Normal pressure in a closed heating system is very important. Firstly, this is a warm room in winter, and secondly, the normal operation of all components of the boiler. But the needle is not always in the range we need, and there can be many reasons for this. High and low pressure in the heating system leads to blocking of the pump and the absence of warm radiators. Let's talk in more detail about how many atmospheres our pipes should have and how to fix common problems.
Some general information
Even at the design stage of the heating system, pressure gauges are installed in different places. This is necessary in order to control blood pressure. When the device detects a deviation from the norm, it is necessary to take some action; a little later we will talk about what to do in a specific situation. If no measures are taken, the heating efficiency drops and the service life of the same boiler is reduced. Many people know that the most detrimental effect on closed systems is caused by water hammer, for damping which expansion tanks are provided. So, before each heating season, it is advisable to check the system for weak points. This is done quite simply. You need to create excess pressure and see where it shows up.
Low and high pressure in the system
Often, the pressure drop in the heating system is due to several factors. Firstly, this is a coolant leak, which is the most common reason for a decrease in the number of atmospheres. Leaks are most often located at the joints of parts. If it is not there, then most likely the problem is in the pump. Scale in the heat exchanger is another reason for low pressure in the system. The same applies to physical wear and tear of the heating element. But an increase in pressure occurs due to the formation of an air lock. The cause may also be difficulty in the movement of the carrier through the pipes due to obstruction in the filter or sump. Sometimes, due to automation failures, the system is overcharged, in which case the pressure also increases.
How to relieve pressure in the boiler if it is high
If the pressure inside the boiler has increased, then there are several methods. How can I get it back to normal?
- Drain the water from the equipment. This is one of the reasons why pressure readings can go off scale. This is only possible if the pump is operating correctly to specification. To solve this problem, you must first turn off the boiler so that it becomes completely cold. Find the place where the water is draining and select a vessel to collect it. Carefully open the drain and pour the liquid out into a plastic container. This must be done until the needle on the pressure gauge reaches the desired value (usually the green zone).
- Bleed the radiators. Another reason for too high pressure is an air lock in the radiator. To solve this problem. You must also first turn off the boiler and let it cool. Find a hole from which air is removed, and also prepare a container to collect water. Next, you need to carefully open the outlet valve - water and air bubbles will begin to leak out. After the process has stabilized, the valve must be closed and proceed to checking the next radiators. After all these procedures, the pressure sensor should be in the green sector. After each drain, be sure to close the hole tightly.
In radiators, air accumulates from a pump, which generates air flows. It is necessary to pay attention that if such pumping is necessary too often (more than once a year), then you should call a specialist to thoroughly check everything.
What to do if the pressure in the boiler is low
If too little pressure develops in the boiler, then first of all you need to check the safety valve. If it is already connected to the system, then when the pressure increases, it may not be tightly closed. This causes leaks. Also, the safety valve can wear out over time, so if a leak occurs, the damaged part must be replaced. After troubleshooting, you can continue using the equipment.
You can also take a few simple steps to restore your blood pressure readings.
If you turn the red part, the red valve will become disconnected, which could allow liquid to leak into the inside. If you turn it further, it will fall into place on its own. These actions will increase and stabilize the pressure in the system. If nothing works and the differences are too noticeable, then you need to replace the part with a new one.
Sometimes it is not possible to find the place of the water leak - in this case, most often the water flows under the floor. However, there are situations when the floor covering is solid - you won’t be able to fix the problem yourself, but some specialized companies can help raise the floor and fix this problem.
How to correct the situation when there is a difference?
Everything here is extremely simple. First, you need to look at the pressure gauge, which has several characteristic zones. If the arrow is in the green, then everything is fine, but if it is noticed that the pressure in the heating system is dropping, then the indicator will be in the white zone. There is also a red one, it signals an increase. In most cases, you can handle it on your own. First you need to find two valves. One of them is used for injection, the second is used for bleeding media from the system. Then everything is simple and clear. If there is a shortage of media in the system, it is necessary to open the discharge valve and monitor the pressure gauge installed on the boiler. When the arrow reaches the required value, close the valve. If bleeding is needed, everything is done in the same way with the only difference being that you need to take with you a vessel into which the water from the system will be drained. When the pressure gauge needle shows normal, tighten the valve. Often this is how the pressure drop in the heating system is “treated”. Now let's move on.
A few general but important notes
In order to be able to talk about the correct operation of the heating system and its setup and adjustment, you first need to make sure that your country house heating system is correctly designed, installed, and the heating equipment is correctly selected.
This approach is dictated by the fact that heating systems in private houses are often “sculpted” by teams of “shabashniks”. But how, what, and on what basis they do it often remains a big secret for homeowners. Therefore, I am forced to draw the reader’s attention to several, in general, truisms, without understanding of which it is not serious to talk about setting and adjustment.
Stage No. 1
The first thing you need to make sure is that the parameters of the boilers correspond to the parameters of the heating system. The arithmetic here is simple. For every kilowatt of boiler power there should be approximately 13 liters of water (coolant) in the heating system. Moreover, deviations in a larger direction are not as critical as in a smaller direction. In this case, by and large, it does not matter who the manufacturer of the boiler is or even what fuel it runs on.
The easiest and most reliable way to determine the volume of water in the heating system is to view the water meter readings by pouring liquid into the system (during the first test fire, when flushing the system). In addition, you can calculate the volume of water in the system. To do this, it is necessary to take into account its volume in the main devices: in the heating boiler, in heating radiators and in pipes. For example, during my first test fire, the water meter showed that 295 liters were poured into the system.
Thus, the specific volume of water in the system in my case was: 295/20 = 14.75 l/kW, which slightly exceeds the required value. But more is not less. Therefore, I did not change anything, and later regretted it.
If the volume of water is too small in relation to the power of the boiler used, it is advisable to adjust the volume of the coolant in accordance with the power of the boiler. The easiest way is to add the number of heating devices to the system.
When determining the boiler power, you need to take into account possible nuances and surprises. So, for example, I bought my boiler as a 16-kilowatt boiler.
When inspecting the equipment and documentation at home, it turned out that the boiler was equipped with a 20 kW gas burner. Accordingly, the boiler power is not 16, but 20 kW.
Owners of imported boilers may be in for another surprise. For example, a boiler with a power of 27 kW (at a nominal gas pressure of 18-20 mbar) in our gas networks at a pressure of 13 mbar will actually produce a little more than 20 kW. In winter, when the pressure drops even lower, the performance of the gas boiler will decrease even more.
After we have made sure that the volume of coolant corresponds to the power of the boiler, and have clarified the volume of water in the system, we can proceed to the next stage.
What should be the operating pressure in the heating system?
But to answer this question in a nutshell is quite simple. Much depends on what kind of house you live in. For example, for autonomous heating of a private house or apartment, 0.7-1.5 Atm is often considered normal. But again, these are approximate figures, since one boiler is designed to operate in a wider range, for example, 0.5-2.0 Atm, and the other in a smaller one. This must be looked at in the passport of your boiler. If there is none, stick to the golden mean - 1.5 Atm. The situation is completely different in those houses that are connected to central heating. In this case, it is necessary to be guided by the number of floors. In 9-story buildings, the ideal pressure is 5-7 Atm, and in high-rise buildings - 7-10 Atm. As for the pressure under which the carrier is supplied to buildings, most often it is 12 Atm. You can reduce the pressure using pressure regulators, and increase it by installing a circulation pump. The last option is extremely relevant for the upper floors of high-rise buildings.
Static and dynamic pressure
If we explain in simple terms the role of static pressure in a closed heating system, we can put it something like this: this is the force with which the liquid presses on the radiator and pipeline, depending on the height. So, for every 10 meters there is +1 Atm. But this applies only to natural circulation. There is also dynamic pressure, which is characterized by the pressure on the pipeline and radiators while driving. It is worth noting that when installing a closed heating system with a circulation pump, static and dynamic pressure are added, taking into account the characteristics of the equipment. Thus, a cast iron battery is designed to operate at 0.6 MPa.
Terminology issues
Network pressure is divided into two components:
- Static pressure. This component depends on the height of the column of water or other coolant in the pipe or container. Static pressure exists even if the working medium is at rest.
- Dynamic pressure. It is a force that acts on the internal surfaces of the system when water or other medium moves.
The concept of maximum operating pressure is distinguished. This is the maximum permissible value, exceeding which can lead to the destruction of individual network elements.
Pipe diameter and degree of wear
It is necessary to remember that the size of the pipe must also be taken into account. Often, residents set the diameter they need, which is almost always slightly larger than the standard sizes. This leads to the fact that the pressure in the system decreases slightly, which is due to the large amount of coolant that will fit into the system. Do not forget that in corner rooms the pressure in the pipes is always less, since this is the most remote point of the pipeline. The degree of wear of pipes and radiators also influences the pressure in the heating system of the house. As practice shows, the older the batteries, the worse. Of course, not everyone can change them every 5-10 years, and it is not advisable to do this, but it doesn’t hurt to carry out preventive maintenance from time to time. If you are moving to a new place of residence and you know that the heating system there is old, then it is better to change it immediately, so you will avoid many troubles.
Pressure surges
A decrease in pressure may be due to the following reasons:
High pressure is more dangerous for the pipeline than low pressure
- a large amount of scale has formed in the pipelines (relevant for regions where the water is hard - the Moscow region, by the way, also applies to them);
- small cracks in the heat pipes that could have formed due to wear or even a factory defect;
- destruction of the heat exchanger itself, which failed due to water hammer;
- expansion chamber is damaged or deformed.
As a matter of fact, such problems, with the exception of problems with the heat exchanger, can be easily eliminated even with your own hands
You can, for example, install an expansion regulator, but do not forget about such an important detail as pressure testing: it must be carried out before starting the entire system! There are many cases when in Moscow, for example, management companies did not go through this procedure before putting a house into operation, and the residents then literally froze from the cold, having paid tens of millions of rubles for housing
True, this applies mainly to high-rise buildings, not private houses.
There are many cases where in Moscow, for example, management companies did not go through this procedure before putting a house into operation, and the residents then literally froze from the cold, having paid tens of millions of rubles for housing. True, this applies mainly to high-rise buildings, and not to private houses.
High blood pressure can be due to the following reasons:
- the movement of water or antifreeze has stopped (here you must check the regulator, as well as the expansion tank and reservoir);
- constant replenishment of coolant is carried out, which can be caused either by a failure of the automation or by incorrect actions of the owner of the house;
- a valve or safety valve was closed along the perimeter of the coolant movement;
- a plug of air has formed (very often this happens when the water circulation system is natural, this is simply the scourge of such systems);
- The dirt trap or filter element is heavily contaminated.
In general, problems with excess pressure are much more difficult to solve.
About Leak Testing
It is imperative to check the system for leaks. This is done to ensure that the heating operation is efficient and does not have failures. In multi-storey buildings with central heating, the cold water test is most often used. In this case, if the water pressure in the heating system drops by more than 0.06 MPa in 30 minutes or 0.02 MPa is lost in 120 minutes, it is necessary to look for places where there are gusts. If the indicators do not go beyond the norm, then you can start the system and begin the heating season. Hot water testing is carried out immediately before the heating season. In this case, the media is supplied under pressure, which is the maximum for the equipment.
A little theory
In order to clearly understand what the working pressure is in the heating system of a private house or high-rise building and what it consists of, we will provide some theoretical information. So, the working (total) pressure is the sum:
- static (gauge) coolant pressure;
- dynamic pressure causing its movement.
Static pressure refers to the pressure of the water column and the expansion of water as a result of its heating. If a heating system with a highest point at a level of 5 m is filled with coolant, then at the lowest point a pressure of 0.5 Bar (5 m of water column) will arise. As a rule, heating equipment is located below, that is, a boiler, whose water jacket takes on this load. An exception is the water pressure in the heating system of an apartment building with a boiler room located on the roof; here the lowest part of the pipeline network bears the greatest load.
Now let’s heat the coolant, which is at rest. Depending on the heating temperature, the volume of water will increase in accordance with the table:
When the heating system is open, some of the liquid will flow freely into the atmospheric expansion tank and there will be no increase in pressure in the network. With a closed circuit, the membrane container will also accept part of the coolant, but the pressure in the pipes will increase. The highest pressure will arise if a circulation pump is used in the network, then the dynamic pressure developed by the unit will be added to the static pressure. The energy of this pressure is spent on forcing water to circulate and overcoming friction against the pipe walls and local resistance.
Important. For setting and monitoring, pressure is always measured at the lowest point, near the boiler, where it is highest. It is for this purpose that pressure gauges are installed in the boiler room.
Why is excess pressure necessary?
Let's imagine a heating system with an open expansion tank. In its upper part, the coolant is under a pressure of about 100 kPa or 10.2 m of water column. In contrast to the upper limit of the filling, which is under normal atmospheric pressure, in the lower part the coolant is compressed even more, the difference is exactly equal to the height difference and is expressed in meters of water column. Changes in atmospheric pressure and altitude above sea level, as well as coolant density, can make their own adjustments. However, in practice such small errors are neglected.
During normal operation of such a system, a significant volume of water is heated inside the boiler heat exchanger. Heating is accompanied by expansion, due to which a portion of water with a higher temperature exerts additional pressure on the adjacent volume of coolant. In this case, a liquid with a lower density rushes upward: the pressure force of the heated coolant is summed up with the pressure of the atmosphere and the internal pressure of the system, which allows the coolant to be pushed along a closed circuit. The higher the speed of movement of the coolant, the more pronounced the convection effect and vice versa.
What happens in so-called closed heating systems? In them, the coolant is isolated from the atmosphere, as a result of which at the upper boundary of the filling the pressure is practically zero, and at the lowest point it is equal to the actual height of the liquid column. An increase in pressure due to water expansion does not always allow one to overcome the hydrodynamic resistance of the system, because during expansion, water is forced in both directions, and its downward expansion is not compensated by additional pressure.
Any coolant tends to increase in volume during heating. In a closed heating system this clearly leads to an increase in pressure
It is possible to launch such a system only if a large amount of coolant is quickly heated, which is impossible in modern heating systems characterized by small displacement and nominal pipe diameter. Thus, the excess pressure in the system serves as a kind of replacement for atmospheric pressure, significantly facilitating natural convection and the operation of forced circulation devices.
Of course, the pressure in the heating system does not have to be equivalent at different points. The highest values are recorded in the heat exchanger and at the return pipe of the boiler; a slightly lower pressure can be recorded at the inlet of the circulation pump and the smallest pressure can be recorded at the most remote and high section of the supply line. One of the main tasks of a heating engineer is to ensure excess pressure inside the heating system and ensure that its various components maintain a differential that fits within the established standards.
Pressure in the system of a multi-storey building
Systems in high-rise buildings are characterized by high static coolant pressure. It increases with the height of the house, as the column of water in the pipes becomes higher. Accordingly, to overcome it, powerful pumps with a dry rotor are used. For example, the pressure in the heating system of a multi-storey building, whose diagram is shown below, must be at least 5 Bar.
It will take about 3 Bar to overcome the rise and about 2 more Bar with a reserve for friction with local resistance. On pressure gauges installed in basement heating units of high-rise buildings, you can see values from 4 to 7 bar. In general, in a central heating system, or more precisely, in the supply line, a pressure of 12-15 bar is often maintained. It all depends on the length of the route to the nearest thermal power plant.
Conclusion. With centralized heat supply in an apartment, measuring, much less trying to reduce, the maximum pressure in the system is pointless. Even if you take the readings of the pressure gauge at the heating point, it will not give anything; in apartments at different heights they will still differ. All that an apartment owner can worry about is the efficiency and service life of the radiators. It is better not to install cast iron batteries in high-rise buildings; they can only withstand about 6 bar.
How is the heating system of an apartment building balanced?
We perform an audit of the heating system with subsequent restoration of heat supply parameters.
One of the main problems when balancing is the lack of exact flow rates for the risers; only data on the total flow rate for the entire apartment building is known. Because the houses were built a long time ago, it is possible that residents will replace heating radiators and make significant changes to the heat supply scheme of the apartment buildings, which will affect consumption.
The result of balancing should be a temperature of the same value at the control points. The return pipeline of each riser should be selected as control points. By the temperature of the return riser, you can understand what the temperature of the battery of the last consumer is.
Set the required flow rate for each heating riser, so that the return coolant temperature is in the range of +/-2 C.
The temperature on the radiators is different as a result
- Slow circulation of coolant through the riser.
- Large heat removal from heat exchange devices.
Reasons affecting the slowdown of circulation in the heating system riser:
- Changing the diameter of the pipe on the riser to a smaller value (narrowing the diameter of the pipeline). Installation of polypropylene (PP) and metal-plastic pipes instead of metal pipes.
- The use of pipeline fittings with high hydraulic resistance. Metal-plastic pipe fittings have a high coefficient of hydraulic resistance due to their small internal diameter.
- Dismantled bypass from the batteries. After dismantling the bypass, the calculated total diameter decreases (water flows not through two pipes, but through one), and the hydraulic resistance of the pipeline section increases accordingly.
Reasons for increased heat removal by heat exchangers:
- Connection of non-standard heat exchange equipment. Using coolant to heat underfloor heating.
- Increasing the number of heat exchange equipment. Installation of additional radiators and increasing the number of battery sections. Installation of heating devices in rooms not designed by the project for heating from the general building heating system - balconies and loggias.
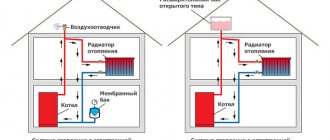
Pressure in the heating system of a private house
Everything is clear when an open system is installed in the house, communicating with the atmosphere through an expansion tank. Even if a circulation pump is used, the pressure in the expansion tank will be identical to atmospheric pressure, and the pressure gauge will show 0 bar. In the pipeline immediately after the pump, the pressure will be equal to the pressure that this unit can develop.
Everything is more complicated if a pressurized (closed) heating system is used. The static component in it is artificially increased in order to increase operating efficiency and prevent air from entering the coolant. In order not to go deeply into the theory, we would like to immediately offer a simplified method for calculating pressure in a closed system. You need to take the height difference between the lowest and highest points of the heating network in meters and multiply it by 0.1. Let's get the static pressure in Bars, and then add another 0.5 Bar to it, this will be the theoretically required pressure in the system.
In real life, an addition of 0.5 Bar may not be enough. Therefore, it is generally accepted that in a closed system with a cold coolant, the pressure should be 1.5 Bar, then during operation it will increase to 1.8-2 Bar.
Important. The higher the pressure can be raised, the better for heating operation. But its value is limited by the technical characteristics of the boiler equipment. Most household heat generators are designed for a maximum pressure of 3 Bar, but there are also “weaker” units with values of 2 and even 1.6 Bar. Therefore, when tuning, it is necessary to achieve 0.5 Bar lower in a cold system than indicated in the boiler passport. Otherwise, the pressure relief valve will constantly operate.
What to do if the CO pressure is unstable
During the heating season, pressure changes in the heating system can be observed. They are tracked by a pressure gauge. If an automated boiler is used, it often has a built-in pressure gauge, and its indicator is located on the body. In other cases, they are placed after the boiler (at the supply in the safety group) or in front of it - in a straight section directly in front of the boiler. If the system does not have a pressure gauge, it can be installed in any area by connecting it to any available free inlet using a piece of pipe and fittings.
To relieve pressure in the heating system and drain the coolant, a shut-off valve is installed at the lowest point of the system (often at the bottom of the last one in the radiator branch). In the normal position it is closed. If the coolant needs to be drained, it is opened. You can drain the liquid into a nearby container or, through a hose, into the nearest sewer pipe.
Make-up line - required for the heating system of a private house
To fill the system there is another inlet with a shut-off valve installed. In some cases, it is installed in boilers, but there are also systems that provide a separate input for pumping coolant. If the coolant is water, this input is connected to the water supply (cold water). If you need to pump in another coolant (for example, antifreeze), you need a special device.
The pressure drops
Sometimes, after starting the system (for the first time or after flushing/repair), the pressure in the heating system of a private home constantly drops. This process may be almost unnoticeable, but after a week or two it becomes significantly lower (at the same coolant temperature). Sometimes the decrease is observed within several hours. The most common reason is a coolant leak, that is, leaks in pipes, radiators, connections, etc.
To get rid of this problem, you need to check all connections. Before checking, we warm up the system to 80 °C, increase the pressure to 2.5 Atm (for a closed system), and then turn off the boiler. Those. Leak testing is carried out while the system is cooling. First, go over all possible leaks with a clean, dry cloth or piece of toilet paper (the heating is on and running under pressure). If, when checking one of the connections, the napkin becomes wet or even a small stain appears, the problem has been found. It is possible that more than one connection is leaking, so it is necessary to do a complete bypass of the system.
Such obvious leaks occur only after some kind of emergency (water hammer)
If all joints are checked, but no leaks are found, try soap foam. It is also applied to all joints and joints, to all seams. This method is good because you can detect even the smallest leaks.
Check the American nuts (flare nuts) especially carefully. Over time, the rubber sealing ring “sags” and micro leaks may appear. Under the influence of heating of the heating system, the water that comes out quickly evaporates and it can be difficult to detect a leak. For this reason, it is recommended to carry out the check when the system cools, as mentioned earlier.
After eliminating all current leaks, the pressure should stabilize. If it does fall slowly, there are two options. The first is to hope that the remaining microcracks (and this is exactly what they are) will be “overgrown” with salts. The second is to keep trying. Maybe you'll find something.
Another option is that the drop is observed for some time after the coolant is pumped in, then stabilizes. If the decrease is not too large (0.2-0.4 Bar), most likely, air has been released that has entered the system with the coolant. In order not to be nervous about this, after adding coolant, go through the entire system and bleed the air (for this purpose, Mayevsky taps or other air vents are installed on all radiators).
Pressure jumps
Pressure surges in the heating system of a private home are possible for two reasons:
- the expansion tank does not work correctly (or does not work at all);
- airing.
With the second option, everything is clear: go through all the heating circuits, open the air vents, drain the coolant until a steady stream of water flows. This bypass must be repeated several times in a row. Only if after the next round there is no air on any device, can we assume that you have bled out all the air. Now the pressure in the heating system of a private home should be stable.
The second option - with the incorrect operation of the expansion tank is a little more complicated. There are options here:
- The expansion tank volume is insufficient. It should be 10-15% of the system volume. To find the volume of the system, find the “displacement” of all its components (radiators + pipes + boiler). This figure is used to determine the volume of the expansion tank. If it turns out that your existing tank is smaller than necessary, you can install a second one. The total volume should not be less than the calculated value.
To find the volume of the system, you need to know how much coolant is placed in the pipes, radiators, boiler - The pressure in the expansion tank is incorrectly set or there is none at all. To do this, we take a measurement (conveniently using a car pressure gauge). For these purposes, there is a special entrance on the tank. As a standard, they come from the factory inflated to 1.5 bar.
- If the readings are approximately the same, and the system is unstable (the pressure gauge fluctuates greatly when heating), check the filter, pipe, etc., which are located in front of the tank. Perhaps the problem is overgrown pipes.
- If the readings are much lower or even “zero”, try pumping up to the desired value (with a bicycle or car pump). If the pressure in the expansion tank does not hold, it means the membrane has leaked and you will have to change it or buy a new tank.
In general, there can be a lot of options. For example, when installing aluminum radiators, hydrogen may be generated. Aluminum interacts with the copper heat exchanger of the boiler (common). As a result of the interaction of this galvanic pair, gas is formed, which is released through the air vents. As a result, the pressure constantly drops.
The pressure is rising
The third problem with pressure in the heating system of a private home is growth. There is a gradual increase. To reduce the coolant, the coolant is drained, bringing the indicator to normal. But, after cooling, the pressure in the heating system is significantly lower than normal. Sometimes it becomes so low that the boiler simply does not turn on.
There are two possible reasons - incorrect operation of the expansion tank or a large amount of air (or other gas) in the coolant. First you need to check the operation of the MB (membrane tank). With such “symptoms,” the tank may be of insufficient volume (15% of the system volume when using water and 20% when pouring anti-freeze), the membrane is torn, the pressure in the tank is low, or the outlet pipe is clogged. In all cases, the tank does not perform its functions, therefore, when the coolant is heated, the pressure increases (due to the thermal expansion of liquids).
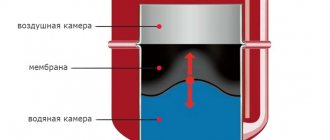
This is what the expansion membrane tank looks like in working condition
The integrity of the membrane is checked by pressing the nipple (spool valve), which is located on the “top” of the tank. If the tank is in good condition, air should hiss out of it. If the membrane is torn and the tank is filled with water, water will flow out of the hole. Just don't confuse it with condensation. There may be a few drops of condensation. In a serviceable expansion tank, after the condensate comes out, air flows. If the membrane is torn, water flows all the time. If this is your case, you can try replacing the membrane or buying a new tank.
Insufficient pressure is checked using a pressure gauge connected to the nipple (you can use a car one). The pressure in the tank should be 0.2-0.3 bar lower than in the system. If it is not high enough, the tank is simply constantly filled with water and for this reason does not compensate for the growing pressure in the system.
If a filter is installed on the outlet to the membrane tank, it must be cleaned
If the volume of the membrane tank is insufficient, the system behaves normally at low and medium heating temperatures of the coolant, but at high temperatures the pressure in the heating circuit increases. After recalculating the volume of the system and comparing it with the volume of the existing tank, you decide whether you need a second one, or, if necessary, you can replace the tank with a larger one.
A blockage at the inlet to the tank gives a similar situation: the pressure in the heating system increases. Depending on the density of the blockage, the flow of water into the expansion tank is either completely blocked or partially blocked. But, in any case, the tank does not work as it should. The solution to the problem is to turn off the tap that goes to the tank, remove the filter, clean it and restore everything.
How to increase or decrease the pressure in the heating system?
Sometimes during operation a large pressure drop occurs in the network, which leads to its inoperability. Knowing the reasons why this happens, you can find a way to eliminate it:
- cracking of the expansion tank membrane. In some models it is possible to change the membrane, otherwise the capacity changes completely;
- The pressure in the expansion tank of the heating system or its capacity was calculated incorrectly. It should be a tenth of the coolant volume in the entire network, and the gas pressure behind the tank membrane should be 0.2 bar lower than the system one;
- severe clogging of the mud trap;
- presence of air pockets. It often happens that it is possible to reduce the pressure by removing air or by replacing the automatic air vent;
- loss of tightness of the fittings separating the system from the make-up water supply. On the other side, the pressure is stronger and water from outside uncontrollably replenishes the heating network;
- failure of the boiler automation;
Pressure increase due to expansion tank
Reasons for increased pressure in the heating circuit due to problems with the expansion tank:
- Small expansion tank volume. When heated to 85-90 °C, water adds about 4% in volume. If a small tank is selected, the coolant expands when heated and fills the container. There is a complete release of air through the valve. With further heating, the tank can no longer compensate for the thermal increase in the volume of water, as a result, the pressure in the system rises. The volume of the expansion tank must be at least 10% of the total coolant volume in the circuit if a gas boiler is installed, and at least 20% if the boiler is solid fuel. The volume of the tank can be taken approximately according to the boiler power: for 1 kW there are approximately 15 liters of water. But it is better to calculate the volume of a separate circuit (based on heating surfaces);
- Damage to the rubber membrane of the tank. In this case, the water will completely fill the container, and the pressure gauge will show a drop in pressure in the system. But, if you open the make-up valve and add water, then when the coolant heats up, the pressure in the heating circuit will become significantly higher than the operating one. To solve the problem, you will need to replace the tank if the membrane is diaphragm type, or replace the membrane if it is balloon type;
- The pressure in the expansion tank is too high or too low. Malfunctions in the expansion tank are one of the main reasons for increased pressure in a closed system. You can check the pressure and pump it up if necessary using an ordinary car pump. Before checking, you need to drain the water from the heating system - the needle on the system pressure gauge should be at zero. If there are shut-off valves and a drain on the water pipeline to the expansion tank, then it is enough to drain the water only from the tank. Then air is released through the nipple, which is located on the side opposite to the water supply. If the boiler operates at a pressure of 2 bar, then the pressure gauge on the pump should show 1.6 bar. You need to open the water shut-off valve and add the volume of water drained from the expansion tank through the make-up tap. This adjustment method works for both tanks with bottom and top water supply;
- The tank is located immediately after the circulation pump. This leads to the fact that the pressure rises sharply, and almost immediately it is released, and pressure surges are observed. This situation can provoke hydraulic shocks in the circuit. To solve this problem in a closed heating circuit, the expansion tank is installed on the return pipe - in a laminar flow zone with a minimum coolant temperature. The pump crashes into the return line after the tank, in front of the boiler.
How to control blood pressure
To control the pressure in the heating system yourself, you need to install monitoring equipment. These are pressure gauges with a Bourdon tube ; their installation calculations are made according to the documents that regulate the installation. Their method of operation is quite simple; they are installed into the system using three-way valves, this ensures purging. If you purchase these taps for insertion, you can install them without even turning off the entire system. It's much better and more convenient.
Determining the choice of installation locations includes the following main items:
- if there are mud traps, then pressure gauges are installed before and after them. This must be included in the calculation of components for the heating system;
- after and before circulation pumps;
- after and before the heating boiler. If you use a fireplace for heating, then pressure gauges are not required;
- if a regulator is used, then the installation of pressure gauges after and before it must be included in the calculation;
- near the exit from the heat generator.
Possible breakdowns and repair work
Whether there is electric or gas heating in a private house, it doesn’t matter. Problems associated with a drop in pressure in the heating system can appear in any system. Electric heating or some other type of heating malfunctions after a few years , boiler equipment refuses to work or does not function as correctly. A breakdown such as a constant decrease in pressure also occurs, but during normal operation, that is, without significant interruptions.
If you see these malfunctions occurring, then you need to take appropriate measures, but first you need to determine which specific malfunction is causing the system to fail. Let's look at the main reasons that occur in heating systems:
- As a rule, a malfunction such as a hidden leak appears during the wiring of the pipeline system. All types of heating systems can be subject to this problem (the only exception is infrared). To determine the cause, the premises must be examined using a thermal imager; it will identify defective areas. A leak can be removed in several ways, most often by installing a new section, tightening a very weak fastening, or tightening a separate section of the system. It is advisable to do this on time, rather than then spending money on a major overhaul of the heating system in the house.
- It also happens that it is not the pipeline that is to blame for the decrease in pressure, but other equipment. The reasons may be such malfunctions as deformation of the membrane in the expansion tank. In this case, you need to inspect the compensation tank directly. Repair in this case consists only of installing a new nipple. This type of problem can be resolved very quickly. But the cause may be a membrane rupture or an incorrect calculation of the tank size. In this case, you need to install new equipment, or rather replace the expansion tank;
- The reason for the decrease in pressure may also be a problem such as the formation of a crack in the heat exchanger. This happens during the operation of water heating, but another possible reason is its complete physical wear and tear or a defect in the manufacture of the boiler. In this case, new equipment will likely need to be installed. It is especially necessary to carefully monitor the gas equipment of a multi-story building;
- Sometimes the pressure drops not due to a breakdown of the heating system. There may be an air pocket in the pipeline; air escapes from it over time, the house begins to heat up worse, and the pressure gradually decreases. It is necessary to find this pocket and remove all air from the system. But if the heating system is installed correctly, then this problem simply will not appear. Therefore, when installation occurs, you must carefully follow all the steps in order to connect the nodes exactly according to the instructions.
What to do when system pressure rises
But the pressure in the heating system does not decrease all the time; it also happens that the pressure in the system of a private home increases. The causes of these malfunctions may be :
Features of open and closed heating systems
According to the design of the heating system in private houses, there can be:
- open - it is assumed that there is an expansion tank and a natural type of circulation of the coolant: when heated, it rises up, and as it cools down, it goes down;
- closed - the heating circuit is isolated from the external environment, and the coolant moves thanks to the circulation pump.
For the successful operation of open-type heating, it is necessary that the boiler be located at the lowest point, and the expansion tank at the highest. In this case, the cross-section of the pipes leaving the boiler must be larger than those entering on the return circuit. This system is used mainly in small one-story houses.
Closed type heating is much more common. In this case, the working pressure in the heating of a private closed house should be at the level of one and a half to two atmospheres, provided that the building is small and there are few batteries. If a private house has many rooms or has several floors, an additional circulation pump will be needed.
If the heating system is filled with water for the first time, air may enter the circuit. Once it is removed, the pressure in the system will drop slightly. It will need to be raised a little more, without, however, bringing it to the working value. As the water warms up, the pressure will increase.
In the off-season, a closed system with a pump allows you to regulate the degree of heating by setting minimum values.
Leak detection
How can leaks be identified and corrected? If the pressure in the system decreases, then you need to find a leak, that is, clearly determine the location of the malfunction. In this case, you need to inspect all the pipes to make sure they are tight . Particular attention should be paid to areas where fittings, couplings, and pipes are connected. Typically, this is where leaks occur.
This is due not only to strong pressure drops, but also to the fact that the installation was done poorly. But when puddles are visible under the areas where the pipes are located, the system requires a more thorough inspection. Repairs and replacement of individual sections may be required.
These inspections must be done regularly in order to promptly identify any faults and change pipes or their connections. But when the pipes are replaced, and the pressure in the heating system continues to decrease, more thorough troubleshooting work needs to be carried out. It is advisable to invite a specialist who, using special equipment, will identify the reason for the decrease in pressure.
In this case, you need to drain the water and fill the pipes with air using a compressor. The batteries and boiler are disconnected from the system, then all pipes are carefully inspected. In areas where leaks are observed, air whistling will be heard, accordingly, it is this area that needs to be repaired.
The repair needs to be done correctly , here you will need:
- replacing the section of pipe in which a leak was detected with a new section;
- if there is a weakening at the connection, then just tighten it; you will probably need to change the fittings for the pipe;
- a winding for compaction is used in the form of a tape, which is sold specifically for this purpose;
- the damaged section of the pipe, including the connection, is completely replaced with a new one.
If nothing was found during the work to identify leaks, then the problem is probably in the performance of the heating system itself, more precisely, the expansion tank and boiler. When installing water heating, you need to carefully inspect all the batteries; leaks and loose connections may also appear here. Auxiliary tools and materials will not be needed at this stage.
To carry out these works, it is advisable to call a specialist rather than buy completely unnecessary materials, because the likely cause of the malfunction is the incorrect installation of some component , the heating boiler itself. But, as a rule, after removing the leaks, the pressure in the system normalizes.
Heating boiler testing
Often, pressure disturbances in the heating system are associated with the boiler. In this case, you need to test it, namely, diagnose it, but only a specialist can do this. A decrease in pressure may be due to a reason such as the formation of microcracks in the heat exchanger . The pressure decreases slowly; it is necessary to recharge at certain intervals.
In this case, the heating boiler must be checked immediately by calling a specialist, and not put off repairs for a long time. Professionals advise testing the heating system before the start of the season, this will make it possible to avoid many problems during operation.
Expansion tanks are installed in closed water heating systems to compensate for temperature expansion. These are tanks divided into two parts by a partition. In one area there is a coolant, that is, water, in the second - gas. During expansion, the coolant creates pressure on the partition , occupying another part of the volume of the tank; during contraction, the opposite situation occurs. In this way, it is possible to control the overall pressure, preventing leaks and other malfunctions.
How to choose a tank size to maintain normal pressure
It is best to select an expansion tank and install it in the boiler room of the house itself, and the pressure in the tank must be 0.2 bar higher than the static pressure in the tank. Static pressure data can be calculated by multiplying 0.1 bar per meter by the height from the highest point of the heating to the expansion tank.
For water heating of a house, you can find out the volume of this expansion tank using the formula V=(e * C) * (Pmax+1) / (Pmax—Pgas) , where:
- V is the overall size for the expansion tank;
- C is the volume of all water in the heating system, in liters;
- e - temperature expansion for the coolant, indicated as a percentage. It is advisable to take with a small margin of 3.5%, this corresponds to the approximate temperature in the system at 90 degrees;
- Pmax is the highest pressure level. As a rule, it is designated equal to 3 bars;
- Pgas - gas pressure directly in the tank.
If a calculation takes place, most experts advise taking into account the safety factor; it is equal to 1.2-1.25. When purchasing a membrane tank, it is advisable to round up the calculation to the larger part; this will make it possible to maintain normal pressure in the system without worrying about its decrease, significant differences, leaks and other malfunctions.