Law of Hydraulics: Any flowing fluid chooses the path of least resistance. In the heating network of a private house, the rule works like this: the coolant pushed by the pump tends to pass through the first radiator or the shortest circuit of heated floors. As a result, remote rooms of the building warm up much less well. To ensure uniform distribution of flows, hydraulic balancing of the heating system is necessary. We'll tell you how to adjust radiators and underfloor heating hinges with your own hands.
Methods for balancing a heating system
A well-equipped heating system means not only the installation of all heating equipment (boiler, pump, radiators).
The key to successful operation and efficiency of the system is proper adjustment and configuration. To do this, a procedure such as balancing is performed, the purpose of which is to distribute heat transfer between rooms in the way that the owner of the house needs. Today, you can balance your heating system yourself or with the help of professionals. Some users believe that such a setting is required only for large buildings, while for private houses and small buildings such a procedure is not a prerequisite.
Of course, this opinion is wrong. Balancing is a mandatory process for any type of premises that have a heating system. If this is not done, then heat will be distributed in excess in some areas, while in others it will not be sufficient. Balancing will avoid these unpleasant moments.
Features of working with different types of wiring
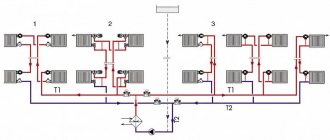
Single-pipe heating systems lend themselves to balancing adjustment most easily. This is all thanks to the fact that the total flow through the radiator and the connecting bypass is always the same and does not depend on the throughput of the installed fittings. Therefore, in systems like “Leningradka” the work is carried out not so much on balancing the flow, but on the equation of the amount of heat released by the coolant in the radiators. Simply put, the main goal of balancing in this case is to ensure that water flows to the most distant radiator at a sufficiently high temperature.
In two-pipe dead-end systems, a slightly different principle applies. Each radiator of the system is a kind of shunt, the hydraulic resistance of which is lower than that of the rest of the group located further along the flow direction. Because of this, a significant part of the coolant flows through the shunt back to the thermal unit, while the circulation further through the system has a much lower intensity. In such heating systems, it is necessary to work on equalizing the flow in each radiator by changing the throughput of the fittings.
Two-pipe associated heating systems do not require balancing at all, but at the same time they have a relatively high material consumption. This is the beauty of the Tichelman loop: the path that the coolant takes in the circuit of each radiator is approximately the same, due to which the equivalence of the flow at each point of the system is automatically maintained. The situation is similar with radiant heating systems and water heated floors: the flow alignment is carried out on a common manifold using float flow meters.
Warm floors and radiant wiring
Since the underfloor heating circuits and radiator radiators are connected to a common comb, balancing is carried out directly on the collector. The setting method depends on the availability of rotameters - transparent flow meter flasks installed on the supply or return lines.
To correctly configure the coolant supply using rotameters, you should calculate the water flow through each loop using the formula:
- G – mass flow rate of heated water flowing through the circuit, kg/h;
- Q – the amount of heat that the circuit or radiator should release into the room, W;
- Δt – temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the loop, the calculated value is taken to be 10 °C.
The power of one floor circuit Q is determined based on the heat demand of a separate room. The parameter is calculated according to the specific ratio of 100 W/m² of room area or according to the method of calculating the heating load. The flowmeter scales are marked in l/min, which means the result must be divided by 60.
Calculation example. Heating a room with an area of 10 square meters requires 1 kW of heat. Coolant consumption will be 0.86 x 1000 / 10 = 86 kg/h or 86 / 60 ≈ 1.43 l/min.
Clarification. If a large area is divided into 2 identical heating monoliths with separate water loops, we also divide the calculated flow rate in half.
Here the rotameters are installed on the supply line of the comb, but can also be installed on the return line.
Further balancing of the underfloor heating loops is carried out according to the instructions:
- With the system filled and pressurized, turn on the underfloor heating circulation pump. It is not necessary to start the boiler.
- Using the manual adjustment caps, close all thermostatic valves on the second part of the comb.
- Open the first valve completely and adjust the corresponding rotameter. The required flow volume is set by rotating the lower ring of the flow meter.
- After adjustment, close the valve again and move on to the next circuit. At the end, open all the regulators and check the water flow again using the rotameters.
Reference. On manifolds from different manufacturers, flow meters are installed on the supply or return manifold (they also differ in design). To adjust the maximum flow, the location of the rotameters does not matter.
Beam batteries are balanced in a similar way. To be sure, you can combine 2 options - according to the calculated flow rate and the temperature of the radiator surface (the method is described in the previous section).
Scheme of flow control with a rotameter. The flow rate through each circuit is shown by control washers in transparent flasks, the unit of measurement is liters per minute
If, in order to save money, you managed to buy a collector without rotameters, the setup will take several days. The goal is to achieve the same temperature in the return pipelines of all loops. That is, the initial installation is made approximately according to the power and length of the circuit, then the return temperature is measured and the flow rate is adjusted.
To check the balancing of the heated floor, you need to start the heating boiler. Negative point: after adjusting the flow rate, you will have to wait several hours until the thickness of the concrete warms up and the temperature of the return lines stabilizes.
Setting by temperature
Very often the homeowner does not have any design documentation, but the system was invented and assembled by the talented welder Uncle Vanya. Then all that remains is to regulate each battery by temperature.
To balance the heating system with your own hands, you need to install a special valve at the outlet of each radiator, such as shown in the photo. Additionally, you will need an electronic thermometer that measures the temperature on any surface.
The process begins with the valve on the farthest and most powerful heating device fully opening. The rest open at a certain number of revolutions. For example, if there are 6 batteries on one branch, and the valve is unscrewed by 5 turns, then on the first radiator we make 1 turn, on the second - two, and so on, opening the last one all the way. Approximate balancing of a two-pipe heating system for a private house is to ensure that the temperature at the outlets of all heaters is the same.
To do this, you need to measure the temperature of the metal valve body. When it is high, cover it a little, if low, open it. The next measurement should be taken after 10 minutes so that the temperature has time to stabilize after the change.
Preparation for the procedure
Before you start balancing, prepare everything you need for it. To get started, you will need the following:
- A special contact thermometer with which you can accurately determine the degree of heating at various points.
- In order to adjust the balancing valve, you will need a hex wrench.
- If it has been preserved, it is advisable to take a heating wiring diagram. It may not exist if the equipment was installed a long time ago or was done without a diagram prepared in advance.
- You will need paper, pencil and marker.
Instead of a contact thermometer, you can use other models. Professional specialists often use a specialized thermal imager for this purpose. You can also use a remote pyrometer.
If there is no wiring diagram, then you need to sketch out a plan for the location of its elements yourself. First of all, the sequence of connecting the radiators and their distance from the boiler room are noted. Balancing a two-pipe heating system is similar to what is done for a single-pipe one.
When heating balancing begins, the mud trap at the inlet of the heating boiler is cleaned. Then it is necessary to warm up the heating boiler. This must be done up to maximum operating temperature. It doesn’t matter whether the weather outside is cool or hot.
Electronic balancing of the system
Temperature balancing is a long and painstaking process. It is very difficult to accurately regulate complex heating systems in this way. It is much easier to use a smartphone with a special mobile application, additional electronics and a circulation pump with a balancing function.
- a circulation pump with a corresponding function (in some cases, a removable pump head is installed on the existing pump, designed to balance the system);
- smartphone and special software;
- wireless communication module installed on the pump head.
Electronic balancing of the system is carried out in four stages:
Preparatory – installing a special application on a mobile device and connecting the communication module to the pump. Entering data about the system (area of heated premises, number of heating devices, coolant temperature, etc.), measuring pressure and flow in each radiator or floor heating circuit (performed using a mobile application). Balancing the system according to the data of the mobile application is done using balancing valves (valves). Dismantling the communication module and saving the balancing report generated by the mobile application.
Instead of a conclusion: correct balancing allows you to fine-tune the operating parameters of the heating.
This significantly reduces the cost of operating the system and ensures the most comfortable temperature in all rooms.
Security group
The security group consists of three elements connected in series or to one housing:
An emergency safety valve that allows you to discharge excess coolant when the pressure in the system increases. The discharge can be placed in a transparent container (for example, a plastic bottle). This will make the device safer and will notify you that an emergency has occurred (even if no one was home). Automatic air vent - removes air from the coolant, which, if present in the heating system, can render it inoperative. Pressure gauge - allows you to visually monitor the coolant pressure in the supply line.
The safety group crashes into the supply line immediately at the outlet of the heating boiler. This is done in order to primarily protect the boiler, which has the highest temperature.
The safety group is installed strictly vertically, and it must be located above the level of the heating boiler.
An additional automatic air release valve should be installed at the highest point of the system. Air will definitely enter the system during its refueling (refueling), and this device will help stabilize the operation of the system, avoid stagnation of the coolant due to air accumulation and extend the life of the circulation pump.
Signs of a critical coolant shortage
Not all owners of private houses monitor the technical condition of their water heating; it works - and that’s okay. When a hidden leak occurs, the system continues to function for some time until the amount of coolant drops to a critical level. This moment is monitored by the following criteria:
- In an open system, the expansion tank is first emptied, then the main riser rising from the boiler is filled with air. Result: cold batteries when the supply pipeline overheats; turning on the maximum speed of the circulation pump does not help.
- The lack of water during gravity distribution manifests itself in a similar way; in addition, the gurgling of water in the riser can be heard.
- On a gas heater (open circuit), frequent starts/turns of the burner are observed - clocking, the TT boiler overheats and boils.
- The lack of coolant in a closed (pressure) circuit is reflected on the pressure gauge - the pressure gradually decreases. Wall-mounted models of gas boilers automatically stop when they fall below a threshold of 0.8 Bar.
- Floor-standing, non-volatile units and solid fuel boilers continue to regularly heat the remaining water in a closed system until the volume vacated by the coolant is filled with air. The circulation will stop, overheating will occur, and the safety valve will operate.
We will not explain why the system needs to be recharged - this is an obvious measure to maintain the functionality of the heating. All that remains is to choose a method for replenishing the heating network.
Automatic debugging
There is a kind of golden mean between the two methods described above. Special equipment for automatic balancing of hydraulic heating systems allows adjustments to be made with very high accuracy and in a fairly short time. Currently, the main technical solution for such purposes is the Grundfos ALPHA 3 “smart” pump, equipped with a removable transmitter, as well as a proprietary application for mobile devices. The average price of a set of equipment is about $300.
What is the essence of the idea? The pump has a built-in flow meter and can exchange data with a smartphone or tablet, where all information is processed. The application works as a guide: it guides the user step by step and indicates what manipulations need to be carried out on different parts of the heating system. At the same time, individual rooms with a specified number of heating devices are saved in the application database; it is possible to select different types of radiators, indicate their power, required heating standards and other data.
The process is extremely simple and fully demonstrates the algorithm of the program. After pairing with the transmitter and preparing for operation, all radiators are disconnected from the system; this is necessary to measure zero flow. After this, the shut-off valves on each radiator are opened completely in turn. In this case, the flow meter in the pump notes changes in the flow and determines the maximum throughput of each heating device. After all radiators are entered into the program database, they are individually adjusted.
The shut-off valve on radiators is adjusted in real time. The application has a sound indication for the ability to work in hard-to-reach places. Balancing requires fine adjustment of the shut-off rod to a position at which the current flow rate in the system is equal to the value recommended by the program. Upon completion of work with each radiator, the application generates a report that includes all heating devices in the system and the coolant consumption in them. After balancing, the ALPHA 3 pump can be removed and replaced with another with similar performance parameters. published econet.ru
If you have any questions on this topic, ask them to the experts and readers of our project here.
Video description
How to supply heating in an apartment building
When the management company's review of claims is unsatisfactory, you can file a complaint with Rospotrebnadzor or the prosecutor's office. It is also possible to defend your rights in court. Residents can not only claim a reduction in heating bills, but also compensation for moral damages.
Using air vents to remove air plugs Source 1-teplodom.ru
Why do balancing?
Any heating system, regardless of its type, must ensure that the calculated volume of coolant is delivered to the radiators so that they, in turn, can properly heat the room. Moreover, each radiator should receive exactly as much hot water as needed. In no case less and, preferably, no more. However, everyone knows that more water will always follow the path of least resistance.
That is, if the hydraulic balancing of the heating system is not done, then most of the heat will go to the batteries closest to the boiler, and the furthest ones will receive practically nothing. Some rooms are hot, others are cold. At the same time, the boiler does not operate in an economical and gentle mode, but at the maximum. The figure below clearly shows the picture of heat distribution throughout the system in two versions: unbalanced and configured as expected:
So, hydraulic balancing is necessary for:
- uniform heating of all heating devices;
- boiler operation in normal mode and energy saving;
- to avoid the noise of large volumes of water flowing through nearby batteries at high speed.