The climatic conditions of central and northern Eurasia require thermal insulation of houses, but insulation alone is not enough. Heat losses must be compensated using a heating system. Water heating in a private home is a common and most effective method.
The quality of operation of the heating circuit directly depends on the design features, choice of heating device and type of wiring. You will learn how to decide on the equipment and the most suitable scheme by reading the article we propose. The information presented is based on the requirements of building regulations.
We described in detail the design principle of a water heating system and examined typical device options. To optimize the perception of a difficult topic, we included diagrams, photo selections and videos.
Single-pipe schemes
The easiest way to calculate and assemble a heating system is with a single-pipe piping scheme for the coolant. The heated water in it sequentially passes from the boiler through all the radiators in the house, starting with the first and ending with the last in the chain. At the same time, each subsequent radiator receives less and less heat.
There are four main advantages of such a heating installation in a private house:
- Ease of implementation;
- Small cubic capacity of coolant;
- Hydraulic stability of the system;
- Low consumption of materials.
Installing a pipeline according to this scheme and connecting it to the boiler with your own hands, even if you have minimal skills, can be completed in two to three days. Plus, the costs of creating a water heating system in a house for single-pipe wiring are minimal compared to other options.
Few fittings, fittings and pipes are required here. The savings on materials are significant. And it doesn’t matter whether laminated timber or brick is chosen for the construction of the cottage. If the home is well insulated, then even a simple one-pipe system for heating it will be more than enough.
Among the weak points of this heating scheme are:
- Inability to accurately regulate the heat supply in each room;
- Limitation on the total length of the pipeline throughout the house (no more than 30 m);
- Small amount of thermal energy in the battery furthest from the boiler;
- Vulnerability to defrosting and gusts.
To mitigate the shortcomings, a circulation pump has to be built into a single-pipe system. But these are additional costs and potential equipment breakdowns. Plus, if there are any problems in any section of the pipe, heating of the entire cottage stops.
Single-pipe horizontal
If a private house is small and one-story, then a single-pipe heating system is best done in a horizontal design. To do this, a ring of one pipe is laid in the rooms around the perimeter of the cottage, which is connected to the inlet and outlet of the boiler. Radiators cut into the pipeline under the windows.
Single-pipe horizontal design - ideal for small spaces
The batteries are connected here using a bottom or cross connection. In the first case, heat losses will be at the level of 12–13%, and in the second they are reduced to 1–2%. It is the cross installation method that should be preferred. Moreover, the coolant supply to the radiator should be done from above, and the outlet from below. So the heat transfer from it will be maximum, and losses will be minimal.
Single-pipe vertical distribution
For a two-story cottage, a single-pipe vertical heating system is more suitable. In it, the pipe from the water heating equipment goes up to the attic or second floor, and from there it goes back down to the boiler room. In this case, the batteries are also connected in series one after the other, but with a side connection. The pipeline for the coolant is usually laid in the form of a single ring, first along the second and then along the first floor, in such a heating distribution in a low-rise building.
Single-pipe vertical design - saving on materials
But an example with vertical branches from a common horizontal pipe at the top is also possible. That is, first a circular circuit is made from the boiler up, along the second floor, down and along the first floor back to the water heater. And between the horizontal sections, vertical risers are laid with radiators connected to them.
The coldest battery in such a heating system for a private house will again be the last one in the chain - at the bottom of the boiler. In this case, there will be an excess of heat on the upper floor. It is necessary to somehow limit the volume of heat transfer at the top and increase it at the bottom. To do this, it is recommended to install bypass jumpers with control valves on the radiators.
Leningradka
Both schemes described above have one common disadvantage - the temperature of the water in the last radiator turns out to be very low, it gives off very little heat to the room. To compensate for this cooling, it is recommended to improve the single-pipe horizontal heating option for a private house by installing bypasses at the bottom of the battery.
Leningradka - improved single-pipe system
This wiring was called “Leningradka”. In it, the radiator is connected from above to a pipeline running along the floor. Plus, taps are placed on the outlets to the batteries, which can be used to regulate the volume of incoming coolant. All this contributes to a more even distribution of energy across individual rooms in the house.
Coolant
The main types of coolants in heating systems are water, various antifreezes and their mixtures in certain proportions.
Antifreeze is a liquid that is an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol, propylene glycol or potassium acetate with the addition of modifying additives. They lower its freezing point.
Heating a house using a coolant to which special inhibitors are added helps prevent oxidation, corrosion, and scale formation. Their content can range by weight from fractions of a percent to 3-4%.
Which coolant to choose is decided individually, depending on the situation. If the probability of boiler failure is low, there are no problems with fuel, it is better to use water. Many boiler manufacturers prohibit the use of antifreeze, and there are frequent cases of warranty denial on this basis.
Two-pipe heating systems
In a two-pipe heating system, the batteries are no longer connected to one common line, but to two - supply and return. This way the heat distribution throughout the building occurs more evenly. The water reaches each heat exchanger at approximately the same temperature. It is not for nothing that such a scheme is usually used in high-rise buildings with a large number of heated rooms. But it is also often installed in cottages, especially if they are large and have several floors.
The two-pipe heating system has the following advantages:
- Possibility of precise adjustment of room temperature;
- Uniformity of heat distribution in individual rooms;
- High operational reliability;
- It is permissible to repair one battery while continuing to operate the entire system.
The two-pipe heating scheme for private houses has only one serious drawback - price. Its high cost is often mentioned in comparison with its single-pipe analogue. However, pipes in this case require a smaller diameter. Their length doubles here. At the same time, due to the reduction in cross-section, the final estimate turns out to be not as inflated as it might seem at first glance.
By analyzing the types of foundations, we can immediately say unequivocally that a monolith will be more expensive than a strip foundation. When arranging heating for private houses, everything is not so simple and easy. When installing it, pipes of different diameters, various fittings and thermostats are used. The total cost of each variety must be calculated individually for the actual structure and for the specific parameters of the required temperature regime.
With bottom wiring
With the bottom scheme, both pipes are laid above or in the floor. And a pair of taps are connected to the batteries from below. This type of connection is often used to hide heating pipelines behind finishing. This is more of a design decision; it does not provide any special advantages in terms of heat transfer.
Two-pipe with bottom wiring
On the contrary, the lower method of connecting radiators involves the highest heat loss. It is generally not recommended for use in heating systems with natural (gravity) circulation. If this wiring is chosen, you will have to take care of the availability of special equipment for pumping the coolant, and choose a battery with more power. A boiler without a circulation pump cannot supply heat throughout the house alone.
With top wiring
In the upper heating distribution, the connection of radiators to the pipes can be diagonal or lateral. This is not the most important thing here. The main distinguishing feature of this type of water heating is the presence of an expansion tank.
Two-pipe with top wiring
The expansion tank is placed in the attic. The water heated in the boiler actually first enters this storage tank. The coolant flows into the supply pipe naturally from top to bottom. And then the water, after releasing heat in the radiator, is sent through the return line back to the heater.
Stop heating the street!
Whether the radiators will be changed during the heating reconstruction process or not, but since they will still have to be removed for some time, it is highly advisable to cut off the outflow of heat to the outside. To do this, you need to cover the wall behind the batteries with heat-insulating mats aluminized on both sides. How such a bedding works in terms of heat can be read in the article on floor insulation; here it is enough to note that in a block Khrushchev house with radiators in niches, double heat shields behind the radiators are equivalent to covering the walls with 20 mm plywood.
In an alternative option for insulating the wall behind the radiator, heat-insulating material (1) and aluminum foil (2) are used separately.
Installing the shielding mat is simple: we cut holes in it for the hooks of the battery suspension, apply thin “sausages” of construction silicone or mounting adhesive using an “envelope” to the side adjacent to the wall, put it on the hooks and press it to the wall.
An indispensable condition: the mat must be organic, made of synthetic or natural fibers. The use of open mineral wool mats in residential premises is unacceptable - it is harmful to health.
Beam system
The collector (radiant) heating scheme is the most advanced and modern in terms of thermal efficiency. In it, each of the radiators is connected to a pair of pipes from two common collectors for the floor, which are themselves connected to the boiler equipment. Temperature control with this wiring is more flexible. Plus, it is permissible to connect not only batteries to the collectors, but also a “warm floor”.
Among the advantages of such a heating system for a private house, the following should be noted:
- Convenient and flexible adjustment;
- High efficiency of thermal energy distribution;
- Possibility of replacing individual elements without turning off the heating as a whole.
In this case, the pipelines can be laid as desired. Often they are simply laid under the poured floor. The main disadvantage of the beam scheme is the high cost of the system as a whole and the long length of the pipes. Plus, it will be difficult to lay the latter in large quantities in an already finished cottage. Their installation should be planned in advance at the stage of designing a home.
Radial design - ideal heat distribution
This slate, if necessary, can be relatively easily replaced with another roofing material. The layout of the heating pipes is more complicated; changing it later is not so easy. Even the rigid dimensions of the ondulin sheet are not so scary; there are a lot of scraps, but this is only a slight increase in the roof estimate. With heating pipelines, especially for radial distribution, everything is much more complicated.
Metal-plastic pipes
Metal-plastic is considered one of the most common materials, however, it has a number of disadvantages that distinguish it from polypropylene:
- Installing heating pipes in an apartment made of such material will require quite a lot of expense.
- The process of replacing pipes can only be carried out with special tools such as a pipe cutter, a flaring press and a pipe bender.
- Considering the thinness of the material itself, there is a large outflow of thermal energy.
- Leaks may occur in places where metal-plastic is attached to other materials.
- Low impact resistance, as well as the impossibility of prolonged exposure to sunlight.
However, metal-plastic heating pipes in an apartment also have a number of advantages, which explains such widespread use:
- Possibility of savings through the use of inexpensive elements to connect the entire heating system.
- Good flexibility of the material, due to which the length of heating lines can be reduced as much as possible.
- Thanks to the special design of connectors for such pipes, inexpensive seals can be purchased.
Gas boilers
An excellent option is to install heating that operates on main gas. In general, hot water gas boilers are very reliable and efficient. The efficiency of the simplest energy-independent unit is at least 87%, and the efficiency of an expensive condensing unit is up to 97%. The heaters are compact, well automated and safe to operate. Maintenance is required no more than once a year, and trips to the boiler room are needed only to monitor or change settings. A budget unit will be much cheaper than a solid fuel unit, so gas boilers can be considered generally available.
Just like solid fuel heat generators, gas boilers require a chimney and supply and exhaust ventilation. As for other countries of the former USSR, the cost of fuel there is much higher than in the Russian Federation, which is why the popularity of gas equipment is steadily declining.
Floor insulation for hidden wiring
Removing heating pipes out of sight is tempting from an aesthetic point of view. To prevent hidden heating wiring from subsequently causing the righteous anger of heating engineers with accompanying sanctions, it is advisable to prepare the floor accordingly. If the decorative flooring is laid on joists and additional floor insulation is not required, then the pipes are simply laid between the joists, and removable access hatches are installed above their connections.
Otherwise, the pipes must be laid in the floor. Methods for floor insulation are described in the corresponding article, and for this case we can recommend the following:
- We lay pipes.
- We form an additional warm screed from foam concrete. We fence the pipe connections until the concrete hardens with boards according to the required dimensions (see at the end).
- We lay 12-18 mm plywood flooring directly over the warm screed, gluing the joints with liquid nails or assembly adhesive. We cut out openings in the plywood above the pipe joints.
- We restore the finished flooring. We cut out the hatches for access to the pipes larger than the openings in the plywood - they will simply be removed.
Note: It is advisable to use sheets of tongue-and-groove plywood. But if there are no wild parties in the apartment, you can also install a simple one - it is much cheaper.
The second method is somewhat more expensive, but it is easier to work with and provides access to the pipes along their entire length. To do this, we use foam concrete or aerated concrete slabs with cement-sand mortar as a warm screed. The rest is the same.
Choice of one- or two-pipe option
The supply of hot water and the removal of cooled water for the heating system of a private house can be done using one or two pipes. Each option has positive and negative sides, as well as features of use depending on the type of wiring.
From an interior design perspective, the presence of a second pipe does not have any effect on the appearance of the heating system due to the lower option for connecting the system to radiators and the ability to reduce pipe diameters
Using a one-pipe connection diagram
A water heating scheme for a private house using one pipe for supplying hot water and discharging cooled water is called single-pipe. The main advantage of such a system is to minimize the length of the pipes.
The main advantages of the option:
- lowest costs for purchasing heating system elements;
- the simplest and fastest installation;
- lowest risk of accident.
The main disadvantage of single-pipe heating is the gradual decrease in the temperature of the water, which passes sequentially through all radiators in the circuit.
Therefore, it is necessary to use a slightly larger surface area of the latest radiators (more elbows), which often offsets the cost benefit from minimizing the length of the pipes.
In addition, due to this disadvantage, there are restrictions for one circuit on the number of connected radiators. If there are too many of them, then the latter will practically not emit heat along the flow of the coolant.
In addition, a problem arises when calculating heat transfer. Here it is necessary to take into account that disconnecting the first radiators from the heating system leads to an increase in the temperature of the incoming water for subsequent devices.
It makes no sense to use single-pipe circuits with vertical bottom wiring, since the length of the pipes will be the same as the two-pipe version, which eliminates all the advantages, but leaves disadvantages.
If the coolant returns along the same route as the supply, then the total length of the pipes in both options is almost the same
The heating device is usually connected through a bypass in order to be able to turn off any of them without stopping the water circulation through the circuit.
To save on taps, you don’t have to bypass the water through the tap, but then you will have to stop the operation of this part of the system and drain the water if it is necessary to replace or repair the radiator.
The most economical option is to use one steel pipe with a diameter of 1.5-2 inches without heating radiators. The absence of taps and fittings makes this system also the most practical because it minimizes the risk of leaks or water breakthroughs.
Read more about calculating a single-pipe heating system in this article.
Application of two-pipe heating option
The heating circuit diagram, when one pipe is used to supply hot water to heating devices, and the second to return cooled water, is called two-pipe.
Its main advantages:
- the temperature of the water supplied to all radiators is the same;
- turning off one or more radiators does not affect the temperature of the water supplied to the remaining heating devices;
- restrictions on the number of radiators for one heating circuit depend only on the throughput volume of the pipes.
The main disadvantage of such wiring is a slight increase in pipe footage.
This leads to some additional disadvantages:
- the costs of purchasing and installing heating system elements increase;
- integration into the interior of a private home becomes more difficult.
The number of fittings and taps for a two-pipe system is almost the same as for a single-pipe system.
For a parallel flow pattern of the coolant, the total length of the pipes when using a two-pipe system increases by the distance between the first and last radiator. Sometimes it is insignificant compared to the entire length of the contour
Depending on the relative movement of hot and chilled water, two-pipe wiring diagrams are divided into two types:
- incidental;
- dead end.
Related scheme. Both flows move in the same direction and, thus, the length of the coolant circulation cycle for each radiator is the same. In this case, they heat up at an equal rate when the heating system starts.
Dead end option. The direction of movement of hot and chilled water is counter. Radiators closest to the boiler heat up faster.
The lower the water speed, the more noticeable this effect is, therefore, with natural circulation, heating of some rooms will occur much more slowly than others.
If a circulation pump is used or the distance between the first and last radiator in the circuit is small, then the effect of uneven heating with a dead-end two-pipe wiring is invisible. Then the choice in favor of one or another option is determined solely by considerations of the convenience of installing the return pipe.
Laying methods
This procedure can be carried out in several ways:
- closed;
- open.
It is worth noting that the closed method is not only characterized by increased labor intensity, but also makes it possible to save space in the room. This is very relevant when it comes to small bathrooms.
At the same time, we can immediately note the main disadvantages of the closed method:
- inability to conduct a preventive inspection of pipes to examine their condition;
- the need to break down walls in order to carry out repairs in the event of a leak and, as a result, the need for further repairs.
As for the open method, its only drawback is the reduction of free space in the room, as well as changes in its appearance.
But the advantages include:
- low labor intensity of installation, which has a positive effect on the speed of its implementation;
- the ability to see a leak in time and eliminate it;
- ease of repairs on any site;
- the ability to improve the system while using it.
Natural and forced heating circulation
It doesn’t matter whether gas, wood, coal or electric heating is planned to be installed in a private house. In any case, there is a boiler (furnace or water heater) for heating the coolant, as well as pipes for its movement along the circuit. In this case, water in pipelines can flow naturally under the influence of gravity and convection or forcibly using a pump.
Scheme of types of heating circulations
The first example is cheaper and quieter than the second. However, forced circulation can greatly improve the performance of the entire heating system. Often, heating a private home cannot be done without a booster pump. Due to the large number of radiators, pipe turns and fittings, the hydraulic resistance in the pipeline is too high. And this can only be compensated for by the operation of pumping equipment.
Types of radiators
The choice of radiators for heating is especially important. Let's look at the types of radiators.
Bimetallic
They have a steel core through which water circulates and an aluminum outer shell. Due to the steel core, such radiators are more durable and have a long service life.
Sectional aluminum
A sectional heater consists of cast elements called sections. There are air ducts inside. Their biggest advantage is fast heating.
Cast iron
Cast iron is a material characterized by high strength and corrosion resistance. The massive design of the heater is associated with high heat capacity and resistance to high pressure in the installation and low hydraulic resistance. However, the parameters of cast iron exclude the use of automatic control, which gives them high thermal inertia.
Steel
Steel radiators are characterized by high strength parameters. You will recognize them by the fact that they are made of plates. On the market you will also find models consisting of one or even three elements. The material from which steel radiators are made is resistant to mechanical damage, so it will be an excellent choice for many years of operation.
Steel radiators are ideal both inside an apartment and in country houses. They will do an excellent job of insulating the room in autumn and winter. Steel radiators heat up quickly, which is a big advantage of this device.
We install heating in a private house
One of the options for a properly planned boiler room.
The heating system is installed in several stages. First of all, you need to arrange a room for the boiler. It should be well ventilated and treated with fire-resistant materials. The boiler itself is not mounted close to the wall, but with a slight indentation. You also need to retreat from the ceiling, floor and other walls. Hang the device so that it is easy to reach.
After installing the boiler, proceed to connecting the pump (if needed) or installing the manifold (if provided). Also secure all control and measuring instruments near the boiler. Only after the above actions should we proceed to the arrangement of main pipelines. Here you cannot do without a hammer drill, since to lay the line you will have to punch holes in the walls.
Important! The slope must be at least 5 mm per meter - it is very important to maintain the slope. The absence of this will negatively affect the operation of the entire system as a whole, so take this issue responsibly.
Schematic representation of the correct slope in the heating system. Water flows by gravity into the radiators and by gravity is sent back to the boiler.
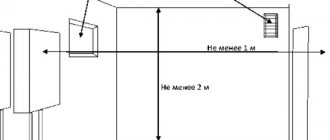
Radiators are installed last. Before installation, you need to mark the wall, then drill holes where the brackets are installed. When marking, keep the following distances: from the floor to the bottom side of the battery - at least 10 cm, from the wall to the back wall - at least 2 cm, and from the window sill - at least 10 cm. It is advisable to install valves at all inputs and outputs of the batteries, which will simplify replacement or repair.
Only after all work has been completed can the system be checked. If you installed a gas boiler, be sure to call a gas service representative for a test run.
In fact, installing a heating system in a private home is not such a difficult task. It is enough to follow all the rules and work without haste. The only problem is the timing. If you don’t have too much time, then look at the prices for the work, figure out what you can do yourself and what is better to entrust to the masters. This way you will save time and money. Buy high-quality materials, then all the elements will last you much longer. Also install good radiators, they will have greater efficiency, which means fuel costs will be reduced.
Heating installation diagram with heated floors in a private house
In the previous sections, we looked at which boiler is best to use to organize heating in your home and how to install the pipes. Here we will look at another option - heated floors.
Like any other installation work, installing a heated floor involves a number of works. You need to start with design. Then, based on the completed project, materials and components are selected. This includes pipes, a manifold with a mixing unit, and insulation. Then the base is prepared where the pipes will be laid and the entire system is installed. When everything is ready, a test run is done. If everything works fine, then the base is poured, the initial start-up and warm-up are carried out.
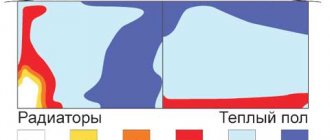
According to the technical design, a heated floor is something like a layer cake, in which all the components are arranged in layers. The base is either soil or a concrete slab, on which a thin film is laid - polyethylene, which acts as waterproofing. Then a thermal insulation material is laid, for example, extruded polystyrene foam. Pipes are placed on top of the thermal insulation material and the whole thing is filled with cement.
How to do heating yourself - option for two wings
It was said earlier that the heating system has two options, one and two pipes. The most common and best for heat conservation is the two-pipe one. It is also represented by two types: dead-end and passing. In a dead-end circuit, the coolant in the supply pipe moves towards the flow of liquid in the return, i.e., simply put, the coolant moves in one direction. This scheme is called a Tichelman loop.
If the length of the pipes is large, then the entire wiring is divided into two parts or, as they say, into two wings. This scheme is especially popular in private homes and country houses.
The length of both parts or wings must be made the same, and all radiators in this network are connected using valves. This will allow you to quickly and efficiently regulate the water supply.
Otherwise, the installation is similar to all others and does not require any special features.
Tips for installing a home heating system
The heating installation begins with the installation of radiators in pre-prepared places under windows or on corner external walls. The devices are hung on special hooks attached to the structure itself or the plasterboard finish. The unused lower outlet of the radiator is closed with a plug, and a Mayevsky valve is screwed in from above.
The pipeline network is installed according to the assembly technology of certain plastic pipes. To protect you from mistakes, here are some general recommendations:
- When installing polypropylene, take into account the thermal elongation of pipes. When turning, the knee should not rest against the wall, otherwise, after starting the heating, the line will bend like a saber.
- It is better to lay the wiring in an open way (excluding collector circuits). Try not to hide the joints behind the sheathing or embed them in the screed; use them to secure pipes.
- Mains and connections located inside the cement screed must be protected with a layer of thermal insulation.
- If for any reason a loop has formed in the pipeline, facing upward, install an automatic air vent on it.
- It is advisable to install horizontal sections with a slight slope (1-2 mm per linear meter) for better emptying and removal of air bubbles. Gravity flow schemes provide for slopes from 3 to 10 mm per 1 m.p.
- Place the membrane expansion tank on the return line near the boiler. Provide a valve to shut off the container in the event of a malfunction.
Installation trick. Do not fill the TP screed until you fill the circuits with water and warm up the system. The goal is to increase the pressure in plastic pipes and force them to lengthen, that is, to put them into operating mode. Then the material will not bend under the weight of the monolith and will not float up if the solution turns out to be liquid.
Types of forced circulation of coolant in heating
The use of forced circulation heating schemes in two-story houses is used due to the length of the system lines (more than 30 m). This method is carried out using a circulation pump that pumps the liquid from the circuit. It is mounted at the inlet of the heating device, where the coolant temperature is lowest.
In a closed circuit, the degree of pressure that the pump develops does not depend on the number of floors and area of the building. The speed of the water flow becomes greater, so when passing through the pipeline lines the coolant does not cool down much. This contributes to a more uniform distribution of heat throughout the system and the use of the heat generator in a gentle mode.
The expansion tank can be located not only at the highest point of the system, but also near the boiler. To perfect the circuit, the designers introduced an accelerating collector into it. Now, if the power goes out and the pump stops, the system will continue to operate in convection mode.
- with one pipe;
- two;
- collector
You can install each one yourself or invite specialists.
One-pipe circuit option
Shut-off valves are also installed at the entrance to the battery, which serves to regulate the temperature in the room, as well as necessary when replacing equipment. A valve is installed on top of the radiator to bleed air.
Valve for batteries
To increase the uniformity of heat distribution, radiators are installed along the bypass line. If you do not use this scheme, then you will need to select batteries of different capacities, taking into account the loss of coolant, that is, the further from the boiler, the more sections.
The use of shut-off valves is not necessary, but without them the maneuverability of the entire heating system is reduced. If necessary, you will not be able to disconnect the second or first floor from the network to save fuel.
To avoid uneven distribution of the coolant, circuits with two pipes are used.
- dead end;
- passing;
- collector
Options for dead-end and passing circuits
The associated option makes it easy to control the heat level, but it is necessary to increase the length of the pipeline.
The most effective is the collector circuit, which allows a separate pipe to be connected to each radiator. Heat flows evenly. There is one disadvantage - the high cost of the equipment, as the amount of consumables increases.
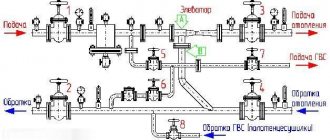
Scheme of collector horizontal heating
There are also vertical options for supplying the coolant, which are found with lower and upper wiring. In the first case, the drain with the supply of coolant passes through the floors, in the second, the riser goes up from the boiler to the attic, where pipes are routed to the heating elements.
Vertical scheme
Two-story houses can have a very different area, ranging from several tens to hundreds of square meters. They also differ in the location of the rooms, the presence of extensions and heated verandas, and their position to the cardinal points. Based on these and many other factors, you should decide on natural or forced coolant circulation.
A simple diagram of coolant circulation in a private house with a heating system with natural circulation.
Heating schemes with natural coolant circulation are distinguished by their simplicity. Here, the coolant moves through the pipes on its own, without the help of a circulation pump - under the influence of heat it rises, enters the pipes, is distributed among the radiators, cools down and enters the return pipe to return to the boiler. That is, the coolant moves by gravity, obeying the laws of physics.
Scheme of a closed two-pipe heating system for a two-story house with forced circulation
- More uniform heating of the entire household;
- Significantly large length of horizontal sections (depending on the power of the pump used, it can reach several hundred meters);
- Possibility of more efficient connection of radiators (for example, in a diagonal pattern);
- Possibility of installing additional fittings and bends without the risk of pressure dropping below the minimum limit.
Thus, in modern two-story houses it is best to use heating systems with forced circulation. It is also possible to install a bypass, which will help you choose between forced or natural circulation in order to select the most optimal option. We make a choice towards coercive systems as more effective.
Forced circulation has a couple of disadvantages - the need to purchase a circulation pump and the increased noise level associated with its operation.
Clients about us:
Object: Mozhaisk district of SNT Khoroshilovo.
Task: Installation of heating in a dacha of 80 m2 Installation of a Kupper solid fuel boiler.
Equipment: Solid fuel boiler, pump for the heating system, heating fluid, radiators, polypropylene pipes.
Customer review: “I contacted the VashKomfort company to install a heating system in my dacha. The guys did the job in two days. I liked everything, I'm very satisfied. I recommend. "
Antonina
How to choose a heating unit
Factors influencing the choice of a boiler (or several water heating devices):
- energy carrier used;
- heat generator power;
- dependence on external energy sources;
- price;
- functionality, ease of use.
Note. The heater selection criteria are arranged in order of priority. It is important for the user that the unit consumes cheap fuel and produces enough heat. Price plays a secondary role; comfort and functionality come in third place.
All household boilers are usually divided into groups according to the type of fuel (energy carrier) burned:
- gas;
- electrical;
- solid fuel;
- liquid fuel, consuming diesel fuel and waste oil;
- universal, operating on 2-3 types of energy carriers.
Each of the listed groups is divided into varieties according to the operating principle, installation method and other criteria. We will review existing boilers and give a number of useful recommendations.
Types of gas boilers
To organize heating in private homes, 3 types of units using natural gas are sold:
- Atmospheric. The combustion chamber is open, combustion air is taken from the boiler room. The operating efficiency is in the range of 86...88%.
- Supercharged (aka turbocharged). Air is forced into the closed firebox by a fan controlled by an electronic circuit. Boiler efficiency is 90...93%.
- Condensation. Structurally similar to turbocharged heaters, but the heat exchanger and burner are designed in such a way that in a certain mode the boiler uses the latent heat of combustion of the fuel. Efficiency – 95%.
Reference. All heat generators are capable of burning 2 types of fuel - natural gas and liquefied propane-butane mixture (LPG). To switch to LPG, the fuel jets are replaced and the automation is adjusted.
Boilers are manufactured in wall, floor and parapet versions. The first group is ready-made mini-boiler rooms, equipped with their own expansion tank and pump. The second type is high-power units, or those that do not depend on electricity. Parapet models are placed near the outer wall, the chimney goes directly to the street.
Among the large assortment of gas water heaters, it is not easy to make the right choice. Our recommendations are:
- If you are on a limited budget, purchase an atmospheric wall-mounted boiler. But remember - open-chamber heaters require a traditional chimney.
- To work together with the gravity system, you will need a non-volatile floor-mounted atmospheric unit.
Floor-mounted non-volatile heater equipped with a single-stage burner, mechanical automatic safety system EuroSIT and a cast iron heat exchanger
- It is better to install a forced-air heat generator in an apartment or cottage without a ready-made chimney. Organize the removal of combustion products through a coaxial pipe laid through the outer wall.
- To supply hot water to 1-2 consumers, buy a dual-circuit model. If the consumption in the DHW network is high, you will need an indirect heating boiler connected to a conventional single-circuit heater.
- Read the detailed description of all gas heaters presented in a separate article.
A condensing boiler is the most economical among gas-using devices. The disadvantage of the unit is the complexity, high price of the equipment and its repair.
Electric hot water installations
A feature of electric boilers of any type is their high efficiency, reaching 99%. The second positive point is the low installation costs and purchase of the heaters themselves. The units should be used as auxiliary heat sources, operating at night at half the light tariff.
There are 3 types of electric boilers (all are available in wall-mounted versions):
- With traditional tubular heaters - heating elements. Modern devices are equipped with an expansion tank and a circulation pump.
- Electrode. Heating of the coolant occurs due to a chemical reaction resulting from the passage of current through the water layer between the 2 electrodes.
- Induction. Here the coolant is heated by the steel core of a sealed coil, which creates eddy currents in it.
Heat generator with tubular heaters (TEN) in section
To install electric heating, it is better to take a classic heating element boiler, which does not require serious wiring. The device is reliable and easy to repair - you can always replace a burnt heating element yourself. An induction heat generator is expensive and cannot be repaired in the event of a breakdown, and an electrode heat generator is highly dependent on the salt content in the coolant.
Advice. Don't listen to salespeople who call induction boilers energy-saving. All electrical installations heat water equally efficiently - losses do not exceed 2%, the rest of the energy is converted into heat.
Classification of solid fuel boilers
For heating country cottages, 3 types of solid fuel units are used:
- direct combustion - atmospheric and turbocharged;
- pyrolysis;
- automatic pellet and coal.
There are many myths about the efficiency of TT boilers. Manufacturers of pyrolysis heat generators claim an efficiency of 85-86%, pellet heat generators - up to 90%. In reality, the figures are much more modest: traditional wood-burning units - 75%, pyrolysis units - 75%, boilers using pellets and coal chips - up to 86%.
Construction of a direct combustion boiler with a fire tube heat exchanger
Reference. In addition to the listed types of heaters, there are long-burning TT boilers with an increased size of the firebox. How to distinguish such installations from classic wood-burning heat generators, read the corresponding publication.
Recommendations for choosing a solid fuel boiler:
- A steel direct combustion apparatus equipped with a chain draft regulator is perfect for burning wood, coal and briquettes. Turbocharged examples are automated and burn wood better, but rely on electricity.
- Pay attention to the volume of the firebox of a traditional boiler - the duration of combustion depends on this indicator.
- Automated pellet units are a good solution for lovers of comfortable heating. You don’t have to chop and carry wood, remove coal dust, just clean the firebox and burner weekly.
- Do not mess with pyrolysis TT boilers, they are a priori more expensive than conventional ones, demanding on the quality of fuel, and in addition they consume electricity.
- Avoid models with water-filled grates if you plan to burn with coal. The temperature difference forms a hard crust on the surface of the grate, which is not easy to knock off.
Grate of a TT boiler made of pipes filled with coolant
When choosing a heat generator, remember the old saying “the miser pays twice.” It is better to take a high-quality classic device with a cast-iron heat exchanger than a cheap “pellet generator” with electronics of unknown origin.
Diesel and combined models
This heating equipment is used much less frequently than gas, wood and electric boilers. Diesel fuel is more expensive than other energy sources, and waste oil is a specific fuel that is clearly unsuitable for the average homeowner. Accordingly, such heating devices are operated only in certain conditions when access to other resources is limited.
Multi-fuel boilers from different manufacturers combine 2-3 energy sources, for example, wood + electricity, gas + coal. Advantage: you buy one heat generator and get two. Disadvantage: the unit cannot boast of high efficiency and functionality. The most popular option is shown in the photo - a TT boiler, equipped with a heating element unit for electrically heating water after the flame in the firebox has died out.
Electric wood heater from the Russian company Teplodar
Heat generator power calculation
To select a boiler based on performance, you should find out the load on the heating system of the house. That is, calculate the heat losses of the building. We propose to calculate this indicator in a simplified way:
- If a living room is separated from the street by one wall with 1 window opening, then 0.1 kW of heat is consumed to heat a square meter of area.
- A room with two external walls (corner) and 1 window – 0.12 kW/m².
- The same, with 2 light openings - 0.13 kW/m².
An important nuance. The calculation is performed for each room separately, then the results are summed up.
The algorithm is suitable for buildings with floor heights up to 3 meters. If the ceilings are higher, heat consumption is calculated based on the volume of the room. Accordingly, in a room with 1 fence and a window, the volume value is 35 W/m³, in a corner room – 40 W/m³, in a corner room with two openings – 45 W/m³.
Having determined the need for thermal energy at home, we select the power of the boiler installation according to the instructions:
- The performance of a unit operating only for heating is taken with a margin of 20%. That is, we multiply the found amount of heat by a factor of 1.2.
- The heat generator providing hot water supply must be taken with a reserve of 50% (coefficient 1.5).
- For TT boilers, the increasing coefficients are 1.5 and 2, respectively.
If you live in an area with a mild southern climate, then the coefficients should not be used. Conversely, residents of the northern regions should increase the initial heat loss figure by 1.5-2 times.
Calculation of heat losses by volume of residential premises
Payment:
- 1. The cost of equipment is paid 3-4 days before the start of work;
- 2. The cost of the work is paid after completion and signing of the work completion certificate.
Wood heating in Solnechnogorsk is a common occurrence and not a problem for local residents, due to the fact that the area is located in the green zone of Moscow and is surrounded by forests on all sides. Local residents prefer wood heating because wood stoves and heating boilers are the most economical equipment, and the most common for this area. Their reliability and efficiency have been tested over the years, since wood heating is the first type of heating used by mankind. It is also natural because when burning wood produces the same amount of carbon dioxide as when rotting, only this happens over a reduced period of time.
Installation and replacement of pumps
One of the main activities of our company is the replacement and installation of water pumps of all types: surface, submersible and semi-submersible. The company’s specialists with extensive experience will install, dismantle and install the following pumping equipment in the shortest possible time:
- borehole pumps;
- well pumps;
- water pumps;
- circulation pumps;
- booster pumps;
- irrigation pumps.
In addition to installing and replacing pumps, we also carry out work on complex pumping stations, carrying out complex operations for installation, dismantling and installation of equipment.
Sources
- https://sdelat-dom.ru/remont/otoplenie/otoplenie-chastnogo-doma/
- https://cotlix.com/otoplenie-v-chastnom-dome-svoimi-rukami-podrobnoe-rukovodstvo
- https://sovet-ingenera.com/otoplenie/razvodka-o/razvodka-otopleniya-v-chastnom-dome.html
- https://master-houses.ru/shemy-otopleniya-dlya-chastnogo-doma-kakie-luchshe/
- https://oboiman.ru/teplo/sistemy-otoplenia-castnogo-doma-svoimi-rukami-shemy-razvodki.html
- https://otivent.com/kak-sdelat-otoplenie-chastnogo-doma-ili-kvartiry
- https://www.tproekt.com/razvodka-otoplenia-v-castnom-dome-svoimi-rukami/
[collapse]
The procedure for providing services in the company:
- Drawing up an installation project;
- Conclusion of an agreement;
- Selection of materials and equipment;
- Direct installation of the heating system;
- After installation maintenance - commissioning, checking the functionality of the system.
We guarantee high quality and professionalism. You will always be warm with us!
High-quality home heating installation
- Autonomous boiler room
- Heating pump distribution
- Copper water heating
- Adjusting the radiator with thermostats
- Heating radiator thermostat
- Heating the veranda
Installation of water heating
Installation of water heating
Nuances of operation
When using a furnace, to improve the operation of the system, the difference between the lower point of cold water (return) and the upper point of hot water is maximized. The riser is brought to the ceiling. In any case, water heating is calculated. If a heating boiler is used, it is recommended to lower it lower, if possible, for example, into the basement. This arrangement allows you to increase the height of the riser and give the water a greater impulse of movement. Consequently, efficiency will increase and the house will warm up more evenly.