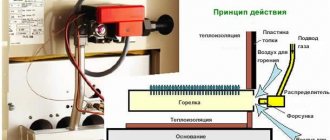
The grate and its purpose
A grate is a grate that allows direct access to air flow to the place where wood is burned. In addition, ash and ashes are given the opportunity to fall down into a specially designated niche. The grating material is usually steel or cast iron.
Thanks to cast iron grates, the following goals are achieved:
- Two compartments are formed in the firebox - the combustion chamber and the ash pan.
- A convenient place appears for storing and drying fuel.
- The air flow from the ash pit is evenly distributed.
- Traction takes on a new level of quality.
- With the help of a door and a rod, it is possible to conveniently adjust the combustion process.
Not every material is suitable for making stove grates. The fact is that it is exposed to significant temperatures, which in combination with atmospheric oxygen provokes a fairly intense oxidation process. Only cast iron can effectively withstand such a set of aggressive influences.
A little history
Previously, firewood was burned on a blind hearth - combustion air was supplied through a slightly open fire door.
This method has a fire hazard - coals may fall out of the firebox. It is also difficult to accurately select the optimal combustion mode - the regulator is very rough. The ash that covered the coals over time also did not contribute to the normal combustion of fuel - it is an excellent heat insulator (in the combustion chamber of a Russian stove, this is exactly how coals were stored in the ash for the next kindling). Therefore, they began to install a grate - a grate on the hearth through which oxygen enters the combustion zone. The ash is also removed through the grate - nothing interferes with the combustion processes. The absence of a grate or its damage is not critical - the stove operates without it. True, the efficiency is somewhat lower. And the zone of intense heating of the masonry moves below the hearth - now the base of the ash chamber is also heated. And here you need to be careful if the stove is installed on a wooden base.
Main types of cast iron grates
According to the type of configuration, cast iron grates are:
- Flat (tiled).
- Beam.
- Basket ones.
- Mobile.
To achieve maximum durability of a cast iron grate for a stove, when selecting it, you should take into account the type of fuel used. Stove grate sizes 250 (300, 330) x 252 mm, 140 (250) x 180 mm and 140 x 120 mm are most often used for firewood and briquettes. If coal is used, the dimensions of the cast iron grate for the furnace should be 300 (350) x 205, because When burned, coal emits much more aggressive combustion products.
Much also depends on the thickness of the rods from which the grating is made. This directly affects the maximum weight of fuel loaded into the stove. Another important criterion is the clearance area, which for high-quality cast iron grates reaches 40%. In this case, there is no big difference whether we are talking about a stacked beam structure or a cast slab.
A decrease in the lumen area usually entails a decrease in the efficiency of the flame: the fuel begins to burn incompletely, and more gases are formed. In such cases, you have to stir the wood from time to time using a metal poker. As a conclusion, we can say that the main criterion for the effectiveness of a cast iron grate for a fireplace is not its shape, but the material of manufacture, the cross-section of the rods and the size of the grate slots.
What functions do grates for furnaces perform?
This element of stove fittings allows you to achieve high-quality combustion of fuel and maintain it while the stove is burning.
When one portion of firewood or coal burns out, the ash is poured out, and the top layer of fuel is shifted to the grate, where it is better blown by the air coming from the ash pit and burns more intensely. Thanks to the presence of grates, the task of drying wet fuel is simplified.
The efficiency of the furnace depends on the design of the elements, and the durability depends on the material from which they are made. It is also important to install the grille correctly so that it fully performs its functions.
Recommendations for choosing a grate for the oven
It is recommended to buy such products in specialized stores, which offer a wide range of stove grate sizes. The main criteria when choosing a suitable option are usually the mass of the grating and its cost. It is important to understand that high-quality cast iron products weigh a lot and are not cheap. The standard manufacturing material is a special refractory grade of cast iron - SCh 15 (20).
Unscrupulous manufacturers often use low-quality steel instead of cast iron to save money. As a result, the cost of such a product is reduced by an order of magnitude, but steel gratings burn out quite quickly and need to be replaced. Such measures are quite difficult to implement: sometimes this can be accompanied by damage to the stove masonry. Beam models with a characteristic ribbed structure are famous for their greatest durability. This design makes it possible to slightly reduce the contact area of the rods with the aggressive environment. As a result, the grate lasts an order of magnitude longer.
Do-it-yourself grate: materials, design, stages of work
As already mentioned, it is easier and easier to make a grate for a stove with your own hands from steel.
There are several options here. The only difference is the purpose for which the lattice needs to be made. For small stoves, which are mainly used for periodic heating of premises, for example, for a potbelly stove, you can use construction fittings with a diameter of 10-12 mm. But for capital heating or heating-cooking stoves, it is better to pay attention to two options - from structural reinforcement or from corners. The advantage of steel reinforcement lies in the availability of this material and the possibility of using previously used sections. In addition, steel reinforcement is more suitable for grates; it does not burn out so quickly, and it is not greatly deformed under the influence of temperature. On the other hand, to assemble this element it is necessary to use reinforcement with a large diameter - 16,18 or even 20 mm. This makes it possible to extend the life of the grille.
The use of steel angles makes it possible to quickly replace a worn-out element; they are not as expensive as other types of rolled products, and by their design they are able to withstand a greater number of heating and cooling cycles than a profile pipe or rod.
The manufacturing technology is quite simple. To assemble a structure from steel reinforcement, it is recommended to first make simple calculations. First you need to calculate the geometric dimensions of the lattice. Here the length, width and height of the product are taken into account. In this case, the height plays no less a role than the length and width; a discrepancy between the height and the cast iron parameter will not allow the grate to be correctly installed in place. A height that is too small will interfere with proper loading of fuel, and a height that is too high will raise the grate above the surface of the bricks, and thus create a space in which ash and unburned fuel will accumulate.
The next step is to calculate the area of the grating. Next, the number of rods is calculated. First, 40% of the area is calculated, approximately how much is occupied by the spaces between the rods. And then the number of rods is calculated. When calculating, it is recommended to round the resulting values; it is not necessary to strictly adhere to the figure of 40%; nothing bad will happen if the gaps are 35 or 45% of the grating area.
The stage of practical work begins with the preparation of material for work - first, the rods are cut; accuracy and precision are required here. After this, a template for assembly is made, markings are made on a section of the board, and nails are simply hammered in to secure the sections of reinforcement. After checking the correctness of the layout, electric welding connects all the elements into one structure. First, tack is done at several points, and then all seams are finally welded around the entire circumference.
Upon completion, the resulting structure is checked in all planes; this is done on a flat surface using a bench angle - all angles must be correct, the lattice itself must be in the same plane. No bends or deformations.
It is possible to make a grate with your own hands. What to make a grate for the oven from? It is better to use heat-resistant steel as a material, because it is impossible to work with cast iron at home. To make the grille, you can use any materials that have heat-resistant characteristics. This could be fittings, corners, steel pipes or strips of metal.
To make grate bars you will need:
- the metal from which the grille will be made,
- steel rods for creating partitions;
- ruler, tool for making marks;
- grinder for cutting material;
- welding.
It is not difficult to make a grate from reinforcement yourself. It is enough to select the desired length of the product and cut the reinforcement with a grinder. It is necessary to determine the number of strips and take into account clearances for ventilation.
When the required amount of material has been prepared, you can begin welding the grate using rods. Do-it-yourself grate bars for the stove made from reinforcement can be seen in the photo below:
Making a grate for a stove with your own hands from a corner is even easier than from fittings. To do this, it is enough to weld two corners of the required sizes together: one side is equal to the width of the product, the other to the length. The result will be a rectangular base for the future part. The grate can be made from reinforcing bars or thick mesh.
Tool
List of required tools:
- welding machine;
- angle machine;
- sander;
- drill;
- vice;
- hammer;
- tape measure and ruler;
- square;
- pencil.
How the grate is mounted and works
The installation site for the cast iron grate for RD-3 furnaces is the lower section of the fuel combustion chamber. There should be a minimal gap between the brick wall and the cut of the grate: sand is poured into it. It acts as an expansion joint, leveling the thermal expansion that occurs with the cast iron element. Thanks to this, the brickwork receives protection from destruction.
Firewood is loaded into the fuel compartment on top of a cast iron grate and set on fire. RD-3 demonstrates high resistance to the destructive effects of heat, combustion products and oxygen. This provides it with a fairly long service life, with full preservation of all operational characteristics.
Classification of cast iron products
The most durable and reliable grate bars are those made from a material such as cast iron. In turn, they are divided into the following categories:
- Having a tiled shape. Such models belong to the category of universal ones. They are most often installed in boilers with a water circuit operating with solid fuel. The basis of choice is the primary determination of dimensions;
- Basket shape. This variation belongs to the old model and was previously used for open combustion chambers. Through such devices it became possible to cook food in such a hearth;
- Beam type. In appearance they are similar to standard beams widely used in construction. They can be either double or single. They are most often used if the heating installation requires the selection of a grate with a non-standard shape and dimensions;
- Movable type. They also belong to the category of universal ones, since, if necessary, they can be adjusted during the installation process, which is especially convenient and relevant. This variation is an ideal option for installation in boilers with a long-burning function.
The grate is necessary for heating units with an open hearth
The grate is necessary for heating units with an open hearth
High sidewalls ensure safety and ease of use
High sidewalls ensure safety and ease of use
Convenient and safe fuel loading basket
Convenient and safe fuel loading basket
For additional information and a more detailed understanding of these points, we also recommend watching the video in this article.
Criteria and basis for selection
Before purchasing or assembling, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the main criteria and tips for choosing:
When choosing, take into account the type of fuel that is used for the operation and functioning of your heating unit. If coal is used for work, the optimal overall dimensions of the grate will be about 300-340x205 millimeters
If the boiler operates on purchased briquettes or standard logs, it is recommended to give preference to a grate with dimensions for the first 14x12 centimeters and 33x25.2 centimeters for the second; Determine the optimal mass of this element. At this stage, it is recommended to consult a specialist or seller. It is also believed that the total total area of the lumen of the grate should be at least 35 percent.
Cast iron structures are
Cast iron structures are versatile and can withstand regular exposure to high temperatures
Steel products are suitable for installation in furnaces
Steel products are suitable for installation in stoves using logs and purchased briquettes
The grate is made in the shape of a basket
The grate is made in the shape of a basket
In this article you can familiarize yourself with the best designs and models in the presented photo selection.
Product Catalog
POLICY FOR PROCESSING AND PROTECTION OF PERSONAL DATA
This Policy for the processing and protection of personal data (hereinafter referred to as the Policy) was developed in accordance with the Federal Law “On Personal Data” and applies to any information that the site located at emz74.ru can receive about the User (personal data subject) during use A user of the site’s website, as well as the site’s programs and products.
- DEFINITION OF TERMS
1.1 The following terms are used in this Policy:
1.1.1. “Site Administration” - authorized employees of the company who organize the processing of personal data, and also determine the purposes of processing personal data, the composition of personal data to be processed, actions (operations) performed with personal data, etc.
1.1.2. “Personal data” - any information relating to a directly or indirectly identified or identifiable individual (subject of personal data).
1.1.3. “Processing of personal data” - any action (operation) or set of actions (operations) performed using automation tools or without the use of such means with personal data, including collection, recording, systematization, accumulation, storage, clarification (updating, changing), extraction, use, transfer (distribution, provision, access), depersonalization, blocking, deletion, destruction of personal data.
1.1.4. “Confidentiality of personal data” is a requirement for the Site Administration or any other person who has access to personal data to comply with the requirement not to allow their distribution without the consent of the subject of personal data or the presence of another legal basis.
1.1.5. “User of the site website (hereinafter referred to as the “User”) is a person who has access to the site via the Internet and uses the site.
1.1.6. “Cookies” are a small piece of data sent by a web server and stored on the user’s computer, which a web client or web browser sends to the web server each time in an HTTP request when an attempt is made to open a page on the corresponding site.
1.1.7. “IP address” is a unique network address of a node in a computer network built using the IP protocol.
- GENERAL PROVISIONS
2.1. The User's use of the site means his full agreement with this Policy and the terms of processing of the User's personal data.
2.2. In case of disagreement with the terms of the Policy, the User must immediately stop using the site.
2.3. This Policy applies only to the site. The site does not control and is not responsible for third party sites that the User can access via links available on the site.
2.4. The site administration does not check and is not responsible for the accuracy of personal data provided by Site Users.
- SUBJECT OF THE POLICY
3.1. This Policy establishes the obligations of the Site Administration to non-disclose and ensure a regime for protecting the confidentiality of personal data that the User provides at the request of the Site Administration when registering on the site or when filling out a request for a call back or message.
3.2. Personal data permitted for processing under this Policy is provided by the User by filling out a form on the website and includes the following information:
3.2.1. last name, first name, patronymic of the User;
3.2.2. User's contact phone number;
3.2.3. email address (e-mail);
3.3. The site protects the following data, which is automatically transmitted when viewing advertising blocks and when visiting pages on which the system’s statistical script (“pixel”) is installed:
— IP address;
— information from cookies;
— information about the browser (or other program that provides access to display advertising);
— access time;
— address of the page on which the advertising unit is located;
— referrer (address of the previous page).
3.4. Any other personal information not specified above (purchase history, browsers and operating systems used, etc.) is subject to secure storage and non-distribution, except for the cases provided for in paragraphs. 5.2. and 5.3. of this Policy.
- PURPOSES OF COLLECTING USER'S PERSONAL INFORMATION
4.1. The Site Administration may use the User’s personal data for the following purposes:
4.1.1. Identification of the User registered on the site to place an order and (or) gain access to the service and (or) conclude a purchase and sale agreement for a particular product remotely.
4.1.2. Providing the User with access to personalized website resources.
4.1.3. Establishing feedback with the User, including sending notifications, requests regarding the use of the site, provision of services, processing requests and applications from the User, etc.
4.1.4. Determining the location of the User (if he has given his consent) to ensure security and prevent fraud.
4.1.5. Confirmation of the accuracy and completeness of personal data provided by the User.
4.1.6. Providing the User with effective customer and technical support if problems arise with the use of the site.
4.1.7. Providing the User, with his consent, with special offers, newsletters and other information on behalf of the site or on behalf of the site’s partners.
4.1.8. Carrying out advertising activities with the consent of the User.
4.1.9. Providing the User with access to sites or services of site partners in order to receive products, updates and services.
- METHODS AND TERMS OF PROCESSING PERSONAL INFORMATION
5.1. The processing of the User's personal data is carried out without a time limit, in any legal way, including in personal data information systems using automation tools or without the use of such tools.
5.2. The User's personal data may be transferred to authorized bodies of state and municipal authorities of the Russian Federation only on the grounds and in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
5.3. In case of loss or disclosure of personal data, the Site Administration informs the User about the loss or disclosure of personal data.
5.4. The site administration takes the necessary organizational and technical measures to protect the User’s personal information from unauthorized or accidental access, destruction, modification, blocking, copying, distribution, as well as from other unlawful actions of third parties.
5.5. The site administration, together with the User, takes all necessary measures to prevent losses or other negative consequences caused by the loss or disclosure of the User’s personal data.
- OBLIGATIONS OF THE PARTIES
6.1. The user is obliged:
6.1.1. Provide information about personal data necessary to use the site.
6.1.2. As necessary, update and supplement the provided information about personal data if this information changes.
6.2. The site administration is obliged to:
6.2.1. Use the information received solely for the purposes specified in clause 4 of this Policy.
6.2.2. Ensure that confidential information is kept secret, not disclose it without the prior written permission of the User, and also not sell, exchange, publish, or disclose in other possible ways the transferred personal data of the User, except for the cases specified in paragraphs. 5.2. and 5.3. of this Policy.
6.2.3. Take precautions to protect the confidentiality of the User's personal data in accordance with the procedure usually used to protect this type of information in existing business transactions.
6.2.4. Block personal data relating to the relevant User from the moment of application or request from the User or his legal representative, or the authorized body for the protection of the rights of personal data subjects for the period of verification, in the event of detection of unreliable personal data or unlawful actions.
- RESPONSIBILITY OF THE PARTIES
7.1. The site administration, which has not fulfilled its obligations, bears the responsibility provided for by current legislation for the unlawful use of the User’s personal data, except for the cases provided for in clauses. 5.2., 5.3. and 7.2. of this Policy.
7.2. In case of loss or disclosure of Confidential Information, the Site Administration is not responsible if this confidential information:
7.2.1. Became public domain until it was lost or disclosed.
7.2.2. Was received from a third party before it was received by the Site Administration.
7.2.3. Was disclosed with the consent of the User.
7.2.4. It was provided based on a request from an authorized government agency.
- DISPUTE RESOLUTION
8.1. Before filing a claim in court regarding disputes arising from the relationship between the Site User and the Site Administration, it is mandatory to submit a claim (a written proposal for a voluntary settlement of the dispute).
8.2. The recipient of the claim, within 30 calendar days from the date of receipt of the claim, notifies the claimant in writing of the results of consideration of the claim.
8.3. If an agreement is not reached, the dispute will be referred to a judicial authority in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
8.4. The current legislation of the Russian Federation applies to this Policy and the relationship between the User and the Site Administration.
- ADDITIONAL TERMS
9.1. The site administration has the right to make changes to this Policy without prior notice and consent of the User.
9.2. The new Policy comes into force from the moment it is posted on the website, unless otherwise provided by the new edition of the Policy.
Manufacturing process
If you build iron stoves for a bathhouse with your own hands, then the price of the finished structure is greatly reduced, since inexpensive metal elements are used in the work process
The aesthetic characteristics of home-made structures, of course, cannot be compared with market products, but in some situations the money issue comes first, and more attention is paid to quality
Location of the firebox and ash hole.
Basic Tools
- Welding machine for connecting individual structural fragments.
- Electrodes (three or four) for a set of equipment.
- A grinder is necessary for cutting out components.
Sequence of operations
- The rolled pipe is cut so that two parts are obtained, one of which should be 90 cm long and the other 60 cm. The first will be used as a base. As for the second piece, it will be useful for the tank.
- Two holes are made in the base pipe, which will correspond to the dimensions of the firebox and blower. Doors are made from the cut parts. Hooks, loops and other accessories are attached to them.
- Next, the grate necessary to maintain solid fuel is fixed. To do this, holes are cut in the side walls. Ears are welded to the grill itself.
- A round hole is made on the back side of the firebox for the chimney. It should be located just above the metal mesh, which serves as a hold for firewood.
- A container for stones is made on top. As for the hot water tank, it is located closer to the combustion chamber. One part is placed on the firebox, and the other part is installed on racks.
- The finished stove is installed on special legs made of metal. There should also be a sheet of iron underneath it to avoid unpleasant moments associated with the floor catching fire.
The diagram shows the location of the stones.