Until you are faced with choosing a pipe, it seems that there is nothing complicated about it. There is a size, and you need to select the material according to it. That’s how it is, but you can measure it both inside and outside. So which measurement is correct? Oddly enough, both. There are standards according to which pipes are marked by outer size, and others that indicate the inner size. And the diameters of steel pipes are only available in a certain set. So, with the same outer diameter, we can have a pipe with different capacities and operating at different pressures.
Let's understand the terminology
Our country has a metric number system. And we measure everything in meters, centimeters and millimeters. Traditionally, the diameter of steel pipes is measured in millimeters. But the pipe has two diameters - internal and external, and is also characterized by wall thickness. So what diameter are we talking about when we talk about the size of steel pipes? Depends on the standard to which they are made. In some cases this means the outer diameter, in others the inner diameter. That's how difficult it is.
Diameters of steel pipes: which one to use
Nominal and nominal diameter
Pipes are used at different pressures. For a higher one, greater strength is required and this is achieved due to the wall thickness. In this case, the outer diameter of the pipe is left fixed. Otherwise, it will not be possible to connect the segments, and difficulties will arise with threads, fittings, etc. So the outer diameter is only an external parameter. Therefore, such a concept as conditional passage was introduced. In general, this is an outdated name and according to modern standards they say “nominal diameter”.
The nominal diameter of the pipe (nominal diameter) is a calculated value that is calculated during design. This value approximately corresponds to the internal diameter of the pipe in millimeters. Approximately, because the walls, with the same outer size, are of different thickness. This means that the clearance is changing. To somehow harmonize all this, a nominal diameter was introduced. This is a specific list of quantities defined by GOST 28338-89. They are shown in the table. Actual dimensions are rounded to the nearest nominal.
A number of standard nominal values of the nominal diameter of gas and water pipes and fittings for them
The designation of this value is DN, sometimes the Russian version is called Dn. After these letters there is a number without metric signs: DN30 or DN150. This is read as a nominal pipe diameter of 30 or 150, or a nominal diameter of 30 and 150. There are no units of measurement, since this is a conventional value.
Once again: all existing elements of water supply and gas pipeline systems are marked in accordance with the list of standard values - nominal diameters Dn. The actual size of the internal cross-section of a pipe or fitting may be larger or smaller. It is rounded to the nearest standard value.
In fact, the nominal diameter of a pipe or nominal size is a value that reflects the throughput. It is approximately equal to the inner diameter. After all, when you assemble a system, you use elements from different materials, with different wall thicknesses. Therefore, it is more reasonable to focus not on the diameters of the internal part, but on the nominal diameter. This will make it possible to ensure the same throughput of all elements of the system.
Calculation methods
How to calculate the diameter of heating pipes? There are several methods:
- According to special tables. However, their use still requires preliminary calculations: the power of the heating system, the speed of movement of the coolant, as well as heat loss along the main line.
- By thermal power.
- According to the resistance coefficient.
What you need to know to calculate
To carry out the calculation you will need the following data:
- Heat demand (thermal power) of the entire house and each room separately;
- The total power of the heating devices used (boiler and radiators).
- Thermal load on individual sections of the circuit.
- The total heat loss of the house and each room separately during the coldest winter period.
- Resistance value. It is determined by the wiring diagram, the length of the line, the number and shape of bends, connections, and turns.
- The total volume of coolant loaded into the heating main.
- Flow speed.
- Circulation pump power (for forced heating).
- Line pressure.
Calculation of pipe cross-sections for heating systems with forced air circulation:
Calculation procedure
- Calculation of required thermal power.
- Determination of the circulation rate of the carrier in the heating system.
- Calculation of heating circuit resistance.
- Calculation of the required pipeline cross-section.
- Calculation of the optimal diameter of the heating collector (if necessary).
Calculation of system thermal power
Method 1. The simplest way to calculate thermal power is based on the established standard of 100 watts per 1 m² of room. Those. with a house area of 180 m², the power of the heating circuit will be 18,000 watts or 18 kW (180 × 100 = 18,000).
Method 2. Below is a formula that allows you to adjust the data taking into account the power reserve in case of severe frosts:
However, these methods are characterized by a number of errors, because does not take into account the range of factors influencing heat loss:
- ceiling height, which can vary in the range from 2 to 4 or more meters, which means that the volume of heated rooms, even with the same area, will not be constant.
- the quality of insulation of the house facade and the percentage of heat loss through external walls, doors and windows, floor and roof;
- thermal conductivity of double-glazed windows and materials from which the house is built.
- Climatic conditions of the regions.
Method 3: The method presented below takes into account all the necessary factors.
- The volume of the entire house or each room separately is calculated using the formula:
V = h×S,
Where:
- V – Volume of the heated room.
- h – Ceiling height.
- S – Area of the heated room.
- The total power of the circuit is calculated:
The following formula is often used:
In this case, the regional correction factor is taken from the following table:
The heat loss correction factor (K) directly depends on the thermal insulation of the building. It is customary to use the following average values:
- With minimal thermal insulation (typical wooden or metal structure made of thin sheets), a coefficient in the range from 3 to 4 is taken into account;
- Single brickwork - 2-2.9;
- Average level of insulation (double brickwork) – 1-1.9;
- High-quality thermal insulation of the facade - 0.6-0.9.
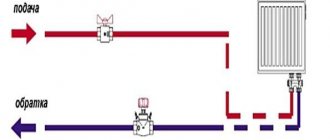
Water speed in pipes
The uniformity of the distribution of thermal energy among the elements of the circuit depends on the speed at which the liquid moves, and the smaller the diameter of the pipeline, the faster it moves. There are speed limits:
- not less than 0.25 m/sec, otherwise air pockets will form in the circuit, preventing the movement of the coolant and causing heat loss. If the pressure is insufficient, the air plugs will not reach the installed Mayevsky valves and air vents, which means they will be useless;
- no more than 1.5 m/sec, otherwise the media circulation is accompanied by noise.
The reference flow rate is from 0.36 to 0.7 m/s.
This should be taken into account when choosing the appropriate pipe section. By installing a circulation pump, it becomes possible to control the circulation of coolant in the circuit without increasing the diameter of the pipeline.
Calculation of heating circuit resistance
When calculating the cross-section of pipes using the resistance coefficient, the first step is to determine the pressure in the pipeline:
Then, by substituting the pipe diameters, the minimum heat loss value is selected. Accordingly, the diameter that will satisfy acceptable resistance conditions will be the desired one.
Heating manifold calculation
If the heating system provides for the installation of a distribution manifold, then determining its diameter is based on calculating the cross-sections of the pipelines connected to it:
The distance between the collector pipes should be equal to triple their diameter.
Diameters of steel pipes according to standard 3262-75
This document describes water and gas pipes (the common abbreviation VGP). They can be made of galvanized steel or regular steel. They can have a thread - short or long, the edge should be smooth, with a small amount of burrs (5%). The edge of the pipe without thread can be smooth or designed for welding - with a chamfer of 35-45°.
Steel pipes manufactured according to the GOST 3262-75 standard, with an equal outer diameter, can have three wall thicknesses. Depending on the wall thickness, the pipe is called:
- lightweight (the thinnest wall);
- ordinary (average in thickness);
- reinforced (the thickest).
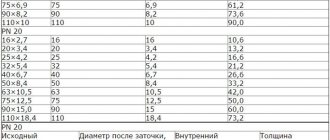
Table of diameters of steel pipes GOST 3262-75
With equal outer diameter and different wall thickness, the inner diameter changes. But to avoid confusion, the concept of nominal bore or nominal diameter is used. Previously it was designated as Du, now it is correct to write DN. Sometimes it is believed that the nominal bore is equal to the internal diameter. Sometimes this is true, but not always. Rather, this happens very rarely. More often, the actual internal cross-section of the pipe is different - the walls are of different thicknesses. How to control the quality of a product? According to the correspondence of wall thickness and outer diameter.
How to check quality
Since the internal clearance can be different, you have to control the external dimensions and wall thickness. Thickness is more important. It must be measured at different points, at both ends of the pipe. Approximately this parameter can be tracked by the mass of a linear meter.
By the way, there can be considerable deviations in wall thickness. The standard allows deviations both upward and downward. If the diameter of steel pipes is no more than 40 mm, permitted deviations are up to 0.4 mm in the direction of increase and up to 0.5 mm in the direction of decrease. There are two categories of pipe production: regular and high precision. For products of increased precision, the deviation towards decreasing wall thickness is slightly less.
Permissible deviations for VGP
Examples of designations for pipes that are manufactured in accordance with this standard: pipe 20*2.8 GOST 3262-75. It should be read as a pipe with a standard diameter of 20 and a wall thickness of 2.8 mm. From the table you can determine that this is a pipe of normal strength with an outer diameter of 26.8 mm. There you can also find the approximate mass of a meter depending on the thickness of the walls.
Bottom line
If we have a private house or apartment, autonomous heating for no more than 5-8 radiators and 2-3 forks, we can easily calculate everything ourselves. We need to know how powerful each heating point is, the heat loss in the room and a good table for selecting the pipe diameter.
However, as has already become clear, trust experienced specialists to calculate a complex multi-level system with numerous junctions and forks. Well, if you still decide to do everything yourself, then at least read articles like ours and consult with experts.
How to deal with import designations
There are not only products from domestic manufacturers on the market. There are pipes marked according to the American system. Let's start with the fact that they distinguish between two types of pipes: pipes and tubes. Both words translate as pipe, but they are intended for different systems and the requirements for them are different.
Pipes type
Type of Pipes - electric welded and seamless. They are designed for transporting liquids and gases. So this is exactly the type that can be used in our heating and water supply systems. The main characteristic of pipes type pipes is the internal diameter. There are two strength standards in this group, which determines wall thickness and operating pressure.
- Schedule 40 or standard. The designation may include st (as in the figure below). These are products with standard wall thickness.
- Schedule 80 or extra heavy. The designation is EX. This is a material for use in high pressure pipelines.
Difference in internal diameters of Pipes of different strength categories: standard and heavy.
As you understand, with the same external size, the clearance will be different. Let's take a two-inch pipe as an example. It is designated as NPS=2″ internal diameter in different designs differs:
- standard (standard) schedule 40 - 2.067 inches (which is approximately equal to 5.25 cm);
- extra heavy schedule 80 - 1.939 inches (approximately 4.925 cm).
These categories standardize wall thickness and maximum operating pressure. The outer diameter remains constant, but the actual inner diameter changes with the wall thickness. That is, NPS=2″ describes the inside diameter, which will be about two inches, but will vary depending on the wall thickness. Here the situation is similar to our standards: there is a certain list of values to which actual parameters are rounded when labeling. Once again: if we are talking about a two-inch Pipe type pipe (the marking says NPS), you need to understand that we are talking about the internal diameter, but it will not be exactly two inches. It will be either a little more or a little less. Same with other sizes in inches.
Type Tubes
The word Tubes refers to pipes that are marked by outer diameter. The internal one will depend on the wall thickness. Therefore, this standard also contains the concept gauge, which can be translated as gauge. It just indicates the wall thickness.
The same diameters of steel pipes do not mean the same weight
The marking is marked with ASTM. The numbers following the abbreviation describe the outer diameter. In this group, we may be interested in copper pipes.
Where can I get the tables?
Everything is simple here. Usually, all detailed tables with all the necessary data can be viewed (or downloaded) on the websites of pipe manufacturers. But it happens that there are still no tables. You can get out of this situation as follows. If there are no tables for the outer diameter, then take the one for the inner diameter and calculate according to it. Yes, there will be inaccuracies, but, as experience shows, for forced circulation they are completely insignificant and acceptable.
Having analyzed a huge number of already installed and perfectly working systems, experts noticed a certain pattern in the choice of pipe cross-section. It is mainly suitable for small-sized autonomous systems.
In private houses, the pipes that come out of the boiler are most often one-half and three-quarters in size. This diameter of the pipe for heating a house is used until the first fork, and at each subsequent fork the cross-section is reduced by exactly one step. But this method is applicable only for apartments and one-story houses; for high-rise buildings, alas, everything will have to be calculated very carefully.
Correspondence table for pipe diameters in inches and millimeters
Let's say right away that pipes are measured not in ordinary inches, but in pipe inches. If a regular inch is 25.4 mm, then a pipe inch according to GOST is 33.249 mm . And pipes with such an outer diameter (or close to it) are usually called inch. But the internal diameter can vary greatly: the wall thickness of an inch pipe can be 2.5 mm, or it can be 8 mm. The correspondence of the nominal diameter in inches and millimeters is given in the table. Note! These are not outer/external size values. This corresponds to the nominal diameters of our standard and the DIN standard.
Correspondence table for nominal bore or nominal diameter of pipes in inches and millimeters
If you look at the correspondence table, you can see that when calculating the nominal diameter, the usual inch is used. We use pipe when it is necessary to convert the symbol into outer diameter. But even knowing the size of the pipe inch will not help to obtain the exact value of the outer diameter. It gives an approximate correspondence by which you can navigate. The exact details are shown in the table below.
Steel pipe diameters in inches, outside size in millimeters and nominal equivalent in our metric system
So, let's summarize. How to convert pipe dimensions in inches to centimeters and vice versa? If you convert Du into inches, you must divide by the usual inch and round the resulting number to the nearest standard. The diameters of steel pipes of common sizes are summarized in tables. If there is no table, the outer diameter can be calculated approximately using the “pipe inch”. We multiply the pipe size in inches by 33.249, we get a number close to the table value. Why not accurate? Because we are trying to convert the nominal (read - conditional) diameter into a real value - the external size. Therefore, the result is only close to the table.
Plastic
Nowadays, their plastic counterparts have become an alternative to metal pipes. Moreover, their sizes vary widely. The material for such a product is:
- Polypropylene;
- Polyethylene;
- Metal-plastic.
Each manufacturer of such pipes sets its own size chart. Therefore, if one system is being manufactured, it is advisable to use parts from the same manufacturer.
Of course, there will definitely be discrepancies, but they will be minimal and will not cause any particular difficulties for a good master. If a person has little experience, he will have to make some efforts to fit all the sizes.
The table of sizes of plastic pipes for water supply using polypropylene of various densities shows the most popular models.
When all kinds of communications are laid, builders also use other diameters of plastic water pipes.
The diameters of water pipes in the table help you select the appropriate product for repairs or other work.
How to measure pipe diameter
If you are not a professional plumber, you are unlikely to be able to determine the size of the pipe by eye. But you need to know this parameter, since the diameters of steel pipes are an important parameter. This value will be required, for example, when replacing a pipeline, installing new fittings, etc. You will need the diameter. It is easier to determine the wall thickness - most often it is 4 mm. Its parameters are sufficient for any household pipeline: water supply (cold or hot), heating. You can measure it on the saw cut. But if you check old pipes, it may well be that the walls have become thinner.
So, to determine the diameter of a pipe, the easiest way is to measure its cross section. If you have access to the cut, use a ruler or measuring tape. If there is no access to the cut, a drawing pen can help.
Measuring pipe diameter using improvised means
If you don’t have a drawing board, you will need a measuring tape or a flexible tape measure. You need to measure the circumference and write the resulting figure in millimeters. To calculate the diameter of the pipe, you need to divide this figure by 3.14 (the number π).
How to determine the diameter from the circumference
For example, you measured 4.4 cm, that is 44 mm. Divide this figure by 3.14, we get: 44/3.14 = 14 mm - this is the outer diameter of the pipe. We look at the table, which shows the diameters of steel pipes. Most likely, our pipe is 13.5 mm in diameter, with a nominal diameter of 8 mm. We attribute the slight discrepancy to measurement inaccuracy.
Cast iron
Such products are used for installing water supply systems outside the building. In residential premises, cast iron water supply is installed extremely rarely. This material has high strength, but increased fragility. Its main disadvantage is its heavy weight and high cost. The operation of such cast iron products is designed for many years.
To compare the sizes of cast iron plumbing products, below is a table showing the dimensions of Class A cast iron pipe.