What is a unit of measurement called a gigacalorie? What does it have to do with traditional kilowatt-hours, in which thermal energy is calculated? What information do you need to have in order to correctly calculate Gcal for heating? Finally, what formula should be used during the calculation? This, as well as many other things, will be discussed in today’s article.
Calculation of Gcal for heating
- 1 What is Gcal?
- 2 What is all this for? 2.1 Multi-apartment buildings
- 2.2 Private houses
- 3.1 Vane meters
- 5.1 Video - How to calculate heating in a private house
What is Gcal?
A calorie is a certain amount of energy that is required to heat 1 gram of water to 1 degree. This condition is met under atmospheric pressure conditions. For thermal energy calculations, a larger value is used - Gcal. A gigacalorie corresponds to 1 billion calories. This value began to be used in 1995 in accordance with the document of the Ministry of Fuel and Energy.
In Russia, the average consumption per 1 sq.m. is 0.9342 Gcal per month. In each region, this value may change up or down depending on weather conditions.
What is a gigacalorie if it is converted into ordinary values?
- 1 Gigacalorie equals 1162.2 kilowatt-hours.
- In order to heat 1 thousand tons of water to a temperature of +1 degree, 1 gigacalorie will be required.
Conversion table from Megawatt to Gigacalories per hour
MegawattGigacalories per hour
| 10 | 50 | 100 | 250 | 500 | 1 000 | 2 500 | 5 000 |
| 8.598 | 42.992 | 85.985 | 214.961 | 429.923 | 859.845 | 2 149.613 | 4 299.226 |
Sources
- https://baltgazservice.ru/stati/otoplenie/formula-rascheta-gkal-po-otopleniyu/
- https://kip-mtr.ru/gkal-chto-eto/
- https://teplo.guru/elektrichestvo/chto-takoe-gigakaloriya.html
- https://stroi-mario.ru/montazh-i-obsluzhivanie/edinica-izmereniya-tepla.html
- https://teplosten24.ru/chto-takoe-gkal-v-otoplenii.html
- https://FB.ru/article/335378/gigakaloriya—eto-chto-takoe
- https://ProUteplenie.com/otoplenie/gkal-chto-eto-kak-perevesti-gkal
- https://o-vode.net/vodosnabzhenie/gvs/gkal-v-1-m3
- https://www.calc.ru/kilovatt-v-gigakaloriy_v_chas.html
- https://www.calc.ru/gigakaloriy_v_chas-v-megavatt.html
- https://www.calc.ru/kilokaloriy_v_chas-v-kilovatt.html
- https://masterfibre03.ru/kotel/perevod-gaza-v-gkal.html
- https://www.calc.ru/megavatt-v-gigakaloriy_v_chas.html
Gcal in apartment buildings
In apartment buildings, gigacalories are used in thermal calculations. If you know the exact amount of heat energy that remains in the house, you can calculate the bill for heating. For example, if a house does not have a communal or individual heating device installed, then you will have to pay for centralized heating based on the area of the heated room. If a heat meter is installed, then the wiring is horizontal, or serial, or collector. In this option, two risers are made in the apartment for the supply and return pipes, and the system inside the apartment is determined by the residents. Such schemes are used in new houses. That is why residents can independently regulate the consumption of thermal energy, making a choice between comfort and savings.
The adjustment is made as follows:
- Due to the throttling of heating batteries, the passage of the heating device is limited, therefore, the temperature in it decreases and the consumption of thermal energy decreases.
- Installation of a general thermostat on the return pipe. In this option, the flow rate of the working fluid is determined by the temperature in the apartment, and if it increases, then the flow rate decreases, and if it decreases, then the flow rate increases.
General principles of calculations
How thermal energy is calculated is established by PP No. 354. The calculations are carried out by utility companies, but residents themselves are allowed to make them. Heat consumption can be determined after calculating the amount of thermal energy spent on heating per year. This period allows us to obtain an average standard, since costs are lower in summer and more in winter. Payment according to the standard provides for equal costs for the heating period or calendar year.
The calculation scheme depends on several factors:
- equipping the house with a thermal energy meter;
- the ability to account for heating of all rooms using individual devices;
- The calendar time for making payment is winter or all year.
It is more difficult to calculate thermal energy for an apartment building than for a private one. This is due to the presence of common places, residential and non-residential premises, and ownership rights. Taking into account the dependence of heat energy on the dimensions of the room, it is worthwhile to refer to PP No. 354 and PP No. 306. They indicate the distribution of the volume of heat used by the house in proportion to the area of the apartments. The readings of the general meter are divided by the proportion of housing owners.
Gcal in private homes
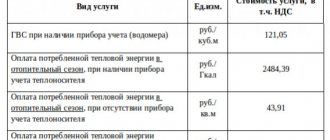
If we talk about Gcal in a private house, then residents are primarily interested in the cost of heat energy for each type of fuel. Therefore, let’s look at some prices per 1 Gcal for various types of fuel:
- Natural gas – 3300 rubles;
- Liquefied gas – 520 rubles;
- Coal – 550 rubles;
- Pellets – 1800 rubles;
- Diesel fuel – 3270 rubles;
- Electricity – 4300 rubles.
The price may vary depending on the region, and it is also worth considering that the cost of fuel increases periodically.
General information about Gcal calculations
To calculate Gcal, it is necessary to make special calculations, the procedure of which is established by special regulations. The calculation is carried out by utility services, which can explain to you the procedure for calculating Gcal, as well as decipher any unclear points.
If you have an individual device installed, you will be able to avoid any problems and overpayments. All you need to do is take the readings from the meter every month and multiply the resulting number by the tariff. The amount received must be paid for the use of heating.
Heat meters
In order to calculate thermal energy you need to know the following information:
- The temperature of the liquid at the inlet and outlet of a certain section of the pipeline.
- The flow rate of liquid that moves through heating devices.
Consumption can be determined using heat meters. Heat meters can be of two types:
- Vane counters. Such devices are used to measure thermal energy, as well as hot water consumption. The difference between such meters and devices for metering cold water is the material from which the impeller is made. In such devices it is most resistant to high temperatures. The operating principle is similar for the two devices:
- The rotation of the impeller is transmitted to the metering device;
- The impeller begins to rotate due to the movement of the working fluid;
- The transfer is carried out without direct interaction, but with the help of a permanent magnet.
Such devices have a simple design, but their response threshold is low. They also have reliable protection against reading distortion. Using an antimagnetic screen, the impeller is prevented from braking by the external magnetic field.
- Devices with a difference recorder. Such meters operate according to Bernoulli's law, which states that the speed of a liquid or gas flow is inversely proportional to its static movement. If the pressure is recorded by two sensors, the flow can be easily determined in real time. The counter involves electronics in the design. Almost all models provide information on the flow and temperature of the working fluid, and also determine the consumption of thermal energy. You can configure the work manually using a PC. You can connect the device to a PC via a port.
Many residents are wondering how to calculate the amount of Gcal for heating in an open heating system in which hot water can be selected. Pressure sensors are installed on the return and supply pipes at the same time. The difference in the flow rate of the working fluid will show the amount of warm water that was spent for domestic needs.
How to calculate how many gigalories per cubic meter. meter as an example
Measures of energy and volume are different quantities. Simple calculations will help you compare them.
Example: The coolant temperature in an apartment building should be at least 55 ⁰C, the cold water temperature should be approximately 5 ⁰C.
To heat a cubic meter you will need:
(55-5)×0.001=0.05 Gcal.
Heat losses due to imperfect thermal insulation are inevitable; losses of 20% are included in the calculations. This means that actually heating will require 0.06 Gcal.
This ratio allows the heat meter to determine the consumption of heated water.
Example: in a 100-apartment residential building, the heat meter showed 150 Gcal in the summer, when only coolant for domestic needs is consumed. In 20 apartments, hot water consumption is determined by individual meters; the total consumption for these apartments was 400 m³.
The whole house consumes: 150÷0.06=2500 m³. This means that the remaining apartments account for: 2500-400 = 2100 m³. Next, 2100 m³ is divided by the actual number of residents.
This technique allows you to convert thermal energy values into volumetric coolant flow rates and vice versa.
In houses with an open heating system, the difference in water meter readings on the supply and return pipes will indicate the amount of coolant consumed for heating and, after recalculation, the heat energy consumption.
The calculations are for reference only and serve to control the consumption of heat and water supply.
Formula for calculating Gcal for heating
If you do not have an individual device, then you need to use the following formula for calculating heat for heating: Q = V * (T1 – T2) / 1000, where:
- Q is the total amount of heat energy.
- V is the volume of hot water consumption. Measured in tons or cubic meters.
- T1 is the hot water temperature, measured in degrees Celsius. In such a calculation, it is better to take into account the temperature that will be characteristic of a specific operating pressure. This indicator is called enthalpy. If there is no necessary sensor, then take the temperature that will be similar to the enthalpy. Typically, the average temperature is between 60-65 degrees Celsius.
- T2 is the temperature of cold water, which is measured in degrees Celsius. As you know, getting to a pipeline with cold water is not easy, so such values are determined by constant values. They, in turn, depend on the climatic conditions outside the house. For example, in the cold season, this value can be 5 degrees, and in warm times, when there is no heating, it can reach 15 degrees.
- 1000 is a factor that gives the answer in gigacalories. This value will be more accurate than regular calories.
In a closed heating system, gigacalories are calculated in a different form. In order to calculate Gcal in a closed heating system, you must use the following formula: Q = ((V1 * (T1 - T)) - (V2 * (T2 - T))) / 1000, where:
- Q – previous volume of thermal energy;
- V1 is the heat carrier flow rate parameter in the supply pipe. The heat source can be water vapor or ordinary water.
- V2 – volume of water flow in the outlet pipe;
- T1 – temperature in the coolant supply pipe;
- T2 – temperature at the pipe outlet;
- T – cold water temperature.
Calculation of thermal energy for heating using this formula depends on two parameters: the first shows the heat that enters the system, and the second is the heat parameter when the coolant is removed through the return pipe.
We calculate indicators of the amount of coolant: theory and practice
In individual residential buildings or apartment buildings the following is usually used:
- process water;
- propylene glycol;
- ethylene solution.
It is important that any coolant meets the requirements specified in regulatory documents. In Russian standard there are 5 conditions that must be met:
- optimal value of coolant movement;
- low viscosity while ensuring flow like ordinary water;
- slight expansion when the system cools;
- elimination of toxicity;
- inexpensive price.
Calculating the performance of a heating system cannot be considered simple; experience is required.
House heating system diagram Source odstroy.ru
To correctly determine indicators using calculation formulas for the further use of a reliable heat carrier, it is recommended to use the services of a specialist involved in the design of individual heating schemes or a competent plumber.
Other methods for calculating Gcal for heating
You can calculate the amount of heat that enters the heating system in other ways. For example, the formula for calculating Gcal can have two other forms:
- Q = ((V1 * (T1 - T2)) + (V1 - V2) * (T2 - T)) / 1000.
- Q = ((V2 * (T1 - T2)) + (V1 - V2) * (T1 - T)) / 1000.
All values in these formulas are the same as in the previous formula. Based on the above calculations, we can conclude that you can calculate Gcal for heating yourself. But you should seek advice from special companies that are responsible for supplying heat to the house, since their work and calculation system may differ from these formulas and consist of a different set of measures.
If you decide to make a “Warm Floor” system in your private home, then the principle of heating calculation will be completely different. The calculation will be much more complicated, since it is necessary to take into account not only the features of the heating circuit, but also the values of the electrical network from which the floor is heated. The companies that are responsible for monitoring the installation of heated floors will be different.
Many residents have difficulty converting kilocalories to kilowatts. This is due to many manuals of measuring units in the international system, which is called “C”. When converting kilocalories to kilowatts, the coefficient 850 should be used. That is, 1 kW equals 850 kcal. This calculation is much simpler than others, since it is not difficult to find out the required volume of gigacalories. 1 gigacalorie = 1 million calories.
During the calculation, it should be remembered that any modern devices have a small error. Mostly they are acceptable. But you need to calculate the error yourself. For example, this can be done using the following formula: R = (V1 - V2) / (V1+V2) * 100, where:
- R – error of a common house heating device.
- V1 and V2 are the previously indicated water flow parameters in the system.
- 100 is the coefficient that is responsible for converting the resulting value into a percentage. In accordance with operational standards, the maximum error that can be is 2%. Basically, this figure does not exceed 1%.
Selecting a circulation pump
Today, not a single heating system is installed without a circulation pump. Two characteristics by which the device is selected:
- Q is the coolant flow parameter for one hour, calculated in m3.
- H is a pressure indicator expressed in meters.
The coolant, which is heated to the temperature required for heating the premises, circulates through the system and releases part of the heat into the walls facing the street. This indicator is the heat loss of the heating system of the house. The pump helps in this situation by moving the coolant through the pipes and radiators in the required mode.
Circulation pump VIEIR TsN25-4 180 mm Source zonacomf.ru
Results of calculations of Gcal for heating
If you have correctly calculated the consumption of Gcal of thermal energy, then you do not have to worry about overpayments for utilities. If we use the above formulas, we can conclude that when heating a residential building with an area of up to 200 sq.m. you will need to spend about 3 Gcal in 1 month. If we consider that the heating season in many regions of the country lasts approximately 6 months, then we can calculate the approximate consumption of thermal energy. To do this, multiply 3 Gcal by 6 months and get 18 Gcal.
It is much easier to calculate gigacalorie consumption in a private home, since you can install your own individual device there. In apartment buildings with centralized heating, it will not be possible to get by with a conventional appliance.
Based on the information indicated above, we can conclude that all calculations on the consumption of thermal energy in a particular house can be done independently without the help of special organizations. But it is worth remembering that all data must be calculated accurately using special mathematical formulas. In addition, all procedures must be coordinated with special bodies that control such actions. If you are not sure that you will perform the calculation yourself, then you can use the services of professional specialists who are engaged in such work and have materials available that describe in detail the entire process and photos of heating system samples, as well as their connection diagrams.