rated thermal power" in other dictionaries: rated thermal power
—
The value of
total
power
,
power
per unit length or unit surface area of the electric heater at
rated
values of voltage, temperature and length, expressed in W/m or W/m2.”>
Skip to content
The rated power of the boiler is the main thermal characteristic of the boiler and is expressed in different measurement systems used in the Russian Federation, in kW (mW) or Mcal (Gcal) with their following ratio - 1 Gcal = 1.163 MW.
Approximate selection
It doesn't always make sense to use complex calculations. For a house with average ceiling heights, built in the middle zone, well-insulated boiler power can be calculated using the formula 100 = 1 sq. m. This means that it is enough to simply multiply the available heated area by 100. In this option, water heating is not taken into account.
Most store consultants use this formula and then add stock. Results are always rounded up, but not according to the principle of 5 after the decimal point. If you get a value like “20.3”, you will immediately be offered a 24 kW boiler.
What else needs to be taken into account when calculating
Previous calculations do not provide an accurate estimate of the power of the boiler room; it is necessary to take into account the preparation of hot water. The power of the boilers needs to be increased by about 20% - that much heat is spent heating the water. For a private home, it is better to purchase automatic double-circuit heating systems - they save fuel consumption, work to heat the room and prepare hot water.
It is better to measure the operation of gas boilers in m³/h or kg/h, so as not to confuse electrical energy with thermal energy. It should be remembered that the combustion of 0.112 m³ of gas is equal to 1 kW of heat.
The geographical location of the heated room is also taken into account. For this purpose, there are maps indicating average temperatures at different times of the year for different areas. The coefficient taken from the map is added to the calculated figure set earlier. For the climate of central Russia it is equal to 1, for the northern regions - from 1.5 to 2. The figure obtained by measuring the area and volume of the heated room is multiplied by this coefficient. The result will be the boiler power required for the given region.
An example of calculating heat consumption in a brick house in Syktyvkar:
- house 3 m high;
- area 100 m².
We calculate the volume: multiply 100 m² by 3 m, we get 300 m³. We multiply 34 W by 300 m³, we get 10.2 kW. The settlement is located in the northern zone, so the last number is multiplied by a factor of 2. The result is 20.4. To this number is added another 20% for water heating and 25% of reserve power. To prevent premature wear of the equipment, add another 10% of power. As a result, the full power of the boiler room is obtained.
If several houses are heated, you need to calculate the energy expended for each of them and add up the resulting values. This amount will indicate the required thermal power.
For more accurate calculations, experts use formulas that include:
- heat loss coefficients;
- number of people in the room;
- types of thermal insulation materials;
- difference between external and internal temperatures.
The larger the heated objects, the more factors are taken into account.
— systems for the production and use of thermal energy
Calculation of boiler room thermal power
Consumers are served by the following types of boiler houses:
- local (for one or more houses);
- block (for houses of an entire block);
- regional (large structures).
All boiler rooms can be heated with the following types of fuel:
- hard (wood, peat, coal);
- gaseous;
- liquid (fuel oil, oil, oil, diesel fuel);
- combined.
When burned, solid fuel releases gases and leaves ash. Pellet boiler houses use pellets, which are produced from the remains of lumber (branches, sawdust) and sunflower husks.
The use of solid fuel requires equipping boiler houses with special grates that allow ash to pass through. The wood must be dry; sheds are used to dry firewood. It is better to use hardwood firewood, because... pine logs clog chimneys with combustion products.
Thermal energy for this type of fuel is calculated as follows: per 1 m² of building area there should be 100 W/h. For a house with an area of 100 m², the power is 10 kW. Knowing the number of days on which heating is produced, the total thermal output can be calculated.
Boiler houses can operate on liquefied and main gas. For gas boiler houses, there are special requirements for laying pipes to ensure the operation of boilers (piping). The simplest option for calculating the power of gas heating equipment is 1 kW of energy per 10 m² of area. In addition, the area of the room, its location in a particular climate zone, and the heat loss of the heated building are taken into account. Accurate calculations can be performed by heating engineers. They will also help determine fuel consumption over the required period of time.
In remote areas, liquid boiler houses are installed. Fuel consumption for them is measured as follows: 1 kg of diesel fuel gives 10 kW.
The thermal energy released is calculated in megawatts (mW) or gigacalories (Gcal).
In combined boiler houses the following is used as fuel:
- gas and diesel fuel;
- gas and fuel oil;
- gas and oil;
- gas and waste oil.
The priority and secondary fuel is determined by the owner of the boiler house. The type of boiler depends on the type of coolant chosen.
When constructing and operating low-power heating boiler houses, several factors are taken into account to calculate thermal energy:
- wear and tear of heated buildings;
- the degree of their insulation;
- sizes of windows and doors.
4.5. Water heating boilers of the KV-TK series for chamber combustion of solid fuels
Boilers of the KV-TK series are designed for chamber combustion of solid pulverized fuel and have a U-shaped layout. Solid fuel dust is fed into six turbulent burners (Fig. 4.6), arranged in opposite directions, three burners on each of the side walls of combustion chamber 7. The boiler is designed with solid slag removal.
The walls of the combustion chamber 7, the rotary chamber and the rear screen are made of gas-tight pipes with a diameter of 60 x 4 mm with a pitch of 80 mm. To ensure gas tightness, strips of 20 x 6 mm are welded between the pipes. In the upper part of the combustion chamber, the pipes of the rear screen cover the inclined slope of the transition chamber and then, before entering the rotary chamber, are spread into a scallop. 2 Blowers are installed on the walls of the combustion chamber with compressed air supplied to them.
Two convective packages made of pipes with a diameter of 28 x 3 mm are installed in the convective shaft. Below them is a three-pass (air) air heater 5, made of pipes with a diameter of 40 x 1.5 mm, providing air heating up to 350 °C. To clean convective heating surfaces, a shot cleaning device (shot cleaning unit) is provided. The boiler is suspended from the frame by the upper collectors. The air heater rests on a separate frame. The boiler has a lightweight lining.
Calculation by area
Heat consumption is calculated based on the area of heated premises. It is considered normal to consume 1 kW of heat per 10 m² of a room up to 2.7 m high. To calculate the consumption of all thermal energy, you need to know the total area of the building.
In this way, the productivity of boilers is calculated depending on the area of the building.
Power units
2.1 Power units used in the energy sector
- Watt – W – unit of power in the SI system, derivatives – kW, MW, GW
- Calories per hour - cal/h - an off-system unit of power, usually in the energy sector derived values are used - kcal/h, Mcal/h, Gcal/h;
- Tonnes of steam per hour - t/h - a specific value corresponding to the power required to produce steam from 1 ton of water per hour.
2.2. Examples of correct use of power units
- Boiler design power
- Heat losses of the building
- Maximum consumption of thermal energy for heating hot water
- Engine power
- Average daily power of thermal energy consumers
2.3. Conversion between power units
1 MW = 1.163 Gcal/h = 1.595 t/h
1 Gcal/h = 0.86 MW = 1.86 t/h
1 t/h = 0.627 MW = 0.539 Gcal/h
Note: When calculating 1 ton of steam, the enthalpy of the source water and water vapor at the saturation line at t=100 °C was taken
Rules and regulations
Maintenance of ship steam boilers is regulated by the Rules for the technical operation of ship steam boilers of the Ministry of the Navy. According to the Rules, the use of ship boilers must be carried out taking into account maximum heat output, without causing damage to their technical condition, ensuring safe operation and the lowest fuel consumption.
Proper organization of work and adherence to the Rules for the Technical Operation of Ship Boilers plays a major role in fulfilling the above requirements. Violation of the Rules is fraught with accidents and unstable work.
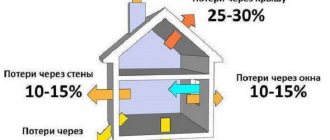
The main figure is heat loss
Of primary importance when accurately calculating the boiler power are heat losses - the amount of heat lost (outgoing) through walls, windows, floors, ceilings: These “problem” areas need insulation. This helps reduce heat loss. The better this event is carried out, the less power the boiler needs.
Heat loss is determined by the formula Q=k*S(t1-t2), where k is the heat loss coefficient depending on the material (for windows it is indicated in the documentation), for other bases it is taken from tabular data, S is the area, t1 is the temperature inside the room ( taken as 20 degrees) and t2 is the lowest external, depending on the region.
The heat loss of each surface is calculated separately. The resulting values are added together. The result is the overall indicator of the entire building, which is measured in kilowatts - a value also used for the power of thermal generators. The power of the equipment is selected with a margin of 10 to 15% of heat loss (especially important for solid fuel boilers). If there is a hot tub, swimming pool - artificial reservoirs, that is, the water is heated using a boiler, as well as ventilation systems, they must be taken into account.