Design of thermostats for heating radiators
The thermostat for a heating radiator consists of two parts - a valve (thermovalve) and a thermostatic head (thermostatic element, temperature regulator). These products are produced for different pipe sizes and different types of heating systems. The thermostatic head is removable; regulators of different types and even from different manufacturers can be installed on the same valve - the seat is standardized.
The thermostat for a heating radiator consists of two parts - a special valve (valve) and a thermostatic head (regulator)
There are different valves and regulators, so before installing a thermostat for a heating radiator, you will have to become at least a little familiar with its structure, functions and types.
Device diagram
The device is used both in systems of one and two pipes. Regardless, it includes:
- valve;
- static element (thermal head);
- sensitive component;
- spool;
- stock;
- compensator;
- retainer;
- scale.
also several fasteners, a drive and a regulator . The device is filled with working fluid or gas, as desired.
Photo 1. Diagram of a thermostat for radiators. Arrows indicate the components of the structure.
Thermal valve - structure, purpose, types
The valve in the thermostat is very similar in structure to a regular valve. There is a seat and a shut-off cone that opens/closes the gap for coolant flow. The temperature of the heating radiator is regulated in this way: by the amount of coolant passing through the radiator.
Sectional view of thermostatic valve
The valves are installed differently for one-pipe and two-pipe wiring. The hydraulic resistance of a valve for a one-pipe system is much lower (at least two times) - this is the only way to balance it. You can't mix up the valves - it won't heat. For systems with natural circulation, valves for single-pipe systems are suitable. When installing them, the hydraulic resistance, of course, increases, but the system will be able to work.
Each valve has an arrow indicating the movement of the coolant. During installation, it is installed so that the flow direction coincides with the arrow.
What materials?
The valve body is made of corrosion-resistant metals and is often additionally coated with a protective layer (nickel or chrome plated). There are valves from:
- bronze (nickel and chrome plated);
- brass (coated with a layer of nickel);
- of stainless steel.
Cases are usually brass or bronze with nickel or chrome plating
It is clear that stainless steel is the best option. It is chemically neutral, does not corrode, and does not react with other metals. But the cost of such valves is high and it is difficult to find them. Bronze and brass valves have approximately the same service life. What is important in this case is the quality of the alloy, and it is carefully monitored by well-known manufacturers. Whether or not to trust unknowns is a controversial issue, but there is one point that is better to keep track of. There must be an arrow on the body indicating the direction of flow. If it is not there, then you have a very cheap product that is better not to buy.
By method of execution
Since radiators are installed in different ways, the valves are made straight (through) and angular. Choose the type that will work best for your system.
Straight (way through) valve and angle
| Name/Company | For which system | Du, mm | Housing material | Operating pressure | Price |
| Danfos, angular RA-G, adjustable | single-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 25-32 $ |
| Danfos, direct RA-G with customizability | single-pipe | 20 mm, 25 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 32 – 45 $ |
| Danfos, angular RA-N, adjustable | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm. 25 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 30 – 40 $ |
| Danfos, direct RA-N with customizability | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm. 25 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 20 – 50 $ |
| BROEN, direct fixed tuning | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 8-15 $ |
| BROEN, direct fixed tuning | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 8-15 $ |
| BROEN, corner, adjustable | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 10-17 $ |
| BROEN, corner, adjustable | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 10-17 $ |
| BROEN, direct fixed tuning | single-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 19-23 $ |
| BROEN, fixed angle | single-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 19-22 $ |
| OVENTROP, axial | 1/2″ | Nickel plated brass, enamel plated | 10 bar | 140 $ |
Types and selection of thermostats
Based on their design, radiator valves are divided into 3 groups:
- straight;
- corner;
- as part of a set for connecting heating devices.
If everything is clear with straight and angular thermostats, then we should say something about the headset separately. It allows you to simultaneously install a thermostat on the radiator and connect it to pipes coming directly from the floor. Although the price of such a headset will be more than traditional pipe connections, such a connection will look much more aesthetically pleasing.
Radiator connection set with built-in thermostat
For two-pipe systems with a heating circulation pump, any of the valves listed is suitable; the only question is how to connect the heating device, and from a technical point of view, they are all the same. Another thing is a single-pipe circuit; for it it is better to buy a special battery temperature regulator with an increased flow area of the seat. Such thermostats have less hydraulic resistance, which is clearly visible in the diagram:
In addition to valves, you should also choose thermal heads for batteries, and here is an immediate recommendation: the valve and head must be from the same manufacturer, and the connecting threads must match. The standard thread on the valve is M28 and M30. In general, the choice of head designs is not too wide - in addition to conventional elements with a built-in bellows, there are also products with an electronic control unit and display. These thermostats are programmable and can be set to maintain different room temperatures throughout the day.
Advice. When choosing a programmable thermostatic head, remember that it requires power from batteries or mains. In order for the thermostat to work correctly, you will have to monitor the availability of power.
In cases where it is planned to install heating devices behind screens or the windows of the room are intended to be covered with thick curtains, conventional thermocouples may not function correctly. Due to weak air movement in the radiator area, the temperature behind the screen and in front of it may differ by a couple of degrees, so in addition to the thermostat, it is worth buying a remote sensor with a capillary tube.
The sensor behind the screen will control the thermostat via a capillary tube, focusing on the correct temperature in the room. There is also a more advanced version in the form of a remote regulator, which is also connected by a capillary tube. But here you need to be more careful: not all valves are suitable for such thermal heads, so when choosing a thermostat you need to consult with the seller.
Finally, a few words about radiator valve manufacturers. Quite a lot of them have appeared, especially Chinese ones, whose quality is more than doubtful. The following brands of thermostats are definitely recommended for use; their reliability is beyond doubt:
Advice. You should not buy and install thermostats on all radiators in the house. The rule is this: in order to ensure normal regulation, in each room it is necessary to equip with thermostats only those batteries whose total power is 50% of the total or more. In simple words: with 2 heaters in the room, the valve must be installed on one (which is larger), with 3 - on two radiators, and so on.
Thermostatic heads
There are three types of thermostatic elements for heating thermostats - manual, mechanical and electronic. They all perform the same functions, but in different ways, provide different levels of comfort, and have different capabilities.
Manual
Manual thermostatic heads work like a regular faucet - you turn the regulator in one direction or another, allowing more or less coolant to flow through. The cheapest and most reliable, but not the most convenient devices. To change the heat transfer, you must manually turn the valve.
Manual thermal head - the simplest and most reliable option
These devices are quite inexpensive, they can be installed at the inlet and outlet of a heating radiator instead of ball valves. Any of them can be adjusted.
Mechanical
A more complex device that maintains the set temperature automatically. The basis of this type of thermostatic head is a bellows. This is a small elastic cylinder that is filled with a temperature agent. A temperature agent is a gas or liquid that has a high coefficient of expansion - when heated, it greatly increases in volume.
Thermostat device for a heating radiator with a mechanical thermostatic head
The bellows supports the rod, which blocks the flow area of the valve. Until the substance in the bellows heats up, the rod is raised. As the temperature rises, the cylinder begins to increase in size (gas or liquid expands), it puts pressure on the rod, which increasingly blocks the flow area. Less and less coolant passes through the radiator, and it gradually cools down. The substance in the bellows also cools down, due to which the cylinder decreases in size, the rod rises, more coolant passes through the radiator, and it begins to warm up a little. Then the cycle repeats.
Gas or liquid
With such a device, the room temperature is fairly maintained at exactly +- 1°C, but in general the delta depends on how inert the substance in the bellows is. It can be filled with some kind of gas or liquid. Gases react faster to temperature changes, but are technologically more difficult to produce.
Technical features of automatic thermostats
The operating principle of thermostats for heating radiators is the same, but there are a number of design differences.
By control method
Thermostats with manual adjustment. Such devices have a valve head, on which divisions from 0 to 5 are applied. By turning the faucet handwheel, we increase or decrease the passage opening for the coolant.
Zero indicates a completely closed battery, the remaining numbers indicate an adjustable temperature range from 14 to 24 degrees.
The structure of a thermostat for a heating radiator
Electronic device. Operates on batteries or accumulator. This is the most massive and expensive device of all, but its capabilities are expanded. The thermostat is equipped with a temperature sensor, remote or built-in. When external conditions change, the sensor sends a signal to the microprocessor and the thermostat is activated.
The cost of the device quickly pays off due to heat energy savings. The device can be programmed to change the temperature throughout the day, as well as by day of the week. For example, from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m., set the temperature to 10-15 degrees, and later raise it to a comfortable 22 degrees.
An example of connecting a thermostat to a cast iron radiator
According to the composition of the working environment
The bellows may contain liquid or gas. A gas thermostat for a heating radiator responds faster to increases and decreases in temperature. But liquid relays respond better to bellows pressure. In addition, they are easier to produce, so they are available in an expanded range.
How to install correctly
They install a thermostat for a heating radiator at the inlet or outlet of the heating device - there is no difference, they work with equal success in both positions. How to choose a place to install?
According to the recommended installation height. There is such a clause in the technical specifications. Each device is configured at the factory - they are calibrated to control the temperature at a certain height and usually this is the upper radiator manifold. In this case, the heat regulator is installed at a height of 60-80 cm; it is convenient to adjust it manually if necessary.
Installation diagrams for heat regulators for radiators
If you have a bottom saddle connection (pipes fit only from the bottom), there are three options - look for a device that can be installed at the bottom, install a model with a remote sensor, or reconfigure the thermal head. The procedure is simple; the description must be in the passport. All you need is to have a thermometer and at certain moments turn the head in one direction, then in the other direction.
Installation is standard - on fum tape or linen winding with packaging paste
The installation process itself is standard. The valve has a thread. The appropriate fittings are selected for it or a matching thread is cut on the metal pipe.
One important point that those who want to install a thermostat for a heating radiator in apartment buildings should remember. If you have a single-pipe installation, they can only be installed if there is a bypass - a section of pipe that stands in front of the battery and connects the two pipes to each other.
If you have a similar wiring (there may not be a pipe on the right), a bypass is required. The thermostat should be installed immediately behind the radiator
Otherwise, you will regulate the entire riser, which your neighbors will definitely not like. For such a violation, a very substantial fine can be issued. Therefore, it is better to install a bypass (if not).
What is required for safe work
If the room is quite hot, and the owner wants to shut off the radiator, then it is possible to install a thermostat on the radiator. If there is a bypass, a thermostat is installed on the heating device to regulate the temperature in the room. When it is not there, a thermostat is not installed, since this will change the temperature regime for all residents along the riser. In such a case, you will simply need to replace the heating device and install a bypass. To carry out work safely you will need:
- Bypass. The device includes pipes that have a smaller diameter than the outlet and supply line piping. The presence of 2 ball valves will make it possible to properly shut off the heating device and direct the circulating flow through the jumper.
- Thermostat. A regulating tap that controls and determines how much water will flow into the battery.
- Mayevsky drain and taps. Using them it is quite easy to overlap. You only need to turn the valve; water will not flow into the radiator.
- Gas outlet device. Can be automatic or manual. Automatically removes the accumulation of gases during their formation in the radiator. Therefore, it is possible to shut off the batteries for the summer season, but only when the gas device is open. Manual ones eliminate residual gas by turning the tap counterclockwise.
How to adjust (reconfigure)
All thermostats are factory adjusted. But their settings are standard and may not match your desired parameters. If you are not satisfied with something in the work - you want it to be warmer/colder, you can reconfigure the thermostat for the heating radiator. This must be done with the heating running. You will need a thermometer. You hang it at the point where you will control the state of the atmosphere.
- Close the doors, put the thermostat head in the extreme left position - completely open. The room temperature will begin to rise. When it becomes 5-6 degrees higher than what you want, turn the regulator all the way to the right.
- The radiator begins to cool down. When the temperature drops to a value that you consider comfortable, begin to slowly turn the knob to the right and listen. When you hear the coolant making noise and the radiator starting to warm up, stop. Remember what number is on the handle. It will need to be set to achieve the required temperature.
Adjusting the thermostat for a radiator is not difficult at all. And you can repeat this action several times, changing the settings.
To connect the batteries to the supply and return pipes, you cannot do without fittings for heating radiators. There are only three types of it, and each node performs its own narrow task. Inappropriate use of fittings leads to rapid wear and failure - we are talking about the use of ball valves to partially shut off the coolant flow.
Removal Features
The structure of the thermostat is shown
The temperature regulator consists of two parts: a valve and a thermostatic element.
Removing the thermostatic element itself does not present any problems: it is easy to do by hand, and if it is clamped a little tighter, you will have to use pliers.
Once the head is removed you will be able to see the stem. It should be moved back and forth several times, and then left wrung out for a while.
In most cases, the battery will begin to warm up normally. Once it has warmed up, you can put the regulator head back in place.
If this does not help, you need to remove and replace the thermostat valve itself.
Battery shut-off valves
Shut-off valves for heating radiators include valves that only work to open/close a nominal bore - these are ball valves. They are installed so that the heat exchanger can be removed from the circuit without stopping the entire system and draining the coolant from it.
Adjustment fittings for heating radiators
Adjustable radiator fittings are needed in order to balance the operation of the entire heating system. Balancing valves are used for this. Thanks to them, the required hydraulic resistance is set on each radiator. This can only be done by employees of the service organization, based on the project. Even at the design stage, all parameters are calculated so that the circuit works correctly. If these parameters are violated, system failure is inevitable.
As you know, water moves along the path of least resistance, and if the heating system were not balanced, it would hardly go further than the first heat exchanger. Thanks to balancing valves, the coolant moves throughout the entire circuit, releasing temperature evenly.
What types of balancing valves are there:
- straight;
- corner;
- with and without rubber seals.
If you close the balancing valve completely, you can cut off the heat exchanger from the general circuit. This is a backup option if it is not possible to shut off the coolant flow with a shut-off radiator valve.
If you want to heat your garage with your own hands, then pay attention to Bulelyan stoves - very convenient, that’s a fact.
How to heat a garage from a house is described here.
We understand the types of devices
According to the method of adjustment, valves are divided into mechanical and automatic . The first require manual rotation of the mechanism for narrowing the flow in the pipes.
Automatic models do not require manual adjustment. When the temperature around the thermostat decreases, they independently detect this and adjust the coolant flow.
Manufacturers also offer different thermostat designs:
- Common for two-pipe systems - the simplest device. If you need hydraulic linking of radiators along one branch, it is recommended to add a shut-off and control valve to the supply (return) circuit.
- With hidden and open hydraulic superstructure - such devices have a coupling with an internal rod, so hydraulic adjustment is possible.
- For single-pipe, gravity systems - due to the increased passage, the throughput of these devices is increased to 5.1 m 3 / hour, so they can be installed in non-pressure systems.
- 3-way for circuits with bypass - they can regulate and distribute the coolant in conjunction with the bypass. When the set temperature reaches the valve, the coolant is sent to the bypass; when it drops, the bypass is partially closed.
The percentage of thermal valves for two pipes is much greater than for single pipes, and the latter in our country are about 80%.
This is due to the fact that the device was originally invented for the former, where the coolant is distributed among the devices forcibly under high pressure. Pre-setting by valves is designed to distribute pressure evenly throughout the system.
Only some manufacturers have valves for single pipes - Heiz, Danfoss, Heimeier, Oventrop.
In single-pipe schemes, you cannot use conventional “two-pipe” thermostats : they have a lower capacity, they can only operate with a large difference in pressure between the supply and return, so there will be a risk of redirecting the coolant to the bypass.
Externally, “one-pipe” valves are larger in size.
Thermostatic valves also differ in shape. They can be straight, angular or included in sets with jumpers for pipes. Direct ones are suitable for regular batteries. Angular ones are needed in schemes with lower pipe connections, when the CO is partially disguised under the floor.
A separate type of thermal valves is electronic. They have wider functionality than regular ones. With their help, you can set different room temperatures for each day of the week and even hourly.
Electronic thermostats provide significant savings in coolant consumption. If there is no one in the apartment or house from 8 am to 6 pm, the device will properly maintain the minimum temperature. And when the owners arrive, it will heat the premises to a comfortable level.
Valves with anti-vandal casing are also available for sale. They are reliably protected from unqualified intervention and are suitable for installation both in a home with small children, and in kindergartens and schools.
Radiator control valves
Thermal heads screwed onto thermostatic valves.
These are units thanks to which you can change the temperature in the room by adjusting the intensity of the coolant supply to the battery. Control valves are used to connect heating radiators to a common circuit and are installed on the supply side. There are two adjustment options:
- manual;
- automatic.
Manual adjustment is possible when installing valves in which the flow of coolant is gradually blocked when you turn the stem. The disadvantage is that the coolant supply temperature in central networks changes depending on the weather, but the valve settings remain unchanged. It turns out that it is impossible to maintain the room temperature always at the same level.
Automatic control valves for heating radiators include thermostatic valves and heads.
A thermostatic valve performs the same function as a regular valve, but instead of manual adjustment, the commands come from a thermostatic head (mechanical or electronic).
The heart of a mechanical thermostatic head is a capsule made of elastic material (bellows), inside which the working substance is located. The working substance can be gas, liquid or solid material. Principle of operation:
- the air heats the working substance, which expands;
- the elastic bellows increases in volume and puts pressure on the rod;
- the rod blocks the flow of coolant.
Electric thermal heads, based on their operating principle, are either normally open or normally closed. From the name it is clear in what position the curtain that blocks the flow is when the thermal head is not energized. The most modern heads are equipped with a liquid crystal screen and a programmable “brain”.
The problem with thermal heads is that they are guided by the air temperature near the radiator, since they are installed at the end. Installing a battery in a niche, installing a decorative screen, and even curtains with curtains make convection difficult. Thus, the temperature in the room will not be as high as near the thermal head. To solve this problem, thermal heads with a remote sensor were developed, which is installed at a distance from the radiator.
The heating system often includes control mechanisms and mechanisms that ensure safe operation. They are otherwise called heating system valves. With the help of these adjustment elements, the heat supply parameters change; they also ensure stable operation and perform automatic adjustment. Let's look at the valves and regulators of the heating system, since their purposes and functions differ.
Best models
Manufacturers offer customers various models of mechanical and automatic thermostats for radiators. The following devices received the greatest number of positive reviews.
Valtec corner 1⁄2
The Valtec brand has been trusted by plumbing experts for several decades. This thermostat model is an angle valve for installation in a system with a maximum temperature of up to 110 degrees and a pressure of no more than 10 bar.
Advantages of the model:
- compactness and ease of installation;
- durability (up to 30 years) and maintainability;
- combination of quality and low price.
The disadvantages of the model include:
- risk of flooding of the apartment if the pressure in the pipes rises to more than 10 bar.
Danfoss RA 2994
Model with gas filler, combined with the RA-G valve, which allows servicing single-pipe heating systems. The thermostat of this brand is designed for diameters from 15 to 25 mm. Danish-made equipment has been familiar to domestic specialists since the 70s of the last century. The devices are compatible with any heating boilers.
The clip connection of this model allows for simple and precise attachment of the thermocouple to the valve. Technical characteristics of RA type radiator thermostats comply with European standards EN 215–1 and Russian GOST 30815–2002.
Advantages of the model:
- easy installation and setup;
- possibility of precise temperature control;
- acceptable cost.
Many users consider the disadvantage:
- low maximum temperature threshold - only up to 26 degrees.
Techem HKR
Universal automatic mechanism with a large informative display.
Powered by batteries, which ensures autonomous operation. Equipped with an effective safety system and protection against lime deposits, freezing and jamming of valves. It is possible to program several modes. Users note the ease of control of the mechanism and simplicity of settings. Separately, it is worth noting the ability to set a certain temperature for several days in advance. This model has practically no drawbacks, other than the instructions being too small.
FIBARO. The Heat Controller for Apple Homekit
A smart device running Apple HomeKit to control room temperature using Bluetooth wireless technology. An advanced control algorithm and scheduled operation allows you to save up to 42% on heating bills.
The FIBARO thermostat works with 98% of radiators available on the market. The built-in battery, charged via USB, is enough for the entire heating season. Operating temperature: 0-40 degrees.
Advantages of a thermostat:
adaptation to weather and indoor conditions;- compatibility with different heating sources;
- schedule adjustment with the ability to make temporary changes;
- temperature adjustment depending on the geolocation of users;
- raising the temperature to an optimal level when motion is detected in the room;
- turning off the heating when an open window is detected;
- use voice commands to adjust temperature;
- child lock;
- the presence of an automatic descaling mode;
- Temperature measurement accuracy is up to 0.5 degrees.
Sibling Powerswitch-ZK
Smart thermostat with remote control: according to a set schedule, according to sunrise/sunset, set temperature or air humidity outside. Maintains the set temperature by controlling a conventional damper rod of a home radiator. It is possible to add a device via a gateway to a security system and other elements of a Sibling brand smart home. Operating temperature range – from 0 to + 40 degrees.
Zigbee Ya-HY368
The smart temperature controller is battery-powered, is a wireless device and is used in conjunction with the Ya-ZB1 multifunctional ZigBee gateway “I am Smart” controlled by the “I am Smart” mobile application. Easy to install, mounted in the same way as a traditional manual radiator temperature controller.
The screen and buttons provide intuitive operation. Using the Ya Smart application allows you to remotely set schedules, view and set the temperature. Equipped with built-in clock and calendar
Advantages of the model:
- schedule for a week in advance, energy saving modes;
- four independent time periods for setting temperatures throughout the day
- mode selection by pressing one button;
- control of several thermostats installed in different places (for example, in a country house, administrative buildings or office center) from one mobile application;
- control via the Internet without a subscription fee.
- local (from the controller display) and remote (from a mobile application) mode of monitoring and setting the temperature of the rooms or heated floor;
- the ability to work without connecting to ZigBee and the Internet; in the absence of a Wi-Fi network or the Internet, the controller operates according to the specified parameters. The schedule is stored in the thermostat's memory;
- creating various scenarios together with other “I am Smart” devices;
- automatic calibration and regular self-testing prevent valve sticking and lime deposits;
- safety: frost protection, child protection, automatic protection against valve clogging through independent actions without human intervention.
- automatic switching of heating to economical mode in the house when leaving home (based on geolocation or the presence of a phone in the home Wi-Fi network);
- setting a schedule for setting different operating temperatures throughout the day and week.
The only drawback is the high price.
Three way heating valve
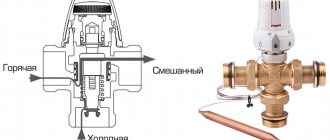
Typically, boiler automation cannot meet the need for water at different temperatures for several circuits of the heating system. A three-way thermostatic mixing valve of the heating system comes to the rescue, which maintains the necessary thermal parameters of the coolant in the circuits of the heating system, as well as in the small circuit of the system. The valve looks like a simple tee, the metal is bronze or brass. An adjusting washer is installed at the top of this tee, under which there is material sensitive to temperature changes. And if necessary, it presses on the working rod coming out of the housing. The main task of the valve is based on maintaining the temperature of the coolant at the outlet within specified limits by adding cold or hot water . During unsuitable temperature changes, the external valve actuator presses on the stem. Next, the cone leaves the saddle and a passage opens between all channels. During operation, the three-way valve is controlled according to temperature by an external actuator.
Control valves for radiators
To manually regulate the operation of heating devices, special valves are used. Such taps are sold with straight or angular connections. The procedure for regulating heating batteries using these devices manually is as follows.
When the valve is turned, the shut-off cone lowers or rises. In the closed position, the coolant flow is completely blocked. Moving up or down, the cone regulates to a greater or lesser extent the amount of circulating water.
Due to this operating principle, such valves are also called “mechanical temperature controllers”. They are installed on batteries with threads, and connected to pipes with fittings, most often of the crimp type.
The control valve used for heating devices has the following advantages:
- the device is reliable, it is not dangerous from blockages and fine abrasive particles present in the coolant - this applies exclusively to high-quality products in which the valve cone is made of metal and carefully processed;
- the product has an affordable price.
Control valves also have disadvantages - each time you use the device, its position has to be changed manually and for this reason it is quite problematic to maintain a stable temperature regime.
For those who are not satisfied with this procedure and are thinking about how to regulate the temperature of the radiator using another method, the use of automatic products that allow them to control the degree of heating of the radiators is more suitable.
Heating check valve
A complex heating system contains a fairly large number of auxiliary elements, the task of which is to ensure reliability and uninterrupted operation. One of these elements is the heating system check valve. A check valve is installed to prevent flow in the opposite direction . Its elements have very high hydraulic resistance. Due to this circumstance, there are restrictions on the use of check valves in a heating system with natural circulation. There is too little pressure in such a system. At minimum pressure, it is necessary to install gravity valves with a butterfly valve; some of them can operate at a pressure of 0.001 bar. The main part of the check valve is the spring, used in almost all models. It is the spring that closes the shutter when normal parameters change. This is the principle of operation of a check valve.
It is necessary to take into account the operating parameters in a particular heating system. Therefore, select a heating system valve that has the required spring elasticity. Shut-off valves used in heating systems are usually made of the following materials: steel; brass; stainless steel; gray cast iron. Check valves are divided into the following types: disc valves; petal; ball; bivalve. These types of valves are distinguished by a locking device.
Adjusting batteries using a thermostat
To ensure constant maintenance of the desired temperature in the room, thermostats for radiators are used. These devices have other names - thermostatic valve, thermostatic valve, etc. There are many names, but they all refer to one product.
The thermal valve and thermal valve are the lower part of the device, and the thermal head and thermoelement are the upper part. Most of these products operate without power sources. The exception is models equipped with a digital screen, in which batteries are placed in the thermostatic head. There is no need to change them often, since the current consumption is negligible.
The radiator thermostat consists of several components:
- thermostatic valve, which is called “housing”, “thermal valve”, “thermal valve”;
- thermostatic head or “thermostatic element”, “thermoelement”, “thermal head”.
The body (valve) is made of metal, usually bronze or brass. Externally, its design resembles a manual valve. Many manufacturers make the lower part of the radiator thermostat unified. This means that different types of heads can be mounted on one housing, regardless of their manufacturer.
Thus, it is possible to install a thermoelement with different controls on the thermal valve - manual, mechanical or automatic, which is very convenient. If you want to change the adjustment method, there is no need to buy the entire device, you just need to install a different thermostatic element.
Automatic regulators differ in the principle of influencing the locking mechanism. In a manual device, its position is changed by turning the handle. As for automatic models, they usually have a siphon that puts pressure on a spring-loaded mechanism. In electronic products, the workflow is controlled by a processor.
The bellows is the main element of the thermoelement (thermal head). It looks like a small sealed cylinder containing liquid or gas inside. Both of these substances have a common property - their volume depends on temperature. When heated, gas and liquid begin to significantly increase in volume and thereby stretch the cylinder.
The bellows, when pressed on the spring, blocks the flow of coolant. When the volume of the working medium decreases as it cools, the spring rises and thereby the fluid flow increases, and the radiator heats up again. Thanks to the use of such a device, depending on its calibration, the set temperature can be maintained with great accuracy - up to one degree.
Before using a radiator, anyone who decides to purchase a thermostat for it must decide what type of temperature control it should have:
- manual;
- auto;
- with built-in or remote sensor.
Heating control (shut-off and control) valves
Regulating and shut-off and control heating valves systematically change the flow of coolant, from maximum to minimum , with the valve open and closed. Shut-off or shut-off valves control the coolant discretely when the valve is in the fully open or fully closed position. A control valve consists of three main blocks: the body, the throttle assembly, and the valve actuator. The closing and regulating element of the valve is the throttle assembly. When choosing a sleeve, seat, or plunger, you should pay attention to the operating conditions of the valve. The medium and its temperature, the presence of impurities, and throughput are taken into account. The main and important importance in the operation of the valve is the correct direction of supply of the working medium. It is usually marked with an arrow on the working surface of the case.
Place and role of mixing valves in the heating system "warm floors"
The main task that consumers have to face when deciding to install heated floors in their home is to achieve the required coolant temperature. For radiators, water at a temperature of 75 0 C is quite acceptable, which cannot be said about pipes that are laid in the thickness of a concrete screed.
Important! Excessive heating of the concrete screed leads to a deterioration in the temperature balance inside the heated room. At high temperatures, flooring (in most cases wood-based) quickly loses its aesthetic and technological qualities, becoming unusable.
In accordance with sanitary standards, the normal heating temperature of heated floors should not exceed 26 0 C. Then the middle layers of the air mass inside the room are heated to comfortable values of 20-22 0 C. In order to obtain such temperature parameters, the water entering the loops the water circuit must be heated to 50 0 C. Slightly less than 50% of the thermal energy of the heated water is spent on heating the layered cake of the heated floor. Taking into account the thickness of the concrete layer, material and type of floor covering, the temperature on the floor surface decreases.
A mixing unit, which is a set of interconnected instruments and devices, helps to achieve a significant reduction in the temperature of the boiler water at the entrance to the heating water circuits. One of the main roles in the operation of the mixer is played by the thermomixing valve, which mixes water for the heated floor. Thanks to this small device, two streams of water are mixed, cold and hot, so that the output is water at the required temperature. Valves installed in mixing units are of two types, three-way and two-way. Each type of crane performs its own tasks and functions determined by the technological process. Which device is best to use for your heated floors? What is behind the choice of the type of mixing and control device?
Thermostatic valve
In modern realities, a thermostatic valve is a prerequisite for modern and reliable equipment in a heating system. The valve temperature is automatically adjusted. The operation of a heating system mixing valve for radiators is to limit the supply level to an individual heating radiator. The valve stem makes movements to open and close the hole. Through this hole, coolant enters the radiator. When the valve with a thermostatic head heats up, the inlet opening is closed, as a result of which the coolant flow rate decreases. The thermostatic valve constantly changes its position. And an important factor is the quality of the materials on which this product is made. The product may fail due to sticking of the rod, as well as significant corrosion and breakthrough of sealing materials. But even if the thermostatic valve fails, you can extend its service life by replacing the thermostatic element.
Heating system valves with thermal heads differ depending on the shape and type of supply to the heating system. They can be angular when connected to radiators from the floor, or they can be straight, which connect the pipes to the battery relative to the wall surface. Axial, mainly when connecting pipes from the wall to the battery. When connecting batteries sideways, a special kit is required. It uses thermostatic heads and valves. Batteries that come with a bottom connection are obviously equipped with valve-type inserts.
Bypass device and its functions
In winter, it is not allowed to close the common riser, with the exception of emergency situations. The presence of a bypass allows you to carry out repairs without turning off the heating system of your neighbors. The device is made of pipes with a smaller diameter than the supply and discharge lines. Two ball valves allow you to properly shut off the battery even if it’s hot, directing the water circulation through the bypass.
When replacing the radiator, the water is shut off, and after the work is completed, it opens again. If the room is hot, the bypass again allows you to temporarily shut down the system: hot water stops flowing into the battery and the room is cooled. But it is better to install thermostatic valves to regulate the temperature, maintaining a normal temperature in the room.
Using such a device, the radiator can be properly disconnected from the system at any time if it is necessary to perform painting, washing, replacing batteries, as well as when changing gaskets and nipples without blocking the risers.
Correct Bypass Installation
The bypass functions, depending on the type of heating system, are as follows:
- Energy carrier adjustment. When the room temperature is higher than normal, the thermostat reduces the supply of hot water, which negatively affects the operation of the entire system. This device is used to return coolant that did not enter the battery into the system.
- Emergency adjustment of coolant circulation in a system with an electric pump. When a power failure occurs, a bypass with a valve closes the hot water supply tap to the pump through the bypass pipe, at which time the valve opens and the coolant is directed through the central pipe. In this simple way, the system goes into a state of natural circulation without the participation of a pump.
- Reanimation of a single-pipe system. It works quite effectively: apartments are warm, even hot. The bypass also helps out in this situation, allowing you to reduce the supply of hot water, thus acting as a thermostat.
Thermostat on the radiator
The bypass must be installed next to the radiator. It is recommended to make the bypass pipe directly on site during installation using a welding machine. You can also use ready-made equipment on threaded connections. The control valve or radiator thermostat must be located between the radiator inlet and the bypass.
The supply side is equipped with a valve with a thermal head.
Pressure regulator
The operation of the batteries and the pump is disrupted due to high or low pressure levels. Correct control of the heating system will help to avoid this negative factor. The pressure in the system plays a significant role, it ensures that water gets into the pipes and radiators. Heat loss will be reduced if the pressure is standard and maintained. This is where water pressure regulators come to the rescue. Their mission is primarily to protect the system from too much pressure . The operating principle of this device is based on the fact that the heating system valve located in the regulator works as a force equalizer. Depending on the type of pressure, regulators are classified into: statistical, dynamic. It is necessary to select a pressure regulator based on throughput. This is the ability to pass the required volume of coolant, in the presence of the required constant pressure drop.
How to remove a thermostat from a battery - nuances of the process
In some cases, it becomes necessary to remove the thermostat from the heating radiator.
For what? If the riser passing through your apartment heats up normally, but the radiators remain completely cold, then first you should try to bleed out the air (perhaps it is because of the airlock that this problem arose). If bleeding the air does not help, there is nothing left to do but remove the thermostat from the battery: there is a high probability that the problem lies with it.
The fact is that if the thermostat has an electronic head, then it carries out “decalcification” once a week. But thermostats with a regular head cannot perform this procedure, and, as a result of contamination of the water used as a coolant, the valve gradually becomes “overgrown” with scale and sediment. Over time, it simply stops opening normally.
Heating bypass valve
To relieve the working medium, use the bypass valve of the heating system thermostat, which operates in the return direction when the pressure increases significantly . As a rule, the pressure increases due to the achievement of the maximum temperature set manually, the supply of coolant to the radiator decreases, as a result of which the pressure increases. Heating system bypass valves are basically designed to ensure a stable difference between the return and supply pipes. When the heat load decreases, the thermostatic valves close, resulting in a pressure difference between the pipelines. As a result of using a bypass valve, the load on the pump is reduced, the return temperature increases, and the boiler is protected from corrosion. The scope of application of the heating system bypass valve is quite wide; it is also used to prevent noise generation of thermostats. Bypass valves are installed not only on an unregulated pump, but also on riser jumpers.
Where is the device installed?
The operation of the device is influenced by 4 factors:
- exposure to sunlight on the body;
- temperature outside the room;
- air circulation in the room;
- additional heating sources.
In apartment buildings, thermostats are placed high up, near the roof , as heat rises. This helps balance the temperature differences in the building. In single-story ones, on the contrary, they are mounted near the heater.
Photo 2. Electronic thermostat installed on the heating radiator. The device is connected to the coolant supply circuit.
It is considered most favorable to place a highly sensitive device on the feed. This principle has a limitation: the strapping elements should not be covered with anything. The thermostat is placed in front of the battery, after the branch from the main line. This allows it to regulate the temperature of the room without affecting the neighbors below.
Important! Otherwise, you must use a device with a remote sensor.
Safety valves
Any boiler equipment is a source of danger. Boilers are considered explosive because they have a water jacket, i.e. pressure vessel. One of the most reliable and widespread safety devices that reduces the danger to a minimum is the safety valve of the heating system. The installation of this device is due to the protection of heating systems from excess pressure . Often this pressure occurs as a result of boiling water in the boiler. The safety valve is installed on the supply pipe, as close to the boiler as possible. The valve has a fairly simple design. The body is made of good quality brass. The main working element of the valve is the spring. The spring, in turn, acts on the membrane, which closes the passage to the outside. The membrane is made of polymer materials, the spring is made of steel. When choosing a safety valve, it should be taken into account that full opening occurs when the pressure in the heating system increases above the value by 10%, and full closure occurs when the pressure drops below the response value by 20%. Due to these characteristics, it is necessary to select a valve with a response pressure higher than 20-30% of the actual one.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of thermostatic valves:
- does not require special maintenance;
- compact dimensions;
- aesthetic appearance;
- automatic adjustment of water temperature in the pipeline;
- ensuring a comfortable microclimate in the home;
- the ability to set the desired temperature in each individual room.
Flaws:
- complexity of setting up the device;
- Thermostat failure can occur under the influence of a draft or a nearby stove;
- dependence on hot and cold water supply.
Balancing valve
The balancing valve of the heating system is intended to regulate the coolant passing through . Liquid consumption depends on pressure. The higher the pressure, the more fluid is consumed. This device is installed on risers. A balanced system ensures continuous operation. The manual valve is used as a diaphragm, and the automatic valve maintains pressure and consumption in the risers. A manual balancing valve can shut off the system. The design is a valve type device. Manual valves can be installed in conjunction with shut-off valves.
Definitions
Let's start getting acquainted with the design of thermostatic equipment, moving from simple concepts to more complex ones.
Thermostat
This is a general name for all devices capable of maintaining a stable temperature of any environment under changing external conditions.
In relation to heating, a thermostat is understood as a control valve capable of ensuring a constant air temperature in the room when changing:
- weather conditions and, accordingly, heat loss through the building envelope;
- coolant temperature.
Thermostatic valve
The thermostatic radiator valve solves the problem of stabilizing the temperature in the room in the simplest and most obvious way - by limiting the flow of coolant through the heating device. The less water or antifreeze passes through the battery per unit of time, the colder it is; the more, the more its heat transfer increases.
What is the working principle of a thermostatic radiator valve? The vast majority of devices in the lower and middle price categories use the expansion of liquids and gases when heated and the reduction of their volume when cooled.
When the contents of the bellows heat up, it lengthens and forces the valve against the seat, thereby limiting the coolant flow. Some time passes, and due to the decreased heat output of the heating device, the air in the room becomes colder. Compression of the working medium leads to a decrease in the length of the bellows; the opened valve allows the coolant to warm up the battery again.
A more complex and expensive version of the thermostatic valve is an electric drive with digital control, which is carried out based on the analysis of data from a built-in or remote thermocouple.
Thermal head
Strictly speaking, a thermostatic head for radiators is a simple device for manually adjusting the valve position of a thermostatic valve. By rotating its handle, you can set the target temperature in the room, which will then be maintained automatically.
Thermostatic kit
A typical heating device piping includes a certain gentleman's minimum, which allows you to flexibly regulate its heat output. The set includes:
In some cases, the valve on one of the threads can be replaced with a check valve that stops the supply of coolant during counterflow (read: water is being discharged from the battery), or an additional throttle. In this case, the throttle provides preliminary balancing of the heating device (adjusting the permeability to equalize the temperatures of near and far heating devices).
A thermostatic kit is a set of shut-off valves from one manufacturer, including at least a thermostatic valve and a thermal head; More often, the kit additionally includes a balancing throttle.
In addition, the package can be supplemented with:
- radiator plugs;
- American ones for quick-connection of the radiator (they can be a separate element of the fittings or be part of thermostatic valves);
- Brackets for mounting the battery.
The price of a kit from a decent manufacturer starts from about 1000 rubles; the upper limit is 3 - 5 thousand, depending on the brand level and configuration.
Flow regulator
Having installed energy metering devices, the question naturally arises of how you can regulate and control the supply of coolant, limit or add its flow. For this purpose, there are all kinds of automatic regulators, the use of which allows you to save money; they operate from outside air temperature sensors and return pipeline sensors. Another advantage of temperature controllers is that they control the temperature directly at the radiator installation site, unlike other devices. This advantage gives priority in obtaining a uniform temperature background for a comfortable stay in the room. The regulator will prevent overheating of the air in the room, which sensors on centralized automation cannot always track. It is possible to adjust the temperature for each room separately. Sometimes, when solving the adjustment issue, ordinary taps are installed. Of course, this solution reduces financial costs, but deprives a number of useful advantages. The faucet has limited functionality to open and close. There is a danger of stopping or airing the riser. By adjusting the heating using taps it is impossible to achieve the required temperature. Using automatic regulators, you can adjust the system accurately and efficiently.
Purpose of installation and operating principle
Properly selected and correctly adjusted thermostatic valves help save money on energy costs and maintain a comfortable room temperature. Modern boilers can be equipped with similar devices. But in this case it will change, heating all the rooms at the same time.
Unlike sensors on boilers, thermostats allow you to set the required level of radiator heating for each room. This mechanism is indispensable for centralized systems.
The thermostatic valve regulates the amount of coolant entering the battery depending on the ambient temperature. The mechanism works to lower temperatures, but is not capable of increasing them. The heating is limited automatically; it is enough to adjust the mechanism after installation.