Many owners of modern buildings, especially suburban ones, use stoves to heat their premises. The market for thematic devices offers a wide range of products that vary in size, function and dimensions, as well as technical characteristics.
Unfortunately, not all homeowners know that the height of the firebox in a stove must be of a certain size, and this element is present in all designs without exception; it also differs in configuration and size, which depends on the type of device and the type of fuel used. Taking this fact into account, it is necessary to consider in detail the question of what size of the firebox will be ideal in a given case.
Ready to use oven
How does the power of a stove depend on the size of the firebox?
The power of the heating device depends on many factors. Let's look at some of them:
- Constructive. The heating device must be folded so that all its component elements are in the correct relationship to each other. Consequently, only the correct design provides the required furnace power depending on the size of the firebox, the height of the pipe and the cross-section of the chimney.
- Operational. The more moisture the fuel holds, the more heat and energy must be expended to evaporate it. The same applies to fuel temperature. Only coals brought from the street will take part of the heat for heating. The combustion temperature is reduced by a large amount of air, causing incomplete combustion of the fuel. Lack of air leads to underburning of the fuel, which reduces the combustion temperature and leads to soot deposition.
The power of the heating device depends on the parameters.
The larger the firebox capacity, the more powerful it is. For 1 kg of dry fuel it is usually considered 4 kW. If the heating device places 3 kg of fuel, then it will produce 12 kW of heat.
Typically, per 10 m2 of heated room area, 1 kW of heating device power is taken.
When laying stoves, only heat-resistant materials are used that do not deform from high temperatures. It is also necessary to take into account that materials have different expansion properties. Clay and bricks are the basis of any good stove. The type of brick should be the first, and all auxiliary materials should be heat-insulating.
Making the solution
Most often, when lining a furnace, a solution of clay and sand is used in a ratio of 1:2. Many home craftsmen recommend the following proportions for mixing: 4 parts clay, 8 parts sifted sand and 1 part water. It is advisable to take clay from a depth of 1.5-2 m, clean, without various impurities. In order for the clay to acquire the desired viscosity, it must be soaked in water for 2-3 days and then rubbed through a sieve. If this is not done, small pebbles or plant debris may end up in the solution, which will not only complicate the laying process, but will also negatively affect the strength of the structure.
The following solution is also used for masonry: 1 part clay, 1 part sand and 100 g of table salt per bucket of solution. The clay must be pre-soaked in water and the sand must be sifted. When kneading, water is added in small portions so that the mixture does not become too liquid. The finished solution holds its shape well, does not stick to the trowel, and easily slides off the walls of the container.
Clay mortar mixed with fireclay powder and cement has excellent qualities. To prepare it, take 60% of the total mass of clay, 35% fireclay powder and at least 10% cement. If you do not want to select the proportions for the mortar, use a ready-made masonry mixture, which only needs to be diluted with water to the desired consistency. The solution should be mixed in small portions so that it does not have time to dry out before application.
Primary requirements
As mentioned above, furnace fireboxes are available in any design. If the combustion chamber meets all regulatory and technical requirements, then the home owner does not have to worry that the design will consume a lot of fuel or poorly heat the house.
If you install modern stoves for a bathhouse or home, then they already have a properly thought-out system for convection of air flows in the area where the combustion process itself occurs. Moreover, they are equipped with spacious fireboxes that allow maximum storage of wood and coal, thereby saving fuel used, and at the same time being able to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house for as long as possible.
This product is made of cast iron, and is subsequently installed inside the combustion chamber. It serves to maintain the poured volume of solid fuel used during the combustion process. The grille has holes located along its base, which facilitate the penetration of air flows into the chamber. To improve traction, there is a blower, through which ash is also removed.
Typical firebox design
The location of the grate should be in the middle of the firebox of a stove for a bathhouse or a country house, slightly below the firebox door, approximately two bricks apart, and the horizontal holes are directed along the combustion chamber.
The slope of the grate is from two to five centimeters, which is determined by the size of the ovens. For better kindling and creation of proper draft, the element is mounted with a slope towards the chimney pipe. It is in this way that ideal conditions are created for uniform combustion of fuel inside a metal or brick stove, when the smoke flakes off the fire without collecting inside the firebox.
It is also important to observe this point: if the heating device is made of metal, then it is necessary to additionally design protection for the firebox so that it does not overheat, but in stone products, in order to build a chamber, it is better to use fireclay bricks that are resistant to high temperatures. As for the fuel used, to purchase the required volume of material for the cold season, it is worth correctly calculating the number of days when the stove will burn, the area of the house and taking into account the thermal conductivity of the material
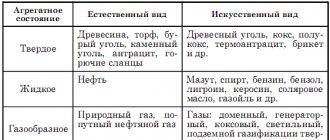
The highest indicators are coal (5500-6500 kcal/kg), peat gives off heat a little worse (2500-3500 kcal/kg), as well as firewood, but the latter must be dried in natural conditions
As for the fuel used, to purchase the required volume of material for the cold season, it is worth correctly calculating the number of days when the stove will burn, the area of the house and taking into account the thermal conductivity of the material. The highest indicators are coal (5500-6500 kcal/kg), peat gives off heat a little worse (2500-3500 kcal/kg), as well as firewood, but the latter must be dried under natural conditions.
Use of firewood
To correctly calculate the size and shape of the heating chamber, you need to focus on the height of the flame that comes from a particular type of fuel. If you can make a small firebox for coal, then larger dimensions are extremely necessary for peat and wood, since these substances burn actively.
How to properly burn with wood: 9 ways to prolong combustion, increase heat transfer and reduce consumption
The same amount of wood can burn at different speeds and produce different amounts of heat. Next, we will tell you how you can increase the efficiency of burning wood: extend its burning time, increase heat transfer and reduce consumption without special costs.
This is the second article in a series about efficient wood burning:
Proper stacking of firewood
Typically, firewood is set on fire like this: they build a pyramid of logs, put paper and wood chips in the center and set it on fire. First, the wood chips flare up, and over time, the firewood itself. The disadvantage of this method is that you do not control the combustion. The firewood ignites all at once and entirely, burning unevenly and quickly. When some of the logs burn out, you throw in new ones, which will also quickly flare up and burn.
The burning time of firewood can be increased by changing the way it is placed in the firebox. For example:
- Lay the first bottom row of firewood.
- Place the second row on top, shifted to the right or left by 5-10cm to form a ledge. Place the third and subsequent rows on top.
- Place paper or wood chips near the edge with the ledge and set them on fire.
Laying using fuel briquettes as an example. The briquettes do not ignite entirely, but burn evenly: the flame gradually moves from left to right. A stack of firewood burns for a long time and produces a sufficient amount of heat.
Subtleties:
- Do not place firewood close to each other. Leave a small gap between them for air movement.
- The denser and drier the wood, the more evenly it burns and the easier it is to ignite.
Close the valve in a timely manner
The stronger the draft, the faster the wood burns. But if there is not enough air, they burn poorly and form a lot of soot. Balance is important so that the minimum amount of air necessary for combustion reaches the firewood.
- Before ignition, open the heater damper to the maximum to ensure good draft for igniting the wood.
- When the wood starts to burn, begin to gradually close the valve. If the firewood starts to go out, open the valve slightly and increase the draft. Over time, you will find the optimal valve position.
The drier and denser the wood, the less air is required to burn it.
What kind of wood is better to burn?
The heat output of the heating device and the burning time greatly depend on the type of wood.
At the molecular level, wood consists of many empty cells with walls made of woody matter. The density of this woody substance (walls) is the same for all types of wood, but the size of the cells is different.
The smaller the size of the cells, the higher the density of the wood and each square centimeter contains a lot of flammable wood matter. And vice versa: the larger the size of the cells, the lower the density of the tree. It contains a lot of air and little flammable wood matter.
Imagine that a circle is 1 square centimeter of wood. In the first case, the cells are small and there are many walls between them. In the second case, the number of cells and walls is smaller, and there are more voids filled with air. The density of such wood is low.
What conclusions can be drawn:
- Less dense wood burns quickly . When wood burns, air is released, which fuels the combustion. The more air, the firewood burns faster and less evenly.
- Dense firewood produces more heat because it contains more combustible wood matter per unit volume.
- Dense firewood leaves more coals , which take a long time to smolder. Soft woods hold their shape less well, crumble into small coals and go out quickly.
All wood is divided into three density categories: low, medium, high.
| Density | Wood species |
| Low density 0.15 – 0.55 g/cm3 | Spruce, Willow, Aspen, Pine, Linden, Alder, Siberian Fir, Poplar |
| Average density 0.56 – 0.70 g/cm3 | Maple, Walnut, Birch, Cherry, Larch, Beech, Oak, Sycamore, Pear, Apple tree |
| High density 0.75 – 1.08 g/cm3 | Ash, Plum, Boxwood, Ebony persimmon, Acacia |
Prepare firewood in advance
Bring the wood into a warm room 2-3 days before lighting to increase its initial temperature.
The warmer the wood is initially, the:
- They spend less heat on their own heating and more on heating the room. You use heat more beneficially.
- Firewood reaches its optimal combustion mode faster, which further increases its calorific value and reduces the amount of soot emitted. This happens because the resin, creosote, tar, essential oils and other substances contained in wood do not burn at low temperatures and are deposited on the walls in the form of soot. And under optimal conditions, the combustion temperature is sufficient for them to burn entirely and release additional heat.
The difference between the combustion of “warm” and “cold” firewood is immediately noticeable: cold firewood produces a lot of smoke, which characterizes incomplete combustion. And warm, dry wood burns with virtually no smoke.
Preheat the firebox
When wood starts to burn in a cold firebox, then:
- part of the heat is spent on heating the firebox, and not heating the room (as in the previous point).
- It is more difficult for them to flare up, since warm air overcomes the resistance of cold air in the chimney.
Basic firewood is best lit in a preheated firebox so that it does not waste extra energy heating the firebox and chimney. You can use the heat from the previous stack of firewood or pre-burn the prepared torches and paper in the firebox.
Use bottom combustion (if possible)
There are two ways to burn wood: grate (bottom) and hearth (top burning).
Bottom burning is traditional, when air enters the firewood from below and the flame gradually moves upward. With top burning, air is supplied to the wood from above, the fire also burns at the top and gradually falls down.
With hearth burning, the largest logs are laid below, and paper and smaller firewood are placed on top.
Advantages:
- The completeness of combustion of wood increases, due to which they release more heat.
- You reduce the release of volatile substances that pollute the chimney with soot.
- This is a more environmentally friendly way of burning.
How to do it
For hearth burning, the firewood is stacked in a pyramid: the largest logs are placed at the bottom, and the smaller ones at the top. At the very top, wood chips and paper are set on fire.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NAWT_M_XH-c
While the wood chips and paper are burning, the firebox warms up. The flame then begins to move downwards and ignite the main wood. At this point, the combustion temperature and flame intensity are sufficient for the volatile substances that make up the wood to begin to burn. Due to the completeness of combustion, firewood releases more heat, and due to uniform combustion, it burns for a long time and economically.
Do not allow wood to burn too high
There are three wood burning modes: low, high and optimal.
When the mode is reduced, the firewood does not burn completely and produces a lot of soot. If it is higher, you waste firewood: part of the heat flies away through the chimney, since the heat exchanger and the room do not have time to remove it completely. This occurs in two cases: you use too much wood or supply too much air. It is necessary to reduce the volume of the bookmark or draft.
The best option is when the wood burns in the optimal mode: not weakly and not strongly. The easiest way to determine the combustion mode is to use a combustion indicator, which shows the current mode in real time. If the temperature of the flue gases is more than 320 degrees, then the firewood burns at high speed.
The combustion indicator determines the flue gas temperature and combustion mode in real time
Change the volume of firewood depending on the outside temperature
The warmer it is outside, the less heat the building loses. Accordingly, he needs less wood for heating. If you put the same amount of firewood at 0˚С or -10˚С, then in the first case you spend more firewood than necessary.
The combustion indicator allows you to monitor the combustion mode in real time and, over time, experimentally set the required amount of firewood depending on the street temperature.
Remove soot promptly
Soot needs to be removed not only when the chimney is clogged and there is no draft, but regularly. Soot not only impairs chimney draft, but also serves as thermal insulation. It covers the internal walls of the heating device and the heat exchanger, which reduces their heat transfer. If soot is removed in a timely manner, the volume of wood burned can be reduced without loss of heating power.
See the article on how to clean soot from a chimney.
Obvious, but worth remembering: the firewood must be dry. Wet wood does not ignite well, goes out quickly and emits 2-2.5 times less heat than dry wood.
Conclusions: how to properly heat with wood
- Stack firewood carefully so that it burns evenly and for a long time.
- Close the air valve in a timely manner. The minimum amount of air required for combustion must reach the firewood.
- Dense wood burns longer and leaves more long-smoldering embers.
It is best to burn with wood from hard deciduous wood: maple, walnut, birch, cherry, larch, beech, oak, sycamore, pear, apple tree - Bring the firewood into the house 2-3 days before lighting it and place it in the firebox an hour before lighting it.
- Preheat the firebox with a small amount of splinters.
- If you have a fireplace or stove, use bottom combustion.
- Maintain optimal combustion conditions. If the wood burns too hot, some of the heat escapes into the chimney rather than remaining in the room.
- Change the volume of firewood depending on the outside temperature.
- Remove soot in a timely manner. Soot is a thermal insulator and reduces the heat transfer of the heating device and heat exchanger.
- Firewood should be as dry as possible.
Add your own ideas to the comments.
How to properly burn with wood: 9 ways to prolong combustion, increase heat transfer and reduce consumption
Parameters when using peat
Calculation of the sufficient volume of the firebox in which peat is used is based on the recommended chamber height parameters, corresponding to an average of 75 cm, varying by 5 cm up or down.
Depending on how wet the peat is, the size of the grate will differ. If the briquettes are dry, then the same element as for wood stoves will do, but if the product is wet, then it should be a little larger. The length of the gaps is within 0.8-1 cm.
If the peat is wet, then for a room or sauna stove it is necessary to choose a larger grate, since here it is recommended to use a firebox height of at least 80 cm, with a width of 40 cm or more. You will also have to drill additional holes in the valve.
Depending on the selected type of fuel, the size of the firebox and the volume of material for one stack will be determined:
- If measured from the grate, the height of the combustion chamber should be about 65 cm (if using peat), 80 cm (if using firewood) and about 70 cm for coal.
- The width of the firebox in small stoves is about 20 cm; for large structures, 30 cm will be enough.
If you rely on the recommendations given regarding the requirements for the fuel used and the parameters of the combustion chamber, you can avoid overconsumption of materials, thereby saving a decent amount during the heating season.
Parameters when using peat
Calculation of the sufficient volume of the firebox in which peat is used is based on the recommended chamber height parameters, corresponding to an average of 75 cm, varying by 5 cm up or down.
Peat briquettes from a press
Depending on how wet the peat is, the size of the grate will differ. If the briquettes are dry, then the same element as for wood stoves will do, but if the product is wet, then it should be a little larger. The length of the gaps is within 0.8-1 cm.
If the peat is wet, then for a room or sauna stove it is necessary to choose a larger grate, since here it is recommended to use a firebox height of at least 80 cm, with a width of 40 cm or more. You will also have to drill additional holes in the valve.
Depending on the selected type of fuel, the size of the firebox and the volume of material for one stack will be determined:
- If measured from the grate, the height of the combustion chamber should be about 65 cm (if using peat), 80 cm (if using firewood) and about 70 cm for coal.
- The width of the firebox in small stoves is about 20 cm; for large structures, 30 cm will be enough.
If you rely on the recommendations given regarding the requirements for the fuel used and the parameters of the combustion chamber, you can avoid overconsumption of materials, thereby saving a decent amount during the heating season.
Furnace device
For a good flow of air to the firewood, the furnace firebox is mounted with a grate and a blower. The grate is made of cast iron and serves to support burning wood or coals.
It is made with longitudinal through holes or slots. For larger fireboxes, the grate is made from special single parts - grates.
Blower is an opening in the furnace under the firebox, designed to improve draft and remove burnt ash. If the heating device is made not of brick, but of metal, then it is necessary to provide protection for the firebox from overheating. It is also recommended to build a chamber of heat-resistant fireclay bricks in stone heating devices.
This is interesting: How many liters of water are in a 7-section cast iron battery
Primary requirements
As mentioned above, furnace fireboxes are available in any design. If the combustion chamber meets all regulatory and technical requirements, then the home owner does not have to worry that the design will consume a lot of fuel or poorly heat the house.
If you install modern stoves for a bathhouse or home, then they already have a properly thought-out system for convection of air flows in the area where the combustion process itself occurs. Moreover, they are equipped with spacious fireboxes that allow maximum storage of wood and coal, thereby saving fuel used, and at the same time being able to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house for as long as possible.
This product is made of cast iron, and is subsequently installed inside the combustion chamber. It serves to maintain the poured volume of solid fuel used during the combustion process. The grille has holes located along its base, which facilitate the penetration of air flows into the chamber. To improve traction, there is a blower, through which ash is also removed.
Typical firebox design
The location of the grate should be in the middle of the firebox of a stove for a bathhouse or a country house, slightly below the firebox door, approximately two bricks apart, and the horizontal holes are directed along the combustion chamber.
The slope of the grate is from two to five centimeters, which is determined by the size of the ovens. For better kindling and creation of proper draft, the element is mounted with a slope towards the chimney pipe. It is in this way that ideal conditions are created for uniform combustion of fuel inside a metal or brick stove, when the smoke flakes off the fire without collecting inside the firebox.
It is also important to observe this point: if the heating device is made of metal, then it is necessary to additionally design protection for the firebox so that it does not overheat, but in stone products, in order to build a chamber, it is better to use fireclay bricks that are resistant to high temperatures. As for the fuel used, to purchase the required volume of material for the cold season, it is worth correctly calculating the number of days when the stove will burn, the area of the house and taking into account the thermal conductivity of the material
The highest indicators are coal (5500-6500 kcal/kg), peat gives off heat a little worse (2500-3500 kcal/kg), as well as firewood, but the latter must be dried in natural conditions
As for the fuel used, to purchase the required volume of material for the cold season, it is worth correctly calculating the number of days when the stove will burn, the area of the house and taking into account the thermal conductivity of the material. The highest indicators are coal (5500-6500 kcal/kg), peat gives off heat a little worse (2500-3500 kcal/kg), as well as firewood, but the latter must be dried under natural conditions.
Use of firewood
To correctly calculate the size and shape of the heating chamber, you need to focus on the height of the flame that comes from a particular type of fuel. If you can make a small firebox for coal, then larger dimensions are extremely necessary for peat and wood, since these substances burn actively.
Laying a square stove with bottom heating
The stove in the photo has a combined or mixed smoke circulation system. The parameters of this design are 102x102x238 centimeters. Its heat output is 4200 kcal/hour.
The design of square-shaped heating stoves with bottom heating suggests that the firebox in it has a relatively large height. Side openings located symmetrically on both sides (2 pieces each) serve to drain gas into the chambers. They are located in the outer side walls of the structure. The gas then descends through chambers connected by a channel under the firebox behind the ash compartment.
If it is planned that the stove will operate on hard coal or anthracite, the walls of the firebox should be laid exclusively from refractory bricks.
Plank lining of the rough ceiling on wooden beams
The ideal option for a rough ceiling may well be considered to be padding the wooden floor beams with a regular shalevka or edged board.
There are three most proven flooring methods:
- Fastening long boards along the lower ends of the rough floor;
- Installation of boards on skull strips;
- Flooring on the outer surface of wooden beams.
At first glance, the material options are not much different, but this is not entirely true, there are certain differences
Before hemming the rough ceiling along the beams, you need to pay attention to the structure of the attic and ceiling
Laying a wooden batten along the upper plane of the beam is used only in case of a serious need to increase the height of the ceiling or to arrange winter-type attic rooms. In this case, to reduce losses, the floor is insulated with an additional layer of mineral wool over the rough sheathing of wooden beams. Removing the logs from the insulation layer reduces heat loss and significantly improves vapor barrier.
Glass cleaning system
Separately, I would like to dwell on the glass cleaning system. There are several systems:
- Cleaning glass with cold air.
This is done through the gap between the glass and the cast iron frame of the stove. Air flows from top to bottom, creating a barrier between the source of ignition and the glass. The disadvantage is that carbon deposits remain on the glass, which are very difficult to clean. - Glass cleaning with hot air (CB).
In my opinion, the most effective glass cleaning system. The air into the firebox is supplied already hot, thanks to the double body of the furnace. Through special channels in a double housing, air is supplied to the glass and cuts off soot from the glass. - Double glass.
The effect is better than cleaning glass with cold air, but there are additional cleaning difficulties due to double glass. — pyrolysis spraying. This coating on glass, in the form of a film, protects the glass from the formation of soot on it. But it burns out over time and the effect disappears.
Stones
reliable information about bath stones
Types of stones
- nephritis;
- gabbro-diabase;
- dunit;
- soapstone (separately about soapstone tiles);
- porphyrite;
- jade;
- crimson quartzite and white quartz.
Each article discusses the physical and chemical properties of the stone, its origin and suitability for bathing.
Choice
But for some, it is more interesting to first get acquainted with the selection criteria. You will find an overview of all candidates for your heater in another article. By the way, we also published a rating there, thanks to which you can find out the opinions of other site visitors about what they consider the best stone.
Laying
Well, when the stone has already been selected, the next question arises: how to lay it correctly to get light steam? Since there is a difference in which stove we place stones in, we wrote two articles - one for electric heaters, the second for all other stoves.
Manufacturers of ceramic bricks
The increase in construction volumes in our country in recent years has had a positive impact on companies producing relevant materials.
Fireclay bricks whose technical characteristics meet the requirements of standards and are produced at affordable prices by the following companies:
- TEREX Group of Companies;
- Bogorodsky plant of ceramic wall materials;
- Verkhnevolzhsky brick factory;
- Wienerberger Brick;
- Kerma;
- "Ceramics" (Lomintsevsky brick;
- Brick factory BRAER.
The named enterprises produce fire-resistant bricks in a wide range and of adequate quality. The products of these plants are in demand among builders and the population of both the regions where they are located and in neighboring areas. Competition between manufacturers of building materials has a positive effect on quality and range.
If you notice an error, a non-working video or link, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Furnace construction procedure
The layout of the stove in question is carried out in accordance with the order. This, as already noted, is a special diagram on which the order of laying out each row of the structure is indicated. There are standard procedures. If you do not have the skills to lay out ovens, it is strongly recommended to use one of the standard schemes.
A well-designed order will allow you to significantly reduce the time and money spent on stove construction. The work will be carried out in a precise and easy to understand manner to ensure maximum efficiency.
Having figured out the order of the Swedish stove before the start of construction, you will be able to lay out the unit yourself, without involving third-party craftsmen in the work and without spending money on paying for their labor.
The detailed order additionally indicates which materials should be used and at what stage of the work.
Study the proposed order and additionally pay attention to the following points:
- The design of the Swedish stove includes a blower. This point must be remembered in the process of independently arranging the stove;
- The first row of bricks must be laid perfectly evenly. Any displacements will lead to various violations that will negatively affect the quality and reliability of the finished furnace unit. To check the evenness of the masonry, use a building level;
- The correctness of the angles must be checked - they must be strictly 90 degrees. Check the angles using a suitable tool called a square.
The reliability, efficiency and durability of a Swedish oven largely depends on the correct layout of the first row; remember this.
Error correction
When building a stove firebox, there are several common mistakes that can be corrected during the process:
- When forming the walls, the solution must be applied and leveled by hand to avoid the formation of cavities.
- be moistened with water during laying so that they do not draw moisture from the mortar.
- If one brick block has moved, cannot be moved to the desired position. It must be removed, cleaned of the mortar and re-installed.
Cracks in the masonry caused by temperature changes are repaired with mortar. The cracked brick is removed from the structure, the area is cleared, it is moistened and a suitable brick is laid back. If the fastening of the door is not secure, remove it by disassembling the seams nearby, and if necessary, replace the brick blocks with new ones.
What is a grate and why is it installed?
The grate is a grate that allows the air flow to penetrate directly to the combustion site from below, and the ash to fall through the holes into the compartment reserved for it. It can be cast iron or steel. Installing this accessory solves a number of problems. in particular, he:
- Divides the firebox into two zones - the combustion chamber itself and the ash pan.
- Used for placing and drying fuel.
- Distributes the air flow from the ash compartment.
- Provides high-quality traction.
- In combination with the door, it allows you to control and adjust the flame.
It is not possible to make a grate intended for installation in a furnace from every metal. After all, it is exposed to high temperatures and under the influence of atmospheric oxygen can oxidize quite quickly. Only cast iron can resist such a complex destructive influence for as long as possible.
Do-it-yourself masonry of stoves, fireplaces and barbecues
One layer of trench masonry is unacceptable according to fire safety rules; it will quickly burn out, and three layers will not provide intensive heat removal. So that leaves only two. The cross sections of smoke wells before exiting the first floor premises must in any case be at least cm2, one brick per die.
If you plan to burn the stove with wood, then the grate should be installed closer to the back wall, slightly raising the far edge, this will improve draft. Under coal fuel, the grates are laid horizontally and a row below the firebox door; for this, piece cast iron grates are used, and not one solid one, since it is less durable and can quickly break.
Building a stove at your dacha yourself is not such a difficult task; the main thing is to take into account some of the features of stove construction. With proper construction and use of the stove, frequent repairs of the grate, bricks above the door or cast iron stove will not be required.
In order for it to burn well, a sufficient amount of air must enter the firebox through the ash pan; the supply is regulated using the door. It is best to build the stove in such a way that everything that gets into it burns completely, and does not settle in the chimney in the form of unburnt particles.
Winter promotion!
The approximate width of the firebox is cm. The height of the combustion chamber or, in other words, the distance from the grate to the stove is ideally cm. The ash pan is the main air chamber of the stove; air enters through its door, cooling the grate and supplying the firebox, which means the fire with oxygen.
In addition, the ash pit serves as a collection point for ash and other fuel waste, which can be conveniently removed through the door, so it should be of a comfortable size. It is laid on the second row of the stove masonry, then it can be used as an additional lever to control the chimney draft.
The stove in the country is rarely used and therefore, when the wood burns, it may initially smoke until the chimney warms up. Heating of stoves depends not only on the fuel, but also on the ability to properly fire the fire, as well as on the condition of the stove itself.
The stove should be systematically looked after, that is, clean the pipes, cover up even the smallest cracks, which are not only dangerous in terms of fire, but also greatly reduce the heating of the stove as a whole, and can also lead to the formation of condensation.
Furnace firebox
For example, if there is a 2-mm crack around the perimeter of the valve frame, the crack allows up to 15 cubic meters to leak through it within an hour. All this shows how harmful various cracks and crevices are.
It is enough to clean and repair stoves once a year in the summer, but chimneys have to be cleaned of soot two to three times during the heating season. It must be remembered that the heating of the furnace walls depends primarily on the state in which they are. If there is a lot of soot on the walls of the stove or in the chimneys, then they heat up very weakly and much more fuel and time have to be spent on the firebox.
The soot thickness in mm significantly impairs the heat perception of the walls. Before burning, you need to clean the grate and remove all the ash, which will ensure free passage of air to the burning fuel.
Preparing the base
When erecting a brick screen, it is necessary to fulfill all the conditions specified in SNiP 21-01-97 (Fire safety of buildings and structures).
SNiP 21-01-97. FIRE SAFETY OF BUILDINGS AND STRUCTURES. File for download
Installation of a sauna stove in a brick case
Although brick does not heat up as much as metal, it should not be laid close to the wooden walls of a bathhouse or on unprotected floorboards. It is also necessary to leave a gap between the walls of the stove and the brick, 5 to 10 cm wide. If there is no gap, the stove will overheat and, as a result, its service life will noticeably decrease. If the distance is made more than 10 cm, heating of the steam room will slow down and fuel consumption will increase.
When constructing a brick screen, remember the necessary clearances
The base for the stove and the brick screen must be common, otherwise uneven distribution of the load will cause subsidence of individual elements. If, when installing the furnace, the heat-resistant base was made with a margin of area, additional preparation for the brickwork is not required. If there is no such reserve, and the edges of the platform protrude from under the stove body no more than 2-3 cm, it is necessary to disconnect the chimney pipe, dismantle the stove, and carefully and according to all the rules prepare a new base.
Base for stove and screen
For the lining of stoves, solid red brick is usually used, which is characterized by heat resistance and durability. Fireclay brick is also suitable for these purposes, but it is more difficult to process and is more expensive. There is a ceramic refractory brick with a decorative surface, which has the same properties as ordinary bricks, but it looks much more impressive. With its help, you can not only improve heat transfer and protect yourself from harsh radiation, but also make the stove a decoration for your steam room.
Bricks for lining a metal sauna stove
It is also acceptable to use hollow red brick, especially if you want to reduce the load on the base. It just holds the temperature worse and cools down faster. And the most budget option is to use used red brick, you just need to thoroughly clean it of the remnants of the old mortar.
Used red brick
Please note that building material must be taken in reserve, since brick waste is inevitable during the laying process.
First you need to calculate the total weight of the stove and brickwork. The easiest way to find out how many bricks are needed for one row of screen is to lay them around the stove at a distance of 4-5 cm. Usually you get a square of 3x3 or 4x4 bricks, that is, from 9 to 16 pieces in one row. To calculate the number of rows, the height of the stove must be divided by the height of the brick - 65 mm. On average, this is 11-12 rows of masonry. Next, we multiply the number of bricks in a row by the number of rows and the weight of one brick, and we get the weight of the screen. Now all that remains is to add the weight of the stove and the water tank to this value.
Parameters for hard coal
Experts note that the combustion process of wood fuel occurs when a smaller volume of oxygen is consumed than required by coal. Based on this, it is necessary to take into account the fact that the dimensions of the grate area in furnaces that use this type of fuel must be larger.
In the combustion area, in the combustion chamber, conditions for maximum oxygen penetration must be created. That is why a grate of the same size as the bottom part of the chamber is installed for coal.
Definitely a big coal fire.
As for the material used to make this element, it must be resistant to high temperatures, and also have a thickness of at least 4 cm. Experts note that if the stoves have cooking surfaces, then fuel can be added through the holes in them.
A characteristic feature of Anthracite coal is that the volume of volatile substances is significantly less than that of other coal or firewood. Accordingly, under such conditions, a small flame burns inside the furnace, which makes it possible to reduce the size of the firebox by almost half.
The immersion depth of the grate should be 30 cm, and to increase the efficiency when using coal of this grade, it is necessary to narrow the firebox in the area of the lower part of the grate. The fuel layer will be larger, which means heat transfer will increase.
Model range overview
offers customers several lines of bath stoves with some modification features:
Russian steam - durable units made of cast iron with an open or closed heater. The stoves operate in Russian bath mode, the steam is fine, dry and transparent.
President (Hurricane, Legend) - models with a cast-iron firebox, an enlarged heater grid and a closed heater module.
Rusich - made of especially durable boiler steel grade 09G2S 6-8 mm. The thickness of the top of the combustion chamber and the rear wall of the furnace has been increased to 8 mm, since these areas are the most thermally loaded.
Skiff - made of structural steel up to 8mm thick and has a minimum of welds. High-strength cast iron parts are used in areas exposed to high temperatures.
Classic is a classic stove with an open heater and a remote tunnel of increased length for simultaneous heating of the steam room and adjacent rooms. On the side of the rest room, the model is equipped with a large cast-iron door with glass.
Premium – elite and expensive stoves lined with natural stone.
Elite – models with an external tunnel designed for heating the steam room and adjacent rooms. On the firebox side, the stoves are equipped with a large fireplace door with glass.
Sensation - cast iron firebox with convector casing. This stove has a small heater, but will warm up the bathhouse faster.
Vertical - a type of units with an open heater, equipped with an additional chamber for burning previously generated gases that appear during smoldering fuel, double flame circulation technology has been introduced.
Sanduns are models with a cast iron firebox and a barrel-shaped heater, closed by a stainless steel heater and a funnel for supplying water to the closed heater. Conceptually, it is somewhat similar to the Geyser and Barrel furnaces from TMF, only made of cast iron.
In addition to high technological characteristics, all Vesuvius brand furnaces have an aesthetic appearance. The design of the body can be selected to suit any interior and style of bath or sauna.
Traction
Thrust is the difference between the pressure of gases inside a technical device and the pressure of the environment when they communicate freely. The draft occurs because the gases inside the furnace, in the flues and in the chimney are lighter than the colder air outside, and are therefore displaced by colder, heavier air.
The theoretically calculated thrust (Pa) is expressed by the formula
P = 9.81H(ρg – ρa), (1) where H is the height of the technical device, m; ρg – average gas density in the gas duct, kg/m3; ρа – average density of atmospheric air, kg/m3.
In absolute value, thrust is negative. The ideal gas laws are used to calculate the average density of air and flue gases.
Combustion air from the atmosphere is supplied to the burners, where the fuel is burned mixed with air in the furnace, and the hot flue gases are discharged through flues and a chimney into the atmosphere (Fig. 1–4).
Rice. 1. Technological furnace with natural draftFig. 2. Technological furnace with smoke exhausterFig. 3. Technological furnace with air blowerFig. 4. Technological furnace with air blower and smoke exhauster
When passing through the convection section and flues, gases overcome their aerodynamic resistance.
The height of the chimney is set in such a way as to provide a draft sufficient to overcome this resistance and guarantee negative pressure (or vacuum) inside the furnace.
As can be seen from formula (1), draft is not a constant value and depends on the state of the surrounding atmosphere, the temperature of the gases inside the furnace, in the flues and chimney. All other things being equal, thrust is maximum in the cold season and minimum in the warm season.
Air humidity also significantly affects draft: increasing humidity reduces draft.
The following example illustrates the influence of atmospheric conditions on the operation of furnaces.
The draft of a chimney H = 100 m for the release of furnace flue gases into the atmosphere at a temperature tg = 200°C will be: – for the warm season (t = 20°C): ρа = 1.198 kg/m3; ρg = 0.725 kg/m3 (flue gas density at 200°C);
P = 9.8·100(0.725 – 1.198) = – 464.0 Pa; – for the cold season (t = – 20°C): ρа = 1.387 kg/m3;
P = 9.8·100(0.725 – 1.387) = – 649.4 Pa.
The difference in chimney draft in summer and winter due to the difference in atmospheric air density ΔP = 185.4 Pa.
Taking into account that the recommended operating range of the vacuum value in the combustion chamber of the furnace is in a particular case –10... –40 Pa, we can conclude that in the absence of regulation, the optimal operating mode of the furnace can easily be disrupted due to seasonal changes in the atmosphere. All this determines the need to regulate traction during operation.
All this determines the need to regulate traction during operation.
There are four types of traction systems in furnaces:
- natural (Fig. 1), adjustable using a slide;
- using a smoke exhauster (Fig. 2), regulated by its performance and, possibly, using a damper;
- using an air blower and, possibly, using a damper (Fig. 3);
- together with the help of a smoke exhauster and an air blower (Fig. 4), regulated by the performance of both.
Features of choosing cast iron grates
When choosing a particular model, you must first of all take into account the type of fuel used. Let’s say, if you plan to heat the stove with coal, then give preference to a design with dimensions of 30 (35) x 20.5 centimeters, but if with wood briquettes or firewood, then the dimensions of the product should be from 14 x 12 centimeters to 33 x 25.2 centimeters.
Note! In addition, when choosing a grate, it is necessary to focus on the calculation that the rods of the product will be able to withstand the maximum weight of one portion of loaded fuel. In order to find out exactly how many kilograms a particular option can withstand, talk to a sales consultant
If in doubt, it is better to consult a specialist.
Another important point is the width of the gaps. In order for you to easily clean the grate from ash in the future, the area of these gaps must correspond to at least 40 percent of the total area. If this indicator is lower, then the combustion chamber will not function as efficiently, because the volume of incoming oxygen will not be enough for proper combustion. And if there is little ventilation, then gases can also accumulate there. And on the contrary, if the area of the cracks exceeds 40 percent, then incompletely burned fuel will fall into the cracks along with the residues.
Classification of grate
Cast iron grates for stoves were and are still the best option. Steel is less resistant to this mode of operation and is not able to accumulate heat, as cast iron does. Therefore, despite the heaviness of the material, it is cast iron wood-burning stoves - Harvia, for example, and cast iron grates that are considered the best. Moreover, this applies to models both for baths and for heating living quarters.
However, this classification exists:
- steel gratings are lighter. If you know how to handle a welding machine, they can be made with your own hands - for a bath structure, for example. However, the material burns out faster because it is less resistant to chemically aggressive substances.
- Cast iron grates for sauna stoves or other structures are much more stable and, therefore, have a long service life.
Another classification of devices is related to the type of device.
- Fixed - usually a lattice with different sizes for different types of construction. This element does not change its parameters and does not move. There are several types of grating: tiled flat - lattice flat rectangle. This is the most popular option and is used for any wood-burning sauna stoves, solid fuel heating boilers, fireplaces, and so on. The photo shows the Harvia model.
- basket - designed for open fireboxes and originally developed for cooking. This device is no longer used, and there are almost no open fires, so the popularity of this model is not great;
- beam - in appearance they resemble a construction beam. The lattice of them is assembled with your own hands, choosing the appropriate size and quantity. This is the best method for fireboxes of non-standard sizes.
The chain grate belongs to the same category: its elements are connected by chains. However, in practice it is extremely rare, since it does not ensure complete combustion.
Design safety
Violation of stove masonry technology at any stage of construction can lead to danger when using the firebox. The main mistake can be incorrect laying of the foundation.
The main signs of malfunctions that occur when the foundation is laid incorrectly:
- The roof of the firebox is destroyed.
- The doors fall out.
- Burning coal spills out.
- The brickwork is cracking right through the entire area of the stove.
- Chimneys become unusable.
It is impossible to heat the stove in this condition - there is a high risk of fire and poisoning of people from flue gases . Damage caused by an unsuitable foundation cannot be corrected. You will have to disassemble the entire stove and rebuild all the elements.
In past centuries, the only means of heating for households was a stove, and stove specialists lived in good prosperity and enjoyed great respect among people. Today, stoves have not gone into oblivion and are still very popular in homes, baths and saunas.
With the development of the Internet, anyone can become a stove maker. To do this, you just need to set a goal, purchase the necessary materials and find the necessary tools. You can fold the oven yourself.