systems meet the specified requirements. However, when purchasing a device, it is recommended to double-check the operating parameters.
Taking into account individual characteristics
When choosing valves, it is also necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the apartment’s heating system, which include:
diameter of pipes supplying radiators. The diameter of the valve must fully correspond to the diameter of the pipes; position of the valves on the battery. Availability of free space for installing straight or corner valves; valve installation method
If the pipes have threads, it is important to take into account its dimensions. If there is no thread, then when choosing a valve it is necessary to determine the installation method of the device.
Thermostatic mixer
Thermostatic mixer (two or three-way) serves as a basic element of underfloor heating complexes - water heated floors. The main structural elements of the device are poppet valves located on the rod near the inlets of the cold and hot coolant into the mixing chamber.
In accordance with the specified temperature parameter (set manually or using a thermal head), the valves open the passage of coolant in the required proportion. After mixing hot and cooled water in the mixing chamber, the mixture at a given temperature is supplied to the outlet pipe of the device. Sometimes the working element of thermal mixers is a bimetallic plate.
Thermostatic mixers are made of brass and have a threaded connection. There is a combined arrow on the body indicating the final direction of the finished coolant and markers for the entry of hot and cold water.
Check valve
A check valve is a simple device designed to prevent the reverse flow of coolant. A spring-loaded poppet valve is installed in the body, which is in the normal “closed” position - pulled by a spring. When the coolant moves in the permitted direction, the spring expands and the valve opens the passage.
When pressure arises behind the valve, the disc element closes the passage, preventing the reverse flow of coolant. A check valve is most often installed at the pump discharge - when other pumps are operating, it performs a locking function and maintains the directions of coolant movement specified in the network.
The valve is made from various materials - brass, steel; small and medium diameters have a threaded connection, large diameters have a flange connection. There is an arrow on the body indicating the permitted direction of water movement and the values of operating parameters - pressure, diameter.
Mixing and control valves
A prominent representative of this group of devices is the thermostatic three-way valve. Its task is high-quality regulation of the coolant, that is, by temperature, and not by flow. A three-way valve does not act like a shut-off valve, it works like a mixing unit. Configured to produce coolant at a certain temperature, the element mixes the two flows in the required proportions.
Heating mixing unit
The device is a brass body with three pipes, inside of which there is a rod controlled by a thermostatic drive. The rod passes through 2 seats, regulating the flow of the required amount of water through them from two pipes, in order to obtain a mixture of the set temperature in the third.
Operating principle of three-way valve
It must be said that not every heating system needs such fittings. The scope of application of mixing devices is maintaining the temperature in underfloor heating circuits, individual radiators or entire groups of heating devices, as well as in small circulation circuits of solid fuel boilers. In general, it is quite difficult to list all the special cases of using mixing valves, since there can be a lot of them in modern water heating schemes.
Make-up valve
The refill valve is designed to automatically replenish the heating system with coolant to a predetermined pressure. It is usually installed on the return pipeline and the cold water supply line is connected to it.
The design of the product is based on the properties of a membrane supported by a spring. The heating fluid exerts pressure on the membrane and compresses the spring. When the set pressure drops, the membrane releases the spring - a passage opens for the volume of water from the cold water network. When the set pressure is reached, the membrane compresses the spring and the replenishment stops. The device has standard markings - direction, diameter, pressure.
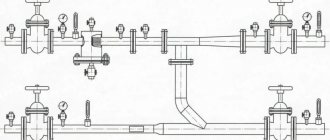
Testing of pipeline fittings
To ensure trouble-free operation of pipelines, pipe shut-off valves and other connecting elements are tested. The tests include the following stages:
- Hydraulic loads to check the strength, impermeability of the material, and the absence of shear of structural elements.
- Checking the tightness of the locking elements.
At the first stage, industrial shut-off valves are tested under pressure from pumps. Test conditions are specified in the technical documentation.
Pressure is applied to the open working element when the hole in the pipe is closed. If leaks are found at welding points and other connections, the fittings are considered unsuitable for use.
When testing devices for leaks, liquid under pressure is supplied in turn from different directions to the device. The fitting is inspected on the opposite side of the pressure supply. Valves, dampers, valves are subject to pressure from one side.
Important: to classify products by sealing class, they are guided by GOST R 9544 - 75 “Pipeline fittings”. The standard specifies three classes of tightness, determined by the purpose of the pipelines.
Safety relief valve
The safety relief valve in the PSK safety group
performs a safety function and is usually installed on boiler safety groups. Its design is simple - the spring-loaded valve is preset by the manufacturer to the opening pressure. For autonomous heating systems it is 3 kgf/cm2.
When there is an uncontrolled increase in pressure in the system, the valve opens and releases a certain volume of coolant, protecting pipelines, equipment, seals of threaded and flange connections from damage by excess pressure.
The material of manufacture is steel or brass, the connection is threaded or flange, the marking indicates the response pressure of the device.
How to adjust the balancing valve in a heating system
Setting up a mechanical balancer
Before setting up the balance of the radiator network, you need to study the instructions for the valve, which are included when purchasing it. It indicates an adjustment scheme; if the user installs everything correctly, he can actually reduce the cost of thermal energy. The valve can be adjusted in two ways.
The first way to adjust the valve
This is the simplest and most proven adjustment option, which is recommended by experienced thermal regulators in water heating networks. To do this, you will need to divide the number of valve revolutions by the number of batteries installed in the heating circuit around the perimeter of the room. This technique makes it possible to correctly determine the step of the tuning algorithm. The method consists of closing all the valves in the reverse order - from the outermost to the first battery in relation to the heating source.
For example, for a dead-end circuit with 4 radiators equipped with mechanical balancing valves and a 4.5-turn spindle adjustment:
4.5:4 = 1.1 turns
Opening diagram:
- The first balancing valve is 1.1 turns.
- Second balancing valve – 2.2 turns.
- Third balancing valve – 3.3 turns.
- The fourth balancing valve is 4.5 turns.
The second way to configure the balancer
There is another, very high-quality method of balancing. It runs much faster, and contains the ability to take into account some of the specific location of the battery. The only thing you need to do this is a contact thermometer.
The complete process goes like this:
- Open all the valves and allow the network to enter temperature equilibrium with the operating temperature, for example, 80 C.
- Measure the temperature of all heating devices.
- Eliminate the difference by shutting off the first and middle taps. The end valves are not adjustable.
- Typically, the first valve turns no more than 1.5 revs, and the middle ones - 2.5 revs.
- Allow the system to reach temperature equilibrium for 20 minutes
- Temperatures are measured and valves are adjusted further if necessary.
Air vents
Air vents perform the task of freeing equipment from air that impedes normal circulation in the network. There are mainly 2 types of these devices:
- Automatic;
- The Mayevsky tap (valve) is manual.
Automatic air vent
The float-based automatic air vent device allows air to be discharged from the system in an independent mode. It is recommended to install them at the highest points of the complex - places where air is most likely to accumulate. They often serve as a standard element of the boiler safety group and have an external thread for connection.
Types of Mayevsky cranes
The Mayevsky faucet is based on a needle valve that opens manually. Most often, these devices are installed on heating devices for periodic release of air.
What is needed for installation
Installation of heating radiators of any type requires devices and consumables. The set of necessary materials is almost the same, but for cast iron batteries, for example, the plugs are large, and they do not install a Mayevsky valve, but instead, somewhere at the highest point of the system, they install an automatic air vent. But the installation of aluminum and bimetallic heating radiators is absolutely the same.
Steel panel ones also have some differences, but only in terms of hanging - they come with brackets, and on the back panel there are special arms cast from metal, with which the heater clings to the hooks of the brackets.
These are the arms that hook the hooks
Mayevsky crane or automatic air vent
This is a small device for releasing air that may accumulate in the radiator. Placed on the free upper outlet (collector). It must be on every heating device when installing aluminum and bimetallic radiators. The size of this device is significantly smaller than the diameter of the manifold, so you will also need an adapter, but Mayevsky taps usually come complete with adapters, you just need to know the diameter of the manifold (connection dimensions).
Mayevsky crane and method of its installation
In addition to the Mayevsky crane, there are also automatic air vents. They can also be installed on radiators, but they are slightly larger in size and for some reason are only available in a brass or nickel-plated case. Not in white enamel. In general, the picture is unattractive and, although they deflate automatically, they are rarely installed.
Bypass valve
A bypass valve is a safety device whose task is to transfer part of the coolant from a high-pressure zone to a low-pressure zone. They are most often installed between the direct and return heating pipelines.
When adjusting the flow to heating devices (manual or automatic), situations may arise when most radiators reach the set temperature and the input to them is closed or severely limited. Then the pressure in the system increases sharply - this can lead to the activation of the PSC or damage to the system in the absence of one.
This situation is mitigated by a bypass valve - it allows excess coolant to pass into an area with lower pressure and closes when it drops to a set value in the controlled area. The device has standard markings.
Shut-off, control and safety valves are mandatory elements of the heating system. With their help, an acceptable operating mode of the complex is achieved, a comfortable temperature is achieved, shutdowns are carried out for repairs and preventive maintenance, and the integrity of equipment and pipelines is maintained in the event of emergency situations.
( , 1 today)
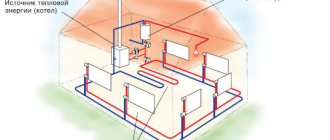
Heating wiring diagrams
They are distinguished by the following characteristics:
- The number of pipes - single or double pipe. With a single-pipe distribution, hot water sequentially passes through all the radiators of one riser. It is clear that the first of them receives more heat, the last - less. Ensuring uniform heat distribution is achieved by using a tap at the battery inlet and a bypass - a pipe of smaller diameter that creates a path for water to bypass the radiator.
- The location of the risers is vertical or horizontal.
- Organization of circulation - natural or with an installed circulation pump.
When organizing a heating system for an apartment in a multi-story building, you have to rely on the already installed wiring. For example, in Soviet-built houses, single-pipe vertical distribution with a natural coolant circulation was used. When renovating such premises, you have to adapt to this, although it has more disadvantages than advantages. Strictly speaking, there is only one advantage - the length of the pipes is half that of the two-pipe version.
In modern construction, attention is constantly paid to saving energy resources. You can save heat, including by quickly regulating its output and choosing the optimal heating mode
Therefore, new buildings are often initially equipped with a two-pipe heating system. With higher initial costs, it opens up opportunities for effective management of energy consumption.
Number of sections of bimetallic radiators
How many sections there will be on a bimetallic radiator has a direct impact on the choice of connection method. A battery of up to 8 sections can be connected with a side, bottom saddle or diagonal connection. If there are more than 8 sections, it is better to use a diagonal connection.
When using side switching, a flow extender will be required. This refers to a tube inserted into the supply manifold. It helps out in situations where the side connection provides heating only for the first sections. Thanks to the tube inserted inside, the coolant flows further than the inlet, heating the surface of the device more evenly.
Flow extension length options:
- 2/3 batteries.
- To the center of the last section.
Different cases show the effectiveness of both the first and second options. The main thing is that a noticeable optimization of radiator heating is achieved. Sometimes it happens that installation to the middle of the last section provokes a decrease in the heating level of the first sections. In this case, it is recommended to shorten the tube. But such situations rarely occur, which is influenced by the pressure in the riser and the cross-section of the liner.
Shutters: practice of use
Gates are the most important part of shut-off valves of any type. It is thanks to the serviceability of the valve that timely and complete (or, if necessary, partial) blocking of the movement of liquid or gas flow in the pipeline is possible.
Accordingly, if the valve is faulty or poorly manufactured, the consequences can be anything - from a minor, harmless leak, eliminated by simply replacing structural elements, to a full-fledged environmental disaster or explosion of the carrier
Therefore, special attention is paid to the material used to make the valves and their operating conditions. The most common type of valves is butterfly valves.
They are used in heating systems, water supply, steam supply, non-aggressive working environments or petroleum products. Flange valves are also used, the distinctive feature of which is the presence of a flange in the design.
The most common type of valve is a butterfly valve. They are used in heating systems, water supply, steam supply, non-aggressive working environments or petroleum products. Flange valves are also used, the distinctive feature of which is the presence of a flange in the design.
Gates can be made of cast iron, but the use of steel products (alloy, stainless or carbon steel) is preferable.
Steel valves have a number of significant advantages:
- operation at temperatures down to -60°C is possible;
- such valves can operate in environments with temperatures up to 700°C;
- designed for use in aggressive working environments;
- withstand high pressure (up to 10 MPa).
How rotary shutter mechanisms differ:
- ease of installation and repair;
- compactness (they can be mounted in confined spaces);
- small, compared to gate valves, weight and dimensions;
- ease of replacement when the product wears out and has a long shelf life;
- low price;
- no risk of jamming or sticking during use.
Therefore, the selection, quality and installation of shut-off valves should be approached as responsibly as possible, basing your decisions not only on the price of the product or country of origin, but also on pre-made calculations. And, of course, we must not forget about timely maintenance and scheduled replacement of elements that are so important for any pipeline.
Purpose of shut-off plumbing
Shut-off valves are designed for manual regulation of coolant supply
In heat generation systems, shut-off type fittings act as a regulator of the flow and movement of coolant, and also allow the heating circuit to be opened. In this case, the heating process becomes controlled, its rationality and efficiency increases.
The shut-off valve is most often installed at the interval in the line where the battery is connected with pipelines. This technique allows you to adjust the heating of the radiator and facilitates the task of maintaining and repairing the heater without the need to turn off the entire heating circuit.