Here you will learn:
- Features of the MS-140-500 radiator
- Technical characteristics of cast iron radiator
Despite the fact that steel, aluminum, copper and bimetallic radiators have appeared on the market, the cast iron batteries familiar to many people have not gone away. They are still sold in plumbing stores and are in some demand. In this article we will talk about the cast iron radiator MS-140-500 and its characteristics, and also tell about its features, advantages and disadvantages.
Purpose, advantages and disadvantages of MS 140 radiators
The technical parameters of cast iron radiators of the MC 140 brand allow them to be used in steam heating systems of any buildings with virtually no restrictions: in private houses, country cottages, apartments in apartment buildings, administrative offices, public buildings, industrial, warehouse, and retail premises. The equipment is intended for operation in temperate and cold climates (MCC).
Advantages of heating radiators MS 140
- Long service life. This is one of the most durable types of radiators, with a service life of 50 years.
- Reliability. The hundred-year history of this type of radiator in the heating equipment market has confirmed in practice its high reliability.
- Anti-corrosion resistance. Cast iron does not deteriorate over time under the influence of water.
- Undemanding to the quality of the coolant. Cast iron radiators are not sensitive to the quality of the water used inside them. The presence of sand, dirt, high content of salts, acids, alkalis in water does not have a strong effect on the life of cast iron radiators.
- Simplicity of steam heating systems. Cast iron radiators can be used in networks with natural water circulation, without the use of a pump. They are compatible with all types of boilers - solid fuel, gas, pellet, liquid fuel.
- Thermal inertia. Cast iron takes a long time to heat up, accumulates heat well, and cools slowly. In a heating system, this is considered a great advantage, since after the burner is turned off, the cast iron radiator remains warm for a long time, releasing heat into the room.
Disadvantages of heating radiators MS 140
- Sensitivity to water hammer.
- Tendency to slagging of internal surfaces, which over time leads to a decrease in heat transfer.
- Radiators are assembled from separate sections, the joints of which are sealed with rubber gaskets. The lifespan of gaskets is significantly less than cast iron. To avoid leaks, after several years of operation, failed intersection gaskets must be replaced.
- The appearance of such radiators is not sophisticated enough; the surface requires painting.
General provisions and algorithm for thermal calculation of heating devices
The calculation of heating devices is carried out after the hydraulic calculation of the heating system pipelines using the following method. The required heat output of a heating device is determined by the formula: where is the heat loss of the room, W; when installing several heating devices in a room, the heat loss of the room is distributed equally between the devices; - useful heat transfer of heating pipelines, W; is determined by the formula: where is the specific heat transfer of 1 m of openly laid vertical/horizontal/ pipelines, W/m; is accepted according to the data in Table. 3 of Appendix 9, depending on the temperature difference between the pipeline and the air; - the total length of vertical / horizontal / pipelines in the room, m. Actual heat transfer of the heating device: where - the nominal heat flow of the heating device (one section), W. Accepted according to the data in the table. 1 of Appendix 9; - temperature pressure equal to the difference between half the sum of the coolant temperatures at the inlet and outlet of the heating device and the room air temperature: where - coolant flow through the heating device, kg/s; - empirical coefficients. The parameter values, depending on the type of heating devices, coolant flow rate and flow pattern, are given in Table. 2 Appendix 9;— correction factor, method of installing the device; is accepted according to the data in Table. 5 of Appendix 9. The average water temperature in a heating device of a single-pipe heating system is generally determined by the expression: where is the temperature of the water in the hot line, °C; is the cooling of water in the supply line, °C; is the correction factors taken according to the table. 4 and table. 7 of Appendix 9;— the sum of heat losses of the premises located before the room in question, counting along the direction of movement of water in the riser, W;— water flow in the riser, kg/s /determined at the stage of hydraulic calculation of the heating system/;— heat capacity of water equal to 4187 J /(kg deg);—the coefficient of water flow into the heating device. Accepted according to the table. 8 of Appendix 9. The coolant flow through the heating device is determined by the formula: The cooling of water in the supply line is found according to the approximate relationship: where is the length of the line from the individual heating point to the design riser, m. The actual heat transfer of the heating device must be no less than the required heat transfer, that is . The opposite relationship is allowed if the discrepancy does not exceed 5%.
The Hungarian company NAMI also produces high-quality products, although its quality is slightly inferior to that of Italian companies.
- weight of one section – 1…1.5 kg;
- capacity – 0.25…0.46 l;
- distance between axles – 20/35/50/80 cm;
- Guaranteed service life is 10...20 years.
Chinese appliances. In most European countries, they are abandoning the use of cast iron radiators in favor of aluminum or bimetallic ones, which have more compact dimensions, high efficiency and an attractive design. But they are characterized by two significant disadvantages:
- High price;
- Increased wear and tear due to poor quality coolant in the centralized system.
Therefore, for the CIS countries, heating devices made of cast iron are still relevant and in demand. They are characterized by:
- Long service life;
- Resistance to corrosion;
- Compliance with existing heating systems.
Technical characteristics of radiators MS-140 - 500
Radiators of the MC group belong to the category of sectional ones - they are assembled into a single whole from separate sections.
MS 140 cast iron radiator section.
The sections are connected into a radiator using intersection gaskets.
Intersectional gasket for cast iron radiator MS 140.
One section is pressed against another using a nipple.
Cast iron radiator nipple ms 140.
The ends of the radiator are closed with plugs, which can be shut-off or pass-through.
Radiator shut-off plug ms 140.
Radiator passage plug ms 140.
Sections are cast from gray cast iron with graphite additives. Individual parameters of MC 140 radiators may vary slightly in models from different manufacturers.
Main characteristics of the cast iron radiator model MC 140:
| Radiator type | sectional |
| Number of coolant channels, pcs. | 2 |
| Number of sections, pcs | from 2 to 10 |
| Nominal heat flow of one section, W | 160 |
| External casing coating | primer GF-021/0119 |
| Section material | gray cast iron in accordance with GOST 1412-85 |
| Intersectional gasket material | rubber according to GOST 1412, capable of withstanding temperatures up to +150ºC |
| Nipple material | cast iron or steel. GOST 1412 or 1050 |
| Heating area of one section, m2 | 0.195 |
| Center distance, mm | 500 |
| Nipple hole thread size | G11/4 |
| Type of coolant | water |
| Maximum coolant temperature, 0C | + 1300С |
| Operating excess coolant pressure, MPa (kgf/cm2) | 0.9 |
Other technical data:
| Number of sections, pcs. | Weight, kg | Length, mm | Nominal heat flow, kW | Capacity, dm3 (l) |
| 2 | 12.8 | 227 | 0.32 | 2.50 |
| 3 | 18.8 | 331 | 0.48 | 3.75 |
| 4 | 24.8 | 435 | 0.64 | 5.00 |
| 5 | 30.8 | 539 | 0.80 | 6.25 |
| 6 | 36.8 | 643 | 0.96 | 7.50 |
| 7 | 42.8 | 747 | 1.12 | 8.75 |
The basic characteristics of the radiator can be determined by the model name and markings.
For example , model MC-140-500-0.9-7 designates a radiator with the name MC, depth 140 mm, center distance 500 mm, maximum pressure in the system 0.9 MPa, with the number of individual blocks in the radiator equal to 7.
Types of heating devices
There is no official classification of cast iron batteries. We can roughly divide heaters into 3 types:
- Soviet-style “accordion” type MS-140;
- devices with an increased heat exchange area, simulating new bimetallic and aluminum heaters, only cast from cast iron;
- designer batteries made in retro, modern style.
Comment. Let us remind you: all cast iron heating devices are sectional, that is, stacked.
It is unrealistic to classify products based on other criteria. Technical characteristics - weight, dimensions, heat transfer - vary widely. Let's look at the properties of batteries by group.
Pros and cons of traditional accordions
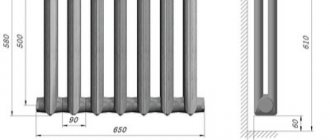
To begin with, we present the technical parameters of one fin of the MS-140M radiator, taken from the technical data sheet:
- total height – 588 mm, between holes – 500 mm, depth – 14 cm (the number is included in the marking);
- heat flow (power) – 160 W, surface area – 0.21 m²;
- working pressure – no higher than 10 Bar;
- the volume of water inside the section is 1.45 liters, the maximum temperature is 130 °C;
- weight – 7.12 kg;
- material – gray cast iron SCh-10, plugs – malleable cast iron KCh-30 or steel;
- gaskets - rubber.
Dimensions of the MS-140 heater and recommended installation distances
Note. The amount of heat flow is indicated under certain operating conditions: the difference Δt between the temperature of the room air and the coolant is 70 degrees. The calculation of heat transfer of section 1 is described in a separate instruction. The letter "M" in the marking means "modernized".
“Accordions” are produced by several Russian enterprises and the Minsk Heating Equipment Plant. The average price for a MS-140M battery section is 10 USD. e., minimum – 6 cu. e.The mentioned Belarusian plant also produces modified versions of the “accordions”, shown in the photo below:
- lightweight model 2K60 with a power of 120 W, the fin weighs 5.1 kg;
- 2KP100-90-500 depth 9 cm, heat output - 140 W;
- modification BZ-140-300 with an interaxial distance of 30 cm, power - 120 W.
The undoubted advantages of radiators remain their affordable price, durability and corrosion resistance to chemically active substances. However, the latter advantage is inherent in all batteries made of cast iron.
- Soviet “accordions” of the MC type do not meet current interior design requirements. The new modifications look better.
- Fragility. A slight impact can cause a microcrack to form in the metal, and then a leak. Freezing of the coolant definitely leads to destruction; the expansion of water causes cast iron to split.
- Significant mass of the heating device, aggravated by spaciousness. Due to the coolant, each section is made heavier by 1-1.5 kg. The multi-section heater cannot be hung on a wall made of aerated concrete or a plasterboard partition, only placed on the floor.
- Limited scope. Due to the maximum operating pressure of 10 Bar, the radiator cannot be used in an apartment with central heating, where the water pressure reaches 12 Bar (at the time of testing the network).
- There is no bottom connection to the heating system, pipes are connected only from the side.
Inertia (long heating and cooling) cannot be attributed to the pros or cons of radiators. This is a feature of thick cast iron walls that does not affect the quality of heating.
Important note. The efficiency of the boiler and the efficiency of the system do not depend on the amount of water in the batteries. The load on the circulation pump is like fairy tales. If the volume of coolant is large, then only the time of initial heating and final cooling will change. Listen to the expert's opinion in the video:
It is worth mentioning one more advantage of the M-140 series batteries. Since “accordions” were previously used everywhere, working sections can be found for free or purchased from scrap metal. According to reviews from owners of private houses, used cast iron radiators are often used for heating outbuildings and utility rooms.
Radiators with increased heat transfer area
The uniformity of the shapes of cast iron appliances is due to the manufacturing technology - casting. The extrusion method used to produce aluminum sections is not applicable here. But in recent years the picture has improved - products with a flat front panel and side ribs, reminiscent of light alloy heaters, have appeared on the market.
Reference. The aluminum-look batteries shown in the photo are produced by Russian, Belarusian and Chinese companies: Konner, STI NOVA, Minsk Plant.
As an example, we list the characteristics of the KONNER Modern section with a standard center distance of 500 mm:
- total height – 60 cm, depth – 96 mm;
- heat transfer at Δt = 70 °C is 150 W;
- maximum water pressure in operating mode – 12 Bar;
- capacity – 0.9 liters;
- weight – 4.1 kg.
The outside of the heater is covered with polymer enamel (usually white). Gaskets are EPDM rubber, the kit includes 4 end plugs. The cost of one KONNER Modern rib is 500 – 12 USD. That is, at least 4 pieces are sold. For rooms with low window sills there is a series of low KONNER G1 batteries with a center distance of 300 mm and a power of 120 W.
Externally, Konner heaters are very similar to products made of aluminum alloy - the front section is flat, heat exchange fins are cast on the sides. Why are these batteries better than “accordions”:
- The heat transfer surface has increased thanks to the side fins and flat front panel.
- Accordingly, the share of infrared heating has increased. That is, the radiator began to transfer more heat through radiation.
- The depth of the fins has decreased without reducing heat transfer.
- The operating pressure is increased to 12 atmospheres.
The disadvantages of batteries are typical - the products are fragile and limited in coolant pressure. But we managed to solve the problem of appearance - now the heaters look no worse than bimetal. Prices have increased slightly - a section costs between 10...17 USD. e.
Note. The cost of a Belarusian radiator 2K60PP, equipped with a flat panel, is 21 USD. e. by the rib. The reason is the complication of the manufacturing process; mechanical processing of the frontal plane and painting were added.
Designer retro batteries
The selection of antique radiators is impressive in variety. In this case, technical parameters fade into the background, giving way to other characteristics:
- beauty;
- compliance with the design of the rooms;
- overall dimensions.
In addition to traditional two-channel devices, you can choose heaters with 3-4-5 channels. There are radiators with smooth surfaces and a relief pattern, designed for floor installation. Batteries in the Art Nouveau style have angular outlines, while retro ones are more rounded.
Explanation. Two-channel radiators have 2 vertical coolant flows, three-channel radiators have 3, and so on.
High-quality retro batteries are produced in the Czech Republic, Germany, Turkey, the Russian Federation, and more recently in China. Famous brands:
- Viadrus;
- Guratec;
- Demir Dokum;
- EXEMET;
- Retro Style;
- Iron Lion;
- taps and other retro-style fittings are produced by the Italian brand Carlo Poletti.
It is pointless to provide technical data for heaters, since the variation in power, dimensions and weight is too great. Prices also vary widely - from 20 to 250 USD. e. per section. Chinese and some Czech devices cost 20...30 USD. That is, Turkish and German are significantly more expensive. The cost greatly depends on the massiveness and design of the product.
The only parameter that remains unchanged is the operating pressure. In this regard, designer heating radiators are no better than “accordions”, since cast iron walls can withstand 15 Bar (maximum). The average value is 8…10 Bar. The table below shows the characteristics of several models:
| Radiator brand and model | A country | Weight, kg | Coolant volume, l | Thermal power, W | Price, y. e. |
| Viadrus KALOR 500/70 | Czech | 4 | 0.8 | 70.3 | 20.05 |
| Viadrus Bohemia 450/220 | Czech | 9.9 | 2.4 | 110 | 78.25 |
| Demir Dokum Nostalgia 500/200 | Türkiye | 9.6 | 2.3 | 163 | 52.20 |
| Retro Style Anerli 560/230 | Russia | 17 | 3.29 | 189 | 229.60 |
| EXEMET Modern 600/100 | Türkiye | 4.3 | 0.7 | 102 | 32 |
| EXEMET Classica 500/176 | Türkiye | 9.3 | 1.95 | 145 | 76.85 |
The negative and positive properties of retro heating devices in general repeat the advantages of previous varieties. The main difference is the high cost and massiveness of some batteries; the weight of 1 rib reaches 17...20 kg.
Transportation and storage The design of MS-90 cast iron radiators is ideally suited to Russian heating networks. They are unpretentious to the quality of the coolant, and allow the use of contaminated water, typical of central heating systems in Russia. MS-90 cast iron radiators are distinguished by their high thermal power and compact sectional design. Thick walls and the chemical properties of cast iron give radiators resistance to corrosion, which is important in the summer when the water from the heating system is drained and the radiator is left to rust “dry.” Due to its large mass, cast iron smoothes out temperature fluctuations.
Transportation and storage.
| 400 rub./section | from 210 sections |
| Basic | |
| Manufacturer country | Russia |
| Thermal power |
Technical characteristics of one section Operating conditions: operating pressure - 1.2 MPa (12 bar) test pressure - 1.5 MPa (15 bar) coolant temperature - up to 130 °C pH value - from 6.5 to 9 Product description Cast iron radiators have long established themselves as a simple and practical source of heating. Cast iron radiators MS-90 are reliable and time-tested heating devices, affordable and in no way inferior in quality! The design of MS-90 cast iron radiators is ideal for Russian heating networks. They are unpretentious to the quality of the coolant, and allow the use of contaminated water, typical of central heating systems in Russia. MS-90 cast iron radiators are distinguished by their high thermal power and compact sectional design. Thick walls and the chemical properties of cast iron give radiators resistance to corrosion, which is important in the summer when the water from the heating system is drained and the radiator is left to rust “dry.” Due to its large mass, cast iron smoothes out temperature fluctuations. Cast iron heating radiators MS-90 have been used effectively in our country for a long time. Cast iron radiators have become widespread due to their advantages: - high reliability and durability - wide range of applications - long useful life, more than fifty years - ease of maintenance and repair - if one or more sections fail, they can be replaced with new ones . Transportation and storage Transportation of radiators is permitted by any type of transport that ensures the safety of the devices from mechanical damage. Radiators are transported in bags. Package contents: 12 seven-section and 1 four-section radiator. Cast iron radiators should be stored indoors or under cover and protected from moisture and corrosive chemicals. The supplier is not responsible for transport damage to radiators. Warranty obligations Service life – up to 50 years. The manufacturer guarantees that radiators comply with the mandatory requirements of GOST 8690-94, provided that the consumer complies with the conditions of transportation, storage, installation and operation. If a defect is discovered due to the fault of the manufacturer during the warranty period, the radiator must be replaced by the organization that sold the device. Technical characteristics: Radiator type - sectional two-channel. Section length - 78 mm, height - 571 mm, depth -90 mm. Nominal heat flow - 0.130 kW. The capacity of one section is 1.15 l. Nipple hole thread: G 1/4-B. Radiators MS-90, unlike MS-140, have less weight, the weight of 1 section is 5.6 kg. for MS-140 -7.1-8kg. They are more compact, “thin” and can be easily hidden even under a small window sill. Their heat output is less than that of the MS-140, but due to less heat loss, the general characteristics are close to them.
The calculation of heating devices is carried out after the hydraulic calculation of the heating system pipelines using the following method. The required heat transfer of the heating device is determined by the formula: where is the temperature of the water in the hot main, °C;
If, during the renovation, a neighbor narrowed the hot water riser, installed a heated floor system, began heating a loggia or glassed-in balcony on which he built a winter garden, the pressure of hot water entering your radiators will, of course, decrease. This will depend on the type and quality of the material used in the manufacture of radiators. The main varieties include:
- made of cast iron;
- made of bimetal;
- made of aluminum;
- of steel.
Each of the materials has some disadvantages and a number of features, so to make a decision you will need to consider the main indicators in more detail.
Made from steel
They function perfectly in combination with an autonomous heating device, which is designed to heat a significant area. The choice of steel heating radiators is not considered an excellent option, since they are not able to withstand significant pressure. They are extremely resistant to corrosion, lightweight and heat transfer performance is quite satisfactory. Having an insignificant flow area, they rarely become clogged. But the working pressure is considered to be 7.5-8 kg/cm2, while the resistance to possible water hammer is only 13 kg/cm2. The heat transfer of the section is 150 W.
Made from bimetal
They do not have the disadvantages that are found in aluminum and cast iron products. The presence of a steel core is a characteristic feature, which made it possible to achieve colossal pressure resistance of 16 - 100 kg/cm2. The heat transfer of bimetallic radiators is 130 - 200 W, which is close to aluminum in terms of performance. They have a small cross-section, so over time there are no problems with contamination. Significant disadvantages include the prohibitively high cost of the products.
Made from aluminum
Such devices have many advantages. They have excellent external characteristics and do not require special care. They are strong enough, which means you don’t have to worry about water hammer, as is the case with cast iron products. The working pressure is considered to be 12 – 16 kg/cm2, depending on the model used. Features also include a flow area that is equal to or less than the diameter of the risers. This allows the coolant to circulate inside the device at tremendous speed, which makes it impossible for sediment to deposit on the surface of the material. Most people mistakenly believe that too small a cross-section will inevitably lead to low heat transfer rates. This opinion is erroneous, if only because the level of heat transfer from aluminum is much higher than, for example, that of cast iron. The cross section is compensated by the area of the fins. The heat output of aluminum radiators depends on various factors, including the model used, and can range from 137 to 210 W. Contrary to the characteristics given above, it is not recommended to use this type of equipment in apartments, since the products are not able to withstand sudden temperature changes and pressure surges inside the system (during the run of all devices). The material of an aluminum radiator deteriorates very quickly and cannot be subsequently restored, as is the case when using other materials.
Made from cast iron
The need for regular and very careful maintenance. A high rate of inertia is almost the main advantage of cast iron heating radiators. The level of heat transfer is also quite good. Such products do not heat up quickly, and they also give off heat for quite a long time. The heat output of one section of a cast iron radiator is equal to 80 - 160 W. But there are a lot of shortcomings here and the main ones are considered to be the following:
- Tangible weight of the structure.
- Almost complete lack of ability to resist water hammer (9 kg/cm2).
- There is a noticeable difference between the cross-section of the battery and the risers. This leads to slow circulation of the coolant and fairly rapid contamination.
Heat transfer from heating radiators in the table
Technical instructions
1. Installation of heating equipment should be entrusted to organizations specializing in the field of construction and installation work that have the appropriate license.
2. Radiators with a number of sections less than 10 can be connected in any way - bottom, top, diagonal. If there are more than 10 sections, then it is recommended to connect in a diagonal way: the coolant inlet is at the top, the outlet is at the bottom.
Diagonal connection of the radiator ms 140.
3. Before installing the radiator, you should conduct a hydraulic test of the integrity of the device, the tightness of the gaskets, and the strength of the nipple connections. To do this, hydraulic testing is carried out under a pressure of 1.5 MPa. If a leak is detected due to loose nipple connections, they need to be tightened and the test performed again.
4. When changing (increasing or decreasing) the number of blocks in the radiator, it is necessary to use only gaskets that are established by the requirements of GOST 1412. After assembling the radiator, the strength of the intersectional connections is checked.
This is done in a standard way - hydraulic tests are carried out under high pressure of 1.5 MPa, exceeding the maximum permissible loads. During the test, the prefabricated structure must not leak or allow air bubbles to pass through.
5. After completion of the installation work, the entire water heating system is pressure tested, based on the results of which a certificate of commissioning of the facility is drawn up.
How to choose cast iron heaters
When choosing radiators, we follow the standard algorithm. We determine the required thermal power, calculate the number of sections, and assemble heating devices for each room from them. Then - the purchase of heaters, installation kits and control valves.
What type of radiators is better to choose:
- For heating technical, utility and utility rooms of a private house, the MS-140M series or its variants are quite suitable.
- In residential premises, “accordions” are clearly inappropriate. Buy nicer “aluminum-look” batteries.
- If your budget allows, install designer appliances - domestic or imported, there is practically no difference. Find out the weight of the sectional heater in advance and consider the installation method - wall or floor.
Vintage taps for retro batteries from Carlo Poletti - Conventional ball valves and balancing valves are not suitable for retro radiators purely visually. We need similar Carlo Poletti fittings.
- Place any batteries you like in a private cottage; they will easily withstand the pressure of an autonomous system.
- What devices are best for an apartment? The answer depends on the method of heat supply. With a centralized supply, it is not recommended to install cast iron due to periodic testing of the network. If the pressure “jumps” to 12 bar, the sections may crack.
Note. Before purchasing radiators, you can contact the heat supply organization and formally request the operating parameters of the pipeline network. But if the pressure is exceeded and the cast iron is destroyed, you will suffer losses that are difficult to compensate.
terms of Use
The radiator is used in water/steam heating systems with any type of boiler, in which the coolant is ordinary water, without specific requirements for its quality.
Installation should only be carried out in a heating network that is designed, installed and operated in accordance with regulatory documentation adopted by government industry organizations.
For Russia, such a regulatory act is the rules SP 60.13330.2012 or 73.13330.2012.
Installation
How and with what do you tighten the plugs in heating radiators when installing them? How to seal connections? The instructions depend on the cork material.
The fitting is screwed into aluminum radiators using an adjustable or open-end wrench. Tightness is ensured by a standard paronite or silicone gasket.
The gasket under the plug is clearly visible in the photo.
The plugs for cast iron heating radiators are screwed in with gas wrenches No. 2 - 4.
The procedure is as follows:
- The carving is made with your own hands, without the use of tools.
- In the gap between the bottom of the plug and the section, a strand of plumbing flax impregnated with any quick-drying paint or silicone sealant is placed along the pipe thread.
- The fitting is tightened until excess impregnation is squeezed out.
Selection rules
Radiators with a flat surface have higher efficiency.
The recommendations are simple:
- The most important thing is the correct calculation. The power of the section is assessed and the efficiency of the entire heater is calculated. If there are not enough sections, increasing the temperature of the coolant will not improve the situation; the room will be cold.
- You need to choose the height. If the product is mounted under a window, there should be at least 20–15 cm between the radiator and the window sill, and at least 5 cm between the floor and the bottom edge of the product. For large windows, choose low radiators and compensate for the small height with a large number of sections. Tall radiators are mounted near blank walls.
- Batteries with a flat surface have higher efficiency and are more attractive in appearance. Models with artistic casting and decorative coating fit perfectly into retro, classic, and rustic interiors.
- Radiators are mounted on the wall using special brackets. However, there are floor-standing models. The latter are used if the walls cannot withstand such a heavy load.
The appearance of the battery can be radically changed by covering them with a decorative grille or screen.
Why is cast iron so in demand?
Cast iron radiators have advantages over other heating devices. They differ:
- Highly resistant to corrosion. This property is explained by the fact that during operation the surface of the battery becomes covered with “dry rust”, which is unable to enter the corrosion stage. Cast iron is wear-resistant and will not be affected by various debris from heating pipes.
- Good thermal inertia. While steel radiators retain 15% of their heat after the boiler is turned off, the cast iron analogue of the MC 140 can radiate up to 30% of heat even after an hour.
- Long service life. High-quality models of cast iron radiators can reach a hundred-year operational period. But manufacturers are reducing these periods and promising reliable operation in the interval between 10-30 years.
- Large internal cross-section. Thanks to this technical characteristic, the cast iron radiator MC 140 500 rarely needs cleaning.
- This material cannot cause electrochemical corrosion. That is, cast iron comes into excellent contact with steel or plastic pipes.
Installation Rules
The number of sections has been calculated, the radiators have been purchased, and all that remains is to install them. There are two options here - seek help from specialists or do everything yourself. If financial possibilities are limited, then we carry out the installation process ourselves.
For fastening cast iron radiators, the following are used:
- Pin brackets - when the wall is made of gypsum concrete blocks or bricks.
- Corner brackets - when the wall is wooden.
1 sectional radiator requires 3 brackets, which are secured using a drill and dowels. The next step is to remove the film from the cast iron structure and connect the supplied pipes to the battery so as not to damage the threads and avoid water leakage from the heating system. The distance from the floor to the bottom edge of the radiator is at least 10 centimeters, and between the wall and sections - up to 5 centimeters.
Radiators can be connected either in series or in parallel. Regardless of the method chosen, you first need to turn off the coolant supply through your riser. To do this, you will have to contact a service organization - a housing office or a housing department. After the riser is closed, you need to drain the remaining coolant from the old radiators and pipes. After dismantling the old heating devices, you can connect new cast iron sections.
Assortment in the store
You should work carefully so as not to strip the thread, otherwise you won't have any problems. Having opened the Mayevsky tap, it is necessary to release the air accumulated in the heating system and supply coolant by opening the riser
Installation of radiators with parallel connection is carried out similarly to the first method and differs only in that if there are shut-off valves, you will not have to block the central riser. If desired, modern temperature sensors and thermostats are inserted into the radiators, which allow you to regulate the heating temperature of the radiators.
Peculiarities
All heating radiators, regardless of the materials used in their creation, as well as regardless of shape and size, are equipped with an inlet and outlet. In the bulk of commercially available devices, these holes are duplicated to allow both bottom and top connections.
Not all available technological holes are used during the installation process. To ensure the tightness of the device, special plugs are used that are screwed into unused holes.
The standard package of the heating battery does not include the necessary plugs (plugs) and fittings (connecting elements for joining with the pipeline). As a result, you will need to additionally buy a special kit for installing radiators.
Typically, these kits are universal and suitable for cross or side connections. But there are devices designed for the lower supply of the inlet and outlet pipes. In such a situation, along with the main installation kit, it will be necessary to purchase a special unit for connecting to closely spaced pipes.
Such different diameters
Due to the difference in the naming system for pipes made from different materials, some confusion inevitably arises in the mind of a potential buyer. I will try to clarify this issue.
- The steel pipe is marked with a conditional bore, or DN. It is approximately equal to the internal diameter; small deviations of the actual size from the DU are due to the variation in the wall thickness of ordinary, light and reinforced water and gas pipes;
The nominal bore of a steel pipe is approximately equal to its internal diameter.
- The DN marking indicates the same DN (conditional bore). However, DN is often specified in inches. An inch is 2.54 centimeters; only markings in inches are traditionally rounded to several whole and fractional values, which aggravates the confusion. For the convenience of the reader, I will provide a table of correspondence between the sizes of steel pipes in millimeters and inches;
| DU | Size in inches |
| 15 | 1/2 |
| 20 | 3/4 |
| 25 | 1 |
| 32 | 1 1/4 |
| 40 | 1 1/2 |
| 50 | 2 |
- Pipes made of cross-linked and ordinary polyethylene, polypropylene and metal-polymer products are marked with an outer diameter . On average, their diameter is one step larger than the internal section: a pipe measuring 25 mm has the same internal cross-section as a steel pipe DN 20, 32 mm corresponds to DN 25, and so on;
Internal and external dimensions of polypropylene pipes. Different operating pressures determine the variation in wall thickness.
- All polymer products have lower hydraulic resistance than steel due to minimal wall roughness. In addition, they do not become overgrown with rust and lime deposits over time, so their diameter is selected without reserve. But it is better to buy steel pipes for a central heating system taking these factors into account, rounding the calculated pipe diameter up.
An exposed steel line in the central heating system of an apartment building.