Other articles on this topic:
⇒ How to reduce the high gas consumption of a boiler for heating a house ⇒ DHW boiler for a double-circuit boiler or water heater ⇒ Malfunctions and error codes of a gas boiler Ariston, Protherm, Baxi ⇒ Setting the pressure in a heating system with a membrane expansion tank
For heating and hot water supply of apartments and small private houses with one bathroom, double-circuit gas boilers are usually used.
In large houses with several sanitary rooms, single-circuit gas boilers with a storage boiler for preparing hot water are more often used for heating. This system provides more comfortable use of hot water in the house.
Read: Hot water supply for a private country house
The apartment in the new building with apartment heating is equipped with a Protherm Gepard 23 MTV double-circuit gas boiler. Next, let's look at setting the boiler power using this apartment as an example.
Gas boilers of the Protherm Gepard series are almost a complete analogue (a simpler version) of the Protherm Panther boilers. This article describes in detail the adjustment and power settings of gas boilers Protherm Gepard and Protherm Panther.
It should be noted that the company that produces Protherm series boilers at its other plant produces gas boilers of the famous Vaillant brand. Vaillant gas boilers are in a higher price category due to the use of higher quality materials for the manufacture of heat exchangers. But in design, other parts used, and service menu settings, Vaillant brand gas boilers are very similar to Protherm boilers.
The principles of regulation and power settings described in this article are also suitable for gas boilers of many other brands and manufacturers.
Internal structure of the double-circuit gas boiler Protherm Gepard 23 MTV and Panther 25.30 KTV (Panther)
Reasons for clocking (pulse operation) of the boiler in heating mode
The operating manual states that the useful thermal power of the Protherm Gepard 23 MTV boiler is adjustable from a maximum of 23.3 kW. to a minimum of 8.5 kW. The factory setting for power in heating mode is 15 kW.
The total area of the apartment, which is heated by the boiler, is 60 m2. To heat the apartment, heating devices (radiators) with a total maximum thermal power of 4 kW are installed.
How to determine the maximum thermal power of a heating circuit in a house or apartment
How to determine the maximum thermal output of a heating circuit? On the websites of radiator manufacturers and sellers we find the thermal power of each radiator installed in the house. In manufacturers' catalogs, the heat transfer of radiators is presented in 2 modes: 1) 90/70/20 degrees and 2) 75/65/20. You need to look at the heat transfer according to the “75-65/20” parameter. The sum of the powers of all radiators connected to the boiler will be equal to the maximum thermal power of the heating circuit. For the apartment in our example, this value turned out to be 4 kW.
The installers installed the boiler and put it into operation, “forgetting” to carry out the commissioning work. The boiler was started to work with the factory setting of maximum power in heating mode of 15 kW.
It is obvious that a heating system with a maximum power of only 4 kW will not be able to accept the thermal energy produced by the boiler with a power of 15 kW. The power of the boiler burner is controlled automatically within certain limits. But the huge difference in the power of the boiler and heating devices leads to the fact that the boiler automation is not capable of bringing the boiler power in line with the needs of the heating system without additional settings.
Building regulations do not recommend installing boilers with a useful power that significantly exceeds the power of the heating system in a house or apartment.
The large difference between the power of a gas boiler and the power of heating devices, among other disadvantages, leads to cyclical operation of the boiler.
By the way, about other disadvantages of an overly powerful boiler. The service instructions for the Protherm Gepard 23 MTV boiler indicate its efficiency in heating mode: 93.2% at maximum thermal power (23.3 kW.) and 79.4% when operating at minimum power (8.5 kW.) Imagine how The efficiency will further decrease if this boiler has to work with a 4 kW heating system. Please note that a double-circuit boiler operates in heating mode most of the time throughout the year, with minimal power. At least 1/4 of the gas spent on heating will literally fly uselessly down the chimney. This will be the price to pay for installing overly powerful heating and hot water equipment in the house.
Tips on the topic “How to increase the efficiency of a gas boiler” can be found if you read this article to the end.
Excessive cyclicality, impulsiveness of work, or, as people say, “boiler clocking” is manifested in the fact that the boiler burner, after being turned on, quickly turns off when the set temperature is reached in the straight pipe at the outlet of the boiler. But the radiators remain not heated to this set temperature - the water heated in the boiler simply does not have time to reach the heating devices. That is, the boiler produces more thermal energy per unit time than a less powerful heating circuit is capable of receiving. Therefore, the temperature of the water leaving the boiler rises quickly and it turns off earlier, without having time to heat the radiators.
After a short time, the circulation pump supplies the heat exchanger with the remaining cool water from the heating system return pipe and the burner turns on again. Then everything repeats again.
A high-power heating system has an increased pipe diameter and radiator volume, which means less hydraulic resistance. In larger systems, water does not flow exactly the same, it flows faster, at a higher flow rate (liters per second). During the rapid passage through the boiler heat exchanger, each liter of water only manages to heat up by 15-20 degrees Celsius. And in order to heat this liter to a given temperature, the water in the heating system must pass through the heat exchanger several times.
Low-power heating systems have thinner pipes, smaller radiators, higher hydraulic resistance and water flows slower. If you heat slowly flowing water with the same power, then the water that enters the heat exchanger immediately, at one time, will heat up by 40-60 °C, immediately to the maximum temperature, and the boiler will turn off. And the water remaining in the system, which has not reached the boiler, will remain cold until the next clock cycle. This is what happens in the boiler if its power is not adapted to the heating system.
The size of the flame (burner power) in the boiler is controlled electronically using a complex algorithm, which takes into account the time from the start of the burner, the temperature value, the rate of temperature change in the heating circuit, and the temperature difference in the forward and return pipes. I don’t know all the intricacies of the control algorithm, but the automation, without additional service settings, does not ensure normal operation of the boiler at a power below the minimum specified in the technical specifications.
In a properly configured heating system, the temperature difference in the forward and return pipes should be no more than 20 °C.
Clocking reduces the service life of the boiler and increases gas consumption
Any person, even without being a mechanic or electrician, knows that the most difficult operating mode for equipment is the moment of startup, turning on mechanical and electrical equipment. During the start-up period, the greatest wear is observed, and failures most often occur. An increase in the number of starts as a result of cyclicity consumes the operating life of very expensive parts of the boiler the most - gas and three-way valves, circulation pump, exhaust gas fan.
To ignite at the moment of starting, the maximum amount of gas is supplied to the burner. Part of the gas, before the flame appears, literally flies into the pipe. Constantly “re-igniting” the burner further increases gas consumption and reduces the efficiency of the boiler.
Some cyclical operation of a gas boiler is provided for by its normal operating mode. For example, regulating the temperature in a room without a thermostat or using a two-position thermostat occurs by periodically turning the boiler burner on and off.
The task of regulating the boiler power is to eliminate excessive cycling - clocking caused by the lack of adaptation of the boiler settings to the heating system.
To eliminate boiler clocking, it is necessary to equalize the power of the boiler and the heating circuit
You can do this in two ways:
- Reduce the boiler burner power to a level at which the automation can ensure normal operation of the boiler with the connected heating system.
- Increase the maximum power of the heating circuit by installing additional radiators or replacing existing ones with more powerful ones.
You can use both methods at once. Reduce the difference between the power of the boiler and the heating circuit by replacing and installing more powerful radiators. And then, compensate for the remaining difference by adjusting the boiler power.
The second method is more expensive, but sometimes you have to choose it. The fact is that, in order to save money, builders often install radiators in the house without a reserve of thermal power. As a result, in order to maintain the required temperature in the premises, in frosty conditions it is necessary to supply heating water to the radiators at a maximum temperature of more than 75 °C. At this temperature, organic dust particles decompose (burn) on the radiators and an unpleasant odor appears in the rooms. In addition, the high temperature of the coolant shortens the service life of polymer pipes and other parts of the heating system made of plastic and rubber.
Sometimes, the power of radiators is simply not enough to maintain the required thermal conditions even at the maximum heating water temperature. Before adjusting the boiler power, I recommend determining the need, and, if necessary, increasing the power of the radiators by 30 - 100%, at least in the coldest rooms.
Above is the standard operating temperature of the radiator in systems with plastic pipes. Below are the maximum radiator temperatures for comfortable, soft heat. To switch from standard mode to soft heat, the power (size) of the radiator must be increased by approximately 2 times.
The main advantage of low-temperature heating is the ability to use modern technologies. We are talking about condensing boilers, solar collectors and heat pumps. They require that the heating water temperature in the system be low.
When replacing radiators, it is necessary to take into account that the expansion tank built into the boiler is designed for a volume of water in the heating system of no more than 50 liters for a Gepard boiler, and 70 liters for a Panther. If the amount of water as a result of installing new radiators turns out to be greater, then it is necessary to install an external expansion tank.
The external expansion tank is connected to the return line of the heating system closer to the boiler. In this case, it is better to disable the built-in expansion tank.
Read: “Membrane expansion tank - volume calculation, pressure setting, connection”
Buy radiators in your city
Heating radiators
⇆
Measuring instruments for setting up heating systems
Due to rising energy prices, proper adjustment of heating equipment is becoming an important component for optimizing utility costs. Testo portable flue gas analyzers will help you complete any task of setting up, commissioning and servicing heating equipment
Professional gas analysis with testo 330-1 LL h4>
The testo 330-1 LL gas analyzer with extended sensor life is a reliable device for diagnosing faults in heating equipment and for monitoring the level of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere or for the daily work of heating system specialists. It is able to meet the highest demands placed on a gas analyzer: the highest sensor accuracy and sensor service life.
Professional gas analysis with testo 330-2 LL h4>
In addition to all the advantages of the Testo 330-1 LL gas analyzer, you can use the testo 330-2 gas analyzer with higher CO concentrations in the flue gases. This is achieved through the built-in function of automatically diluting the flue gas sample with a factor of 5. You will receive additional convenience by using the pressure/draft sensor zeroing function with the probe remaining in the chimney.
Highly efficient gas analysis with testo 320
h4>
Gas analyzer Testo 320 is a multifunctional flue gas analyzer for heating system specialists. The intuitive menu structure and ease of operation of the testo 320 gas analyzer, combined with a high-resolution color display, allow you to carry out all the necessary measurements during installation, commissioning, service and maintenance of heating boilers and burners.
Basic level gas analysis testo 310 h4>
The testo 310 gas analyzer combines ease of use with high measurement accuracy and is ideal for all basic measurements on gas boilers and burners. The long battery life guarantees the possibility of long-term use of the device, including for a series of measurements of flue gas concentrations
Soot number analyzer Testo 308 h4>
The Testo 308 soot number analyzer helps you measure the soot number. The built-in pump and the automatic display of the measured value on the backlit display allow you to obtain data on the soot content in the chimney using a modern measurement method. This measurement method is comparable to traditional soot number measurement methods using a hand pump.
How to regulate the burner power of a gas boiler
The useful thermal output of a gas boiler can be reduced by reducing the gas supply to the burner. They do this by changing the gas valve settings.
Gas valve Honeywel gas double-circuit boiler Protherm Gepard (Panther)
Honeywell gas valve for Protherm Gepard (Panther) boiler - operating diagram.
EVS1 - safety solenoid valve; EVS2 - electric control valve drive; Vm - the stepper motor controls the gas flow through a control valve.
In modern Protherm Gepard and Protherm Panther boilers, the basic settings of the Honeywell gas valve are changed using a stepper motor. The stepper motor is controlled from the boiler control panel through the service menu.
It should be noted that the manufacturer, in some versions of gas boilers Protherm Gepard (Panther), Vaillant, instead of a Honeywell gas valve, installs a SIT 845 Sigma gas valve. The maximum and minimum burner power settings for this valve are made by rotating the adjusting screws located on the valve body. Read about the features of adjusting the SIT gas valve below, on page 2.
The electromechanical devices of the boiler (electric valves, stepper and conventional electric motors, sensors) are controlled by a microprocessor of the electronic control board in accordance with the programmed program. The boiler operating program settings can be changed on the control panel using two menus - a public user menu and a hidden service menu.
Access to the service menu of the Protherm Gepard boiler
The Protherm Gepard boiler is controlled from the control panel through a publicly accessible user menu. How the owner can operate the boiler is described in the operating manual.
On the control panel you can call up another, hidden menu - a service menu intended for specialists. The service menu becomes available on the display screen after entering the code.
Press and hold the mode button (1) for about 7 seconds; The display will change and the number 0 . — Using the + or — (2), enter the code, number 35 . — Confirm entering the code by pressing the mode button (1). After this, the display will show the 1st line of the menu in the form of symbols alternating on the screen: d. 0 .
— Using the + or — (2), enter the number with the required menu line number: d.** .
To change the value of a parameter in the menu bar: - Press the “mode” button to move from the menu line number “ d.** ” to the parameter value (the display alternates between the “=” symbol and the parameter value). — Change the values of the displayed parameters using the + or — buttons (3) on the boiler panel. — 3 seconds after the change, the new values are automatically confirmed. To return the display to its original state, press the “mode” button for 3 seconds. After 15 minutes of inactivity, the display returns to operating mode on its own.
Access to the service menu of the Protherm Panther boiler (Panther)
The control panel of the Protherm Panther boiler has some differences from the Protherm Gepard boiler. The boiler control panel has a hidden service menu, which becomes accessible when the code is entered.
Boiler control panel Protherm Panther (Panther)
To access the service menu of the Protherm Panther boiler, you must: Press and hold the mode button (1) for about 7 seconds; The display appearance will change. — Using the buttons on the left + or — (2), enter the access code to the service menu — number 35 in the left half of the display. — Confirm entering the code by pressing the mode button (1).
After this, the display will display the 1st menu line in the form of symbols d.00 with the menu line number in the left half of the display, and the numerical value of the line parameter in the right half of the display. — Using the buttons on the left + or — (2), enter the number with the required menu line number: d.** .
To change the value of a parameter in the menu bar: - Change the values of the displayed parameters in the line using the buttons on the right + or - (3) on the boiler panel. — 3 seconds after the change, the new values are automatically confirmed. To return the display to its original state, press the “mode” button for 3 seconds. After 15 minutes of inactivity, the display returns to operating mode on its own.
The service menu commands and the procedure for setting the power of the Protherm Panther boiler are similar to those given for the Protherm Gepard boiler.
Description of some service menu commands
Line d.00 - maximum heating output (net power) of the boiler in heating mode, kW. The range of possible parameter values is from =9 to =23, factory setting = 15 (for Protherm Gepard).
Line d.01 - run-on time of the circulation pump in heating mode, min., select a value between 2 and 60 minutes. Factory setting =5
Line d.02 - Time delay after operation in heating mode for anti-cycling, min. Protects against frequent switching on and off of the burner in heating mode (this function is not applicable in DHW mode). Select a value between 2 and 60 min. Factory setting = 20 minutes. This delay (called anti-cycling time) prevents a rapid restart in heating mode after the burner has stopped due to the set temperature or the room thermostat TA. It depends on the coolant temperature setting: - at 80 °C, it is set for 1 minute and is not adjustable. - at 20 °C, it can be adjusted from 1 to 60 minutes using parameter d.02 in the service menu. At intermediate temperatures, between 20 °C and 80 °C, the delay varies proportionally in the range of 1 min. to the parameter set in d.02 .
Dependence of the anti-cycling time on the parameter setting in line
d.02 and the heating temperature
Line d.18 - operating mode of the circulation pump; Operating mode options: = 0 - with burner: the pump operates together with the burner. =1 - continuous; with RT thermostat: the pump is activated by the command of the room thermostat. =2 - constantly in winter: the pump runs all the time while the boiler is in WINTER mode. Factory setting =1 .
Line d.19 - speed of the circulation pump; Operating mode options: =0 - burner is running; speed in heating mode is selected automatically, maximum - in DHW mode, minimum - if the burner is turned off = 1 - min. speed in heating mode, max. – in DHW mode =2 – automatically selected in heating mode, max. – in DHW mode =3 — max. speed in heating and hot water mode. Factory setting =2 . Each time the burner is started in heating mode, the pump is switched on at a limited speed for at least 30 seconds. If the temperature difference between flow and return reaches 20 oK, the pump switches to maximum speed until the burner is turned off (even if the temperature difference has decreased). The same cycle occurs at the next ignition.
Household products
⇆
Line d.35 - shows the position of the 3-way valve, heating/DHW (read only); =99 - hot water =0 - heating =40 - middle position
Line d.36 - shows on the display the hot water consumption measured by the flow sensor, l/min. when dispensing hot water (read only)
Line d.40 - shows on the display the temperature of the water leaving the boiler in the direct pipeline of the heating system, °C. (only for reading)
Line d.41 - shows on the display the temperature of the water at the entrance to the boiler, in the return pipe of the heating system, °C. (only for reading)
Line d.44 - Control of ionization current. This parameter informs that the ionization current is in the optimal range. The displayed value does not represent the actual current value! Range of values: 0 – 10. In the range: =0 – 4 – ionization current is sufficient – flame is present; =4 – 8 – ionization current is slightly below a sufficient level – there is a possibility of flame loss; =8 – 10 – ionization current does not correspond to a sufficient level – there is no flame.
Line d.52 - setting the minimum power of the boiler burner by shifting the minimum position of the Honeywell gas valve stepper motor. The range of possible parameter values is from =0 to =99. The lower the parameter value, the weaker the intensity of gas combustion.
Line d.53 - setting the maximum power of the boiler burner by shifting the maximum position of the Honeywell gas valve stepper motor. The range of possible parameter values is from =0 to =-99 (negative values with a minus sign). The lower the parameter value, the weaker the intensity of gas combustion.
Line d.62 - lowering the heating temperature at night. Setting range 0 - 30 °C. If you connect a timer or even a manual switch to the boiler, you can switch the boiler into two modes: day or night. In night mode, the heating temperature setting is reduced by the amount set in d.62. Those. During the day, the temperature of the heating water and the temperature in the house are higher, and at night lower. You can set it the other way around.
Line d.67 - Displays the time between boiler starts. This parameter displays the cooling time in minutes before the boiler is turned on again. The countdown of minutes begins at the moment the boiler turns off due to exceeding the maximum set operating temperature of the heating water on the boiler control panel and the room regulator is permanently closed. This parameter is important for the anti-cycling function of the boiler, when the cooling time until the next switch-on is calculated based on the set boiler heating water temperature and the set anti-cycling time interval in line d.02.
Line d.70 - Setting the position of the three-way valve. In this mode, it is possible to set the position of the three-way valve, regardless of the heating requirements for a particular circuit. Three-way valve position: =0 - the valve is controlled based on standard requirements from the control system; =1 - three-way valve is set to the middle position to empty the boiler (both heating and domestic hot water); =2 - the three-way valve is set to the heating position of the extract air.
Line d.71 - Setting the maximum temperature in the heating system. Select a value between =45 and =80 °C. Factory setting =75 °C.
Line d.88 - Protection against water hammer in cold water distribution (for KTV and KOV boilers). The ability to change the parameter eliminates the reaction to water hammer, which in some cases occurs in cold water pipelines. For example, when the automatic valve in the flush cistern of a toilet (or washing machine, or dishwasher) closes, a pressure surge (water hammer) may occur in the water supply pipes. The consequence of this may be a false activation of the flow sensor (turbine) of tap water, which will lead to a short-term unwanted activation of the boiler’s DHW mode. Factory setting =0 - activation of the ignition process for heating tap water at a flow rate of 1.5 l/min. Changing the parameter to value =1 - activation of the ignition process for heating tap water at a flow rate of 3.7 l/min. In this case, the flow duration should be at least 2 seconds.
Line d.90 - Identification of the connected room sensor. Using this parameter, it is possible to verify that the room regulator is correctly connected, or that the communication between the room regulator and the boiler is working properly. Please note: this description only applies to controllers that support eBus communication. If a conventional regulator with a switching relay was connected, this function cannot be used. Display: =0 - the regulator is not connected or does not communicate with the boiler; =1 - the regulator is connected and there is communication between it and the boiler.
Line d.96 - Setting the boiler to the parameters set at the factory. If the settings lead to incorrect operation or failures, it is possible to restore the boiler to factory settings. Setting: =0 - replacement with factory settings will not be performed; =1 - a return to factory settings will be made Note: when entering the setting of this parameter, the display always shows parameter “0”
Automation from different manufacturers
Wall-mounted gas boiler
If we talk about a standard wall-mounted gas boiler, then it can operate according to the coolant temperature. A room thermostat or chronothermostat can be connected to it. It is also possible to connect an openterm protocol regulator.
A special case of using wall-mounted boilers is the possibility of using weather-dependent automation. Due to the use of an external temperature sensor, additional variables appear that make it possible to more quickly adjust the burner power and supply temperature, depending on the changing conditions outside the building.
Automation Arbat
The devices have 5 degrees of protection. There is thermoelectric flame protection. The gas supply is blocked when switched off. A modulating thermostat will provide comfort in use, and a coarse mesh filter will extend its service life.
Some models are equipped with a circulation pump. The device distributes the coolant evenly throughout the heating system. It is also possible to connect to an external thermostat inside or outside the room.
Automation Honeywell
Honeywell has a wide range of automation systems for gas boilers, from the most budget (mechanical) to multifunctional automatic systems.
Main features:
- the coolant automatically maintains the temperature;
- turning off the boiler in case of gas supply interruptions;
- shutdown in the absence of draft or during reverse draft;
- blocking the gas supply when the gas burner goes out.
Some models are equipped with programmable automation with the ability to set temperature periods depending on the time of day, weather, and even develop a heating/cooling mode by day of the week. And the Smile series models control several temperature circuits at once (heating, ventilation, “warm floor”, hot water, etc.).
Automation Eurosit 630 (Eurosit 630)
The Eurosit gas valve is one of the most used. It can be found on both domestic and imported boilers. Main advantages: multifunctionality of the gas supply regulator, modulation thermostat and the function of full modulation switching on the main burner. It works both from liquefied fuel cylinders and from a gas tank, without the use of electricity. Used in various types of gas-consuming equipment that require precise temperature control.
Basic principles of operation of Eurosit 630 automation.
Ignition of the pilot burner.
- Check that the knob position matches the “off” icon.
- Move the control knob to the “asterisk” position.
- Keep the control knob pressed for a few seconds. Then release and make sure the pilot burner turns on. If the pilot burner goes out, repeat step 3.
Temperature selection.
Use the control knob to set the temperature. The gas will begin to flow into the main burner, where it will be ignited using the pilot burner.
Power modulation.
The thermostatic system regulates gas flow and gas pressure in the main burner depending on the system capillary sensor. The colder the sensor, the greater the power and vice versa. The graph schematically shows how the power changes from maximum to minimum and then until the burner is completely turned off.
Duty position.
Move the control knob from the set temperature to “asterisk”. The main burner will go out, but the pilot burner will remain lit.
Shutdown.
Set the knob to the off position. The valve will close completely, but the thermoelectric protection magnet will remain temporarily activated until the thermocouple sensor cools down. During this period of time, restarting of the thermoelectric system is mechanically prevented. The function is called "interlog". It ensures ventilation of the combustion chamber before the next burner start-up.
Adjusting the maximum heating power of a Gepard or Panther boiler through the service menu
At the first stage, in the service menu, as described above, we find line d.0 , press the “mode” button and look at the value of the boiler power parameter, kW, on the display. In our example, the factory setting =15 was visible. It is necessary to set a new boiler power value equal to the power of the heating devices connected to the boiler. This setting will only work in heating mode.
If the power of the heating system corresponds to the operating range of boiler power
The maximum power of the heating system in the house may fall within the operating power range of the boiler specified in the instructions. For example, the total maximum power of radiators in a house is 11 kW. The operating power range of the Protherm Gepard 23 MTV boiler is 8.5 - 23.3 kW.
In the service menu, as described above, find line d.0, press the “mode” button and look at the value of the boiler power parameter, kW, on the display. For example, the factory setting =15 will be visible. Using the “-” button we set the new boiler power value = 11.
I recommend trying to set the boiler power to 20 - 30% less than the heating circuit power, for example, d.00 = 9 kW. This power should be enough to compensate for heat losses at home, since the power of radiators is usually chosen with some reserve.
Increasing the anticycling time
At the second stage, we increase the anticycling time in line d.02 of the service menu.
Factory setting d.02 = 20 minutes. According to the schedule (see above), we determine that, for the heating water temperature set on the display of 70 ° C, restarting the burner is possible after 4 - 5 minutes, not earlier.
In line d.02 we set a new value for the anticycling time, for our example the maximum possible = 60 minutes. Line d.67 displays the time in minutes until the boiler is turned on again. Breaks in burner operation became approximately 10 minutes long. Twice as much as with the factory setting, which is still too often.
Increasing the anti-cycling time results in the burner turning on later, at a lower heating water temperature. The heat flow from the boiler to the heating circuit is reduced.
Thus, by selecting the settings of the boiler power and anti-cycling time through the service menu, we ensure that the cycle duration between turning on the boiler burner is at least 15 minutes. That is, the boiler should be turned on no more than four times within one hour.
I note that not all brands of gas boilers have the ability to adjust the anti-cycling time. In this case, you only have to select the boiler power settings.
On some brands of gas boilers, the rotation speed (performance) of the circulation pump is set manually using a switch on the pump. To reduce the boiler clock, it is recommended to increase the pump speed.
Setting up a Gepard or Panther gas boiler for power below the minimum
At the third stage , the minimum boiler power is adjusted .
Such adjustment is not necessary in all cases, but only when the first and second stages do not bring the required result. As in our case, when at the first stage we use the “-” button to set a new boiler power value = 9 (the minimum possible setting corresponds to 8.5 kW). The newly established maximum heating power of the boiler (8.5 kW) is still very different from the power of the heating devices (4 kW).
It should be noted that adjusting the boiler power using the method described below is also useful in other cases, since it allows, through an experiment, to adjust the heating power of the boiler in accordance with the actual power of the heating circuit. The actual power is usually less than the calculated one.
Before carrying out work on setting the minimum burner power, you must:
- Fully open thermostatic and other valves on radiators and set the room thermostat to maximum temperature. The thermostat that controls the heated floors is set to the maximum permissible temperature so as not to overheat the floors.
- In the user menu of the boiler, set the maximum operating temperature, which is set by the owners in the coldest weather, adding another +5 °C. Usually this is not less than 65 °C. If the owners do not remember it, or on a new boiler, set the factory setting of the maximum temperature of 75 ° C in the menu. The boiler burner will have to automatically turn off at a temperature 5 °C higher, i.e. at 80 °C.
- Cool the heating circuit to a heating water temperature below 30 °C.
Next, we start the burner in heating mode, select line d.52 , press the “mode” button and see on the display the value of the gas valve stepper motor position parameter in the factory minimum power mode.
By removing the front cover of the boiler, we visually observe the size of the flame in the burner. In our example, the factory setting was displayed on the display, the number = 72, and the flame height in the burner was quite high.
Using the “-” button we set a new parameter value in line d.52, for example =20. 3 seconds after the change, when the new value is automatically confirmed, we observe a significant decrease in the flame height in the burner. This indicates that the useful power of the boiler with the specified setting will be greatly reduced.
Next, observe on the display the increase in temperature in the direct heating pipeline at the outlet of the boiler. Typically, the temperature increase stops when it reaches a value less than the set value, for example 52 °C. The boiler is running, but the temperature does not increase (or changes very, very slowly). This means that a power balance has been achieved between the boiler and the heating system at this established water temperature. At this moment, we increase the parameter in line d.52 of the service menu, set a new value = 30 - the temperature begins to rise again and stops again, for example at 63 ° C. Again we add the parameter value in line d.52 =35 and so select the parameter until the temperature stops at a value slightly higher than the maximum, for example 77 °C. In this way, a balance is achieved between the power of the boiler and the heating circuit at maximum operating temperature. The boiler power will be set to the minimum level required to operate with the connected heating circuit. In this case, the cyclic operation of the boiler will be minimal.
If the radiators do not warm up well in height, the temperature difference in the forward and return pipes at a maximum temperature is more than 15-20°, then increase the response pressure of the bypass valve. Read below on how to adjust the bypass valve. The water temperature in the forward and return pipelines can be seen on the display if you enter the service menu, lines d.40 and d.41.
In case of adjusting the bypass valve, the gas valve setting in line d.52 must be repeated.
In our example, the burner heated the water to a maximum temperature of 77 oC with a minimum parameter value in line d.52 equal to =28 (factory setting was =72). With a lower parameter value, the burner could not heat the water to the specified temperature. And at a higher value, the burner heated the water to 80°C and the boiler automatic switched off the combustion.
It should be noted that the method described above for adjusting the gas valve, which allows you to balance the boiler power with the power of the heating circuit through an experiment, is not included in the recommendations of the boiler manufacturer. This is the idea of the author of the article, successfully implemented when setting up autonomous heating systems with gas boilers.
Factory calibrated gas valve
Honeywell gas valve. 1 - fitting for measuring the gas pressure at the outlet to the burner; 2 - fitting for measuring inlet pressure.
The boiler manufacturer prescribes calibration of the minimum power on the gas valve as follows:
In line d.00 of the service menu, set parameter =9, which limits the boiler power to the minimum level specified in the instructions. Turn on the boiler in heating mode.
A pressure gauge tube is connected to the upper fitting at the gas valve outlet. Before connecting, it is necessary to unscrew the locking screw on the fitting 1-2 turns.
Call line d.52 of the service menu. And using the + and - the value of the line parameter d.52 , set the minimum pressure at the gas valve outlet specified in the boiler operating manual. For example, for a Gepard 23 MTV boiler, the minimum pressure in front of the burner is 1.5 mbar or 15.5 mm water column.
This setting will ensure that the boiler operates with the minimum power specified by the manufacturer - 8.5 kW. The boiler manufacturer's service instructions do not answer the obvious question of what to do if the power of the heating circuit connected to the boiler is less.
In our example, after setting and setting parameter =28 in line d.52 , measuring the pressure at the outlet of the gas valve in front of the burner showed a value of 4 mm.water column.
Readers in the comments ask the question: “Isn’t such a significant decrease in gas pressure on the burner dangerous for the boiler?” Boilers have many different protections, but there is no protection against low gas pressure on the burner. From this we conclude that low pressure in itself is not dangerous for the boiler. It is important to ensure stable ignition and stable combustion of gas, since the boilers have appropriate protection.
A home mechanic can roughly assess whether the gas valve settings correspond to the factory settings without resorting to measuring the gas pressure on the valve.
To do this, set parameter =9 in line d.00 of the menu and turn on the boiler in the minimum heating power mode. Record gas meter readings. After 15 minutes (1/4 hour), the meter readings are recorded again and the gas consumption during this time is determined. For example, we determined the gas consumption from the meter to be 0.289 m3/15 min. This value is multiplied by 4 and the gas consumption calculated for 1 hour in the minimum power mode is 1.156 m3/hour. Compare the obtained value with the data from the factory instructions. For example, the standard gas consumption in minimum power mode for the Gepard 23 MTV boiler is 1.15 m3/hour. Gas consumption according to the meter readings approximately corresponds to the factory norm. We conclude that setting the gas valve in minimum power mode meets the requirements of the factory instructions. If not, then the gas consumption is adjusted by changing the parameter in line d.52.
Similarly, based on gas consumption, you can evaluate the setting of the gas valve at maximum power by switching the boiler to DHW mode.
Power 23.3 kW. corresponds to a maximum pressure at the valve outlet of 85 mm.water.
U-shaped pressure gauge
A simple pressure gauge for measuring a gas valve can be made from a clear plastic tube, filled with water and bent into a U shape. One end of the tube is placed over the valve fitting and the other is left open. A ruler is used to measure the difference in water levels in the branches of the tube. The measured distance will be equal to the pressure in millimeters of water column - mm.water column.
A tube with an internal diameter of 8 mm can be tightly pulled onto the gas valve fitting. For a tube of a different diameter you will have to select an adapter.
At the end of the measurements, do not forget to carefully tighten the screw on the measuring fitting and check its tightness.
choosing a device for measuring gas pressure and adjusting the heating device
A pressure gauge exists to measure the pressure in a system. It connects with the emergency safety valve and air vent, thus guaranteeing safety.
If the pressure readings are outside the permissible limits, it means that the system is not working properly. Excessive pressure can lead to pipeline rupture and even equipment explosion.
Odnoklassniki
Classification of pressure gauges for setting up gas boilers
The operating principle of all pressure gauges is based on the fact that the measured pressure is balanced by the force of a tubular spring or a double-plate membrane.
One end of it is soldered to the holder, and the other is connected to the arrow through a special mechanism. This mechanism converts the linear movement of the sensing element into the movement of the arrow along the dial.
Exemplary
Measuring instruments that are used to calibrate others are called exemplary. This type of device is used to test equipment and accurately measure liquid and gas pressure; they have a higher accuracy class - 0.015-0.6 units. The increased measurement accuracy of these devices is due to the design features: the gear element in the transmission mechanism is made very accurately.
Electric contact
These devices monitor the pressure limit and notify the system when it is reached. Typically, this type of measuring equipment is used for gas, steam, and quiet liquids that are not prone to crystallization. The devices can control external electrical circuits when critical pressure is reached using a contact group or an optical pair.
Photo 1. Electric contact pressure gauge for a heating gas boiler. The device has a dial with divisions.
Instructions for preparing for launch
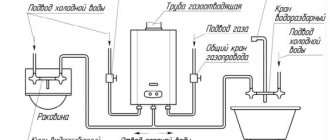
To use gas, you need to follow simple instructions. The first launch is carried out when the installation of equipment and piping are completed, and the correct installation is checked. All fastenings and location of the boiler must be made in accordance with fire safety rules. A certain distance must be maintained from the boiler to the wall. Which one you need to look at in the instructions for the boiler. For some models of gas boilers, this condition is not necessary. You need to make sure that there are no flammable objects or materials nearby. The boiler should not be placed near windows, as its operation will be disrupted.
Great attention must be paid to ensuring that the body is mounted smoothly and that there are no distortions.
After this, the equipment is connected to the cold water supply, all plugs are removed from the pipes, and a special filter with a ball valve is installed at the inlet. This helps protect the system from contaminants that could cause breakdowns. Ball valves must be installed on each pipe used for piping.
When solving the problem of how to start a boiler, great attention must be paid to the installation of gas pipes. In this case, it is not recommended to carry out the work yourself; for this, an employee of the relevant service is invited to perform such a connection, sealing, and, if necessary, install a gas meter
What else needs to be connected before launch? It is necessary to install a separate power line for the boiler. The equipment is supplied with an electrical cable and plug; during installation, it is necessary to ensure that there is an outlet next to the boiler; it is better to separate it from the others. Next, a connection is made to the chimney pipe, its draft and performance are checked. The pipe itself must go outside; the conditions for its installation depend on what type of chimney is chosen. The last part of the preparation for starting is to disconnect the boiler from the electricity so that it can be filled with cold water. Next, the absence of leaks is checked, the thermostat is turned on to the maximum value so that the mode switch automatically lights up.
Thermocouple in the gas control system (gas control)
If you decide to install a solid fuel boiler in your country house, you do not need to worry about what will happen if the fire suddenly goes out. However, when you use gas equipment, you need non-volatile automation that can shut off the gas supply as quickly as possible if the burner suddenly goes out. For these purposes, modern gas boilers are equipped with a gas control system. How does it work?
The system consists of two main parts: a solenoid valve and a thermocouple. One end of the sensor is placed directly in the burner flame, and the second is connected to an electric valve, which consists of a core with a winding, a cap, a return spring, an armature and a rubber band that shuts off the gas supply.
Photo 4: Non-volatile gas control system for stoves and boilers
The gas control works quite simply. By pressing the gas button, you push the rod inside the coil, charging the spring. According to the instructions for igniting a gas boiler, the supply valve must be held pressed for about several tens of seconds. This time is necessary for the thermocouple to warm up and sufficient voltage to appear at its ends to hold the valve inside the coil.
At the moment when the burner goes out, the thermocouple begins to cool, the voltage at the ends of the thermocouple decreases and at some point, the return force of the spring outweighs the electromagnetic force holding the rod inside and returns the valve to its original position, cutting off the gas supply. This process usually takes several tens of seconds.
Examination
Checking the measuring equipment with a three-way valve is carried out as follows:
- In the working position, notice the readings of the device.
- The three-way valve is slowly turned to the left a quarter turn . The pressure gauge is disconnected from the boiler and connected to the atmosphere; the needle should smoothly return to zero.
- Slowly turn the tap back to the right a quarter turn , the arrow of the device should return to its previous position .
If the arrow moves jerkily, this means that the fitting and tap are clogged and need to be blown out . To do this, turn the tap so that water (gas) flows out, then return it to its operating position.
Important! The accuracy of the pressure gauge can only be verified using a reference instrument.