To regulate the flow of water, other liquids and gas in process pipelines and water and gas transmission structures, various types of hydraulic systems and mechanisms, control, as well as shut-off and control valves and devices for regulating and maintaining system parameters are used. This type of fittings can be classified as technical devices, the operation of which allows you to perform operations to shut off the flow, regulate, mix flows, and also allows you to change the area (diameter) of the design cross-section of the pipeline within the required parameters.
The used control and shut-off equipment, blocking completely or partially, distributing the hydraulic flow, ensuring mixing of the flowing working fluid and gas, allows you to regulate several parameters in the system. This includes equalizing and regulating pressure, pressure, volume, and in some cases the temperature of the liquid can be adjusted.
Shut-off valves are components of hydraulic and gas systems used in level sensors and flow meters, as well as in industrial installations and general purpose pipelines, used in the construction of hydraulic systems of residential and public buildings and industrial facilities. Shut-off valves for pipelines, when used, allow, first of all, to stop the flow of working fluid or gas, which is why it got its name. The shut-off valve is not used (not recommended for use) as a control valve to regulate flow; mixers, control valves, throttles and other types of process control devices are used for this purpose. Depending on the shape, purpose, design, purpose of use, shut-off valves can perform the function of shut-off and control.
When is the best time to replace batteries?
So, let's start, first let's look at the simplest case when the batteries need to be replaced during apartment renovation.
It is best to replace batteries at the stage of finishing the rough finishing, that is, when the walls have been plastered and the screed has been poured. It often happens that an old heating device (convector or cast iron radiator) prevents you from plastering the wall behind it; in this case, you need to plaster wherever possible around the old radiator, so that the radiator installer understands what level the wall is at and installs the radiator as the required distance from the wall and parallel to it. Plaster the space behind the radiator by removing the new radiator after installation. You should also understand the technological process that first the radiator is installed on the brackets, blanks of new bends are attached to it on the union nut of the ball valve, and only then the bends are welded to the riser. And not vice versa. The reason is the need for clear alignment of the radiator outlets and collectors. An example of a job I reworked that did not follow the required workflow.
Heat consumption for ventilation
To find out how much heat a private house loses as a whole, you need to add up the losses of all its rooms. But that’s not all, because we must also take into account the heating of the ventilation air, which is also provided by the heating system. In order not to go into the jungle of complex calculations, it is proposed to find out this heat consumption using a simple formula:
Qair = cm (tв – tн), where:
- Qair – required amount of heat for ventilation, W;
- m – amount of air by mass, defined as the internal volume of the building multiplied by the density of the air mixture, kg;
- (tв – tн) – as in the previous formula;
- с – heat capacity of air masses, is taken equal to 0.28 W / (kg ºС).
To determine the heat demand for the entire building, it remains to add the value of QTP for the house as a whole with the value of Qair. The boiler power is taken with a reserve for the optimal operating mode, that is, with a coefficient of 1.3. Here you need to take into account an important point: if you plan to use a heat generator not only for heating, but also for heating water for domestic hot water supply, then the power reserve must be increased. The boiler must operate effectively in 2 directions at once, and therefore the safety factor must be taken at least 1.5.
How to adjust the balancing valve in a heating system
Setting up a mechanical balancer
Before setting up the balance of the radiator network, you need to study the instructions for the valve, which are included when purchasing it. It indicates an adjustment scheme; if the user installs everything correctly, he can actually reduce the cost of thermal energy. The valve can be adjusted in two ways.
The first way to adjust the valve
This is the simplest and most proven adjustment option, which is recommended by experienced thermal regulators in water heating networks. To do this, you will need to divide the number of valve revolutions by the number of batteries installed in the heating circuit around the perimeter of the room. This technique makes it possible to correctly determine the step of the tuning algorithm. The method consists of closing all the valves in the reverse order - from the outermost to the first battery in relation to the heating source.
For example, for a dead-end circuit with 4 radiators equipped with mechanical balancing valves and a 4.5-turn spindle adjustment:
4.5:4 = 1.1 turns
Opening diagram:
- The first balancing valve is 1.1 turns.
- Second balancing valve – 2.2 turns.
- Third balancing valve – 3.3 turns.
- The fourth balancing valve is 4.5 turns.
The second way to configure the balancer
There is another, very high-quality method of balancing. It runs much faster, and contains the ability to take into account some of the specific location of the battery. The only thing you need to do this is a contact thermometer.
The complete process goes like this:
- Open all the valves and allow the network to enter temperature equilibrium with the operating temperature, for example, 80 C.
- Measure the temperature of all heating devices.
- Eliminate the difference by shutting off the first and middle taps. The end valves are not adjustable.
- Typically, the first valve turns no more than 1.5 revs, and the middle ones - 2.5 revs.
- Allow the system to reach temperature equilibrium for 20 minutes
- Temperatures are measured and valves are adjusted further if necessary.
Advantages and disadvantages
- The valves have high tightness with small sizes and can be used at high temperatures and pressures, but have high hydraulic resistance and are used for small diameters.
- The valves have a simple design and small dimensions, quickly open/close the passage, but do not operate at high pressures (and ball valves at high temperatures) and are not tight enough for use in gas systems.
- The valves are highly reliable over a wide range of temperatures and pressures, but have a long response time. Knife gate valves have a locking body in the form of a plate capable of cutting dense inclusions, which makes them suitable for use in thick and dusty environments (powders, pulp, dusty gases).
- The valves have a simple design, high reliability, can be used in large-diameter pipelines, but have high hydraulic resistance and are difficult to control.
Heating system installation
We will begin the description of installation work with the installation and piping of the boiler. In accordance with the rules, units whose power does not exceed 60 kW can be installed in the kitchen. More powerful heat generators should be located in the boiler room. At the same time, for heat sources that burn different types of fuel and have an open combustion chamber, it is necessary to ensure a good air flow. A chimney device is also required to remove combustion products.
The location where the heat generator will be located must be selected taking into account the minimum permissible distances to walls or other equipment. Typically these intervals are specified in the manual supplied with the product. If this data is not available, then we adhere to the following rules:
- passage width on the front side of the boiler is 1 m;
- if there is no need to service the unit from the side or rear, then leave a gap of 0.7 m, otherwise - 1.5 m;
- distance to the nearest equipment – 0.7 m;
- when placing two boilers next to each other, a passage of 1 m is maintained between them, and opposite each other - 2 m.
Shut-off and control elements of systems
These include the following devices:
- balancing valves;
- automatic differential pressure regulators;
- thermostatic radiator valves.
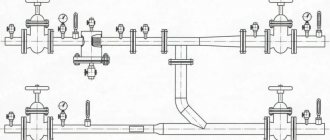
Balancing valve
The listed types of shut-off and control valves are designed to carry out quantitative regulation of the coolant. That is, by partially blocking the flow section of the pipeline, these elements provide a certain flow of water entering a section of the system or into a heating device. Balancing valves are installed both at the outlet of the batteries and at the beginning of a branch or riser of the system, as a rule, on the return line.
Valve diagram
With a large number of batteries, the disposition may change and the installation of shut-off and control valves is carried out using automatic differential pressure regulators. They are placed together with valves and connected to them by a capillary tube. The balance valve provides the required coolant flow to the branch or riser, and the regulator adjusts it in accordance with the operation of the radiator thermostats.
Application of automatic valve
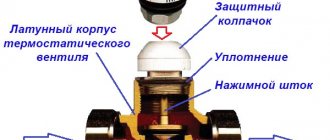
Automatic thermostatic valves are fittings for radiators that reduce or increase the flow of hot water through the radiator depending on the room temperature.
Valves with thermal heads
It is installed on the supply line and can be additionally equipped with a thermal head and a remote thermostat for more precise control of coolant flow. It is considered an integral element of modern schemes and one of the main means of saving energy.
Thermostatic valve
Shut-off valves
This type of fitting reduces/stops the supply of coolant in a certain location of pipelines or radiators. This is done forcibly.
As a rule, it is presented in the form of faucets, sliding elements with various design features. When choosing a shut-off valve model for heating systems, you should take into account the installation method and the material from which it is made.
A quality element must withstand the peak temperatures that the system is capable of producing and the maximum pressure level. This information is recorded by the manufacturer in the operating instructions or on the valve body.
Shut-off valves are one of the most important components of a heating system. Installation is carried out around the entire perimeter in places where it may be necessary to restrict coolant flows.
Almost all factories that produce these products provide a wide range of models to choose the right one.
There are special parameters that you should pay attention to when purchasing
For connection to the main line, the shut-off valves are equipped with branch pipes. The diameter of which plays a significant role. The device must not cause any restrictions on the flow or volume of water when open. The accuracy depends on the level of adjustment. Ball valves can be used to quickly stop coolant flows, and wedge-shaped valves allow gradual adjustment of the volume of supplied liquid
The possibility of installing an automatic control element for opening the tap is also taken into account when choosing products
It is important not only to understand how to carry out installation correctly, but also to take into account the performance qualities of the fittings and know its structure. Independent attempts to install fittings without special skills and knowledge can lead to many problems.
For example, incorrectly installed fittings will allow coolant to pass through itself or air. The pressure will be low and fluid flow will increase. Not to mention leaks and other malfunctions.
Types of heating taps
The use of such elements is easily explained by the design features and range available on the market. Shut-off valves are expressed in two types of taps:
- ball;
- stock
The first ones are equipped with a ball that has a hole. When the handle is turned, the diameter inside is adjusted. In this way, the force of fluid flow in the pipeline system is adjusted. This element is characterized by simplicity in blocking the flow.
Example of a ball valve with detachable connection
Rod valves, or valves, use a rod equipped with a rubber or ceramic gasket for locking. To stop/restore the water supply, you will have to perform several turns of the handle. This element is applicable as a tool for more precise adjustment of the flow force.
Shut-off valve
Installation and selection of fittings is carried out taking into account the operational parameters of the heating system. Otherwise, it will not be easy to achieve the necessary functionality and tasks assigned to the fittings.
Heating valves
Externally they resemble valves, but differ in larger sizes. The internal channels also have a different appearance. Due to the wave structure inside, such elements provide exceptional protection against noticeable pressure drops. Valves allow you to maintain the integrity of the stem and ensure sealing of the fittings. Their installation is carried out on pipeline areas whose diameter is above 100 mm.
How often does it need to be serviced?
The average service life and maintenance schedule for a particular shut-off valve depends on the type, place of use, and regulatory periods, which are determined by the manufacturer and operating organization. On average, for residential shut-off and control valves, the inspection period is one year. At least once a year, shut-off valves must be checked for leaks and serviceability. It is advisable to carry out inspections of shut-off valves in an apartment at least once every six months. Pipeline fittings on trunk networks, at distribution points and at other technological units are serviced at least once a year, most often during technological breaks in operation or during scheduled repair work.
Components of water supply networks, including elements of shut-off and shut-off and control valves used in the water supply system, should be selected taking into account the corrosive activity of water in order to ensure standard service life. Water supply installations may only be made from materials that have a valid hygienic certificate. Approval is required not only for pipes, fittings or fittings, but also for other materials in contact with water, such as seals, adhesives, paints. This should be remembered when choosing one or another fitting for the water supply network.
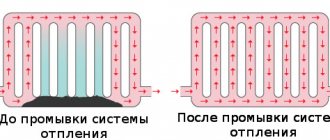
Stagnation of water in the installation can affect the operation of shut-off and control valves due to an increase in the concentration of various types of active dissolved substances, suspended solids and bacterial growth, which can have a negative impact on the operation of system components. The degree of wear depends on the materials from which the installation is made, its technical condition, and the composition of the water from the water supply network. The deterioration in quality will be greater the higher the temperature and the longer the immobility of water in the system, therefore, if a particular system is not operated, the frequency of inspections and maintenance may be carried out more often.
For hygienic reasons, it is necessary to flush the system after periods of inactivity. Parts of installations that are used infrequently or for short periods of time should be isolated after use and washed before restarting. Also, before starting the system, maintenance of the shut-off and control valves should be performed in order to remove oxides, rust, and rinse off mechanical deposits and accumulations of sand and other suspended matter that may appear as a result of long-term downtime of the system.
Purpose of shut-off plumbing
Shut-off valves are designed for manual regulation of coolant supply
In heat generation systems, shut-off type fittings act as a regulator of the flow and movement of coolant, and also allow the heating circuit to be opened. In this case, the heating process becomes controlled, its rationality and efficiency increases.
The shut-off valve is most often installed at the interval in the line where the battery is connected with pipelines. This technique allows you to adjust the heating of the radiator and facilitates the task of maintaining and repairing the heater without the need to turn off the entire heating circuit.
What it is
This is a type of pipeline fittings that combines the functions of control and shut-off mechanisms and regulates the parameters of the working environment:
- consumption;
- pressure;
- temperature;
- liquid level;
- mixing media in given proportions and some others.
The main control method is to change the flow rate of the medium by changing the cross-section of the passage of the fittings (up to complete shutdown of the pipeline)
Mixing and control valves
A prominent representative of this group of devices is the thermostatic three-way valve. Its task is high-quality regulation of the coolant, that is, by temperature, and not by flow. A three-way valve does not act like a shut-off valve, it works like a mixing unit. Configured to produce coolant at a certain temperature, the element mixes the two flows in the required proportions.
Heating mixing unit
The device is a brass body with three pipes, inside of which there is a rod controlled by a thermostatic drive. The rod passes through 2 seats, regulating the flow of the required amount of water through them from two pipes, in order to obtain a mixture of the set temperature in the third.
Operating principle of three-way valve
It must be said that not every heating system needs such fittings. The scope of application of mixing devices is maintaining the temperature in underfloor heating circuits, individual radiators or entire groups of heating devices, as well as in small circulation circuits of solid fuel boilers. In general, it is quite difficult to list all the special cases of using mixing valves, since there can be a lot of them in modern water heating schemes.
Types of shut-off and control valves
To begin with, let’s make a reservation that in this topic we are considering only elements of heating circuits of private houses and apartments, since in the general case the range of fittings used is quite wide. It will be difficult to review it within one article.
Types of heating taps
So, shut-off and control valves are elements of a system designed to control the flow of coolant by partially or completely blocking the flow area of pipelines.
By and large, all flow control elements installed in heating systems of private houses can be divided into the following groups:
- constipation;
- shut-off and regulating;
- mixing and regulating.
You should not confuse concepts such as shut-off and control valves and control and measuring instruments (thermometers, pressure gauges). Also, various safety and air vent valves, filters - mud traps and metering devices have nothing to do with the control of the coolant.
Installation of shut-off valves
Most often used in distribution systems of various types of process liquids and gases, shut-off and adjustable valves are designed in the form of a ball valve. Due to their properties, they are necessary for the proper functioning of installations in private homes, industrial premises, industrial enterprises and wherever plumbing and gas supply are required. Ball valves turn off the water supply by using a lever that moves a steel ball in the valve seat. However, they do not regulate the flow rate adequately; they only close or open the stream. Thanks to their characteristic structure they are very strong and reliable. Their resistance to mechanical damage and minimal risk of contamination makes them durable and guarantees their functionality for many years after installation.
By design, a ball valve is assembled in a body that has a groove for a seat, a shut-off ball, and a valve opening lever. Process fluid or gas flows through the hole in the ball when the valve is open. When it is closed, the ball moves in the socket with the sides without the hole and blocks the flow. To close, just turn the lever a quarter turn. This feature is extremely important in the event of a breakdown, such as a burst pipe, where the water flow must be shut off quickly to prevent leakage.
The most popular types of ball valves:
- half-inch ball valve - such a ball valve is used in hydraulic systems for connecting hydraulic systems in houses, apartments, distributing water supply inside buildings, and is also used for heating systems;
- two-inch ball valve - installed as the main valve in residential buildings, at the inlet in industrial buildings and other facilities on central pipelines;
- flanged ball valve - mounted in distribution devices, on large pipes to strengthen mechanical connections;
- ball valve with filter - in addition to its normal function, it also filters contaminants.
When performing installation work, shut-off and control valves can be installed in almost any position - you just need to pay attention to the correct direction of movement of the main medium, which must correspond to the mark on the body
Additional heating devices
These primarily include thermometers and pressure gauges. They are necessary to control the condition of hot water. By default, such devices are installed in the heating boiler. But in addition to this, their installation in critical areas of the system is necessary. This applies to control fittings for heating a warm water floor (collector unit). The pressure gauge must be present in the safety group along with the air vent.
For each valve for heating systems, shut-off or control, the main performance indicators are often indicated on the body - the maximum (minimum) level of pressure and temperature. How can you choose the optimal model even without having a passport for it?
As an example, you can familiarize yourself with the range of shut-off valves from Valtec:
Types
Shut-off valves for heating make the operation of all equipment included in the system efficient and significantly save energy and material resources. It is installed between radiators or pipes and comes in several types:
- ball valves with different threads;
- shut-off valves;
- butterfly valves;
- flanges and fittings;
- check valves;
- valves
Ball valves
For ease of connection of heating system radiators, ball valves made of brass are chosen. A similar shut-off and control design is available with an internal thread, a union nut, an air release device and a plug. The last two are used in cases where it is necessary to remove air from the system or, conversely, to introduce air into it. Ball valves are also used when installing a pressure gauge.
Such devices are equipped with full bore balls. Each of them has a special system installed that protects the housing from damage when water freezes and prevents the spread of bacteria that appear as a result of stagnation of liquid in the pipeline.
Most ball valve models have O-rings that contact each other rather than the body surface. This increases the wear resistance of the entire crane. This type of shut-off and control part contains important information on the body regarding its installation.
Shut-off valves
To connect or disconnect a separate radiator (for the purpose of dismantling it or preventing it) in the heating system without emptying it, shut-off valves are used. They come in two types: straight and angular. Such devices are made of brass coated with nickel.
Some models are equipped with a drain valve (also made of brass), which is used to remove water from the radiator or fill it with liquid.
A hose nozzle of this design can be rotated in any direction.
Butterfly valves
This is a shut-off and control valve made in the form of a disk. The element rotates around an axis located perpendicularly or at an angle to the direction of movement of the coolant. Butterfly valves are used not only in heating systems, but also for water supply.
Check valves
Such devices are used to protect the system from unexpected loads and regulate the coolant flow in the pipeline. They can be mounted in different places. Coupled valves made of brass have threads and a gasket located on the inlet side. The entire structure operates on a spring that holds the rod. It, in turn, is recessed at a certain pressure, thereby allowing the coolant to pass through. Such equipment lasts a long time and is inexpensive.
To connect the heating system, check valves made of brass, with a stainless steel spring and a plastic rod are used. They are installed in the circuit after the circulation pump. The maximum permissible temperature for such mechanisms is 120 °C.
Also, such elements can be installed on high-pressure tanks.
Flanges
These connecting parts are used to connect fittings to pipes, connect individual parts of the pipeline, and install additional equipment. They are produced in the form of a disk or ring with holes. They are flat or collar-shaped (with a protrusion, depression, tenon, groove).
Made from steel. They are characterized by durability, a wide temperature range, and excellent anti-corrosion properties.
Fitting
Fittings are connecting elements for the heating system pipeline. These include:
- couplings (do not change the direction of the pipeline, have different outlet diameters);
- squares (change direction by 45-90°);
- tees (designs with 3 outlets for combining pipes of different diameters at different angles);
- crosses (for 4 pipes perpendicular to each other or located at a certain angle);
- plugs (put on the end of the pipe).
Valves
The design of this part includes a metal body, a control lever, and a butterfly valve. Such a mechanism is equipped with a locking element located perpendicular to the coolant flow. The regulating function of this element is not provided. It operates in 2 positions: “open” or “closed”.
The cross-section of the valves almost coincides with the diameter of the pipes. Such elements are distinguished by their simplicity of design and low level of hydraulic resistance. It is especially advantageous to use them in main pipelines.
Today, plastic and metal-plastic pipes are increasingly being chosen for heating systems; accordingly, polypropylene fittings for heating radiators are used with them.
It is placed on each element of the system separately. Date: September 25, 2022
Classification and types
Classification by control method:
- with manual control;
- drive – large equipment is controlled using a pneumatic or electric drive;
- with remote control - controlled using transition devices (all kinds of rods, speakers, etc.);
- with automatic control - adjustment occurs without operator participation: either directly when the pressure of the working medium is applied to the valve, or when the drive is turned on by a signal coming from the control and measuring equipment.
Classification by functional purpose:
- shut-off and regulating;
- regulating;
- distribution and mixing (three-way or multi-pass);
- mixing and adjustment;
- safety;
- protective;
- control room (used to determine the liquid level in boilers, tanks, connect pressure gauges, thermometers, level indicators);
- reduction or throttling (reducing pressure in the system);
- phase separation (condensate traps, air vents and oil separators).
By installation method: on threaded connections (coupling, pin-type), on flanges. Control valves are not installed during welding.
Types of shut-off valves by design:
- control valves (gates); including shut-off and control and mixing valves;
- taps;
- valves;
- flaps.