Plastic products have long entered our lives, successfully replacing metal ones. Today, polypropylene pipes for heating are widely used, the technical characteristics of which have made it easier to install heating systems. Even a non-professional can install them independently.
Features of polypropylene pipes
The main feature of polypropylene is resistance to high temperatures, and additional reinforcement is designed to protect it from expansion when heated. Due to the special hardness of the material, the pipes have a perfectly smooth surface, which has a positive effect on their high resistance to corrosion and the influence of external factors.
Using polypropylene pipes for heating, taking into account the characteristics of the material and size, they not only install internal networks, but also main ones.
Advantages
The popularity of polypropylene pipes is due to the following advantages:
- withstand pressure more than 10 Bar;
- aesthetic appearance;
- not subject to corrosion, not electrified;
- smooth inner surface prevents dirt from settling;
- attractive price;
- the chemical purity of the material allows it to be used in the food industry;
- ease of transportation, transportation is possible in bays.
Flaws
Disadvantages of polypropylene:
- does not tolerate direct exposure to ultraviolet radiation, under the influence of which it is quickly destroyed, additional protection is required;
- at high temperatures it begins to melt;
- installation requires a special welding machine;
- difficulty in repair work and maintenance.
Disadvantages of PPR pipes
Unfortunately, polypropylene has more disadvantages than advantages. Practical experience of experts and reviews of the material say the following:
- It is difficult to weld and install propylene; the contractor is required to strictly adhere to the technology;
- pipelines, even those reinforced with aluminum, tend to significantly elongate when heated;
- it is impossible to control the quality of joints;
- due to the fact that the pipes do not bend and are supplied in 4 m long sections, joints on the highways can occur in the most unexpected and inconvenient places;
- It is not recommended to assemble the system at low temperatures, and in frosty conditions it is prohibited;
- greater wall thickness makes a polypropylene pipe larger than a metal-plastic pipe of the same diameter;
- Thickened tees, elbows and other fittings take up a lot of space.
A significant difference between polypropylene and other polymer pipes is the large wall thickness
Note. The disadvantage of propylene’s flammability is not specifically mentioned, since it is also inherent in metal plastic. Permanent connections are also not one of the disadvantages of PP-R, because it is better to join metal-plastic pipes by pressing. These joints cannot be disassembled later.
The most controversial statement that causes a lot of dissatisfaction among propylene supporters is the complexity of installation. On all Internet sites they are trying to prove that it is very easy to learn how to solder polypropylene parts; a 15-minute training session is enough for a beginner to master the technology.
This is demonstrated in the video, where a worker famously joins PPR fittings to pipes, placing a soldering iron on the table. In real life, everything is much more complicated; connections will have to be soldered on the fly, in hard-to-reach places, while simultaneously holding the welding machine and the pipe section with your hands.
Kinds
Pipes are produced for various applications, for example, products made of solid polypropylene with a small internal diameter are successfully used for installing heated floors, and materials with additional reinforcement perform well when laying a heating circuit.
With fiberglass
Glass fiber reinforced polypropylene is made by coextrusion, where the fiber is embedded between two layers of plastic used.
Features of products with fiberglass:
- less susceptible to stretching when heated;
- keep their shape well;
- withstand changes in network pressure;
- do not delaminate during operation;
- considered the most durable of all varieties;
- during installation they do not require additional stripping at the soldering points.
With aluminum
Materials with an aluminum layer withstand temperature fluctuations well, have minimal thermal expansion and practically do not lose their original shape at high temperatures, which is an undeniable advantage.
A special feature of reinforced products during installation is proper cleaning at the joints with fittings. If you refuse this procedure, the heating system will quickly fail, and you will have to redo everything during operation.
Made from solid plastic
Products made of solid plastic are good for installing heated floors and using hidden wiring. The concrete base serves as an excellent reinforcing material, protecting the pipeline from external influences and helping to reduce thermal expansion. Simplicity of installation and reliability of soldering allow you to forget about the problem of leaking connections for the entire service life.
The positive aspects of using pipes include:
- flexibility;
- length reaching 200 meters;
- a special molecular memory that promotes a return to its original form during cooling.
Metal-plastic
A heating system made of metal-plastic is advantageously used in houses where fluctuations in coolant temperature exceed 90°C. Pipes do not sag under high temperatures, maintaining their original appearance. The weak point in the system is the connecting fittings, which can leak when the coolant cools down and therefore require constant additional maintenance.
It is not recommended to use this material for hidden wiring, for example, for heated floors and water collection devices without access to the connections.
Pros and cons of metal-plastic
Let us make a reservation that metal-plastic pipes for heating should be compared with polypropylene pipes under equal conditions. Therefore, detachable joints on collapsible fittings are not considered - they are expensive and unreliable, although convenient for craftsmen without experience. Good tightness will be ensured only by the joint with the press fitting.
The condition also applies to the method of reinforcing the pipe; for comparison, let’s take metal-plastic and PPR reinforced with aluminum. Now about the advantages of metal plastic:
- Having special pliers, it is quite simple to install heating from metal-plastic parts.
- The pipe is bent and supplied in coils, and therefore is cut into sections of the required length, without any unnecessary joints.
- Thermal elongation of the material is insignificant and does not require a scrupulous approach when securing long sections.
- Can be installed in any weather.
- Laying in any hidden way is allowed, including under the screed along with the joints.
The reinforcing layer of the metal-plastic pipeline is only aluminum.
What is better in systems made of metal-plastic is the technology for connecting the elements. The end of the cut section is calibrated, pulled onto the fitting and crimped with pliers, and that’s all. A minimum of space is needed, since there is no need to insert a healthy soldering iron between the parts to be joined; the pliers are applied after joining. With the help of a spring, the metal-plastic bends well under a safe radius, which greatly simplifies the installation.
Separately, it is worth mentioning about heated floors, where it is customary to lay metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene, but not PPR. These materials do not need compensation and feel good inside the monolith, providing effective heating of the entire surface. It is worth imagining polypropylene in their place with its thick walls, extension and 90° joints, and it immediately becomes clear which pipes are best used in heated floors.
Press connection pliers are not a cheap tool; for 1-2 installations it is better to rent them
Reference. Cheap, low-quality metal-plastic is often found on sale; in practice, it often delaminates at bends. Fixing a leak under a screed is not easy; you can’t do it without opening it. Those who like to save on materials should think about using cheap metal-plastic pipes for heated floors.
Now about the disadvantages of metal-plastic, of which there are actually two:
- high cost of all elements;
- The range of pipes is limited to a maximum diameter of 63 mm (DN50).
Proponents of heating made from polypropylene constantly pay attention to another disadvantage of metal-plastic - a reduction in the flow area at connections where brass fittings are installed. They say that this leads to an increase in the hydraulic resistance of the network and the rapid “overgrowing” of passages when working in a central heating system, where the coolant can be dirty. The statement is true regarding collapsible fittings; in them, there is actually a narrowing of the diameter relative to the passage in metal-plastic.
High-quality fittings for press joining metal-plastic pipes also have a narrowing, but it is not so large as to significantly affect the hydraulics of the system. It is better to use them for heating, especially when laying hidden lines. Our expert Vladimir Sukhorukov shares the same opinion, whose video we recommend watching:
Specifications
The production of polypropylene pipes (PP) is regulated by GOST 21553 and GOST 15139 standards.
Pressure resistance
In heating systems, it is not always possible to maintain constant pressure; its indicators may vary depending on the temperature regime and the throughput of the collector. Therefore, when using PP in the heating circuit, it is necessary to take into account the reserve of the internal diameter of the pipe, which will have a positive effect when pressure changes and will protect the system from ruptures.
Paying attention to the markings, you can easily select the required bore diameter, taking into account the margin. So, with a design diameter of 20 mm, a manifold with a bore diameter of 25 mm is selected, which takes into account the expansion margin when the pressure in the system changes. The letters PN and two numbers on the marking indicate the pressure for which the materials used are designed.
Attaching pipes to the wall
To attach pipes to the wall, special fasteners are provided (they are often called clips); they are selected according to the diameter of the pipes and must fit exactly to them. There are fasteners that firmly fix the position of the pipe and ensure its stable location. They also use movable fixing fasteners; in some places you can’t do without them, for example, on long sections where pipes are subject to significant thermal expansion; take this into account not only when choosing the fastening material, but also the frequency of their use.
Fastenings - clips
Holder fasteners help pipes withstand loads in the event of increased pressure and protect them from sagging.
What to look for when choosing
For a heating circuit where input parameters are unstable, it is more correct to use reinforced materials.
You should pay attention to the following characteristics:
- pressure;
- wall thickness;
- reinforcement;
- temperature regime;
- bore diameter.
Types of pipes according to the maximum permissible pressure value
For correct selection, follow the standard TU 2248-010-33137731-2012:
- PN 10 are designed for a pressure of 10 bar at a coolant temperature not exceeding 40°C.
- PN 16 – 16 bar at a water temperature of 60°C, and with significant changes in temperature conditions, performance sharply decreases.
- PN 20 – 20 bar, designed for temperatures up to 80°C and recommended for hot water supply.
- PN 25 - 25 bar - these are only reinforced products with a temperature range not exceeding 95°C, suitable for heating systems in private homes.
Prices for polypropylene pipes class PN10
Polypropylene pipes PN 10
High temperature resistance
When marking pipes, the manufacturer indicates the temperature conditions for which the products are designed. So, on reinforced ones this parameter is 90-95 °C, on ordinary polypropylene – 60 °C.
No rust
The main positive characteristic of polypropylene is its corrosion resistance. Even with the poorest quality coolant, the collectors do not become overgrown with dirt. Thanks to perfectly smooth walls, a reaction that contributes to the destruction of the material is eliminated. At the same time, we should not forget about radiators, which, before winter operation, it is advisable to rinse from accumulated dirt.
Low thermal conductivity
Plastic has poor thermal conductivity, so this fact is taken into account when installing heating. The same temperature regime of the coolant and the wall has a positive effect on the absence of condensation on the surface of the circuit, which led to its use for the installation of heated floors. The heating system power is calculated exclusively using radiators.
Long service life
Manufacturers have endowed the plastic with characteristics that allow it to retain its original qualities for a long time, of course, subject to operating rules. The warranty period is more than 25 years.
Varieties for heating systems
Modern heating systems use rolled pipes and parts made of materials such as metal or plastic. The first category includes ordinary steel, alloy steel and copper pipes. The second includes polypropylene, metal-plastic and polyethylene cross-linked communication elements.
They all have certain positive qualities and manifest themselves effectively in different situations. The choice of a specific type of pipe is made individually, depending on the expected operating conditions and other important parameters.
Features of steel pipes
Until recently, steel pipes were used in the vast majority of heating systems and were the only material available. Today their positions have significantly weakened, and serious competitors have appeared nearby.
However, it was not possible to completely oust steel pipes from the market. Until now, they have been successfully used, but mainly in autonomous gravity-flow complexes, where the laying of large-diameter communications is required.
The laying of steel pipes is carried out by professional craftsmen before finishing activities begin, since welding work can damage wall or floor decor
Among the main advantages of steel pipes are a high tendency to thermal conductivity, low linear expansion during active heating, and resistance to intense pressure.
Justified advantages are considered to be unprecedented strength, both on straight and rounded sections, the ability to withstand aggressive temperature conditions and the affordable cost of elements.
To assemble a system of steel pipes, in addition to welding, there is an alternative method - installation on threaded connections using additional parts and fittings. To prevent joints from leaking, they are sealed with plumbing flax
Among the shortcomings, they point to problematic and labor-intensive installation, which is impossible without the presence of specialized expensive equipment, which can only be operated by professionally trained craftsmen with extensive experience in carrying out such activities.
The process of arranging a heating complex is also complicated by the impressive dimensions of the pipes. You won’t be able to do everything alone; it’s better to involve one of your friends or relatives who has the skills of welders and installers. It’s easier and faster to work with a team; everything can be organized clearly and accurately, ensuring the system has the necessary tightness.
Steel pipes demonstrate a good level of resistance to water hammer and have an impressive melting point (up to 1500°C), unlike other materials
Steel pipes and steel fittings used to connect them are absolutely not suitable for organizing hidden heating systems. The metal has a low anti-corrosion threshold and in humid conditions quickly rusts, rots and leaks.
To fix the problem, complete dismantling of the decorative covering is required if the pipe runs indoors, or large-scale excavation work when the problem arises on the approach to the house.
What is the difference between alloy steel?
Alloy steel is a durable material that, in addition to traditional impurities, contains various additives that improve the physical properties of the metal.
An example of an alloyed material is stainless steel - this is a special steel alloy containing at least 12% chromium. This additive ensures pipe resistance to corrosion and easy processing with special tools.
When purchasing stainless steel pipes, it is important to take into account the carbon content of the metal. The more it is, the higher the strength, but the lower the flexibility. At low temperatures, such products become brittle and their scope of application is reduced.
For the production of pipes with a welded seam, cold- or hot-rolled steel sheets with a working thickness of 0.4 - 5 mm and 2 -50 mm, respectively, are used.
Finished products have less weight than conventional steel ones and have good resistance to structural destruction and mechanical damage. Due to the low coefficient of thermal expansion, they can easily withstand severe temperature loads during operation. They function perfectly at pressures up to 16 bar.
The cost of alloy pipes is slightly higher than that of analogues made of ferrous metals. However, the costs are justified, because simple steel communications last on average 15-20 years, while stainless steel works reliably at least 3 times longer
Another indisputable advantage of alloyed stainless steel pipes is the ability to transport not only coolant heated to high temperatures, but even heated steam.
Types of stainless steel pipes
Alloy stainless steel pipes are made in two ways: welded and seamless. In the first version, sheets of metal are connected to each other using electric welding, producing a longitudinal or spiral seam. To prevent heat-affected corrosion, the joint area is subjected to special treatment and grinding.
Welded pipes with a spiral or longitudinal seam are cheaper than their seamless counterparts, but their service life is shorter. In addition, they have restrictions on maximum operating pressure and are vulnerable to mechanical damage
Seamless products are made by cold or hot deformation of solid pipe blanks made of stainless alloy steel. The cold method produces thin-walled pipes, and the hot method produces thick-walled pipes. The finished product has a perfectly smooth surface and is characterized by unprecedented reliability.
Seamless steel pipes are ideal for arranging heating systems of any complexity. Despite their high physical characteristics, they are reasonably priced, and thin-walled models successfully compete with more expensive copper products
Pipes made using seamless technology are not afraid of corrosion, function perfectly in harsh and aggressive operating conditions and can easily withstand record temperatures and enormous pressure.
Copper pipes for heating
In the manufacture of pipes for heating systems, high-quality copper is used, and in rare cases, a copper-zinc alloy, where the volume of the zinc component does not exceed 5%. To reduce the level of heat loss and give the products a more attractive appearance, the outer surface is covered with a polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride layer.
Copper pipes for the heating system undergo additional phosphorus treatment. This significantly increases their physical characteristics, and in particular, resistance to water.
Among the main advantages of the material for copper pipelines, the unsurpassed strength is first noted, thanks to which the products last for 100 years during intensive use and are not subject to corrosion.
Their thermal conductivity is 389.6 W/mK, which significantly exceeds the actual performance indicators of cast iron, steel and metal-plastic.
Copper pipes, when heated even to high temperatures, do not emit any harmful fumes, therefore they are absolutely safe for humans
The operating temperature range of copper pipes is very wide. They perform well both at high (up to +250°C) and low (up to -100°C) temperature conditions, do not melt during intense heating, do not crack or deform during operation.
They ideally hold their original shape, are not afraid of high pressure in the system, and even in the area of soldered joints they can easily withstand a load of 200-400 atmospheres, and this is tens of times greater than the ability of metal-plastic in the same area.
The thermal expansion rates of copper pipes are simply minimal. With regular exposure of metal to a coolant temperature of more than 90°C, each linear meter of communications lengthens by approximately 0.1%. All other materials here are significantly inferior to copper.
Due to the ability to maintain an aesthetic, attractive appearance over time, they are suitable for laying pipelines of not only internal, but also external heating systems and can serve not only for their intended purpose, but also serve as a decorative interior element.
Among the disadvantages, professionals note incompatibility with other metals. In order to reduce the cost, it is not recommended to use connecting parts made of cast iron or stainless steel for copper pipes. Such “savings” will subsequently backfire on the owner, since the chemical reaction between the elements will ultimately provoke corrosion of the entire heating system.
In the assembly of copper pipelines, only copper fittings are used. They are used to make connections by crimping, high-temperature and low-temperature soldering.
Among the disadvantages of copper pipes, their high cost is most often mentioned in comparison with other types of materials.
Distinctive features of polypropylene products
Polypropylene is a rigid, non-toxic synthetic polymer with high physical and mechanical characteristics. Pipes made from this modern material demonstrate exceptional impact resistance and multiple bending capabilities, low gas and vapor permeability, wear resistance and complete dielectricity.
Advantages of PP material
Thanks to these qualities, PP pipe material is actively used for arranging heating systems both on an industrial scale and in the private sector.
You can install a heating system made of polypropylene pipes yourself. But it is necessary to ensure that there are no sudden changes in pressure and temperature. Installing a boiler that limits the maximum possible water heating (no more than 70C°) will help create such conditions.
Polypropylene pipes are included in the category of budget communication parts and are lightweight, making them easy to transport and install alone.
Other advantages include the following:
- a perfectly smooth inner surface that does not contribute to the accumulation of lime deposits, which significantly complicate the free circulation of the coolant;
- quick and affordable installation that does not require the use of expensive professional equipment (all work can be done using a soldering iron, which is so easy to use that even a person very far from such work can easily “obey” it);
- long service life without loss of efficiency (on average about 25 years at full load);
- good resistance to negative temperatures;
- neat, aesthetic appearance that does not deteriorate over time.
The disadvantages of polypropylene pipes include the weak rigidity of the plastic, which in the future can cause sagging of the heating main and, as a result, lead to a crack in the joint or breakage.
To fix the problem, simply patching the fragment will not work. For subsequent correct operation and restoration of the integrity of the heating complex, it will be necessary to replace the section of pipe located between the two fittings.
The parts of a polypropylene pipeline are connected by welding, the specifics of which are described in the article we recommend.
You can also familiarize yourself with the features of choosing a welding machine for constructing a polypropylene pipeline and the recommended operating temperature limits for soldering on our website.
Types of polypropylene pipes for heating
In order for a home heating system to work longer and demonstrate the highest possible efficiency levels throughout the entire operational period, reinforced polypropylene pipes are used. They are classified according to the type of reinforcing material.
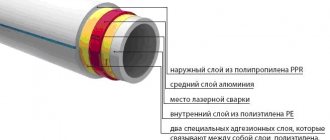
The PP pipes used in the heating device are reinforced with aluminum foil along the outer layer, in the middle or along the inner edge. In this case, sheets of metal can be discontinuous, solid or corrugated.
Polypropylene is highly plastic and can increase in size upon contact with a hot coolant. If communications are built into walls or floors, this may cause cracks in the coating. Reinforced pipes are subject to minimal expansion due to the presence of a protective frame
The foil reduces the actual thermal expansion of the material and creates a diffusion barrier, preventing oxygen from penetrating the walls. As a result, calcium sediment does not form and does not provoke oxidation processes on the walls of the radiators and boiler.
Fiberglass is also an effective reinforcing material for pipes. By coextrusion, it is placed in the middle layer of a polypropylene pipe. Due to the fact that both materials are similar in composition and basic properties, during welding with a fitting, a high-strength alloy is formed that is not subject to delamination even during long-term operation.
Polypropylene pipes with fiberglass reinforcement are simple and easy to install, unlike aluminum pipes, they do not require additional cleaning of the edges before soldering, and demonstrate excellent sound insulation properties.
Polypropylene pipes reinforced with fiberglass are considered the most suitable option for arranging home heating systems and last much longer than their counterparts.
Another modern reinforcing element is composite. It is a mixture of polypropylene and fiberglass. Added to the pipe, it increases the adhesive properties of the reinforcing layer and enhances performance characteristics such as strength and resistance to mechanical damage.
Rules for assembling pipelines for heating systems made of polypropylene pipes are given in the following article, the contents of which we advise you to familiarize yourself with.
XLPE pipes
Cross-linked polyethylene is a progressive material made using modern technologies. It is a polymer of ethylene with molecules connected cross-linked by chemical or physical cross-linking. It has a homogeneous structure, flexibility and a high level of tensile strength.
The list of main advantages of cross-linked polyethylene pipes includes:
- excellent shrinkage properties;
- the ability to clearly hold its shape along the stitching line even when heated to 200 C°;
- excellent wear resistance during intensive use;
- absence of halogens and heavy metals;
- immunity to corrosion and high pressure;
- low vulnerability to chemically active aggressive substances;
- normal impact strength at low temperatures (down to - 50 C°);
- minimum percentage of expansion under the influence of heat;
- suitable for hidden installation;
- minimal need for preventative maintenance.
Due to its plasticity, the material can be easily processed and does not require special tools, special professional abilities or serious experience. Even an amateur can handle installing a heating system if he has step-by-step instructions on hand to describe the necessary work.
Another distinctive feature of cross-linked polyethylene pipes is the “memory effect”, when a fragment “remembers” its position in the system and does not change it even over time
The most significant disadvantage of cross-linked polyethylene is its high vulnerability to ultraviolet radiation and the objective technological impossibility of producing large-diameter pipe material.
Methods and technology for welding polyethylene pipes are described in an article entirely devoted to this interesting issue.
Metal-plastic for pipeline construction
Metal-plastic products are the most common and practical material for arranging home heating systems. They harmoniously combine the advantages of plastic and metal, only absorbing the disadvantages of both materials to a minimum.
Compression fittings are used to assemble a heating system from metal-plastic pipes. They provide a reliable connection of all elements, but require subsequent additional maintenance
Metal-plastic pipes have a complex design and multi-level structure. The outer plastic layer acts as a fuse and protects the product from aggressive environmental influences. Next are aluminum foil and a polymer of increased smoothness, which prevent sediment and deposits from accumulating inside.
The connection of metal-plastic pipes is made using specialized fittings designed for crimping and clamping. In the first case, theoretically detachable connections are created, which are still not recommended to be disassembled unless absolutely necessary. In the second - one-piece.
No expensive tools are required to form connections with press fittings. The article we recommend for reading will familiarize you with his choice. The system can be assembled by a completely inexperienced performer.
Of the distinctive features of metal-plastic pipes, the most important are:
- minimal linear expansion under the influence of the coolant, which does not lead to deformation and sagging of the pipeline system or its individual fragments;
- pronounced smoothness of the inner surface, due to which the passage does not become clogged and the coolant circulates as expected; good temperature resistance (lower than metal parts, but higher than other plastic products);
- bending and tensile strength, ductility within acceptable radii (if the threshold is exceeded, “breaking” is possible);
- light weight, greatly facilitating the installation process;
- corrosion resistance;
- possibility of processing without the use of special equipment.
The disadvantages include the not very long service life of pipe products (up to 15 years according to manufacturers) and the significant cost of connecting fittings.
The meaning of markings on pipes
An important selection criterion is the marking applied to the surface of the manufactured product, where, in addition to the operating parameters of pressure and temperature, the diameter of the pipe is indicated. This is the main indicator for the heating system of a private home.
Product diameters:
- 16-20 mm - intended for installation of heated floors and water supply;
- 20-25 mm - for heating systems in private homes;
- 25-32 mm - for centralized highways;
- 200 mm and above are used for heating administrative and economic facilities.
Particular attention should be paid to the diameter of polypropylene pipes used for heating a private home, where one type is not enough.
Correct combination and selection of materials with different markings helps to increase heating efficiency several times. Thus, the transition from a larger pipe diameter to a smaller one increases the pressure in the system, promoting excellent coolant circulation and increased heat transfer.
Polypropylene pipes for heating technical characteristics
Dimensions of plastic pipes for heating systems: how to choose the right one
The correct choice of diameter determines how successfully the system will function. When calculating the cross-section of pipes, it is necessary to take into account:
- wiring diagram;
- coolant movement speed;
- diameters of the boiler pressure and return pipes;
- calculated decrease in fluid temperature in batteries;
- the value of the resistance coefficient.
However, with a complex wiring diagram, especially when, in addition to radiators, a heated floor is also planned, standard calculation methods are not suitable. Then, to determine the diameter of the pipes, you will have to contact a specialist or consult with neighbors who have a similar system. If you plan to install heating with forced water circulation, it is preferable to choose options with a smaller cross-section. This will make installation easier and reduce the volume of heated water. However, you should not get carried away with minimizing the diameter, as this will cause a decrease in heat transfer due to an increase in water speed and the appearance of noise. The optimal speed varies from 0.2 to 1.5 m/s.
To independently determine the diameter of plastic pipes, you should assume that heating 1 m² of a room up to 3 m high requires 100 W of thermal energy. This means that for a room with one or two batteries of 20 m², you need 2 kW plus 20% reserve, resulting in 2.4 kW. The table indicates that pipes with a diameter of 8 and 10 mm are suitable for transmitting such power. The result is approximate, but it will help determine the cost of purchasing pipes.
Recommendations for selection
It is worth giving preference to reinforced products, which allow you to carry out high-quality installation of the heating circuit and forget about problems associated with leaks for a long time.
Experts recommend:
- purchase materials from trusted suppliers, products must have a quality certificate;
- pay attention to the labeling containing complete information;
- make a choice in favor of reinforced products;
- For the heating system, choose pipes with fiberglass reinforcement. Read about long-burning stoves for heating with wood on our website.
Prices for pipes with fiberglass reinforcement
Fiberglass reinforced pipes
Installation
Installation of the heating system occurs in several stages.
Lining
To ensure effective heating, the floor must be prepared before installation.
If there is no base as such, first make a rough screed from sand-cement mortar. If concrete slabs serve as the base, they are leveled, covering all the cracks and ensuring that there is no level difference above 1 cm.
The rough screed is cleaned of dirt and dust, after which a layer of waterproofing is laid. The material for this is usually a thick film. Experts recommend placing the film on the walls at a distance of 10–20 centimeters. In rooms with high humidity, in country houses, this is mandatory. The film is overlapped by 10–20 centimeters and taped at the joints with mounting tape.
Damper tape is glued around the perimeter of the room. Its edges should be approximately 20 mm higher than the future screed. After the screed has dried, the edges of the tape are usually cut off.
Then thermal insulation is laid so that the warm floors heat the room most efficiently. There are different heat-insulating materials, both rolled and in the form of plates; the choice of coating depends on personal preferences, price, thickness. All cracks between them should be sealed with polyurethane foam to eliminate the possibility of heat leakage. The thickness of the thermal insulation when installed on a cold floor or ground should be from 5 centimeters, otherwise 3 centimeters is sufficient.
If the thermal insulation material is not foil-coated, a foil film is placed on top of it. At the joints it should be taped with aluminum tape.
Once completed, the floor is ready for installation of the heating circuit.
Pipe laying
When working with polypropylene indoors, it is necessary to maintain the operating temperature above 5°C.
There are two ways to fasten the pipe: using dowels through thermal insulation and fastening to a reinforced mesh. The preferred option is to attach it to a grid as it is more reliable. Plus, the mesh allows you to strengthen the layer of screed that will cover the heating system.
The mesh for fastening is placed on a heat-insulating substrate. Then pipes for a warm water floor are laid along it according to the previously chosen scheme and secured with plastic clamps or wire. The fastening should not be over-tightened - this can lead to deformation of the pipes during operation and reduce their service life. At the junctions they are fastened together using a special welding machine. It comes in several variants and is easy to work with.
Laying begins with the collector. First, one end is connected to it, and after laying the pipes throughout the room, the second is connected.
Testing
After laying and securing the pipes, they are connected to the collector and tested. To test heating equipment, water is supplied while simultaneously removing air. In this case, the water pressure should be higher than the working one, but not more than 6 bar.
After a day, the pressure is checked, and if it has dropped by no more than 2 Bar, then you can start coating. If the pressure is less, then there is an error in the gasket.
Final stage
After successful testing, they begin laying the concrete screed. If the room is small, you can additionally use another reinforcing mesh, which is placed on top.
Low thermal conductivity pipes
Plastic pipes made in Germany, with a wide range of applications.
A piping system made from the innovative fusiolen material, specially designed for heating, cooling, surface heating, transport of aggressive media and compressed air, as well as for geothermal energy systems.
Pipes made in Germany, with a wide range of applications.
The system is perfect for supplying water to swimming pools, both on a private and industrial scale. It is also used for transporting chemical media.
Estimated indicators
To calculate the power of heating equipment, as well as to find out the scale of heat loss during transportation of the coolant, it will be necessary to remove heat from the pipe at certain temperatures of the liquid inside it and the air outside. The thermal insulation layer serves as an additional parameter.
The formula for calculating the heat transfer of a steel pipe looks like this:
Q=K×F×dT, in which:
Q – the desired result of heat transfer from a steel pipe in kilocalories;
K – thermal conductivity coefficient. It depends on the pipe material, its cross-section, the number of heating circuits, as well as the temperature difference between the outside air and the coolant;
F is the total surface area of a pipe or several pipes in the device;
dT – temperature pressure, that is, ½ the total temperature of the liquid at the inlet and outlet of the pipe minus the air temperature in the room.
If the pipes are additionally wrapped in a layer of thermal insulation, then its efficiency in percentage terms (the amount of heat passed through it) is multiplied by the resulting heat transfer rate.
For example, let’s calculate the heat transfer of a register made of three pipes with a cross-section of 100 mm and a length of 1 m. The temperature in the room is 20 ℃, and the coolant, when passing through the pipe, cools from 81 to 79 ℃.
According to the formula S=2pirh we calculate the surface area of the cylinder:
S= 2×3.1415×0.05×1=0.31415 m2. If there are three pipes, then their total area will be 0.31415 × 3 = 0.94245 m 2.
Indicator dT = (79+81):2-20 = 60.
The value of K for a register of three pipes with a temperature head of 60 and a cross-section of 1 meter is taken equal to 9. Therefore, Q = 9 × 1 × 60 = 540. That is, the heat transfer of the register will be equal to 540 kcal.
Thus, we examined the concepts of heat transfer, as well as ways to minimize the heat loss of a steel pipe for certain cases. There is nothing very complicated about this. The main thing is to approach the issue responsibly.
We calculate the return for 1 m of product
Q = 0.047*10*60 = 28 W.
- K = 0.047, heat transfer coefficient;
- F = 10 m2, pipe area;
- dT = 60° C, temperature difference.
It's worth remembering
Do you want to make a heating system correctly? You should not select pipes by eye. Heat transfer calculations will help optimize construction costs. In this case, you can get a good heating system that will last for many years.
Today the issue of energy saving is very acute. This applies to literally every user. Therefore, when designing heating systems in private construction on their own, zealous owners immediately think about heating systems and their efficiency.
It is more difficult for those who operate previously created heating systems, since they are faced with the question of increasing the share of heat transfer in already completed objects.