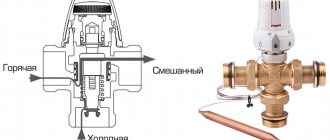
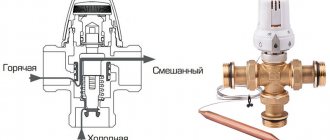
A three-way valve for heating regulates the flow of coolant. This is possible in two ways: the heat flows of the forward and return heating lines (supply and return) are mixed, as a result the flow temperature decreases. And secondly, the flow is divided, part of it is discharged from the supply into the return.
What is a three-way valve?
Content
A three-way valve for heating with a thermostat looks like a brass tee (sometimes steel or cast iron). But it works differently. There is a special thermoregulatory mechanism inside it. Based on the structure of the mechanism, there are two types of such mechanisms: rotary and saddle.
In the first, due to the rise of the rod, the pipes open, the cold and hot flows are mixed, and the overall temperature of the exiting liquid decreases.
The other (rotary) is based on the rotation of a spherical shape. The space between the nozzles is opened fully or partially by turning the ball with the opening (reminiscent of a ball valve).
Types of taps
Classification of the product according to various criteria:
Depending on the valve, they are distinguished: Regulating. It is equipped with an electromechanical device that opens the required valves
It also includes a rod with manual or automatic adjustment. Important! The rod cannot be knocked out even with the strongest water pressure, since it is located inside the device. Locking
It comes with a ball device that switches the flow of water.
Constipated. It comes with a ball device that switches the flow of water.
The peculiarity of this device is that it is installed on low pressure systems. It is very simple in design, requires constant maintenance and wears out quickly.
According to the product material: Brass is the most popular material due to its long service life, small dimensions and low weight.
Carbon steel is an excellent alternative to brass.
Cast iron - used for large diameter pipes (40 mm and more). It is not practical for private houses.
Bronze is a material with a long service life.
Depending on the installation method: coupling; flanged; pin; for welding; fitting-end.
For the heating system, the following types are used: With constant hydraulic mode - regulated in accordance with quality indicators. It is suitable for consumers with high-quality coolants of a certain volume.
With variable hydraulic mode – adjustable according to the required amount of water. It is more suitable for those for whom quantity matters.
From the variant of the flow part of the device: test and drain; full bore.
From the type of built-in shutter: conical; cylindrical; ball.
Based on the shape of the plug valve, the following types are distinguished: T-shaped; L-shaped; S-shaped.
From the mechanics of the valve element: Stuffing box – controls the adjustment of the water jet from above the valve due to the stuffing box;
Tensioners - controls the adjustment of the water jet from below the fittings due to the nut.
Depending on the heating of the housing: with heating; without heating.
Depending on the technical parameters, the following valves are distinguished: T-shaped - the adjustment knob can be in 4 positions;
L-shaped - the adjustment knob has two modes, including a rotation angle of 180 degrees.
From the device control mechanism: Manual - connects water flows in approximate proportions, cheap, looks like a standard ball valve;
Electric drive - for operation, additional equipment is used - a motor or a magnetic method, there is a possibility of getting a shock from the current;
Pneumatic drive is the most optimal option for use. Important! With an electric drive, you can easily balance the heat so that the temperature level in the rooms farthest from the boiler is the same as in those near it
Diagram of operation of a valve with a seat mechanism:
With fifth wheel actuator
The cone (3) fixed to the rod (4) overlaps the seat (5).
Valves differing in their actuators can be of two types: separating and mixing.
The mixing valve (SV) has two inputs for one output. The main application is for heated floors. Different temperature streams arrive at the inputs, which, when mixed, equalize the temperature to the specified level.
A separating valve (VV) has the opposite situation: there are two outputs per inlet. The flow is divided by the valve into two different directions.
The differences are related to the number of balls: one in the SK, two in the RK. They are built into the outlet pipes. There are as many outputs as there are ball valves. The movement of water is indicated by arrows.
SCs are used more in heating lines. Separating – for DHW. One divided stream will have a constant thermal regime (the quality of the liquid is important here), in the second stream the regime can change (only the quantity is important).
Adjusting the rod allows you to achieve the required temperature in a constant circuit. A variable circuit can completely overlap.
Areas of application
Modern valves are in wide demand and are actively used in various areas of human activity. They are often installed in modern heating mains, which require constant adjustment of proportions when mixing different coolant flows. For such purposes, it is customary to use electromagnetic devices or models with a thermal head.
As for domestic use, in this case it is enough to purchase a thermostatic mixing device that will allow you to regulate the temperature of the coolant. It is supplied both to the underfloor heating piping system and to heating radiators. And if the household device is equipped with automatic control, then changing the temperature in the room will be much easier.
The use of a three-way valve in a heating system is profitable and economical
It should be noted that using a tee in a heating system to balance possible temperature surges is not only beneficial, but also economical. The device allows you to reduce the volume of fuel consumed several times, while the final efficiency indicators of the system will increase noticeably. In some rooms, the presence of such a device is simply necessary. For example, if a heated floor is installed in the house, then the device will prevent excessive heating of the floor covering.
The principle of operation of the valve in the heating system
The flow enters the device from the left. It gradually heats up, and at some point the expansion of the special liquid in the thermal head begins. Which ultimately leads to the lowering of the rod with the opening of the pipe below for less hot water from the heating return line. It is mixed with hot inlet water. A less hot flow is already flowing onto warm floors. The thermoelement contracts and the rod moves down.
While the coolant is heating up, the rod continues to descend. It can drop to the very bottom, stopping the flow of hot water, opening the warm water pipe as much as possible. This will continue until the coolant cools to the required level. Then the top valve will open and hot water will flow from the inlet again.
Purpose of the device
Even with accurate thermal calculations when designing houses in a microdistrict, excess heat may appear in the apartment due to external factors: hot sun, strong wind, household appliances purchased by the owners that produce heat. It is not possible for individual apartments to reduce the temperature of the coolant, since the weak point of simple boilers is the heat exchanger, which cannot withstand low temperatures. A different type of boiler is needed - a condensing boiler, but it is significantly more expensive. If you have a simple boiler, you can reduce the amount of hot water to the radiator.
This is why a three-way heating valve is included in the connection.
Specific use cases of three-way valve:
- Heating of floors (warm floors). The two inputs of the valve are supplied with return and supply respectively. A mixed (cooled) flow flows through the outlet. This does not affect the rest of the circuit in any way.
- Maintaining return temperature. The boiler operates normally as long as the water entering it is not colder than the outgoing water by more than 600. To do this, the water from the supply is divided, and part of it is sent to the return to heat it up.
- So that condensation does not collect. The water in the heat exchanger must not pass the dew point. Therefore it cools down.
- To prevent the boiler from overheating. Achieved by similar cooling.
- Combined operation of the boiler with the boiler - the valve thermostat is activated when the water in the boiler cools below a predetermined level, the mechanism opens.
- If you need a bypass - a parallel path, then the easiest way is to use the valve.
Areas of application
The three-way valve, the operating principle of which was discussed above, has a fairly wide range of applications.
Thus, its varieties, such as an electromagnetic device or a device with a thermal head, are often found in modern pipelines, where it is necessary to adjust the proportions when mixing two separated liquid streams, but without reducing power or volume. As for household use, the most popular here is considered to be a thermostatic mixing device, with which, as noted above, you can regulate the temperature of the working fluid. This liquid can be supplied both to the “warm floor” pipeline and to heating radiators. And if the valve also has automatic control, then you can control the temperature in your home without any problems!
Note! The use of a three-way valve in a heating system to balance temperature changes is extremely beneficial not only in terms of comfort and convenience, but also in terms of cost savings. The fact is that by regulating the temperature of the liquid at the “return” of the heating device, you can significantly reduce the volume of fuel consumed, and this will have a positive effect on the efficiency of the system itself
In some systems, a valve is simply necessary. For example, in a “warm floor” system, this device prevents overheating of the floor covering above a given comfort level, thereby relieving users of unpleasant sensations
The fact is that by regulating the temperature of the liquid at the “return” of the heating device, you can significantly reduce the volume of fuel consumed, and this will have a positive effect on the efficiency of the system itself. In some systems, a valve is simply necessary. For example, in a “warm floor” system, this device prevents overheating of the floor covering above a given comfort level, thereby relieving users of unpleasant sensations.
Regulating devices of this kind are also used in water supply systems in order to obtain a permanent flow at the required temperature. The simplest example is an ordinary mixer, in which you can make water hotter/cooler by opening/closing a cold tap.
Safety valve for boiler
Previously, we described how to select and connect a safety valve for a boiler, talked about its areas of application and internal structure. In addition to this article, we recommend that you read: all the details here
How to choose a three-way thermostat valve
There are several selection criteria:
- by the method of temperature regulation;
- by capacity;
- according to the material.
By temperature control method
There are manual three-way valves:
The rod is connected to a handle or valve, which is set to marks that set the temperature. The cheapest and most reliable option, but it cannot react to a changing external environment on its own; human intervention is necessary.
In thermostatic valves, the built-in thermostat is responsible for adjusting t.
It is configured, then it itself connects the position of the rod with the temperature of the passing flow. The principle of operation is based on a special liquid or gas that changes volume at the slightest change in temperature. When the latter increases, they increase the size and push the rod.
Thermostatic valves are divided into mechanical and electronic. Their two main advantages over manual valves: automatic monitoring of the installed temperature and the same heating of water throughout the entire system. But much more expensive.
The most accurate regulators are electronic, with electric drive. From the thermostat, the signal reaches the controller, which moves the rod vertically.
For residential buildings and other cases that do not require special precision in temperature control, a simpler thermostatic valve - a mechanical one - is considered optimal.
Material of manufacture
It is better to exclude silumin devices from consideration; the material (low-strength alloy of aluminum with silicon) is too bad.
Black steel - products made from it are durable and not expensive, but they rust. And chrome or nickel plated ones are much more expensive. It's the same with stainless steel.
Cast iron is durable, essentially eternal, not afraid of corrosion, but fragile and can crack due to sudden temperature changes. Scope of application: with solid fuel boilers.
Brass and bronze are also good for everyone, but they are not suitable for industrial conditions (t up to 2000C). But for household needs they are better suited than others. Mostly brass is used since bronze is more expensive.
Bandwidth
At the valve, it should slightly exceed the design capacity of the general heating system. When passing through a circuit of 2 m3/hour, a valve of 2.5 m3/hour is needed. But the condition of the valve also affects how open or closed it is. A hundredfold difference in flows is considered ideal. But ratios of 50:1 and even 30:1 are sufficient.
Functional Features
An analogue is a two-way valve. Also considered a shut-off valve. But the three-way works fundamentally differently. The constant flow is not completely blocked.
But with variable flow this is quite possible. Thanks to these features, it is possible to regulate the flow/pressure.
From two two-way valves, you can get one three-way valve if you connect them in reverse, that is, when one closes, the other should open.
Popular valve manufacturers
Drive types
During operation, the three-way valve is controlled by temperature by an external drive; it comes in several types:
- A simple thermostatic actuator presses on the rod due to the expansion of the liquid medium placed in it, which is sensitive to changes in temperature. Typically, household three-way thermostatic mixing valves of small diameters are initially equipped with this type of actuator; it can be easily removed to install another type of device.
- Instead of a standard drive, the tap can be controlled by a thermostatic head, which has its own sensitive element that responds to the ambient temperature. To regulate the water temperature, the three-way mixing valve with a thermal head is additionally equipped with a remote temperature sensor. The latter is placed in a pipeline with a coolant and connected to the drive by a capillary tube. Such regulation is more precise.
- An electric drive controlled by a controller can also act on the rod. Electrical sensors, called temperature transducers, continuously measure the parameters of the coolant and signal their exceedance to the controller, on which the operation of the three-way valve with electric drive depends. The most common and most accurate method of regulation.
- A simplified version of the previous type of product is a three-way mixing valve with a servo drive. The difference lies in the absence of a controller; the drive controls the faucet directly, receiving signals from the temperature sensor. Most often used in conjunction with three-way valves with a ball or sector distribution element.
Installation of three-way valves in the heating system
Mixing valve installation
When installing SVs, several rules should be followed:
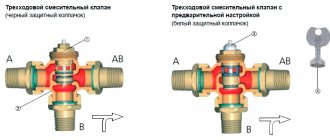
- Follow the arrows on the valve indicating the direction of flow. You also need to know the designations of directions: A - straight, B - perpendicular, AB - common input/output.
- Consider the existence of two three-way models:
- symmetrical;
- asymmetrical.
For symmetrical ones, flows come from the side ends. At the exit through the central end, the flow is already mixed. In the case of asymmetrical ones, the warmer flow comes from the end, and the cooler flow comes from the bottom. The exit of the already mixed flow is through the second end.
3. Connect the valve with the thermal head (drive) facing up.
Inset
SK insertion options depend on the layout of the heating system.
- Excessive heating of the coolant in the heating return line leads to excess pressure in the system. This can be eliminated by installing a jumper (to input B).
Blue triangles connected by vertices indicate a pump, thanks to which water circulates in the system.
In autonomous heating systems, the valve is usually connected to the boiler. Then the balancing valve cuts in (blue in the diagram).
- If it is possible to bypass the coolant into the return (usually in an autonomous boiler room), the mixing valve also performs separation functions. Then another balancing valve cuts in (to inlet B of the three-way valve).
Dividing valve installation
A separating valve is used when it is necessary to reduce the temperature of the coolant from the source. After the flow is divided, the coolant reaches the consumer without overheating.
This situation requires a pump.
Recommendations
Mandatory rules when installing any three-way valve:
- It is mandatory to install pressure gauges on both sides of the valve;
- a filter is mounted in front of the device to protect against any impurities;
- the device body is not loaded;
- install devices in front of the valve that reduce excess pressure;
- the valve is not located above the actuator;
- Maintain straight sections on both sides of the device if recommended by the manufacturer.
Layout diagrams
- The simplest scheme with a solid fuel boiler:
A three-way valve in such a heating circuit protects against condensation and overheating and maintains the temperature in the circuit.
- A more complex scheme - with an electric boiler and heated floors:
Hydrocollectors are used to organize several floor contours.
- A boiler with a three-way valve and a boiler allows you to get by with one circuit:
The best known manufacturers and models: characteristics and prices
Now I want to talk about the most popular and reliable three-way valves to make it easier for you to choose the right model.
Manufacturer from China. It offers fairly high-quality products for heating and water supply at a relatively low price.
| Photo | Model | Specifications | Peculiarities | Cost, rub. |
| (ZEISSLER) BL3110C04 | Material: brass Temperature range: 35-60 Operating pressure: 2-5 bar Diameter: 1 inch | Mixing, for heating and hot water supply | 2 300-3 000 | |
| BL8803 | Material: brass Temperature range: 38-60 Operating pressure: 3-10 bar Diameter: ¾ inch | Mixing, external connection via American connection | 2 800-3 500 | |
| BL8804A | Material: brass Temperature range: 38-60 Operating pressure: 3-10 bar Diameter: 1 inch | Mixing, electrically driven | 2 000-2 600 |
This Swedish company produces various models of valves and controllers. I believe that the products from this company are of the highest quality. Although expensive.
| Photo | Model | Specifications | Peculiarities | Cost, rub. |
| VTA321 | Material: brass Temperature range: 35-60 Operating pressure: 2-10 bar Diameter: ¾ inch | Mixing, for heating and hot water supply | 6 000-6 500 | |
| VTA372 | Material: brass Temperature range: 20-55 Operating pressure: 3-10 bar Diameter: 1 inch | Mixing, high throughput | 7 000-8 000 | |
| VTC511 | Material: cast iron Temperature range: 60-75 Working pressure: 3-10 bar Diameter: 1 inch | For solid fuel boilers | 8 000-9 000 |
STOUT
Joint production of Russia, Italy, Spain and Germany. The products are perfectly adapted to Russian conditions.
| Photo | Model | Specifications | Peculiarities | Cost, rub. |
| SVM-0120-164325 | Material: brass Temperature range: 20-43 Operating pressure: 3-10 bar Diameter: 1 inch | Mixing, for heating and hot water supply | 4 500-5 000 | |
| SVM-0125-186520 | Material: brass Temperature range: 30-65 Operating pressure: 3-10 bar Diameter: ¾ inch | Mixing, for heating | 4 000-4 300 | |
| SVM-0120-256025 | Material: brass Temperature range: 35-60 Operating pressure: 3-10 bar Diameter: 1 inch | Mixing, high throughput | 5 200-5 800 |
WATTS
One of the largest manufacturers of heating equipment in Europe. Huge range of products.
| Photo | Model | Specifications | Peculiarities | Cost, rub. |
| Aquamix 61C | Material: brass Temperature range: 32-50 Operating pressure: 3-10 bar Diameter: ¾ inch | Mixing, for DHW | 5 200-5 700 | |
| Aquamix 63C | Material: brass Temperature range: 25-50 Operating pressure: 1-10 bar Diameter: ¾ inch | Mixing, for heated floors | 5 500-6 000 | |
| V3GB Watts Classic | Material: brass Temperature range: 20-50 Operating pressure: 3-10 bar Diameter: 1 inch | Mixing, electrically driven | 12 500-14 000 |