Although manufacturers of radiators made of steel, aluminum and bimetal say that cast iron analogues have already outlived their usefulness, this is not so. Indeed, 160 years have passed since the first time heaters made of this metal were installed, and at one time they made a real breakthrough in supplying homes with heat.
At the present time, old Soviet batteries are hardly attractive to anyone, but their modern analogues have become completely different. Starting from appearance to how much water is in one section of a cast iron battery, everything has changed in these “old-timers” of heating systems.
How long does it take for cast iron batteries to cool?
Cast iron batteries
withstand pressure surges of up to 15 atm, while bimetallic ones - up to 40 atm.
However, in the central heating network the pressure does not rise above 15 atmospheres, thanks to which numerous
cast
iron
batteries work perfectly for decades.
Interesting materials:
What's wrong with the moon today, why is it red? What are fine motor skills and why is it so important to develop them? What is fitness and why is it relative? What is taiga and where is it located? What is the Who Called service? What to take with you on the road If you are on a diet? What to close to turn on the computer? Who is characterized by bilateral body symmetry? Who needs a gluten-free diet? Who does the LP write songs for?
How much water is in one section of a bimetallic radiator
As with aluminum, there are many options for manufacturers and brands of bimetallic radiators. Their structure, appearance, and channel diameters differ in the same way.
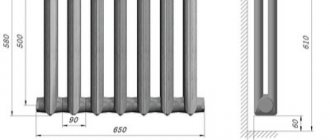
The volume of water in a bimetallic radiator depends on its height and is (in liters):
- 35 cm – 0.1-0.15;
- 50 cm – 0.2-0.3;
- 60 cm – 0.25-0.35;
- 90 cm – 0.3-0.5;
- 120 cm – 0.4-0.6.
To calculate the volume of a section of a bimetallic radiator of non-standard height, use the formula (V – volume in liters, h – height in meters):
V = hx 0.35
This will give you an approximate value, which may vary within 20%.
Modern life of cast iron batteries: new pros, old cons
Like other types of heaters currently on the market, cast iron structures have a set of both positive and negative qualities. The advantages include:
- This type of metal is not susceptible to corrosion even when the water is completely drained from the system. They can be installed in houses where the coolant is not clean and has a uniform Ph level.
- The service life of these devices is 35 years or more.
- The volume of one section of the cast iron battery is only 0.8 liters, which increases the rate of heating of the coolant, and therefore reduces the level of energy consumption. This, in turn, leads to cost savings during their operation.
- Like old-style radiators, they are cheaper than other types of heating devices.
- The heat transfer, taking into account the volume of the cast iron heating radiator, is high enough to effectively heat the apartment.
- This type of heating device does not require special care. Occasionally you should wipe off the dust, otherwise new cast iron heaters are as easy to maintain as, for example, steel or aluminum sectional models.
- If the system is turned off, the cast iron batteries cool down long enough to keep the apartment warm. This is one of the properties of this metal.
If we talk about the disadvantages of these devices, they remain the same:
- Cast iron is still the same brittle metal that does not withstand even minor impacts. During transportation, special attention should be paid to protecting cast iron batteries from falls. As a rule, major damage does not occur with weak external impacts on the body, but microcracks may well appear. During operation, they become larger until the seal is completely broken.
- Even though the volume of a cast iron radiator section is small, their weight remains quite heavy compared to analogues made of other metals.
Currently, new types of cast iron batteries are presented on the market, the stylish appearance of which is suitable for any interior. If the design requires the installation of antique-style radiators, then vintage models can also be found in construction stores.
Critical stage: calculating the capacity of the expansion tank
In order to have a clear idea of the displacement of the entire heating system, you need to know how much water is placed in the boiler heat exchanger.
You can take averages. So, on average, a wall-mounted heating boiler contains 3-6 liters of water, while a floor or parapet boiler contains 10-30 liters.
Now you can calculate the capacity of the expansion tank, which performs an important function. It compensates for the excess pressure that occurs when the coolant expands when heated.
Depending on the type of heating system, tanks are:
- closed;
- open.
For small rooms, the open type is suitable, but in large two-story cottages, closed expansion joints (membrane) are increasingly being installed.
If the tank capacity is smaller than required, the valve will release pressure too often. In this case, you have to change it, or install an additional tank in parallel.
For the formula for calculating the capacity of the expansion tank, the following indicators are needed:
- V(c) is the volume of coolant in the system;
- K is the coefficient of water expansion (the value is taken as 1.04, based on the water expansion rate of 4%);
- D is the expansion efficiency of the tank, which is calculated by the formula: (Pmax – Pb)/(Pmax+1)=D, where Pmax is the maximum permissible pressure in the system, and Pb is the pre-pumping pressure of the compensator air chamber (parameters are indicated in the documentation for the tank );
- V(b) - expansion tank capacity.
So, (V(c) x K)/D = V(b)
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
1. Cast iron batteries can withstand temperatures up to 150°. Such radiators resist corrosion well. Cast iron is difficult to corrode.
2. The radiator walls are made very thick. Therefore, such batteries have a long service life. Radiators can be used in an open heating system and one that is occasionally emptied. Steel radiators under such conditions would become rusty in a few years or completely unusable.
3. Due to the large cross-section of the battery, they can be cleaned less often, unlike other radiators.
4. If a cast iron radiator is made according to all standards and from high-quality material, then it will last a very long time. It is possible to use a radiator for up to 50 years, and sometimes up to 100 years.
5. Such radiators are difficult to damage or dissolve.
6. When the radiator is turned off, it will continue to heat the room by 30%. Cast iron batteries have heat transfer several times greater than radiators made of other materials. In case of irregular heating of the coolant, a battery made of cast iron will cope with its function perfectly. All these qualities are possible thanks to the good heat-storing properties of the cast iron battery.
Flaws:
1. Heavy radiator weight. When lifting the radiator into the apartment, it will be problematic to bring it.
2. The working pressure is much less than other radiators.
3. Due to the number of sections, the surface area of the radiator is reduced. It is smaller than other radiator models.
Along with all the advantages, the disadvantages are insignificant.
Selection of circulation pump
The circulation pump helps to identify pressure losses in all sections of the pipeline. To determine the pressure required by the pump to pump coolant through the system, use the formula: P = Rl + Z, where:
- P - decrease in pressure in the line (Pa);
- R - relative resistance to adhesion (Pa/m);
- l is the length of the pipe of one section of the heat pipeline (m);
- Z—pressure reduction in narrow-gauge zones (Pa).
Such calculations are extremely inconvenient and time-consuming, whereas to determine the Rl value of all sections of the pipeline it is enough to use Shevelev’s tables. It must be remembered that pump performance is the total coolant consumption, and not the capacity of the heating system.
What situations can be avoided if you correctly calculate the volume of coolant
Many people install a heating system, relying on the advice of experts, friends or their own intuition. Choose a more powerful boiler and increase the number of radiator sections “just in case.” But the result is the opposite picture: instead of the expected heat, the batteries do not warm up evenly, the boiler “winds” fuel idle.
You can avoid the following unpleasant situations if you know how to calculate the amount of water in the heating system:
- uneven heating of the water circuit in the rooms;
- increased fuel consumption;
- emergency situations (broken connections, leaks in radiators).
All these “surprises” are quite predictable if the volume of coolant is incorrectly calculated.
Attention! Antifreeze should not be used in a heating system that uses galvanized pipes or other elements.
Water volume in the heating radiator table
| Radiator type | Height (mm) / model | Minimum section volume (l) | Maximum section volume (l) |
| Aluminum | 350 | 0,2 | 0,3 |
| 500 | 0,35 | 0,45 | |
| 600 | 0,4 | 0,5 | |
| 900 | 0,6 | 0,8 | |
| 1200 | 0,8 | 1 | |
| Bimetallic | 350 | 0,1 | 0,15 |
| 500 | 0,2 | 0,3 | |
| 600 | 0,25 | 0,35 | |
| 900 | 0,3 | 0,5 | |
| 1200 | 0,4 | 0,6 | |
| Cast iron | MS 140-300 | 0,8 | 1,3 |
| MS 140-500 | 1,3 | 1,8 | |
| MS-140 | 1,1 | 1,4 | |
| MS 90-500 | 0,9 | 1,2 | |
| MS 100-500 | 0,9 | 0,2 | |
| MS 110-500 | 1 | 1,4 |
We hope that we were able to help you determine the volume of water in one section of the battery. Let us remind you: if you are going to make any manipulations with the heating system, it is better not to take risks.
When working with non-standard models, calculate their volume with a small margin of 10-20%. This will not complicate the task, but will help avoid trouble. Don't forget to share the article with your friends!
Do you want to get help from a master, a specialist in this field? Go to the professional search portal. This is a completely free service where you will find a professional who will solve your problem. You do not pay for posting an ad, views, or choosing a contractor. If you are a master of your craft, then register on Pro and receive a flow of clients. Your profit is just one click away!
How to improve heat transfer
The specified power factor of the convector in its technical data sheet takes place under almost ideal conditions. In fact, the amount of heat flow is slightly reduced, and this is due to large heat losses.
First of all, to increase the coefficient, it is necessary to reduce heat loss - carry out work to insulate the house, paying special attention to the roof, since about 70% of the warm air and window and door openings escape through it. It is advisable to install reflective material on the wall behind the heat device to direct all the useful energy inside the room. It is advisable to install reflective material on the wall behind the heat device to direct all the useful energy inside the room
It is advisable to install reflective material on the wall behind the heat device to direct all the useful energy inside the room.
When installing a heat pipeline, preference should be given to metal pipes, since they also carry out heat exchange, and accordingly, the efficiency increases significantly.
To summarize, it should be noted that copper, bimetallic and aluminum radiators have the best heat transfer. The former are quite expensive and are used extremely rarely.
Based on the declared radiator power by the manufacturer, we can conclude that bimetallic heat devices are superior to aluminum ones.
However, in practice, devices made of aluminum give off more heat, since the steel included in bimetallic convectors has high thermal conductivity, which means it cools down in a shorter period of time.
Advantages
Among the advantages of cast iron batteries, it is worth noting the following:
- durability: the service life specified by the manufacturer is 50 years, but with proper care it can last much longer;
- resistance to pressure of 9–12 atmospheres, which provides protection against water hammer (this is why cast iron radiators are usually used in high-rise buildings with central heating);
- temperature endurance from 100 to 130 degrees;
- the ability to produce one section of power up to 160 kW;
- resistance to exposure to aggressive environments that provoke corrosion;
- no need for frequent cleaning;
- the ability to distribute heat to other objects due to infrared radiation;
- simple modification;
- the ability to install a battery of the required power;
- affordable price.