Steel heating radiators have become widespread due to their affordable price and significant range of technical characteristics. They can be used both in individual heating systems of low-rise buildings and in multi-apartment buildings of any number of floors.
There are panel and tubular steel radiators, which have their own characteristics. Both types can be either side or bottom connection types, which facilitates their installation and expands the selection. In the article we will look at the differences between the types, give recommendations on choice, and compare the characteristics of the best models.
Panel steel heating radiators
Modern panel radiators have fairly high technical and operational characteristics, are affordable and have an aesthetic appearance that does not require modification or painting.
They combine the functions of a radiator and a convector, since they pass air through their structure, enhancing its convection in the room, due to which they have relatively high heat transfer rates and provide comfortable and fast heating.
Panel steel heating radiators can have a heat transfer rate from 179 to 13,173 W with a panel length from 300 to 3000 mm. Most models are designed for an operating pressure of 10 atm., which is enough for central heating of apartment buildings with up to 10 storeys, in which the pressure in the system is within 8-9 atmospheres.
Design and device
The design of steel panel batteries is simple. The basis is stamped steel sheets. During the stamping process, vertical (along the plane) and horizontal (along the edges) channels are extruded onto them, two sheets mirrored to each other are welded at the edges, sealed spaces are formed between them, which will be filled with coolant (water).
This can be clearly seen by looking at a cross-section of a steel panel radiator (photo below).
For the inside of a steel radiator, in order to obtain a convection effect, sheets 0.3-0.5 mm thick with U-shaped ribs are made. They are fixed by spot welding to the previously mentioned panels, between two such elements the pipes necessary for inserting into the pipes of the water heating circuit are welded. At the final stage, all welding seams are polished, painting is done, and the walls and top grill are installed.
The result is two heat-emitting panels, which are filled with coolant through pipes; on the inside of each there are ribs through which air circulates: warming up from the radiation of the radiator, it rises up, the space inside is filled with cold air from below, and so on in a circle (convection effect).
The painting stage is especially important; the quality of the heating device largely depends on it: its resistance to coolant contamination and corrosion, environmental friendliness and service life.
Manufacturers use painting methods such as immersing the radiator in a coloring composition (OP), anodic electrophoresis (AEF) or cathodic electrophoresis (CEF) - the most high-tech and effective. The KEF painting technology makes it possible to reduce the level of solvent in the paint to 2%, due to which the radiator does not emit harmful substances when heated to high temperatures (over 90-100 degrees).
Panel types
Above we described the standard, most common design. In total, there are 7 types of steel panel heating radiators, which differ only in the presence of convection fins, the number of steel panels and, accordingly, width.
The type of panel heating device must be indicated in its name. For example: Buderus Logatrend VK-Profil 22 (500×2000 mm) – the number after the model name is its type (22); Kermi FKV 11 (500×1100 mm) – type 11 radiator. Let's look at the features of each type.
| Type | Appearance (click to enlarge) | Design Features | Width (depth), mm |
| 10 type | It consists of one flat steel panel through which the coolant circulates. Due to the lack of convection fins and the presence of only one panel, it is inferior to standard models of type 22 in heat transfer by 40-60%. But this design also has a lot of advantages: lower cost, no circulating air flow that carries dust, very compact dimensions and ease of maintenance due to the absence of many complex-shaped surfaces. The panels are recommended for installation in children's rooms, children's and medical institutions. | 46-48 | |
| 11 type | Consists of 1 panel 1 fixed on it on the back side of a convection sheet with U-shaped ribs. Essentially it is half of a standard 22nd radiator. The design loses about 35-50% of heat transfer compared to the standard one, it is still relatively inexpensive, but it already tolerates dust masses and requires more careful maintenance | 61-64 | |
| 20 type | They consist of two panels inside which coolant circulates. The panels are connected by a lattice on top and walls on the sides. Due to the lack of convection, it is inferior in heat transfer to 30-35% of the standard design, but does not tolerate dust and is easy to clean. | 66-84 | |
| 21 types | It has 2 panels and 1 convector fixed from the inside of the front. It only loses about 8-10% of thermal power, but costs on average 15-25% less. Some models have more compact sizes. | 76-102 | |
| 22 type | Standard design of 2 panels and convectors on the inside of each. | 100-108 | |
| 30 type | The design consists of 3 panels filled with coolant, connected by pipes, side walls and an upper grille. They are not inferior to the standard 22 type in terms of heat transfer, but do not tolerate dust during convection, are easier to maintain, but cost 25-35% more. | 152-153 | |
| 33 type | It consists of 3 panels and 3 convectors, essentially adding another panel with a convector to the outside of the standard structure. They have increased heat transfer by as much as 50-65% compared to type 22. It is recommended for installation in private houses or cottages with a large floor area and glazing, in 2-level apartments. | 155-170 |
Technical and operational characteristics
Panel radiators are designed for a standard coolant temperature of 70°C, the maximum temperature depends on the model and can reach 90-120°C. The operating pressure of most models, as we have already mentioned, is 10 atmospheres or more with a standard pressure in the central heating system of 8-9 atmospheres (mPa).
However, the disadvantage of steel heating devices is their poor resistance to water hammer, which may occur at the beginning of the heating season (during testing and startup of the system). Therefore, when installed in a central heating system, there is always a risk of reducing the life of the batteries.
In such situations, we recommend installing pressure reducers that are able to control overloads and cope with water hammer (issue price 800-2000 rubles).
| Technical and operational characteristics | Range of values of existing models |
| Heat dissipation (thermal power) | 179- 13 173 W |
| Heated area | 1.79-130.17 m2 |
| Max operating temperature | 90-120 °C |
| Volume of coolant (water) in the radiator | 0.84-22.8 l |
| Weight | 2.76-96.41 kg |
| Guarantee period | 2-12 years |
| Life time | At least 15-40 years |
| Eyeliner | Side, bottom, universal |
| Thread of holes for connection to heating mains | G ½ or ¾ inch, for one-pipe systems - bypass threaded connection |
Bottom or side connection: which is better?
Panel radiator with bottom connection.
Models with bottom connections are more expensive. The advantage of this method is the possibility of laying heat mains along the floor plane and disguising them as a floor covering. Where communications are located, the floor will also be slightly heated.
Pipes can also be hidden in walls. However, the lower supply reduces the heat transfer of the radiator by 20-22%, therefore, when calculating the thermal power, it is necessary to take into account the connection method.
Better from an efficiency point of view is a lateral connection, in which the coolant is supplied to the upper pipe and discharged through the lower one. When choosing, it is important to consider the connection side, since radiator models can be either right- or left-handed.
Option with a side connection, which has all the advantages of the bottom one.
There are even more expensive models that allow both side and bottom connections - universal.
Reviews of steel panel batteries: advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Flaws |
| The widest range of models with almost any heat transfer rate, length and height dimensions. | High sensitivity of welds to water hammer; critical pressure in the system is above 10 atmospheres. |
| Variability of connections and ease of installation. It is enough to hang the device on the brackets (usually included in the kit) and embed it into the water circuit through the threaded connection. | When draining coolant from the system, they are prone to corrosion, especially if the coolant was highly contaminated. |
| Relatively high heat transfer at an affordable cost, which is ensured thanks to convection fins that promote natural air circulation. | Under the extreme operating conditions described above, the service life may be seriously reduced. According to practice and customer reviews - up to one year and even up to 8 months (in the presence of serious water hammer and the absence of methods to prevent them). |
| Quickly achieve heating system control parameters. | Vulnerable to damage during transportation and operation. A relatively light impact can damage the panel and block the coolant flow channel. |
| Small volume of coolant compared to cast iron radiators, which improves efficiency and efficiency. | |
| A safe form that does not have sharp elements that can cause serious injury. | |
| They do not require painting or additional screens, since they initially have an aesthetically attractive appearance. |
What materials are batteries made from?
Radiators not only help create a pleasant temperature in the room, but can also become a real decoration of the room. They differ radically from each other in the material of manufacture.
The following options are in great demand on the heating equipment market:
- aluminum;
- bimetallic;
- cast iron;
- copper;
- steel.
Aluminum appliances are lightweight and have a modern appearance. A characteristic feature is the efficiency of energy resources spent on heating and the ease of installation work. Thanks to the thin walls of the batteries, quick heating and a high level of heat transfer are achieved.
A distinctive feature of the operation of panel devices is the absence of pressure surges, water hammers and temperature changes in the circuits, which are inherent in central heating systems, especially during testing and startup
Bimetallic radiators are models made from steel and aluminum. A successful combination of metals ensures rapid heating and increases the ability to withstand pressure loads. This type of radiator is suitable for both autonomous and central heating systems.
Cast iron equipment is characterized by a high degree of heat transfer, reliability and durability. These are unassuming contours, like those of the old MC-140 models, well known from Soviet times. They also produce more respectable models with modernized and modified surfaces, smoothed inside and out.
Copper batteries are durable, but have a fairly high price. Therefore they are used quite rarely.
Steel heat exchangers are characterized by a simple design, which helps ensure convection heating of the room.
To get to know steel radiators in more detail, you need to understand their classification by type, familiarize yourself with the technical characteristics, features of installation work and operation.
Tubular steel heating radiators
Compared to panel radiators, tubular steel heating radiators are more expensive to manufacture; with the same dimensions, they are designed for a larger volume of coolant, but they do not have such a higher heat transfer, which is why they are much less often used in heating systems.
However, it is worth highlighting high vertical heating devices (height > length), which are not located under window openings, but on the walls of corridors, bathrooms, and near furniture. Vertical heating devices combine perfectly with almost any design and warm the environment through radiation without creating a flow of dusty masses.
An aesthetically pleasing vertical version of the tubular tabletop radiator.
Design and device
Radiators in the form of familiar sections, similar to cast iron, are still produced using the stamping method. However, they are divided into sections only for the convenience of indicating dimensions; the heating devices themselves are always a welded together, non-separable structure.
Sheets of steel 1.5-2 mm thick are stamped, forming mirror halves of the section. The halves at the edges are connected by contact welding, the formed sections are ground. The sections are also connected by spot welding and ground again. The final stage is painting (using the same methods of dipping into the composition, AEF or KEF) and melting of the epoxy coating.
There are rarer (mostly domestic) designs of steel tubular batteries, which are a vertical row of pipes (convectors) mounted on two horizontal collectors through which the coolant moves.
KZTO Harmony model.
Vertical pipes of a certain height are cut and welded from below (less often from both below and from above), then fixed on horizontal collectors. Welding seams are polished, devices are painted, and sometimes decorated with nickel-plated rings. Due to this design, a weak convection effect is created, due to which heat transfer is slightly enhanced. However, its performance is still lower than panel radiators.
Technical and operational characteristics
The characteristics of tubular and panel radiators, despite the differences in design, are not much different. Tubular steel heating devices are designed for a slightly higher operating pressure - 10-25 atm, and can withstand surges up to 15-16 atm.
| Technical and operational characteristics | Range of values of existing models |
| Heat dissipation (thermal power) | 252- 3,900 W |
| Heated area | 2.52-39 m2 |
| Max operating temperature | 95-120 °C |
| Volume of coolant (water) in the radiator | 2, 4-37.2 l |
| Weight | 3.55-60.76 kg |
| Guarantee period | 2-10 years |
| Life time | At least 15-40 years |
| Eyeliner | Lateral, lower |
| Thread of holes for connection to heating mains | G ½ or ¾ inch |
Advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Slightly higher heat transfer. | Significantly higher cost. Tubular batteries are 40-90% more expensive than panel batteries. |
| Higher operating pressure, which in models from the manufacturer Sunerge can reach 25 atm. | Requires a larger volume of coolant in the system. |
| Thanks to the exceptionally smooth, uncomplicated surfaces, they are easy to clean. | The range of available thermal power is smaller compared to panel ones. |
| The range includes special vertical radiators that are perfect for installation in non-standard places. |
Device design
Steel panel-type radiators may vary slightly in design. The main elements are panels. Their number can vary from 1 to 3. Each panel, in turn, consists of metal plates that are connected along a contour to each other. The plates are made of steel by stamping. As a result, vertically located channels appear on the surface of the plates - the coolant will subsequently move along them.
If the design of the device provides for the presence of several plates, they are combined together into a single whole. For this purpose, pipes are used. To increase the heat transfer value, plate convectors are installed between the panels. If the device consists of one panel, the pipes are located at the rear of the panel.
On the sides, the holes between the panels (if there are several of them) are covered with a casing.
Calculation of the minimum required thermal power
Heat transfer is the main criterion for choosing heating radiators. You can calculate the minimum required thermal power by area. For this, a ratio of 1 kW of thermal power is used for every 10 m2 of heated room area. To create a power reserve, we recommend increasing the resulting figure by 15%, that is, multiplying by a factor of 1.15.
For example , to heat a room with an area of 34.5 m2, 3.45 * 1.15 = 3.97 or 4 kW of heat transfer is required. This can be either one large radiator or 2 x 2000 Watts. This simple calculation method is sufficient to create comfortable heating conditions.
There is a more complex method that takes into account all the nuances, which is used by specialists. For convenience and speed of calculations, we recommend using our calculator.
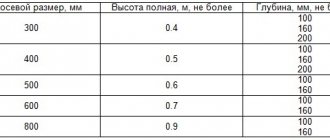
Dimensions
- height – 300, 350, 400, 500, 600 and 900;
- width – from 400 to 3000.
If necessary, you can select devices of non-standard sizes.
Increasing the heating area
To increase heat transfer, steel ribs - U-shaped plates - are welded to the panels. The number of plates increases the power of the radiator, as the heating area increases. Depending on the quantity, radiators are divided into three types:
- low power 11 – one plate;
- average power 22 – two plates;
- powerful radiators 33 – three plates.
What else to look for when choosing
- Operating pressure . We have already mentioned more than once the relatively low operating pressure of steel heating radiators - usually 10-12 atmospheres. This is due to the use of thin plate metal sheets and production technology; moreover, in European countries the standard pressure in the heating system is slightly lower than in Russia. If you choose radiators for an apartment in a house with central heating, we recommend choosing radiators with as much heat as possible higher operating pressure - up to 13-15 atmospheres, and also additionally install a pressure reducer. You can pay attention to the model Sunerge Estet 500 5008, which is oriented to our conditions (described in more detail below). For individual heating systems in private homes, where the pressure in the system rarely exceeds 3-4 atmospheres, any steel radiators can be used.
- Center distance. There are models with side connection with center distances from 300 to 900 mm. This is important to consider when designing a heating system.
- Dimensions . Steel radiators are not limited in size, so knowing the minimum required thermal power, you can choose a heating device of any size. The main thing is that the length of the radiator must be at least 50% of the width of the window opening, preferably the entire width of the window. Along the vertical axis, the recommended height of the radiator above the floor is 80-100 mm, and the distance between the battery and the window sill should be at least 100 mm. When choosing the size of heating devices, take into account the features of the future location.
- Potential service life . The service life is influenced more than others by two factors: the thickness and quality of the steel, processing and painting technology. Heating devices with a wall thickness of at least 1.25-1.5 mm will last the longest. High-tech painting, for example using KEF methods used in the automotive industry, will provide reliable protection against corrosion. Information about the painting method and steel parameters, as a rule, is indicated in the radiator passport; visually there should be no chips, paint sagging or underpainting on the entire surface.
Connection
The standard battery kit, as a rule, already includes everything necessary for its installation: dowels, fasteners, adapters, plug and Mayevsky tap.
Methods
There are four ways to connect a steel radiator to the heating system:
- bottom connection is considered the most optimal: the pipes will be practically invisible, and the built-in thermostatic valve will allow you to independently regulate the air temperature level in the room;
- diagonal (cross) connection - the hot water supply pipe is connected on one side of the radiator from the top, and the return pipe is located on the other side from the bottom;
- lateral connection - used to connect radiators to vertical risers of the heating system and is more often used in multi-storey buildings;
- universal connection - the design of the batteries has holes on the top, sides and bottom, which allows them to be used for any connection.
The best known manufacturers and models: characteristics and prices
Panel
Kermi FTV(FKV) 22 500 500
Well-known German panel heating radiators are distinguished by high reliability and quality at a relatively low cost. There are radiators with side (FTV in the name) and bottom (FKV) connections.
Reliability is achieved by the technology of connecting elements, the thickness of steel sheets of 1.25 mm and their quality, as well as painting technology - KEF. As we have already mentioned, this is the most effective painting method, in which the devices are resistant to corrosion and do not emit harmful substances when heated to extreme temperatures.
All radiators in the line have a working pressure of 10 atm, tested with a system pressure of 13 atmospheres. More detailed characteristics are given in the final comparative table.
Buderus Logatrend K-Profil 22 500 500
Another model from an equally famous German manufacturer. It is not inferior in quality to stamping, welding and processing of elements, is equipped with a thermostat to regulate the temperature of the coolant, and at the same time has a lower cost - 80-90% cheaper. However, it has a lower operating pressure - 8.7 atmospheres, which carries a high risk of depressurization when used in a domestic central heating system.
However, radiators are among the best for use in individual heating of a private home.
ELSEN ERK 22 500 500
Panel radiators from a Czech company known for using the latest technologies in the production of heating equipment. The models in the line have increased heat transfer by 25-30% compared to the previously mentioned analogues. During production, the “Low Seams” technology is used: by bending solid sheets, rather than welding their parts, the number of welds, which are the most vulnerable points of steel panel radiators, is reduced.
The heating device is designed for a standard operating pressure of 10 atmospheres, however, the risk of leaks during operation is significantly reduced, and the service life declared by the manufacturer is at least 30 years. Warranty period – 12 years. The disadvantage is the non-standard center distance, for example, for the specified model (height 500 mm) it is 445 mm. This must be taken into account when designing.
Prado Classic 22 500 500
Steel heating devices of the Russian city of Izhevsk. They can withstand operating pressure up to 9 atm, have high heat transfer and resistance to contamination and extreme heating of the coolant (up to 120°C). For manufacturing, steel sheets with a thickness of 1.4 mm are used, which has a positive effect on service life.
The disadvantage is the less aesthetic appearance and the still imperfect quality of the Russian assembly, however, since 2006 (beginning of installation in private and apartment buildings), no serious incidents have arisen during operation.
Tubular
Zehnder Charleston 3050 500 1196
A German manufacturer whose steel tubular radiators are considered one of the best on the market, thanks to time-tested quality. The batteries are capable of operating with a system pressure of up to 10 atm, have an aesthetic appearance and optimal heat transfer.
However, despite the 5-stage treatment, it is necessary to use radiators with caution in a domestic dirty central heating system subject to pressure changes.
Arbonia 2180 1800 540
Tall vertical radiators of another German brand, designed for installation in non-standard places. The radiator is the thinnest among analogs (depth 65 mm), maintaining optimal heat transfer, does not require masking and can be combined with almost any design, focusing attention on itself. On request they can be painted in any color.
View of the model in the interior.
During the practice of operation, no incidents with the quality of the devices were observed.
Sunerzha Estet 500 5008
A model of tubular steel radiators that is gaining popularity on the Russian market. Heating devices have increased heat transfer and an unusual aesthetic appearance. Estet models are designed for a working pressure of 25 atm, which implies use in the most extreme conditions, including in apartment buildings with 10 storeys or more.
View of the model in the interior.
The disadvantage is the huge weight and equally high cost.
KZTO RS 2-500 1150
Another well-known model of Russian-made steel tubular heating radiators, characterized by adaptation to domestic conditions of heating systems. Maximum operating pressure up to 15 atmospheres and coolant temperature up to 130°C are ensured by especially thick walls. Radiators have optimal heat transfer performance and low cost for tubular radiators.
However, according to practice and customer reviews, questions about quality often arise, which, unfortunately, is typical for most domestic manufacturers.
Comparative findings
As the table below compares the heat transfer of heating radiators shows, the most efficient in terms of power are bimetallic heaters. Let us remind you that they are an aluminum finned body with a strong welded frame inside made of metal tubes for the flow of coolant. In all respects, this type of heater is suitable for installation both in heating networks of high-rise buildings and in private cottages. Their only drawback is their high cost.
The heat transfer of aluminum radiators is slightly lower, although they are lighter and cheaper than bimetallic ones. In terms of test and operating pressure, aluminum devices can also be installed in buildings of any number of floors, but subject to: the presence of an individual boiler room with a water treatment unit. The fact is that aluminum alloy is susceptible to electrochemical corrosion from low-quality coolant inherent in central networks. It is better to install aluminum radiators in separate systems.
Cast iron radiators differ sharply from others, the heat transfer of which is significantly lower with a large mass and capacity of the sections. It would seem that with such a comparison they would not find application in modern heating systems. Nevertheless, the traditional MS-140 “accordion” continues to be in demand, their main trump card is durability and resistance to corrosion. Indeed, gray cast iron, from which MS-140 is made by casting, can easily serve for up to 50 years or more, and the coolant can be anything.
In addition, a conventional cast iron battery has high thermal inertia due to its massiveness and capacity. This means that when the boiler is turned off, the radiator remains warm for a long time. As for the operating pressure, cast iron heaters cannot boast of high strength. Purchasing them for networks with high water pressure is risky.
(no votes yet)
Prices: summary table
| Manufacturer and model | Working pressure, atm | Heat dissipation, W (at 70°C according to GOST 31311-2005) | Coolant volume in the radiator, l | Price, rub | Cost of 1 kW of power, rub |
| Panel | |||||
| Kermi FTV(FKV) 22 500 500, Germany | 10 | 965 | 2,7 | 5 300 | 5 492,2 |
| Buderus Logatrend K-Profil 22 500 500, Germany | 10 | 913 | 3,15 | 2 600 | 2 847,8 |
| ELSEN ERK 22 500 500, Czech Republic | 10 | 1158 | 2,7 | 3 600 | 3 108,8 |
| Prado Classic 22 500 500, Russia | 9 | 874 | 2,82 | 3 200 | 3 661,3 |
| Lemax (Lemax) C22 500×500, Russia | 9 | 1102 | 2,82 | 3 500 | 3 176,0 |
| Purmo Compact 22 500 500, Finland | 10 | 735 | 2,75 | 3 500 | 4 761,9 |
| Tubular | |||||
| Zehnder Charleston 3050 500 1196, Germany | 10 | 1352 | 20,8 | 29 000 | 21 449,7 |
| Arbonia 2180 1800 540, Germany | 10 | 1560 | 18,72 | 25 000 | 16 025,6 |
| Sunerzha Estet 500 5008, Russia | 25 | 1264 | — | 50 000 | 39 556,9 |
| KZTO RS 2-500 1150, Russia | 15 | 1960 | 11,2 | 15 000 | 7 653,1 |
| Dia Norm Delta Standard 3057 1000, Germany | 10 | 1240 | 18,2 | 30 000 | 24 193,5 |
A heating system made from tubular radiators is much more expensive than panel radiators, although it has slightly better characteristics. Even the most budget options are more expensive than bimetallic radiators with much more serious characteristics, which is why they are so rarely used.
As for panel batteries, we recommend taking care first of all about reliability and choosing German or Finnish models that have been proven for several decades: Kermi FKV 22, Purmo Compact 22 or Buderus Logatrend K-Profil 22. In addition, the latter combine high quality, and an affordable price compared to analogues.