Gas is still the cheapest fuel, so if you have a gas main, you should choose a gas boiler without hesitation.
According to surveys and practice, the top three most important selection criteria for most buyers include gas consumption. Despite the fact that it is indicated in the characteristics of almost every modern boiler, this does not allow you to quickly imagine the approximate cost of gas consumed per day, month or for the entire heating season. To make heating budget planning easier, it is enough to once understand the principles of calculating gas consumption by boilers.
What factors affect fuel consumption?
Years of using different types of fuel have proven that gas is 30% cheaper than diesel and electricity. Most users connect to a common pipeline, since when using gas in cylinders, funds are spent on delivery.
Factors that should be taken into account when choosing a heating boiler to avoid high fuel consumption:
- Heat losses. The consumption of a gas boiler directly depends on heat loss through walls, windows, doors, and roof. Therefore, preliminary calculations of the equipment’s power are carried out. The area of the room, the quality of insulation, and the purpose of adjacent rooms are taken into account.
- Settings system. The automatic installation includes sensors that record the external temperature and adjust the operation of the unit in optimal mode. This allows you to save on consumption.
- Type of equipment. When using a condensing unit, gas consumption is reduced by 15–20%. Unlike the conventional convection type, the condenser contains a separate heat exchanger to direct the energy of the combustion products to heat the system. This increases the coefficient of performance (efficiency) to 100%.
The presence of one or two circuits also matters. A single-circuit device works only for heating. Whereas a double-circuit one is used for hot water supply (DHW) and heating. Consequently, its consumption will be greater.
Units with a closed combustion chamber consume less fuel than those with an open combustion chamber. The length of the heating season also affects. After all, in winter the boiler works at maximum, while in summer it works at minimum, only to heat hot water.
Why do appliances consume a lot of gas? This is all due to poor insulation of the building and scale deposits.
What determines the boiler's appetite?
Firstly, from its power. The larger it is, the higher the consumption of gas boilers will be. Moreover, you will not be able to reduce the appetite of a heat-generating device by using it. If you purchased a 20 kW gas fireplace, then even at minimum it will consume more than a 10 kW device at maximum. Therefore, be careful when choosing the power of heat-generating devices.
Secondly, from the temperature “overboard”. In this case, the already mentioned power regulator comes into play. After all, at a low temperature in the house, we will try to squeeze the maximum number of calories out of the heating by turning the regulator knob to the maximum. And if in relatively warm (for winter) weather the regulator is set to “one” or “two”, then in 30- or 40-degree frosts it is switched to “five” or even “seven”. And the number of cubic meters of gas passing through the nozzles into the combustion chamber doubles.
Gas consumption by a boiler depends on many factors
Thirdly, on the calorie content of the gas. This value is not controlled by the consumer. Therefore, gas distribution companies sometimes play around with the composition of “blue” fuel. After all, the same compressed nitrogen pumped into the central pipeline costs 2.5-3 times less than natural gas. Now, fortunately, such fraud schemes are no longer practiced, but gas workers can easily supply “undrained” gas with a high content of water vapor and other impurities into the pipes. And if your kettle boils not in 2-3 minutes, but in 5-7, then what can you ask from the heating system? You approach the boiler and turn the power regulator to maximum, closing your eyes to the accelerated rotation of the gas meter disk.
Fourthly, on the technical condition of the heat exchanger. Heating of water or coolant in gas appliances occurs in a heat exchanger - a special copper pipeline located either in the combustion chamber or behind its walls. And if the heat exchanger becomes clogged with scale or scale residues from the batteries, then you will have to add power, compensating for the decreased heat transfer. Moreover, a clogged heat exchanger steals cubic meters much more actively than real or mythical tricksters from a gas distribution company.
Fifthly, on the number of heating circuits. Almost all modern gas boilers have more than one heating circuit. After all, such heat-generating devices serve not only the wiring of the heating system, but also the home hot water supply line. To do this, a second circuit is installed into the structure of the gas hearth and the throughput of the nozzles is increased, increasing the power. And the more power, the higher the consumption.
How much energy does a home heating system consume?
If we analyze all the reasons that stimulate the appetite of a heat-generating device, it becomes clear that the boiler’s consumption is primarily affected by its power. A clogged heat receiver, low-calorie gas, severe frosts and an additional circuit force us to increase and increase the boiler power. Therefore, before calculating the flow rate, we must determine the needs of the heating system itself.
And for this you do not need to delve into serious mathematical formulas, taking into account the thermal inertia of the batteries, the thermal resistance of walls, ceilings and windows. For an approximate result, a simple proportion will be enough: 10 square meters. m. = 1 kW. Well, for severe frosts it’s worth adding another 20 percent, adjusting the proportion to 10 m2 = 1.2 kW
How to apply this proportion in practice? Yes, very simple:
- Take a house or apartment plan and calculate the area of all heated rooms (including warm corridors).
- Divide the sum of all areas by 10 and multiply by 1.2. As a result, you will get a number that determines the maximum appetite of the heating circuit.
Finally, round the resulting kilowatts to the nearest value of the boiler’s standard power (7, 10, 12 kW, and so on) and get the desired need, based on which you can calculate how much gas your particular heat generator consumes.
For example, you have three rooms of 18, 12 and 20 square meters. Plus a kitchen of 12 m2 and a corridor of 6 m2. The total is 68 square meters or 8.16 kW. We round this figure to 10 kW and get the required power of the heat generating installation. Now we only have to calculate the gas consumption to generate 1 kW of power.
The bitter truth about gas consumption in your home
Now you may be surprised, but not a single person will be able to tell you the gas consumption of the boiler in the case of your home. When performing calculations, an experienced specialist will be able to give average values that will be close to the truth, but in any case they will not reflect the exact essence.
This is due to several factors:
- Winter is different from winter every year. Accordingly, the warmer it is, the less will be spent and vice versa.
- 100 square meters in your house and 100 square meters in your neighbor’s house are two completely different houses. Below we will talk about why
- Different boilers have different flow rates
What volume of gas needs to be burned to generate 1 kW
To answer this question, we need to understand such concepts as the calorific value of gas and the efficiency of the boiler. The first term means the amount of energy released when a kilogram or cubic meter of gas is completely burned.
According to reference books, for the standard main mixture supplied to the boiler, the calorific value is 9.3 kW/m3.
The second term (efficiency) refers to the ability of a heat-generating installation to transfer the energy of burned fuel to the coolant. Typically, gas boilers can transfer no more than 90 percent of the energy of the burned gas to the coolant. Therefore, when burning a cubic meter of gas, the coolant will receive no more than 8.37 kW (9.3x90%).
As a result, about 0.12 m3 of gas (1/8.37) is used to generate 1 kW of thermal power. That is, in order for the heating system to receive 1 kilowatt per hour, the combustion chamber of the boiler must accept and process 0.12 m3 of fuel. Based on this information, we can calculate monthly, daily, and even hourly boiler consumption rates.
Gas valve adjustment
The useful thermal power can be reduced by reducing the fuel supply to the burner as a result of changing the valve setting.
It is important to remember that the burner power is controlled by a complex electronics algorithm that takes into account several basic indicators, represented by the start time, temperature indicators, the temperature difference in the direct pipe and the “return”
Adjusting the power indicators of the gas boiler burner is carried out by rotating special adjusting screws located on the valve body counterclockwise. More modern models are equipped with special automation that easily blocks clocking and changes power indicators. For this purpose, hold down the button with the wrench (5 seconds), and use special buttons to select the optimal duration of the intervals (0-15 minutes).
Average gas consumption per month, day and hour
If you want to calculate the hourly gas consumption in the boiler, then you simply need to multiply its power by 0.12 m3 (this is exactly how many cubic meters it takes to generate 1 kW). For example, for a 10-kilowatt boiler, the maximum hourly flow rate will be 1.2 m3 (10x0.12). But this formula is no longer suitable for determining the daily norm.
In daily calculations, slightly different parameters are used . After all, the burner of a heat generator will not work 24 hours a day. This is not required of her. Typically, 50 percent is allocated for work and downtime. That is, during the day, the heat generating unit consumes fuel for only 12 hours. Therefore, daily consumption is calculated using the formula: daily consumption is multiplied by 12. For example, the maximum daily portion for a 10-kilowatt boiler will be equal to 14.4 m3 (10x0.12x12).
To calculate how much gas a boiler consumes per month, you simply need to multiply the daily consumption by 30 days. For example, the maximum monthly consumption of a 10-kilowatt boiler is 432 m3 (10x0.12x12x30). That's all. Now you know the maximum consumption rates and can adjust the boiler power to your budget. However, remember that in real life any heat generator operates at 50-75 percent of its power, so you can subtract 25 percent from the proportion calculated using the above formula.
Pay attention to heat losses
The following calculation method assumes that the level of heat loss of the building is known - and this statement is true in most cases.
The calculation process is simple:
- The total heat loss is divided in half, and 10% is added to the resulting value for hot water supply and ventilation heat outflow;
- The result of the previous action (measured in kilowatts per hour) allows you to find out the gas consumption for a day, a month or the entire heating period;
- The total gas consumption is converted into cubic meters (for this you will need to find out the specific heat of combustion of the gas) and multiplied by the cost of one cubic meter, as a result of which you can get the cost of heating for the desired period of time.
Using a similar method, you can calculate the consumption of any fuel - you just need to know the heat capacity of a particular energy resource. In addition, it is worth remembering the efficiency of heating equipment, which in the case of gas boilers fluctuates around 90%, i.e. It is worth adding another 10% to the total expense.
Of course, the described technique cannot give an exact answer to the question of how much a gas boiler consumes per month. On cold days, consumption will increase, and on warm days it will decrease, and this is completely logical. However, even a rough calculation allows you to understand how much gas a gas boiler consumes per month and how profitable its installation will be.
How to reduce costs
If you follow our recommendations in the domestic sphere, then you can save on using the boiler:
- Start with choosing a technique. The most economical is a condensing boiler. It saves up to 25% fuel, and efficiency reaches 100–110%. Of course, its cost is much higher, but, according to experts, it will quickly pay for itself. Pay attention to consumer reviews when purchasing. A double-circuit boiler uses 20–25% more thermal energy. Therefore, if the room only needs heating, give preference to a single-circuit installation.
- Take care of insulating the walls, install plastic double-glazed windows. Heat loss through the roof can be easily determined by the build-up of icicles. The more heat goes away, the more icicles there are. In this case, cover the roof and use special materials for insulation.
- Choose modern automatic equipment. It’s not for nothing that manufacturers install sensors, thermostats and regulators. This system works as a single organism, automatically regulating and adjusting the operation of the equipment to the conditions in the room. Timers and special modes allow you to maintain minimum values during vacation or weekend. You can also select the “Winter - Summer” mode.
- Carry out routine maintenance once a year. Be sure to call a specialist for a technical inspection. Clean parts from blockages. Scale accumulations on the heat exchanger contribute to increased thermal energy use. Remove soot and soot from burner nozzles and clean the chimney in a timely manner.
- Install the heat accumulator (TA). This buffer container accumulates coolant and retains heat for a long time (similar to a thermos). Even when the boiler is turned off, the TA will supply liquid to the radiators. Using such a buffer allows you to save 20–30% of fuel.
- Do not select the maximum temperature. Set comfortable indicators, because against the backdrop of average monthly consumption, even 1–2 degrees matter.
This is how the cost of heating a living space is calculated. If you are not sure of the accuracy of the calculations, contact a specialist. He will take into account all the nuances and help you with the selection of economical equipment.
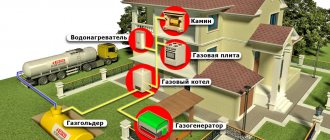
Connection diagram for gas cylinders to a heating boiler
To connect the cylinder to the boiler, a special reducer is used, which converts liquefied fuel into a gaseous state. It is in this form that it is supplied to the heating equipment. If several containers are used at once, then the same number of reducers will be needed to connect to each cylinder. This is much safer than connecting several containers at once through one common gearbox.
To assemble the entire structure, a two-arm collector is used. This is a special ramp that divides all containers into two groups. One group is the main one. From it, gas enters the boiler first. The second group is the reserve group. It is used after the main group runs out of gas. Switching from one group to another occurs automatically. At the same time, a characteristic signal is heard. After refueling and connecting the tanks of the main group, the collector begins to consume fuel from these cylinders.
Gas equipment for home heating - burners for stoves and boilers
All containers with fuel are installed from the boiler at a distance of no closer than 200 cm. It is best to allocate a separate room for these purposes or fence off a compartment in the furnace room. It is prohibited to install cylinders in an uncovered place exposed to sunlight.
To connect containers, metal pipelines with a wall thickness of less than 2 mm are used. In the place where the pipes pass through the walls, protective cases are installed, and all openings are filled with foam. A durite hose is used to connect the pipeline to the heater.
Safety Recommendations
Converting the boiler and reconfiguring it to consume liquefied gas dictates the need to “reconfigure” your attitude towards the device for supplying and storing blue fuel.
You must remember that:
- Cylinders or gas tanks, which are gas storage tanks that supply fuel to household appliances as needed, need to be refilled periodically.
- To fill a group of cylinders or a gas holder with gas, you need to contact certified organizations that have equipment to record the weight of the gas in the cylinder and its actual volume in the gas holder.
- Filling closed gas tanks is carried out to 85% of the useful volume of the vessel. This reserve is necessary in case of thermal expansion of the fuel to avoid an explosion.
A non-hazardous situation that requires special attention when replenishing liquefied blue fuel reserves is the filling of liquid with a density different from the density of the previous liquid. Because of this difference, the remaining liquefied gas may not mix with the newly filled portion.
In the tank, due to the difference in density, a kind of two non-connecting sectors are formed, in each of which liquefied gas circulates. However, convective heat exchange will occur at the sector boundary after a short period. After the temperatures are equalized, the densities will be equal and the liquids will be able to mix.
Liquefied gas, like main gas, is a highly flammable, combustible liquid with a high flame propagation speed. To avoid catastrophic situations, you should strictly follow the operating rules and fill the cylinders no more than 85%
Usually this process, meaning direct mixing, is accompanied by intense evaporation of liquefied gas. To avoid associated losses, mixing devices should be used during the filling process. But it is better to choose a method that eliminates the above-described phenomenon.
Replenishing cylinders and gas tanks with blue fuel in general is a process that requires increased attention, otherwise problems can be very serious and even catastrophic. The rapid spread and evaporation of the liquefied gas mixture is recognized as a significant problem.
If the rules for the safe operation of gas-consuming equipment are not violated, main methane rarely explodes. This only happens with significant leaks, if the technical state of the gas in the surrounding space changes dramatically. For example, in a kitchen with obvious signs of a leak, instead of mandatory ventilation, they turn on the light.
When liquefied gas expands in a closed container due to external heating, it will necessarily explode if there is not enough space left in the container for its expansion. Blue fuel burns extremely intensely. Since the gas is quickly absorbed by the atmosphere, the combustion zone expands at high speed.
Consumption of liquefied propane-butane mixture
Not all owners of country houses have the opportunity to connect to a centralized gas pipeline. Then they get out of the situation using liquefied gas. It is stored in gas holders installed in pits, and replenished using the services of certified companies that supply fuel.
Liquefied gas used for domestic purposes is stored in sealed containers and reservoirs - propane-butane cylinders with a volume of 50 liters, or gas holders
If liquefied gas is used to heat a country house, the calculation formula is taken as the basis. The only thing you need to take into account is that the bottled gas is a G30 mixture. In addition, the fuel is in an aggregate state. Therefore, its consumption is calculated in liters or kilograms.
Formula for calculating fuel mixture consumption
A simple calculation will help you estimate the cost of a liquefied propane-butane mixture. The initial construction data is the same: a cottage with an area of 100 square meters, and the efficiency of the installed boiler is 95%.
When calculating, it should be taken into account that fifty-liter propane-butane cylinders, for safety reasons, are filled to no more than 85%, which is about 42.5 liters
When performing calculations, we focus on two significant physical characteristics of the liquefied mixture:
- The density of bottled gas is 0.524 kg/l;
- The heat released during the combustion of one kilogram of such a mixture is equal to 45.2 MJ/kg.
To facilitate calculations, the values of heat released, measured in kilograms, are converted into another unit of measurement - liters: 45.2 x 0.524 = 23.68 MJ/l.
After which joules are converted to kilowatts: 23.68/3.6 = 6.58 kW/l. To obtain correct calculations, the same 50% of the recommended power of the unit is taken as a basis, which is 5 kW.
The obtained values are substituted into the formula: V = 5/(6.58 x 0.95). It turns out that the consumption of the G 30 fuel mixture is 0.8 l/h.
An example of calculating liquefied gas consumption
Knowing that on average 0.8 liters of fuel are consumed per one hour of operation of a boiler generator, it will not be difficult to calculate that one standard cylinder with a 42-liter refill will be enough for approximately 52 hours. This is a little more than two days.
For the entire heating period, the consumption of the combustible mixture will be:
- For a day 0.8 x 24 = 19.2 liters;
- For a month 19.2 x 30 = 576 liters;
- For a heating season lasting 7 months, 576 x 7 = 4032 liters.
To heat a cottage with an area of 100 square meters you will need: 576/42.5 = 13 or 14 cylinders. For the entire seven-month heating season, you will need 4032/42.5 = from 95 to 100 cylinders.
To accurately calculate the number of propane-butane cylinders needed to heat a cottage for a month, you need to divide the consumed monthly volume of 576 liters by the capacity of one such cylinderA large volume of fuel, taking into account transportation costs and the creation of conditions for its storage, will not be cheap. But still, in comparison with the same electric heating, such a solution to the issue will still be more economical, and therefore preferable.
Weather-compensated automation
You can adjust the power level of a gas boiler using weather-dependent automation. A special feature of the delivery set is the presence of external and internal temperature sensors. Thanks to the automatic mode, you can make changes to the power without overheating the indoor air.
The most popular manufacturers today produce high-precision and modern weather-dependent automation kits for most models of gas boilers. However, the basic supply of equipment, as a rule, does not include such systems, so they must be purchased separately.