Steel panel heating radiators have recently become increasingly popular among owners of country cottages and private houses. Such heating radiators are ideal for houses with an autonomous heating system. Their main advantage is that they have the highest heat transfer rate compared to other types of heating radiators. In addition, panel heating radiators can be chosen in any size that is most suitable for you and with the most suitable power parameters.
Steel panel radiator
The influence of the placement and method of connecting radiators on heat transfer
The best location for the radiator is under the light openings, since the greatest heat loss occurs through the window, no matter how insulated it is. In addition, hot air from the heating device creates a thermal curtain: cold air from the window does not spread throughout the room, circulation improves.
Changes in the thermal power of the radiator depending on the placement and presence of a screen.
If you decide to hide radiators under screens or decorative panels, this will lead to a loss of power. Sometimes such measures are resorted to in order to purposefully reduce the strength of the heat flow by 10-15%.
Reduced thermal power with different connection methods.
The method of connecting radiators also has a significant impact:
- Bilateral or unilateral. Connecting pipes from different sides helps to increase the heat transfer of the battery; with this connection, the power of the device corresponds to the declared maximum. However, for radiators with less than 20 sections, it is better to install pipes from one side.
- Top or bottom. The supply of coolant to the upper part of the battery, when removed through the lower part, has a minimal effect on heat transfer. Feeding from bottom to top reduces the indicator by 20-22%.
How to connect (step by step instructions)
To make it easier to connect panel heating radiators, you should use detailed instructions and a diagram. They are included with the device. The connection is carried out independently or you can use the help of a wizard.
Let's look at the connection versions:
- Diagonal connection method. It differs in that the supply pipe is connected to the upper branch pipe, and the discharge pipe to the lower, but diagonal method of fastening. This connection option is considered the most effective, since the loss of coolant power is only 2%. But the installation process is fraught with difficulties. Unfortunately, the intended visual impression is unattractive. Therefore, it is difficult to combine with the thoughtful interior of a residential apartment or house.
- Side models with one-way connection. The supply or discharge pipe is connected at the top and, accordingly, at the bottom of one side. It is most often used in multi-storey buildings. This option is effective because the heat loss is guaranteed to be no more than 5%. But models with 15 or more sections lose efficiency because they provide uneven heating of the room.
- Bottom or saddle connection option. The supply and discharge pipes are connected at the bottom of the radiator, but from different sides. This connection method assumes an increase in heat transfer loss of up to 15%. This is due to the heat distribution of the battery being too uneven. But this connection method is acceptable in residential premises with a reduced level of associated heat loss. For example, if the walls are insulated with foam plastic.
Now we have understood the differences and capabilities of metal versions of radiators for space heating. We understand the advantages, disadvantages, selection criteria and differences in connection methods. In general, this is enough for a reasonable choice of the right device.
Heating radiator sizes
The standard height of the most popular models of heating devices with the center distance along the connections is 500 millimeters. These are the batteries that in most cases could be seen about two decades ago in city apartments.
Cast iron radiators
. A typical representative of these devices is model MS-140-500-0.9.
The specifications for it include the following overall dimensions of cast iron heating radiators:
- the length of one section is 93 millimeters;
- depth - 140 millimeters;
- height – 588 millimeters.
Calculating the dimensions of a radiator from several sections is not difficult. When the battery consists of 7-10 sections, add 1 centimeter, taking into account the thickness of the paronite gaskets. If the heating battery is to be installed in a niche, it is necessary to take into account the length of the flushing tap, since cast iron radiators with side connections always require flushing. One section provides a heat flow of 160 watts at a temperature difference between the hot coolant and the air in the room of 70 degrees. The maximum working pressure is 9 atmospheres.
Aluminum radiators
. For aluminum heating devices on the market today, with the same center-to-center spacing of the connections, there is a significant variation in the parameters (for more details: “Dimensions of aluminum heating radiators, section volume, preliminary calculations”).
Typical sizes of aluminum heating radiators are:
- the length of one section is 80 millimeters;
- depth 80-100 millimeters;
- height - 575-585 millimeters.
The heat transfer of one section directly depends on the area of its fins and depth. Typically it ranges from 180 to 200 watts. The operating pressure for most models of aluminum batteries is 16 atmospheres. Heating devices are tested with one and a half times higher pressure - this is 24 kgf/cm².
Aluminum radiators have the following feature: the volume of coolant in them is 3 and sometimes 5 times less than in cast iron products. As a result, the high speed of movement of hot water prevents silting and the formation of deposits. Bimetallic radiators
. The steel core in such devices does not in any way affect their appearance and the size of the heating radiators, but the maximum operating pressure increases significantly. Unfortunately, the increased strength of the bimetallic battery leads to high costs. And the price of such a product is already inaccessible to a wide range of consumers.
Bimetallic heating radiators have the following section dimensions:
- length 80-82 millimeters;
- depth - from 75 to 100 millimeters;
- height – minimum 550 and maximum 580 millimeters.
In terms of heat transfer, one bimetallic section is inferior to an aluminum section by about 10-20 watts. The average heat flux is 160-200 watts. Due to the presence of steel, the operating pressure reaches 25-35 atmospheres, and during testing - 30-50 atmospheres.
When arranging a heating structure, you should use pipes that are not inferior in strength to radiators. Otherwise, using durable devices loses all meaning. For bimetallic radiators, only steel liner is used.
Construction of steel panel radiators
- Structurally, panel radiators consist of several steel panels (from 1 to 3) in which there are vertical and horizontal channels for coolant.
- To increase the heat exchange area and convective heat transfer from the inside, U-shaped steel ribs are welded to the panel. The increase in heat transfer is more than 50%.
- The radiator panel is made by welding two stamped sheets of cold-rolled carbon steel sheet with a thickness of 1.2 mm - 1.25 mm. Some manufacturers make radiators from galvanized steel on special order. For convective heating fin plates, steel with a thickness of 0.4mm - 0.5mm is used.
- The outside of the radiators are primed using the cataphoretic immersion method and painted using the powder method. The standard color is white, but some manufacturers produce colored panel radiators on special order.
- Panel radiators with two or three panels usually have decorative grilles on top and solid panels on the sides.
- The standard radiator is equipped with four lateral connecting pipes 4x1/2″ BP, two on each side. To connect the radiator, two pipes are used, and the remaining two are closed with plugs.
Types of radiator connections
If connecting the bottom method of connecting the radiator. it will be equipped with a special valve for temperature control, which will immediately provide the required temperature.
When connecting a steel radiator to the side, a standard scheme for circulating heat in the room is used, and such a connection is cheap and not at all remarkable or noticeable.
Fabrication with multiple panels will result in greater heat input. Various metal alloys can also be mounted to them, as a result the size of the base, which provides heat transfer, will increase.
Types of battery connections
However, these heating systems also have distinctive features, for example, weight. According to this criterion, they can reach the weight level of cast iron installations, which are quite heavy. Also, the volume of water will be a minus, which means that thermal regulation will be lower and, accordingly, heat transfer too. The thickness of the radiator can reach 160 mm, which exceeds the thickness of cast iron. In addition, the inner shell of such batteries is difficult to clean.
Products made from pipes help us remember the times of cast iron batteries. they are similar in external parameters. In most cases, the installation of cast iron batteries is carried out in administrative buildings and residential buildings of the Stalin period. They are resistant to strong atmospheric pressure up to 10, can reach more than one hundred cm in length, and a maximum width of 2 cm. They can also be sectional or non-sectional.
DIY connection
The radiator is connected to an already finished wall. This means that all finishing (painting, wallpapering) must be completed. The batteries are hung on the wall using hooks or brackets. If the wall is not able to support the weight of the radiator, it is attached to the floor. Special legs are available for sale for this purpose.
The radiator is connected to the heating system using special shut-off devices. They will allow you to turn off the water or set the required temperature at any time. The parts are connected using threaded elements (ball valves, tees, bends). All threaded connections are sealed. If you have the skills, the connections can be secured by welding.
Design Features
Water contains a large number of impurities. When in contact with aluminum, they cause corrosion. Over several years of use, these processes will lead to leakage of the device.
The design feature of these radiators is the presence of an internal stainless steel core, which is surrounded on the outside by an aluminum alloy. This way, water does not come into contact with aluminum, which significantly extends the service life of the system.
There are two manufacturing options:
- Pseudobimetal. In this case, the steel core is located only inside the vertical channels. So aluminum is not completely protected, but only in the weakest places. These models are cheaper and have a standard service life of up to 10 years if used in systems with high water pressure (for example, in city apartments).
- Bimetal. It has a solid inner casing made of steel, which is filled with aluminum alloy under pressure. Here the aluminum is protected on all sides. These are more expensive models and their service life under similar operating conditions is up to 30 years.
Design of a bimetallic batteryThe manufacturing method directly affects the volume of water in the section of the bimetallic radiator.
If we compare it with any other battery, the volume of one section here will be significantly lower. The disadvantage is compensated by the presence of two alloys. As a result, the inner steel core prevents the aluminum shell from cooling quickly. There are different ways to join two metals. It is preferable if aluminum is poured over steel under pressure. This battery model will last longer. There is an option when metals are joined together by welding.
According to the technical type of design, radiators can be:
- Collapsible. This means that using a radiator wrench you can unscrew any number of sections and screw them to another radiator. This type is most often installed in private houses with an autonomous heating system, where there is no high water pressure.
- Non-separable. The radiator is monolithic, it cannot be untwisted, cut, or attached to another. Perfect for use in a city apartment, where there is always a high level of pressure.
Possible problems during operation
Bimetal devices have a large number of advantages. Which of their features can be considered disadvantages?
- Despite the possibility of using bimetallic batteries in a system with any coolant, the low quality of the latter negatively affects the service life of the device.
- Different coefficients of expansion of the metals present in the battery design can, over time, lead to instability of heat transfer and a decrease in the strength of the device.
- The use of low-quality coolant in the system can lead to clogging of channels, corrosion, and deterioration of heat transfer.
Low batteries
Radiators with a small center distance have the following advantages:
- they can be placed under a low window sill;
- they have maximum heat transfer per unit area.
Cast iron radiators
.
The dimensions of the MS-140M-300-0.9 heating radiator sections are:
- length 93 millimeters;
- depth - 140 millimeters;
- height – 388 millimeters.
Due to their smaller dimensions, the heat transfer of cast iron heating radiators is reduced - it is equal to 106 watts from one section at an operating pressure of 9 kgf/cm². Among foreign analogues, there are cast iron products with an interaxal distance along the connections equal to 200 and 350 millimeters; the power of a section of a cast iron radiator of this type is much higher.
Aluminum radiators
. For low batteries made of aluminum, both domestic and imported, the spread of the center distances is quite large. You can find radiator sizes of 150, 300 and even 450 millimeters. Since the possible section length starts from 40 millimeters, the device looks compact and unusual. Low aluminum heating radiators have height dimensions starting from 200 millimeters. The depth of many models compensates for the lack of the other two parameters and is 180 millimeters.
As for thermal power, it varies from a minimum of 50 watts per section to a maximum of 160 watts. The determining factor is the fin area of one section. At the same time, the change in dimensions does not significantly affect the operating pressure - low aluminum devices are designed for 16 atmospheres, and when testing - 24 atmospheres. Bimetallic radiators
. All the sizes of heating radiators that they have are also typical for aluminum heating devices. Thermal power is within the same limits. On sale you can find aluminum low radiators with heat output of 80 and 140 watts per section. The working pressure is 25-35 atmospheres.
Bimetallic low radiators, such as in the photo, have two nuances:
- among heating devices there are batteries not with solid steel cores, but with steel tubes placed between aluminum collectors. Their operating pressure, indicated by manufacturers, is usually 12 or 16 atmospheres;
- they often do not have vertically located channels and, in the case of a lateral connection, can be heated by the collectors due to the thermal conductivity of aluminum. The circulation of the coolant is ensured by the last section, since it is flow-through.
Manufacturers
Panel radiators made of steel are available on the market in models from various manufacturers. Both domestic and imported products are available. The following companies produce steel panel radiators:
- Kermi (Germany);
- Buderus (Germany);
- "Korado" (Czech Republic);
- DeLonghi (Italy);
- PURMO (Finland).
Panel steel radiators are an excellent choice for an autonomous heating system. They will allow you to heat the room efficiently and quickly. Thanks to their design, they have a high efficiency, can work with coolant of almost any quality, consume a small amount of energy and do not emit harmful and dangerous substances, that is, they are environmentally friendly.
We talked about calculating radiators, and somehow it turned out that we were talking about choosing the number of sections. That is, it was assumed that the radiators in your house would be sectional. Well, what about panel radiators
?
Perhaps someone will choose them. Therefore, let’s fill the gap: find out how to select panel radiators based on power.
Difference between cast iron and bimetallic batteries
Radiators, consisting of two types of metals at once, came to the domestic market from Italy and quickly won the hearts of consumers, despite their high cost. This can be explained in one word: “reliability”. If you choose which is better, cast iron or bimetallic batteries, then you should compare their technical indicators:
- Structure:
- Cast iron structures now look stylish, but they are also assembled from sections equipped with a fairly wide channel for the coolant. Their weight has become significantly less (3.5 kg versus 8 kg previously), their appearance is more presentable, and their reliability is the same. The market offers classic sectionals and artistic, retro style ones. The latter are very expensive, and mostly imported.
- Bimetallic structures consist of a steel or copper core with aluminum fins and housing. The coolant comes into contact exclusively with stainless steel, which protects the device from corrosion, and the casing ensures high heat transfer. Such a heater weighs little, is easy to install, and additional thermostats allow you to monitor the heating of the coolant.
- Heat dissipation level:
- If you decide whether cast iron or bimetallic radiators heat better, then their performance will be approximately equal. So the heat transfer of a cast iron section ranges from 100 W to 160 W. Many consumers feel that they take too long to warm up, and they are right. At the same time, everyone forgets that these batteries also take a very long time to cool down.
- The heat transfer of one section of a bimetallic radiator is 150-200 W, which, with instant heating, brings this type of heaters to a leading position.
- Operating pressure:
- Although many years of experience in using cast iron batteries suggests that they are strong and reliable, this is not entirely true when it comes to high-rise buildings. Even in five-story buildings, quite strong water hammers can occur in the heating system, let alone buildings of 16 floors and above. The operating pressure of cast iron batteries is 9-12 atmospheres, which may not be enough if the pressure rises sharply, for example, up to 15 atmospheres. In this case, the cast iron sections will simply burst.
- Bimetallic radiators are more reliable, since their operating pressure is 25-40 atmospheres, and in some models even 100 atmospheres. At this point, designs made of two types of metal also lead.
- Coolant resistance:
- Cast iron is absolutely “indifferent” to the quality of water and its acidity. Completely draining it in the summer does not affect it, but the pebbles that sweep through the system gradually weaken the cast iron, drain it and render it inoperable. This process is lengthy, and if the radiator walls are thick enough, it is completely endless.
- A bimetallic radiator is weaker in this regard. It is not afraid of the acidity level of the water as long as it is in the system, but as soon as it is drained, corrosion begins to appear after 2-3 weeks of contact with air. In this indicator, bimetal loses to cast iron.
- In terms of temperature, both types of radiators tolerate temperature changes well. For cast iron, the maximum water heating is +110, and for bimetal - +130 degrees.
- Today you can find cast iron batteries whose age has exceeded 100 years, but on average they have a service life of 50 years. Manufacturers set a limit of 25-30 years for bimetallic radiators, which is less than that of cast iron.
Bimetallic heaters are the best option for replacing old batteries. In key respects, they are superior to cast iron devices, which guarantees their effective operation in the unfriendly environment of centralized heating. In addition, they are much easier to install, they are lightweight and do not require additional maintenance.
If the question is whether to replace cast-iron radiators with bimetallic ones or not, then residents of five-story buildings do not have to do this, especially since the latter devices are twice as expensive. Residents of high-rise buildings will have to abandon cast iron batteries, since they will not withstand the load of the system and will leak. In this option, there is definitely nothing better than bimetallic structures.
Major manufacturers of steel panel radiators
The Russian market offers products from more than 40 manufacturers of steel panel radiators. The share of imported radiators exceeds 80%, the vast majority of them are European-made.
Main manufacturers and brands of steel panel radiators.
- Rettig Heating (Germany, Finland, Poland): Purmo, Vogel&Noot, Dia Norm
- Kermi (Germany)
- Korado (Czech Republic)
- Prado (Russia)
- Lideya (Belarus)
Classification of heating radiators by material of manufacture
Depending on the material of manufacture, there are the following types of radiators: cast iron, aluminum, steel and bimetallic. Copper heating radiators are practically not used today due to their high cost.
Cast iron
Cast iron units are commonly used in older homes. They cannot boast of external attractiveness and compact size.
Their main advantages:
- Corrosion resistance and impressive service life (up to 50 years).
- Possibility of use in systems with high pressure and not very clean coolant.
- After heating stops, they retain heat for a long time.
- Can be combined with pipes made of other materials.
- High heat transfer due to the vertical arrangement of the fins.
- Strength and thermal resistance.
- Low hydraulic resistance inside and protection against blockages.
Among the disadvantages are the impressive weight and rather large dimensions, as well as prolonged heating of the room. A thermostat cannot be built into such devices. The surface needs care and painting.
Technical characteristics of cast iron models:
- thermal power – 110-150 W;
- weight of one section – 8-9 kg;
- working pressure – 9-18 atm.;
- unit height – 37-57 cm;
- width – 60-90 cm;
- coolant temperature – up to 150°C.
Aluminum
Aluminum inverter heating batteries operate on the principle of convection. They radiate heat into the room, which they receive from the heated coolant liquid.
Such units have the following technical characteristics:
- working pressure is in the range of 6-16 atm.;
- maximum coolant temperature – 110°C;
- section thermal power – from 80 to 215 W;
- service life – up to 20 years;
- axial distance – 35-50 cm;
- device height – 38-59 cm;
- width – 80 cm.
There are two types of aluminum radiators - extruded and cast. The last type is a structure cast from molten metal under high pressure. The profile of extrusion batteries is obtained through a pressing process and then divided into individual parts. Then the sections are connected and sealed.
Advantages of aluminum units:
- Light weight and good heat dissipation, as well as an affordable price compared to devices made of copper or cast iron.
- Valves can be installed to regulate the temperature.
- Durability and attractiveness.
Flaws:
- due to the use of sealing gaskets, they are not suitable for systems with antifreeze;
- low corrosion resistance, therefore suitable only for water with low acidity;
- metal oxidation leads to airing of the system;
- weak areas at threaded connections;
- low resistance to water hammer.
Bimetallic
The design of these units has an aluminum body, inside of which there are steel pipes. Some devices have steel pipes inside only in the place where they are needed to strengthen the vertical channels. Such devices are cheaper, heat up faster, but are less durable than models with an all-steel core. They are tubular, panel and sectional.
Specifications:
- Working pressure – 18-40 atm.
- The coolant temperature is 110-130°C.
- Thermal power – from 125 to 180 W.
- Service life – up to 20 years.
The positive aspects of bimetallic batteries:
- do not require maintenance and give off heat well;
- resistant to mechanical stress and water hammer;
- thanks to a special coating inside steel pipes, they are not subject to corrosion;
- easy to install and lightweight;
- visually attractive.
Their disadvantage is their high cost. In addition, the steel core is susceptible to corrosion when exposed to a mixture of water and air.
Steel
These batteries boast a heat output of 1200-1800 W. They are capable of operating at pressures in the region of 6-15 atm. with coolant heated to 120°C. The thickness of the steel walls is 1.15-1.25 mm.
Advantages:
- They heat up quickly and transfer heat well to the room.
- They weigh little, are easy to install and are inexpensive.
- Visual appeal and the ability to combine with pipes made of different materials.
- Easy care thanks to its simple design.
- Temperature regulators can be installed.
The downside is the short service life (up to 10 years). Not suitable for central heating because without water they are susceptible to corrosion. They do not withstand water hammer.
Classification
Steel batteries are available in three types:
- tubular - welded structure made of pipes with a working pressure of up to 15 atmospheres;
- sectional - durable sections are connected by spot welding, operating pressure up to 16 atmospheres;
- panel ones are the most popular, they are made of two welded rectangular sheets with stamped recesses.
In panel pipes, the operating pressure reaches 13 atmospheres at a coolant temperature of no more than 110 degrees.
How to calculate the size of radiators for a room
Knowing the basic characteristics of heating equipment and the area of the room, you can easily determine the required radiator power, and subsequently all the characteristics of the system, including the boiler.
Let's look at a similar calculation using a real example:
Let’s say a room with the characteristics of 4x3x2.7 is planned for installation of heating - a standard bedroom in a Soviet Khrushchev-era building.
First, let's calculate the volume of the room that will have to be heated: 4*3*2.7=32.4 m3. It is this volume of air that our radiator will have to heat.
Then you should determine how much heat will need to be spent to heat this volume. Without taking into account measures to increase energy efficiency (energy saving, wall insulation, etc.), the standard for the temperate climate zone of Eastern Europe is the cost of heating one cubic meter of 41 watts.
Accordingly, to heat our room you will need: 32.4 m3 * 31 Watt = 1.3 kV
This is the amount of energy that the air needs to receive from the radiator for heating. Next, knowing the required amount of heat, you can calculate the technical characteristics of the radiator that will be mounted.
Each radiator has a heat transfer characteristic. This is the amount of energy that the equipment is capable of releasing into the atmosphere while maintaining the quality indicators of the heating system. This figure may be underestimated, but cannot be exceeded. The radiator power is always indicated on the packaging, in the passport or certificate.
Heating our room will require 1.3 kW of energy. To prevent force majeure effects during abnormal frosts, the indicator is calculated with a margin of 15-20%. In total we have 1.5 watts.
One fin of a standard bimetallic radiator is capable of delivering up to 150-180 Watts of energy. Total: 1500/150=10. Those. To fully heat our room, we will need to install a 1.5 kW radiator, consisting of 10 fins.
If the walls are insulated and vacuum metal-plastic windows are installed, the actual energy consumption for heating can be reduced by 2 or more times. Accordingly, there is no point in purchasing a radiator of higher power.
Features of bimetallic radiators
The second option that the store can offer you is a bimetallic radiator. The prefix “bi” in the word “bimetallic” means “two”. This name is given to this type of battery because they are made from two metals: steel and aluminum.
Let's immediately turn to the positive characteristics of this species:
- The steel in the material from which the body is made will perfectly withstand any surges in water pressure. It is also not subject to corrosion. These properties of the metal ensure high strength and many years of faithful service of the device;
- steel sheet provides serious protection of the case from external mechanical damage;
- active coolant circulation;
- Aluminum coating will ensure rapid heating of the air in the living room;
- battery operating pressure can reach 40 atm;
- the maximum possible coolant temperature is approximately 130 degrees, while for aluminum products it is only 110;
- durable paint coating on the body. This stability is achieved through a two-stage dyeing mechanism:
- First of all, the product is placed in a dye solution and completely covered with paint;
- Then another polymer layer based on epoxy resin is sprayed on top of the dried first paint. Radiators processed using this technology not only look very aesthetically pleasing, but also take on clearer geometric shapes;
easy installation and transportation, especially if you seek the help of professionals. The design of bimetallic batteries is no more complicated than that of simple aluminum ones, however, their installation is also best left to professionals. How long the batteries are installed correctly, the longer they will serve you; the ability to add additional sections directly to your home
However, if you assume that you still want to increase their number, when purchasing, pay attention to the design of the radiator housing. Some of the models on the market have a solid steel core, so they are not divided into sections.
Bimetallic radiator section
One of the options for the appearance of a bimetallic radiator
Let's pay attention to the disadvantages of bimetal devices:
- aluminum used in combination with steel loses its high heat-transfer properties. Due to the steel core inside the battery, you will have to wait a little longer than you are used to for the air to reach the desired temperature;
- increased price. Since the price of steel is higher than silicon, the cost of bimetallic batteries also increases by about 30% compared to aluminum ones;
- increased operating costs. Since bimetallic devices boast increased hydraulic resistance, the amount of energy spent on water circulation will also increase;
- Improper use of radiators can lead to corrosion of its steel parts. This will definitely happen if bimetallic batteries are installed in your dacha, which is not used in winter. As soon as the autumn heating season comes to an end, it will be necessary to carry out the procedure of draining the water from the system. It is because of this that corrosion processes will begin: simultaneous contact of steel with air and water instantly starts them.
- The small tube passage inside the device is subject to rapid clogging. This shortens the service life of the device.
Important! The coefficients of thermal expansion of steel and aluminum differ, which is why the battery begins to emit loud crackling sounds after a short period of time. This sound does not mean that there is a problem inside the device.
Don't worry, your health is safe!
These modern radiators can function properly even in rooms where the air humidity level is high. Their surface is resistant to corrosion. The radiator is given such resistance to aggressive environmental influences by sheet steel, which covers the body of the device with a protective layer.
Inside bimetallic radiators there are water channels of small cross-section. Due to their modest size, they are filled as quickly as possible with hot water coming from a centralized water supply system or an autonomous boiler.
Construction professionals consider purchasing bimetallic batteries and installing them during renovations as one of the best functional improvements to an apartment. Over time, the use of these devices will fully pay for the money spent on them.
Power and number of sections
The power of steel radiators is determined during production by the manufacturer itself: it is set according to the type of radiator - 11, 22 and 33 - and height - from 300 to 900. The power indicator will be determined directly by these values: as a rule, 1 section works per 1 m2 of heated area premises.
Factors for calculation
The calculation of steel radiators begins with determining the climate: for temperate - a variation of 60-100 W/m2, for northern regions - the norm is from 150-200 W/m2. These calculation sources rarely produce errors. The second criterion for calculation is heat transfer, which can be seen on the packaging or data sheet.
The height of the ceilings also matters - the standard value is 2.7 m, if more or less, then you need to adjust accordingly. To do this, the actual ceiling height is divided by 2.7, and the resulting coefficient is multiplied by the standard power. It is important to remember that when doing it yourself, it is better to take power with a reserve: the heat will “go away” to corner rooms, thin walls and other nuances that a simple user will not be able to take into account.
Simple formula
The calculation is carried out in several stages. An average power value of 100 watts per 1 m2 is taken. If the area of the house is 30 m2, and the power of 1 section of the battery is 180 watts, then the calculations will be as follows: 30 * 100/180, a total of 17 sections will be required to heat a space of 30 m2. If this is a corner room, then this value is multiplied by a factor of 1.2 - i.e. 20 radiator sections.
Heating devices are installed in almost every living space. Usually these are Soviet cast iron batteries, modern aluminum or bimetallic radiators. The house will be warm and cozy if the heating radiators are calculated
and well made.
Depends on several factors:
- technical feasibility of an autonomous or centralized heating system
- coolant quality
- individual choice of the customer, taking into account his idea of the quality of this device
- price policy
Correct calculation of the number of radiators
will provide a favorable microclimate in a heated building. It will provide the owner with the opportunity to independently regulate the temperature in the room. Will help in selecting the ideal heating equipment for your interior. This will be done with optimal calculation of radiators.
Every year the winters in our country become more severe, and many people are increasingly thinking about or installing an additional new one. Every third buyer wants to do it on their own. To do this, they have to face the issue of the size and calculation of heating radiator sections
. Next we will take a closer look at this issue.
Characteristics of electric radiators.
There is an alternative to central heating, it is an electric heating system. Such a system has a number of advantages: it heats well, is extremely easy to install, compact, and silent in operation. It is worth noting that an electric heating system is more economical than central heating and other heating systems, because... the cost of installing the system and the energy spent working is significantly lower. It is possible to regulate energy consumption depending on the time of day and outside temperature, which also contributes to savings.
Advantages of electric radiators:
Easy installation of the heating system; The system is environmentally friendly; Saves space because
electric heating radiators are very compact; The safety of using an electrical appliance is ensured thanks to the presence of special sensors; Fully autonomous operation with a standard supply voltage of 220 V; Thanks to their design, electric batteries will harmoniously fit into any interior; It is possible to select the number of electric battery sections, depending on the room parameters. Please note that it is necessary to decide on the choice of heating system at the building design stage. The main disadvantage of an electric convector is the cost of electricity
Electricity consumption directly depends on possible heat losses in the room - doors, type of double-glazed windows, window area, size and quality of room insulation
The main disadvantage of an electric convector is the cost of electricity. Electricity consumption directly depends on possible heat losses in the room - doors, type of double-glazed windows, window area, size and quality of room insulation.
Conclusion: If you are the owner of private houses and apartments that are equipped with autonomous heating systems, you can choose batteries based on your aesthetic preferences and financial capabilities, since the risk of water hammer in autonomous heating systems is usually small, and the coolant is of fairly high quality.
How to increase the performance of already installed batteries
Cost 45-150 rub.
An indispensable element of the heating system is the Mayevsky valve.
Many modern radiators come with it included, otherwise you can buy it in addition and easily install it yourself.
The device is mounted in the upper radiator plug, opposite the coolant supply, and makes it easy to eliminate airiness, which results in a significant reduction in heat transfer.
Some resort to the “folk method”, installing heat-reflecting screens made of foil or metal with corrugated ribs between the battery and the wall.
The most effective method is to install additional sections, but this should only be done when the heating system is completely turned off and the additional load from the added sections should be taken into account.
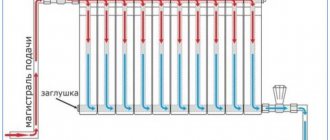
Methods for connecting radiators
Of course, in order for steel heating radiators to perform their functions, they must be properly integrated into the system. Panel radiators can be connected from below or from the side. When choosing radiators, you need to think very carefully about their connection diagram - in some situations you have to combine the bottom connection with the side connection.
The bottom connection has a characteristic advantage - radiators installed in this way allow you to hide the pipes under the floor or in the walls, or to place them at a minimum distance from the floor. You have to pay for this advantage - the cost of devices with a bottom connection is an order of magnitude higher than more traditional batteries with a side connection. Iron heating radiators connected from below are marked with the letter “V”.
Connecting radiators from the side has two important advantages:
- Firstly, installation of the side connection is much simpler than the bottom one;
- Secondly, with proper installation, the side connection will ensure full heat transfer (for comparison, with a bottom connection, the level of heat loss can reach 20%).
Complete set and installation of steel panel radiators
- Panel radiators are standardly designed for wall-mounted installation and have mounting plates on the rear side. Floor installation is possible; for this you need to buy special floor fasteners.
- Some manufacturers supply their radiators with a basic installation kit, which includes: a set of wall brackets, a plug and a manual air vent (Mayevsky valve).
- Valve-type panel radiators (with a thermostatic valve insert) are supplied without a thermal head, which must be purchased separately.
- For radiators that are supplied without an installation kit, you must purchase the appropriate installation kit.
Comparative findings
As the table below compares the heat transfer of heating radiators shows, the most efficient in terms of power are bimetallic heaters. Let us remind you that they are an aluminum finned body with a strong welded frame inside made of metal tubes for the flow of coolant. In all respects, this type of heater is suitable for installation both in heating networks of high-rise buildings and in private cottages. Their only drawback is their high cost.
The heat transfer of aluminum radiators is slightly lower, although they are lighter and cheaper than bimetallic ones. In terms of test and operating pressure, aluminum devices can also be installed in buildings of any number of floors, but subject to: the presence of an individual boiler room with a water treatment unit. The fact is that aluminum alloy is susceptible to electrochemical corrosion from low-quality coolant inherent in central networks. It is better to install aluminum radiators in separate systems.
Cast iron radiators differ sharply from others, the heat transfer of which is significantly lower with a large mass and capacity of the sections. It would seem that with such a comparison they would not find application in modern heating systems. Nevertheless, the traditional MS-140 “accordion” continues to be in demand, their main trump card is durability and resistance to corrosion. Indeed, gray cast iron, from which MS-140 is made by casting, can easily serve for up to 50 years or more, and the coolant can be anything.
In addition, a conventional cast iron battery has high thermal inertia due to its massiveness and capacity. This means that when the boiler is turned off, the radiator remains warm for a long time. As for the operating pressure, cast iron heaters cannot boast of high strength. Purchasing them for networks with high water pressure is risky.
(no votes yet)