An old Russian stove is a very effective source of heat, used to heat country houses, prepare delicious dishes and baked goods. The efficiency of using the energy of burned wood is at least 60%, thanks to which the brick structure is of interest to private developers and homeowners.
This material will be useful for novice stove makers and home craftsmen who want to organize home heating with their own hands. We propose to study the structure of a classic design with a stove bench, then consider the designs and arrangements of modern versions of the Russian stove.
Construction of a traditional oven
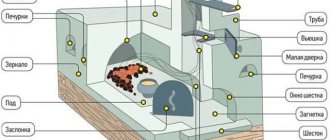
We will not describe the history of the Russian stove and its role in a village house - the topic is widely covered in fiction and technical literature. Let's get straight to the point - let's briefly analyze the traditional design shown in the figure below:
- The lower part of the structure - the guardianship - was built of stone or wood - cedar, larch. The walls of the base form a niche - a stove where firewood was dried and household utensils were stored.
- On top of the guardianship, the first arched vault and a large firebox of the furnace - the crucible - were built. Under and the second arched vault was made with a slope towards the brow - the front part of the structure.
- A roof was placed over the furnace, where the bed was located. The cavity between the second arch of the firebox and the ceiling was filled with sand to increase the heat capacity.
- In front of the mouth of the furnace, a special niche was provided - a bend, ending at the top with a hail (smoke collector) and the chimney itself. The horizontal shelf at the bottom of the opening—the shelf—has a semicircular window facing outward.
- Stoves were installed in the side walls of the brick heater - small niches for drying clothes and other things. The chimney was equipped with a valve and a view located above the heil.
Reference. The history of the evolution of the Russian classic stove is described in great detail in the popular book of the same name, author - Gennady Fedotov, published in 2003.
A real Russian stove is fundamentally different from other brick heating structures in the following ways:
- deep vaulted firebox made with a forward slope;
- the chimney is located in the front - in the center or in the corner of the building;
- An indispensable attribute is a bench located above the fuel chamber.
Now let’s look at the operating principle of the stove, shown in the diagram:
- The firewood is placed closer to the back wall of the furnace and lit. The combustion air enters through the outer window of the hearth and the mouth of the firebox, and moves above the bottom of the chamber.
- The heat generated during combustion heats the body of the furnace - the side walls, sand backfill and bench.
- Light combustion products rise to the roof of the firebox. The slope does not allow gases to immediately leave the chamber - first they give off heat to the ceiling, then they become heavier and are forced out by a new hot flow.
- Having passed under the arch of the furnace, the combustion products exit through the upper zone of the mouth, rise into the smoke collector and leave the stove through the chimney.
Note. During the combustion process, bread is not baked or food is cooked. When the oven is well heated, the coals are first raked out from the firebox, then the food is loaded into metal dishes - cast iron pots - using a grab handle. The outlet is closed by a damper.
Brick heater with access to 2 rooms of a wooden house
Despite its many advantages, a Russian stove with a stove bench is rarely built in a traditional design. Useful space in a modern interior is worth its weight in gold, and a classic heater takes up a lot of space, while poorly warming the lower zone of the room. For construction, it is better to consider projects of modernized structures, where this problem has been solved.
Interesting Facts
At the moment, there are simply a huge number of modifications of the heating stoves of Podgorodnikov and other engineers. And each of these models has its own highlight. For example, in Teplushka-15, the most popular model today, the shelf in front of the furnace is also a stove. The result is a stove, behind the cooking surface of which there is a chamber covered by a damper.
The left firebox in this model is intended for using the stove, and the right one is for heating. At the same time, the gas circulation in Teplushka-15 is organized in such a way that the smoke warms up the entire structure of the stove, no matter how it is used. The dimensions of this model are quite large. However, drawings of a smaller copy of Teplushka-15 have also been developed.
The efficiency of stoves of this type is higher than Russian ones. It may be considered interesting that Podgorodnikov managed to achieve such a result only because he guessed to use the theory of free movement of gases when developing his models. Previously, all attempts by other engineers to improve the Russian stove ended in failure.
Improved heater options
Many Russian masters were involved in the modernization of the classic stove - I. Kuznetsov, I. Podgorodnikov, A Emshanov, A. Batsulin. The essence of the changes is as follows: the details of the old design were taken as a basis - the vaulted furnace, the bend and the high above the mouth. New functional elements were added to them:
- Instead of a hearth, a hob is placed, and a small flood is arranged below. A parallel summer passage shaft is laid out, connected at the top with the main smoke collector.
- Hot gases from the additional firebox are directed through smoke circulations made in the lower part - the stove. Then the combustion products are discharged into a common pipe.
An example of modernization - in winter mode, gases from the furnace and furnace heat the lower part of the structure - At the end or on the sides of the furnace, vertical channels are installed, again leading to the lower zone under the firebox, then into the chimney.
- The channels from the firebox go into the attached heating panel and out through a combined pipe.
- The firebox is made from the bottom of the furnace and communicates with it through a grate installed in the hearth (bottom) of the main firebox. Gas ducts from the furnace penetrate the furnace and converge into a vertical shaft leading into the chimney.
Note. The changes made allow the stove to be heated in two ways: in Russian (the smoke comes out through the mouth and high) and in the heating and cooking mode (gases move around the channels).
Another example - there are vertical passages in the side wall that form a heating shield.
We tried to clearly describe common concepts; there are many more existing options. The purpose of the changes is to improve heat transfer and functionality of the basic design. If desired, a water circuit register or an oven is mounted inside the flues (the cabinet is placed next to the firebox).
Now we will analyze the updated options in detail using specific examples - with drawings and procedures.
How to cook
The heating stove heats the premises, thus very efficiently. Such structures heat up quickly and take a long time to cool down. Heats, as already mentioned, are considered quite convenient in terms of cooking. But of course, you need to use the oven in this way correctly. It is believed that you should start cooking, stewing or frying in the chamber or on the stove of a hotpot only when it is well heated and only coals remain in the combustion chamber.
As in a conventional Russian oven, all dishes can be placed in the oven of such equipment at the same time. Their subsequent preparation will therefore proceed synchronously. However, it is recommended to bake bread separately in modern Russian Podgorodnikov ovens, as in the middle of the last century. In this case, it will turn out especially tasty and aromatic.
Mini-oven project with stove
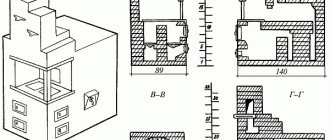
The Russian heating and cooking stove “Teplushka” with an additional combustion chamber has a power of 3.5 kW. The structure is designed for heating a small house or cottage with an area of 30-40 m², as well as cooking in winter and summer. The device of a small heater is shown in the drawing.
The mini-oven can operate in 3 modes:
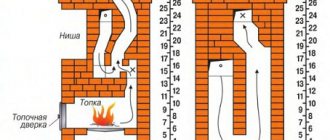
- Summer move. We open valves 1, 2 and 3 (see the picture), load the firewood with firewood. The gases immediately escape through the main channel into the pipe, and the stove heats up. Damper No. 3 plays the role of a hood.
- Firebox for winter. We use the lower chamber again and close valve No. 1. Then the combustion products move through the furnace and flue ducts into the oven, exit through the channel to the front side and then into the main chimney. The entire body of the furnace is heated, from bottom to top.
- Firebox in Russian. We light firewood in the furnace, open the sealed mouth door and valve No. 3, valves 1 and 2 are closed. The smoke goes into the hailo and the main chimney, only the stove bench is heated. For full heating, close the door, open damper No. 2 - the gases will flow through the lower channels of the stove.
Note. The diagram of gas movement under different operating modes is shown in the figure.
Thanks to its efficiency and relatively low cost of materials, a mini-stove can easily be called a housekeeper. One minus is the small size of the bed. The maximum height of the building is 2.1 m, in the area of the ceiling - 147 cm.
Building materials and stove fittings
To make a Russian mini-oven with your own hands, you need to buy components and materials:
- solid ceramic bricks – 670 pieces (the chimney is counted separately);
- fireclay bricks for the firebox – 25 pcs. (brand ША-8);
- fireclay block brand ШБ-94 or similar in size – 1 pc.;
- door of the main chamber mouth 25 x 28 cm, possible with fireproof glass;
- loading door 21 x 25 cm;
- ash pan door 14 x 25 cm;
- two grates measuring 300 x 250 and 220 x 325 mm;
- wooden template - circle - radius 460 mm, length - 65 cm;
- cast iron hob with 2 burners 71 x 41 cm;
- 3 valves: 13 x 25 cm - 2 pcs., 260 x 240 x 455 mm - 1 pc. (brand ZV-5);
- equal angle corner 40 x 4 mm – 3 meters;
- steel sheet 1 mm thick for a shelf in a stove;
- galvanized mesh for reinforcement, cell 3 x 3 cm - 2.1 lm;
- kaolin wool, corrugated cardboard.
Appearance of the finished mini-stove for a country house
Red brick laying is done using sand-clay mortar. When constructing a chimney, it is allowed to add M400 cement. Fireproof stones are placed on another solution - fireclay clay, mortar and the like.
Advice. For beginners, we recommend making solutions from ready-made building mixtures sold in stores.
Laying progress - step-by-step instructions
A reinforced concrete or rubble concrete foundation is cast under the furnace, the dimensions of which are 10 cm greater than the dimensions of the structure. Start construction when the concrete reaches 75% strength; under normal conditions, the hardening process will take about 2 weeks. This assumes an average daily air temperature of +20 °C and proper care of the monolith.
Having installed waterproofing from 2 layers of roofing material, make the first row continuous (40 bricks will be needed). How to fold the stove according to the order, read on:
- An ash chamber is formed on 2-3 tiers, a cleaning door is installed, and columns are built to support the bottom of the furnace. The 4th row continues the main walls of the stove; the ash chamber is covered with cut stones.
- Rows 5-6 form the main smoke channel and the bottom of the firebox made of refractory bricks. The grate is installed without mortar; a row of fireclay stones placed on edge is placed on top.
- On the 7th tier a loading door and a vertical summer shutter are installed. Rows 7-9 are laid according to the pattern, at the end the fireclay brick is covered with kaolin wool (marked in green). Please note: on the seventh tier the walls are reinforced with steel mesh.
- Rows 10 and 11 partially cover the flues and the lower heating chamber; a grate for the furnace and a hob are installed. The 12th tier begins to form the main firebox, and on the 13th tier the door is attached to the mouth of the furnace.
- Rows 14-17 are laid according to the diagram, corners are installed to cover the cooking opening. On the 18th tier, steel profiles are covered, and an arched vault with a radius of 46 cm is built from wedge-shaped stones.
- Tiers 19, 20 are made according to the scheme, the cavity between the vault and the walls is filled with sand or filled with thick masonry mortar. When the filler dries, 21 rows are laid - the roof.
- From 22 to 32 tiers the front part of the heater is built. On the 24th row, both smoke valves are placed, on the 25th - an iron shelf measuring 42 x 32 cm. Having laid the 29th tier, cover the stove with the same sheet.
Recommendation. Create a gap between the ceramic and refractory masonry using regular packing cardboard. Subsequently, the paper will burn out, but the gap will remain. Horizontal seams between red and fireclay bricks are not filled with mortar, only with kaolin wool.
To understand the construction down to the smallest detail, we suggest watching a video with a detailed demonstration of the masonry of each row and explanations from the master:
Brief biography of the creator
Hot stoves have been used to heat country houses for almost 100 years. Their creator I. S. Podgorodnikov was born in the city of Mogilev (Belarus), in 1886, into the family of a mechanic. After graduating from a real school, he entered the Technological Institute in St. Petersburg. After receiving a higher education diploma, Podgorodnikov got a job at the Putilov Shipyard.
During the revolution, the engineer tried to emigrate to Europe. It was difficult to do this then. To leave Russia, Podgorodnikov decided to walk to Crimea and try to board a ship. However, on the way, the engineer was detained by Red Army soldiers on suspicion of being a Denikin spy. Having found out that Podgorodnikov had nothing to do with the whites, he was simply taken out onto the road and released.
After this, Podgorodnikov changed his mind about traveling to Europe at risk to his life. Not believing his release, he went to Crimea, where he later married and got a job as a technician at a paper factory.
Even during his wanderings around the Central and southern parts of Russia for the purpose of emigration, Podgorodnikov drew attention to some imperfections of Russian stoves popular among peasants at that time. As an analytical person, he began to think about how to eliminate the shortcomings of such equipment.
Subsequently, Podgorodnikov shared his findings on this issue with Grum-Grzhimailo, an outstanding metallurgical engineer. Soon after this, he received an invitation to join one of the Moscow design institutes. Subsequently, Podgorodnikov’s main professional activity was the design of metal furnaces. However, in his free time he still continued to make bricks. The result of his efforts ultimately became a convenient and economical heating stove. Subsequently, it was this, essentially handicraft, model that won the enormous sympathy of the common people.
Russian "teplushka" with a couch 127 x 166 cm
The design and principle of operation of this stove are similar to the previous heat source. The difference is in size, power and some design features. There are also 3 modes available here - winter, summer and Russian fire. The heat output is 4.5 kW, the heated area is 45-50 m².
In winter mode, firewood can be burned on the grate of the furnace or in the firebox - the gases will still flow through the lower passages and warm up the entire stove
The size of the stove in plan is 1270 x 1660 mm plus 10 cm for the projection of the foundation. The height of the front part is 210 cm, the height of the bed is 147 cm. Set of materials for construction:
- refractory bricks ША-8 – 26 pcs.;
- red solid brick – 995 pcs. (the chimney is not included in the specified quantity);
- fireclay block type ШБ-94 – 1 pc.;
- main door installed at the mouth - 41 x 25 cm;
- ash pan door 14 x 25 cm, firebox door – 21 x 25 cm;
- 2 grates with dimensions 240 x 415 and 220 x 325 mm;
- stove 71 x 41 cm (2 burners);
- chimney damper type ZV-5, size 260 x 240 x 455 mm;
- 2 valves 130 x 250 mm;
- sheet steel 2 mm thick;
- galvanized reinforcing mesh – 1.5 lm (mesh 30 x 30, wire 1 mm in diameter);
- template for forming an arch, radius – 322.5, length – 645 mm;
- circled under the arch of the main firebox with a radius of 60 and a length of 77 cm;
- corrugated packaging cardboard, kaolin wool.
This is what a large “Teplushka” with a power of 4.5 kW looks like.
Preparatory work - installation of a reliable foundation. Keep in mind that after pouring the foundation, the formwork can be removed after 3-4 days (during the warm period), and the stove can be built only after 2 weeks. The base area is covered with waterproofing - roofing felt folded in half.
How to properly lay out a full-size “Teplushka”:
- Row No. 1 is continuous, consisting of 65 ceramic bricks. On the second tier, we begin to form the walls of the furnace and support columns, and install the door of the ash chamber. We install 8 stones on a poke without mortar and cut them to the height of the 3rd row. We do not connect it with the rest of the masonry - these will be cleaning hatches.
- We place the third tier according to the diagram, on the 4th we cover the ash pan. On the 5th row, we begin to build the walls of the firebox from refractory, insert a grate 415 x 240 mm.
- Rows 6 and 7 continue to be laid according to the pattern, fireclay stones are placed on the edge. After the formation of the 7th tier, we install the firebox door and the summer valve installed vertically. Rows 8-9 are built according to the order.
- On the 10th tier we cover the floodplain and cover the upper ends of the refractory bricks with kaolin wool. The front part of the chamber must be covered with fireclay block ШБ-94 or similar. We begin to reinforce the walls of the furnace with galvanized wire mesh, then we arrange a re-covering of red bricks (row 11).
- On the finished 11th tier we insert the stove and grate bars of the main chamber - the furnace. We make level No. 12 according to the order and install a large door. Then we lay out the 13th tier and arch using a circle.
- We build rows 14-17 according to the drawings, raising the outer walls of the furnace, the smoke channel and the front partition of the furnace. Next we lay an arched vault R = 60 cm made of wedge bricks. We continue to build tiers 18 and 19 according to the diagrams.
- In the twentieth row we block the front arch and raise the outer walls higher. We fill the void above the vault with a solution of clay and sand. After drying, we build tier 21 - the plane of the bed.
- Tiers 22-32 make up the front section of the stove, where the chimney is combined with the side flue. We line up the rows according to the diagrams, on the 24th level we install 2 valves, on the 29th level we place a sheet of metal covering the stove.
The expert will give step-by-step instructions for building a Russian multifunctional stove in his video:
Complete list and quantity of building materials
- Red brick - 1600 pieces
- Fireclay bricks 250 pieces
- Valves of two types - 5 pieces
- Flap for the furnace
- Hob - 1 piece
- Grate – 5 pieces
- Doors for the firebox and ash pan - 4 pieces
- Steel angle and strip
- Clay 100 kg
- Sand
For masonry you also need fireclay clay.
Construction Technology Tips
The construction of a Russian heating stove is a serious matter. It will be very difficult for a homeowner without experience in the stove business, so we recommend stocking up on time and patience. We published detailed instructions for preparing the mortar and laying it in an article about building a fireplace; we advise beginners to familiarize themselves with the specified material.
Here we will give general recommendations regarding the Russian home stove:
- Even the mini version of the heater weighs over 2 tons. The foundation slab must be supported on a stable soil horizon; the depth can be determined by the occurrence of the existing foundation of the dwelling.
- In the finished building, the “sole” must be arranged separately from the foundation of the house, retreating at least 10 cm. At the stage of construction of the cottage, the foundations, on the contrary, are combined - a common formwork is set up and concrete is poured.
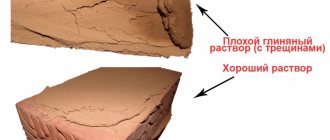
- You need quality bricks and mortar, not a gully clay mixture. The correct geometry of the stones will make your work much easier - uneven bricks will have to be filed down.
- Soak the red brick in the bucket for 2-3 minutes, as shown in the photo. Do not immerse the refractory in water, just rinse it to remove dust.
- It is allowed to lay the furnace and firebox from ceramic bricks, as our ancestors did. But remember: such cameras are afraid of accidental overheating; the material begins to crumble and crumble.
- A bed built on a loose base is also afraid of temperature fluctuations. This is why it is recommended to fill the void above the vault with clay mortar. If you fill the cavity with sand, small cracks may appear on the roof. No sooner had the stove been built than repairs needed to be done.
- The refractory masonry is not tied to the ceramic; cardboard is inserted to provide a gap between the two walls. Horizontal seams are laid with kaolin non-combustible wool.
- The pipe does not have to be made of brick all the way to the top. Lighten the structure - after cutting, install a sandwich - a chimney that goes out onto the roof, as shown in the photo.
Reference. Often, stove makers strengthen the arch and walls with an iron frame welded from corners.
Finally, a few words about how to properly heat a new stove. After drying the stove for 2-3 days (in summer), first build a small fire on the top damper. When the pipe warms up, start heating the furnace little by little, then the lower chamber. Increase the amount of firewood slowly, do not rush. The task is to uniformly heat the furnace body for final drying.
Preparation of oven mortar
To lay a Russian stove with a stove, you will need a special stove mortar, the main component of which is clay. You will need the fattest clay you can find.
The clay is cleaned of debris and filled with water for at least a day. After swelling, it is ground on a sieve with a mesh size of 5 mm.
The second integral component of the solution is sand. It must be thoroughly washed and free of dirt, and then calcined before kneading.
As a rule, the proportion of sand and clay in the solution for a Russian stove with a hob is 1:3. However, a lot depends on the fat content of the clay, so you need to select the exact ratio experimentally. It is worth trying several variants of the solution, making balls the size of tennis balls from each. After three days of drying, we evaluate the results. It is desirable that there are as few cracks as possible, and that at a break the clay does not crumble into dust. It doesn’t hurt to know that Kuznetsov furnaces are built in approximately the same way.
Is it worth building it yourself?
The amount of methodological material on the inventor’s website and serial drawings allow you to build a bell-type stove for a bathhouse or home yourself. In this case, be sure to follow the sequence of work. Property owners who are not confident in their construction skills turn to specialized companies.
It is better to entrust the construction of powerful dome structures to professionals. This will ultimately save time and money.
In any case, it’s worth practicing by building a small-sized Kuznetsov heating stove, for example, in a utility room or barn for pets. Only after this can you begin to build a stove in a residential building. A correctly selected and manufactured design will last for many years without breakdowns.
Varieties for different purposes
Igor Kuznetsov and his team have created a large number of universal and specialized models. Some are intended only for heating rooms, others are supplemented with elements for cooking or heating water. Fireplaces are a separate area.
Drawings of options tested in practice are collected on the inventor's website. For convenience, the structures are assigned alphanumeric designations.
Heating
Kuznetsov's heating stove for a two-story house allows you to save on fuel.
Various dome layout options make it possible to construct designs for heating one- and two-story houses.
Heating models are abbreviated as OIK (heating models by I. Kuznetsov). You can find options with a firebox located inside the room or in the utility room.
For variety and to give the desired qualities, there are stoves supplemented with warm beds (OIK -6 bed. AND OIK 19 bed.) and seats (OIK-7s).
Some products have built-in ovens. In this case, the letter D is added to the code designation, for example, OIK-5D.
Heating stoves also include stoves with a built-in fireplace.
Models RTIC (Russian heated heater by I. Kuznetsov) are needed for heating large rooms. They are massive and need a strong foundation.
Options with fireplace
Model with a fireplace
Fireplaces, in addition to their heating function, serve as interior decoration. In this case, the firebox is open, the fire can be observed visually. The stoves are equipped with a firebox for conventional heating, which can be located on the facade, on the right, left side, or behind.
For construction, they choose an option in which it is convenient to service the stove from a utility room or hallway - you do not have to carry firewood into the living room. Working with waste (ash) also does not imply inevitable dirt in the room when cleaning the ash pan and the vent from the hallway.
Options for OIK-K have been developed with couches, built-in ovens and a corner fireplace.
Boilers
To organize a water heating circuit, options have been developed with the designation KIK (I. Kuznetsov boiler). A steel heat exchanger is built into the second dome. Water circulates through the system due to an electric pump.
Models are designed for power of 16, 17, 34 and 64 kW. The first option (16 kW) is equipped with a hob.
Heating and cooking
A heating and cooking model is a structure that completely exhausts the fuel resource.
Universal heating and cooking stoves are designed for homes with year-round occupancy. The model has built-in hobs and ovens, shelves for heating food and water.
The firebox can be located on the front or side, which allows you to choose an option for any interior design.
Installation of a bed is available as an option. For large rooms, elongated fireboxes are made, which allows the use of large-caliber firewood. They burn longer and you will have to add fuel less often.
The size of the hob depends on the composition of the family. For 2–3 people, choose a reduced surface, which saves fuel.
For the bath
I. Kuznetsov singled out sauna stoves as a separate area. There are three varieties: BIC, BIC BC and BIC PC. The abbreviation BIC corresponds to the purpose, and additional symbols indicate that the structure is equipped with a fireplace.
For different layouts, models are chosen that differ in the location of the firebox and fireplace - in the steam room, relaxation room or in the dressing room.